| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在所有测量中,盐酸双环胺(腹腔注射;8 mg/kg;每日)会增加认知障碍。此外,与盐酸双环胺处理的NonTg模型相比,3xTg-AD模型的记忆障碍更为严重。给小鼠注射盐酸双环胺(腹腔注射;2.0、4.0 和 8.0 mg/kg;7 天)。对模型关联学习(PAL)任务的性能有显着影响。较低剂量的全身治疗效果较小
|
|---|---|
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: C57Bl/6 mice [1]
Doses: 2.0, 4.0, 8.0 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip) injection; behavioral impairment of mice in spatial tasks [3]. Daily; 7-day Experimental Results: Damage due to factors outside the hippocampus. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
The bioavailability of dicyclomine has not been determined, though it is likely well absorbed as the primary route of elimination is in the urine. Dicyclomine has a Tmax of 1-1.5h. Dicyclomine is 79.5% eliminated in the urine and 8.4% in the feces. The volume of distribution for a 20mg oral dose is 3.65L/kg. Data regarding the clearance of dicyclomine is not readily available. Metabolism / Metabolites The metabolism of dicyclomine has not been well researched. Biological Half-Life The mean plasma elimination half life is approximately 1.8 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Like other anticholinergic agents, dicyclomine has not been linked to episodes of liver enzyme elevations or clinically apparent liver injury. The metabolism of dicyclomine is not well defined but it is likely metabolized by the liver. References on the safety and potential hepatotoxicity of anticholinergics are given together in the Overview section on Anticholinergic Agents. Drug Class: Anticholinergic Agents Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Dicyclomine has not been well studied during breastfeeding. However, one possible case of apnea has been reported in a breastfed infant that is similar to reactions that have occurred in infants given the drug directly. Dicyclomine should not be used during lactation. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. The manufacturer reported a breastfed infant who developed apnea during maternal therapy with dicyclomine. Dicyclomine is a possible cause of the reaction. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information in nursing mothers was not found as of the revision date. Anticholinergics can inhibit lactation in animals, apparently by inhibiting growth hormone and oxytocin secretion. Anticholinergic drugs can also reduce serum prolactin in nonnursing women. The prolactin level in a mother with established lactation may not affect her ability to breastfeed. Protein Binding Data regarding plasma protein binding of dicyclomine is not readily available. Interactions ...ANTICHOLINERGIC AGENTS, SUCH AS...DICYCLOMINE...WOULD BE EXPECTED TO INTERACT WITH DIGOXIN... |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
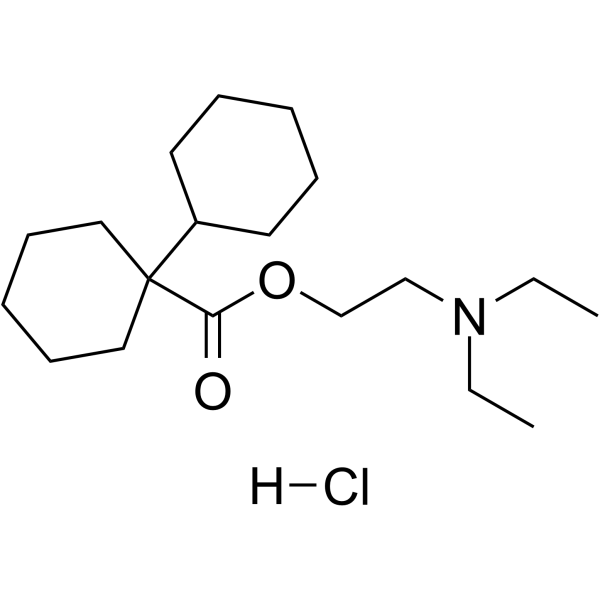
Dicyclomine is the ester resulting from the formal condensation of 1-cyclohexylcyclohexanecarboxylic acid with 2-(diethylamino)ethanol. An anticholinergic, it is used as the hydrochloride to treat or prevent spasm in the muscles of the gastrointestinal tract, particularly that associated with irritable bowel syndrome. It has a role as a muscarinic antagonist, an antispasmodic drug and a parasympatholytic. It is a tertiary amine and a carboxylic ester. It is functionally related to a 2-diethylaminoethanol and a 1,1'-bi(cyclohexyl)-1-carboxylic acid.
Dicyclomine is a muscarinic M1, M3, and M2 receptor antagonist as well as a non-competitive inhibitor of histamine and bradykinin used to treat spasms of the intestines seen in functional bowel disorder and irritable bowel syndrome. Though it is commonly prescribed, its recommendation may have been based on a small amount of evidence and so its prescription is becoming less favourable. Dicyclomine was granted FDA approval on 11 May 1950. Dicyclomine is an Anticholinergic. The mechanism of action of dicyclomine is as a Cholinergic Antagonist. Dicyclomine is an anticholinergic agent used to treat gastrointestinal conditions such as acid peptic disease and irritable bowel syndrome. Dicyclomine has not been implicated in causing liver enzyme elevations or clinically apparent acute liver injury. Dicyclomine is a carboxylic acid derivative and a selective anticholinergic with antispasmodic activity. Dicyclomine blocks acetylcholine from binding to muscarinic receptors on smooth muscle. This agent has a direct relaxing effect on smooth muscle and therefore prevents spasms in the muscles of the gastrointestinal tract, inhibits gastrointestinal propulsive motility, decreases gastric acid secretion and controls excessive pharyngeal, tracheal and bronchial secretion. A muscarinic antagonist used as an antispasmodic and in urinary incontinence. It has little effect on glandular secretion or the cardiovascular system. It does have some local anesthetic properties and is used in gastrointestinal, biliary, and urinary tract spasms. See also: Dicyclomine Hydrochloride (has salt form). Drug Indication Dicyclomine is indicated for the treatment of functional bowel disorder and irritable bowel syndrome. FDA Label Mechanism of Action Dicyclomine achieves its action partially through direct antimuscarinic activity of the M1, M3, and M2 receptors; and partially through antagonism of bradykinin and histamine. Dicyclomine non-competitively inhibits the action of bradykinin and histamine, resulting in direct action on the smooth muscle, and decreased strength of contractions seen in spasms of the ileum. ...MAJOR ACTION APPEARS TO BE NONSPECIFIC DIRECT RELAXANT ACTION ON SMOOTH MUSLCE RATHER THAN COMPETITIVE ANTAGONISM OF ACH. Therapeutic Uses Muscarinic Antagonists; Parasympatholytics ...OFTEN CLASSIFIED WITH ANTIMUSCARINIC AGENTS AS "ANTISPASMODICS," DO NOT PROPERLY BELONG TO GROUP OF ANTIMUSCARINIC AGENTS. ...DICYCLOMINE HYDROCHLORIDE, VSP-DECR SPASM OF GI TRACT, BILIARY TRACT, URETER, & UTERUS WITHOUT PRODUCING CHARACTERISTIC ATROPINIC EFFECTS ON SALIVARY, SWEAT, OR GI GLANDS, EYE, CV SYSTEM... /HCL/ IT DECR MOTILITY BUT DOES NOT SUPPRESS GASTRIC SECRETION. IT IS USED IN TREATMENT OF IRRITABLE COLON, SPASTIC CONSTIPATION, MUCOUS COLITIS, SPASTIC COLITIS, PYLOROSPASM, & BILIARY DYSKINESIA. IN TREATMENT OF PEPTIC ULCER IT IS USED TO DELAY GASTRIC EMPTYING. /HYDROCHLORIDE/ ANTICHOLINERGIC /HYDROCHLORIDE/ Drug Warnings DICYCLOMINE SHOULD BE USED CAUTIOUSLY IN PT WITH PROSTATIC HYPERTROPHY, BLADDER NECK OBSTRUCTION, PYLORIC OBSTRUCTION, & CARDIOSPASM. EVEN THOUGH IT DOES NOT APPEAR TO RAISE INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE IN NARROW-ANGLE GLAUCOMA, IT IS ADVISABLE TO MONITOR PRESSURE OF SUCH PT. CLINICAL USE OF.../BENTYL/ HAS BEEN DISAPPOINTING. A 3-YR-OLD MALE INGESTED APPROX 100 TABLETS OF BENDECTIN & DEVELOPED TONIC-CLONIC SEIZURES FOLLOWED BY CARDIAC ARREST. ANALYSIS YIELDED HIGH LEVELS OF DOXYLAMINE, DICYCLOMINE & PYRIDOXINE. DOXYLAMINE APPEARS TO BE TOXIC CONSTITUENT. Pharmacodynamics Dicyclomine is an anticholinergic drug used to relax the smooth muscles of the intestines. It's duration of action is not especially long as it is usually taken 4 times daily with individual doses of 20-40mg orally or 10-20mg by intramuscular injection. Dicyclomine should not be administered intravenously. |
| 分子式 |
C19H35NO2.HCL
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
345.94764
|
| 精确质量 |
345.243
|
| CAS号 |
67-92-5
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Dicyclomine;77-19-0
|
| PubChem CID |
3042
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 沸点 |
399.8ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
164-166ºC
|
| 闪点 |
116.5ºC
|
| LogP |
5.204
|
| tPSA |
29.54
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
| 重原子数目 |
22
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
326
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
CURUTKGFNZGFSE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C19H35NO2/c1-3-20(4-2)15-16-22-18(21)19(13-9-6-10-14-19)17-11-7-5-8-12-17/h17H,3-16H2,1-2H3
|
| 化学名 |
2-(diethylamino)ethyl 1-cyclohexylcyclohexane-1-carboxylate
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
H2O : ~50 mg/mL (~144.53 mM)
DMSO : ~33.33 mg/mL (~96.34 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.23 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.23 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.23 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 50 mg/mL (144.53 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8906 mL | 14.4530 mL | 28.9059 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5781 mL | 2.8906 mL | 5.7812 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2891 mL | 1.4453 mL | 2.8906 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。