| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
CDK2 (IC50 = 1 nM); CDK5 (IC50 = 1 nM); CDK1 (IC50 = 3 nM); CDK9 (IC50 = 4 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:Dinaciclib 也是一种有效的 DNA 复制抑制剂,可阻断 A2780 细胞中胸苷 (dThd) DNA 的掺入,IC50 为 4 nM。 Dinaciclib 在浓度 >6.25 nM 时强烈抑制 Ser 807/811 上 Rb 的磷酸化,这与在同一细胞模型中 dThd DNA 掺入抑制 50% 需要 4 nM 浓度所需的观察结果一致。值得注意的是,Rb 磷酸化的完全抑制与细胞凋亡的发生相关,如暴露于 >6.25 nM Dinaciclib 的细胞中 p85 PARP 裂解产物的出现所表明的。 Dinaciclib 对多种人类肿瘤细胞系具有活性。在羟基脲暴露期间添加 Dinaciclib 也会以剂量依赖性方式抑制 γ-H2AX 的积累。 Dinaciclib 抑制黑色素瘤细胞增殖,并促使黑色素瘤细胞大量凋亡。 Dinaciclib 诱导多种骨肉瘤细胞系的凋亡,包括对阿霉素和达沙替尼耐药的细胞系。 Dinaciclib 减弱 RNAP II 在丝氨酸 2 处的磷酸化和 CDK 抑制剂 p27Kip1 在苏氨酸 187 处的磷酸化。磷酸化活性在 12 - 40 nM Dinaciclib 时降低(添加 Dinaciclib 后 4 至 16 小时)。 Dinaciclib 还降低 Rb 在丝氨酸 807/811 处的磷酸化。 Dinaciclib 诱导模拟和 p53 耗尽的 U2OS 细胞凋亡,程度相似。激酶测定:重组细胞周期蛋白/CDK 全酶从 Sf9 细胞中纯化,该细胞经过工程改造,可产生表达特定细胞周期蛋白或 CDK 的杆状病毒。细胞周期蛋白/CDK 复合物通常在含有 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0)、10 mM MgCl2、1 mM DTT 和 0.1 mM 原钒酸钠的激酶反应缓冲液中稀释至终浓度 50 μg/mL。对于每个激酶反应,将 1 μg 酶和 20 μL 2 μM 底物溶液(源自组蛋白 H1 的生物素化肽)混合并与 10 μL 稀释的 Dinaciclib 混合。添加 50 μL 2 μM ATP 和 0.1 μCi 33P-ATP 开始反应。激酶反应在室温下孵育 1 小时,并通过添加 0.1% Triton X-100、1 mM ATP、5 mM EDTA 和 5 mg/mL 链霉亲和素包被的 SPA 珠来终止。使用 96 孔 GF/B 过滤板和 Filtermate 通用收集器捕获 SPA 珠子。将珠子用 2 M 氯化钠洗涤两次,并用含有 1% 磷酸的 2 M 氯化钠洗涤两次。然后使用 TopCount 96 孔液体闪烁计数器分析信号。细胞测定:A2780 细胞维持在加有 10% 胎牛血清的 DMEM 中,并通过用胰蛋白酶-EDTA 分离单层每周传代两次。将 100 微升 A2780 细胞(5 × 103 个细胞)添加到 96 孔 Cytostar-T 板的每孔中,并在 37 °C 下孵育 16 小时至 24 小时。 Dinaciclib 在完全培养基加 2% 14C 标记的 dThd 中连续稀释。从 Cytostar T 板上除去培养基;添加 200 μL 各种 Dinaciclib 稀释液,一式四份;细胞在37°C下孵育24小时。使用闪烁邻近法分析放射性标记的累积掺入,并在 TopCounTM 上测量。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Dinaciclib 每天 8、16、32 和 48 mg/kg 腹腔注射给药 10 天,肿瘤抑制率分别为 70%、70%、89% 和 96%。 Dinaciclib MED(最小有效剂量)似乎<8 mg/kg。 Dinaciclib 耐受性良好,最高剂量组的最大体重减轻为 5%。 Dinaciclib 在体内具有剂量依赖性抗肿瘤活性,并且在低于 MTD(最大耐受剂量)的剂量水平下几乎完全抑制肿瘤生长。 Dinaciclib 在小鼠体内的血浆半衰期较短。
通过筛选针对A2780卵巢癌小鼠异种移植物模型的个体化、多样化替代化合物,使用黄吡唑醇作为基准对照剂,SCH 727965被选为临床开发的最佳候选药物。该系统建立了每种受试化合物的最大耐受剂量(MTD)和最小有效剂量(MED)的比值。将每种化合物以不同剂量水平每天一次腹腔注射给裸小鼠7天后,测定MTD,并将其定义为与体重减轻20%相关的剂量。同时,MED被定义为按照相同时间表给予的剂量,与>50%的肿瘤生长抑制相关。在大鼠和狗身上进一步分析了有前景的化合物(21)。表1列出了与SCH 727965相关的筛查数据。因此,SCH 727965的MTD和MED分别大于60和5mg/kg;相比之下,黄吡醇的MTD和MED分别小于10mg/kg和10mg/kg。因此,SCH 727965的筛选治疗指数(MTD/MED比值)>10,而黄吡唑的指数<1,表明黄吡唑在出现剂量限制毒性之前没有达到最低的抗肿瘤效果。这些数据表明,SCH 727965具有优于黄吡醇的有吸引力的体内特征。 1. SCH 727965体内疗效和耐受性[1] 先前描述的用于初步选择活性剂的A2780卵巢癌症小鼠异种移植物模型用于进一步评估SCH 727965的疗效和耐受性;紫杉醇为阳性对照。在初次皮下细胞接种后7天,将具有约100 mm3 A2780肿瘤的裸鼠随机分为10只动物组,并分配到每个SCH 727965剂量组、紫杉醇或载体对照组。SCH 727965腹腔注射,每日8、16、32和48 mg/kg,持续10天,肿瘤抑制率分别为70%、70%、89%和96%;紫杉醇以20mg/kg的剂量腹腔注射,每周两次,可抑制63%的肿瘤生长(图3A)。与早期的体内筛选数据一致,SCH 727965 MED似乎<8 mg/kg。SCH 727965s耐受良好,最高剂量组的最大体重减轻为5%(数据未显示)。这远低于MTD,MTD定义为在本实验过程中体重减轻20%。综上所述,数据显示SCH 727965在体内具有剂量依赖性抗肿瘤活性,在低于MTD的剂量水平下,肿瘤生长几乎完全受到抑制(表4;图3A)。 SCH 7279765在各种间歇时间具有抗肿瘤活性[1] 药代动力学研究表明,SCH 727965在小鼠体内的血浆半衰期较短。因此,小鼠腹腔注射5mg/kg SCH 727965的剂量与约0.25小时的血浆半衰期有关(补充表S2),这可能表明需要频繁给药。然而,之前的研究结果表明,连续暴露于SCH 727965可能不是抗增殖活性的先决条件,因为该药物的短期治疗在体外和体内都会产生长期效应。为了验证这一假设,将260 mg/kg的SCH 727965总剂量(相当于20 mg/kg,每天一次,持续13天)分为几个不同的方案,并给予携带已建立(>100 mm3)A549肿瘤异种移植物的裸鼠(图3B;给药天数由箭头表示)。本研究的主要终点是肿瘤体积/质量和体重。SCH 727965剂量为87 mg/kg,每周给药一次,超过MTD,提前终止。所有方案均观察到类似的肿瘤消退。这些数据与早期的观察结果一致,表明在广泛的间歇SCH 727965给药方案下可以产生类似的体内反应。 SCH 727965暴露后体内基于机制的全身效应[1] 在这项研究中,磷酸化Rb 807/811被用作CDK参与和基于机制的SCH 727965活性的替代标记。为了证明在小鼠异种移植物模型中先前表现出显著抗肿瘤活性的20 mg/kg至60 mg/kg剂量的SCH 727965与CDK机制的调节有关,在SCH 727965-治疗的肿瘤初发裸鼠皮肤样本中分析了磷酸化Rb 807/811的表达。皮肤和毛囊是替代增殖(非肿瘤)组织的良好外周来源。在施用SCH 727965后的不同时间点采集皮肤穿刺活检。小鼠皮肤的免疫组织化学染色表明,单次40mg/kg SCH 727965剂量可诱导基底上皮和毛囊增殖上皮细胞内磷酸化Rb 807/811的快速和持续抑制(图3C)。这些观察结果表明,与A549异种移植物模型中的退化相关的SCH 727965剂量(图3B)与增殖替代组织中基于机制的标记物的调节相关。这些数据与抑制CDKs可以诱导增殖正常组织内细胞周期抑制的假设一致,并表明增殖室可能对SCH 727965敏感。 为了评估SCH 727965对血液学参数的影响,BALB/c小鼠每天腹腔注射40mg/kg,持续5天,对照组未经治疗或服用20%羟丙基-β-环葡聚糖。在最后一剂给药后1天(第6天)以及7天后(第13天)采集血液样本。对血细胞进行计数(区分),以检查几个血液学参数的最低点和反弹动力学。中性粒细胞和网织红细胞对SCH 727965最敏感,在第6天检测到其绝对计数的最低点(图3D)。值得注意的是,中性粒细胞绝对计数(图3D,左)和网织红细胞计数(图三维,右)在第13天恢复到正常水平。在此期间,未观察到对血小板或红细胞的可检测影响(数据未显示)。这些结果与SCH 727965在所检查的剂量范围内的基于机制的活性一致,并表明细胞周期抑制作用在增殖的正常细胞室中是短暂和可逆的。 |
| 酶活实验 |
重组细胞周期蛋白/CDK 全酶是从 Sf9 细胞中分离出来的,这些细胞已被修饰以产生表达特定 CDK 或细胞周期蛋白的杆状病毒。通常,细胞周期蛋白/CDK 复合物在含有 0.1 mM 原钒酸钠、10 mM MgCl2、1 mM DTT 和 50 mM Tris- 的激酶反应缓冲液中稀释至终浓度 50 μg/mL。其中含有 HCl (pH 8.0)。在每个激酶反应中,将 10 μL 稀释的 Dinaciclib (SCH 727965) 与 1 μg 酶和 20 μL 2 μM 底物溶液(源自组蛋白 H1 的生物素化肽)混合。添加 0.1 μCi 的 33P-ATP 和 50 μL 2 μM ATP 启动反应。室温孵育一小时后,添加 0.1% Triton X-100、1 mM ATP、5 mM EDTA 和 5 mg/mL 链霉亲和素包被的 SPA 珠可停止激酶反应。 Filtermate 通用收集器与 96 孔 GF/B 过滤板组合用于收集 SPA 珠子。用2M NaCl和2M含1%磷酸的NaCl洗珠两次。然后使用 TopCount 96 孔液体闪烁计数器测量信号。使用两组八点连续稀释的抑制化合物来创建剂量反应曲线。使用非线性回归分析得出IC50值。
细胞周期蛋白/CDK激酶测定[1] 从Sf9细胞中纯化重组细胞周期蛋白/CDK全酶,这些细胞被工程化以产生表达特定细胞周期蛋白或CDK的杆状病毒。细胞周期蛋白/CDK复合物通常在含有50 mmol/L Tris-HCl(pH 8.0)、10 mmol/L MgCl2、1 mmol/L DTT和0.1 mmol/L原钒酸钠的激酶反应缓冲液中稀释至终浓度为50μg/mL。对于每种激酶反应,将1μg酶和20μL 2-μmol/L底物溶液(一种来自组蛋白H1的生物素化肽)混合,并与10μL稀释的SCH 727965混合。通过加入50μL的2μmol/L ATP和0.1μCi的33P-ATP开始反应。激酶反应在室温下孵育1小时,并通过加入0.1%Triton X-100、1 mmol/L ATP、5 mmol/L EDTA和5 mg/mL链霉抗生物素包被的SPA珠(Amersham)停止。使用96孔GF/B滤板和Filtermate通用收割机捕获SPA珠。用2mol/L NaCl洗涤珠两次,用含1%磷酸的2mol/L NaCl清洗珠两次。然后使用TopCount 96孔液体闪烁计数器对信号进行分析。剂量反应曲线由抑制性化合物的重复八点系列稀释液生成。IC50值通过非线性回归分析得出。 激酶反筛选[1] SCH 727965和flavopiridol使用微孔激酶分析仪服务进行反筛选。使用固定(10μmol/L)浓度的ATP,在1.0和10.0μmol/L下对一组不同的激酶进行了测试。 |
| 细胞实验 |
铺板的 A2780 细胞使用适当的生长培养基在组织培养皿中生长。生长中的培养物通常会受到不同浓度的 Dinaciclib(0.75、1.5、3.15、6.25、12.5、25 和 500 nM)或媒介物对照的影响,持续 7 天。除去培养基后,使用 50% 甲醇/50% 丙酮溶液将细胞固定五分钟,然后使用 2% 乙醇中的 0.2% 结晶紫溶液染色五分钟。染色后用水 (5–10 mL) 清洗细胞。使用 1% 脱氧胆酸溶解染色细胞,并使用 SOFTmax PRO 4.3 读板器测量所得溶液在 600 nm 处的吸光度。绘制用 Dinaciclib 处理的样品的吸光度占媒介物处理对照的百分比,结果以相对于这些对照的 IC50 值表示。 alamarBlue 细胞活力测定试剂盒用于获得悬浮细胞系的细胞活力评估。
dThd摄取生长抑制试验[1] A2780细胞在DMEM加10%胎牛血清中维持,每周通过胰蛋白酶-EDTA分离单层传代两次。将每孔100微升A2780细胞(5×103个细胞)加入96孔Cytostar-T板中,在37°C下孵育16至24小时。将化合物在完全培养基中加上2%的14C标记的dThd中连续稀释。从Cytostar T板中取出培养基;加入200μL各种化合物稀释液,一式四份;细胞在37°C下孵育24小时。使用闪烁邻近度测定放射性标记的累积掺入,并在TopCount 上测量。计算dThd摄取抑制相对于载体对照的百分比,并绘制在对数线性图上,以得出IC50值。 溴脱氧尿苷掺入试验[1] 将A2780细胞接种到六孔组织培养皿中并使其粘附。然后将细胞暴露于不同浓度的Dinaciclib(SCH727965;PS-095760)或DMSO对照载体24小时,然后短暂(30分钟)脉冲暴露于溴脱氧尿苷(BrdUrd)。然后收获细胞,使用特异于BrdUrd的FITC偶联抗体进行免疫染色,用碘化丙啶/RNase A溶液进行反染色,并使用流式细胞术进行分析。荧光激活细胞分选分析在FACSCalibur仪器上进行。FITC阳性BrdUrd染色和碘化丙啶信号可以评估正在进行的DNA复制和细胞周期阶段。针对每种供试品浓度,绘制了每个细胞周期阶段细胞群的百分比。 免疫印迹[1] 将异步生长的肿瘤细胞系暴露于不同浓度的Dinaciclib(SCH727965;PS-095760)。随后,收集细胞并在含有350 mmol/L NaCl、0.1%NP40、1 mmol/L DTT和蛋白酶和磷酸酶抑制剂混合物的50 mmol/L Tris-HCl缓冲液中裂解。测定蛋白质浓度后,在还原SDS-PAGE凝胶上分离细胞裂解物,并用丝氨酸807、811磷酸化Rb、低磷酸化Rb或p85聚ADP核糖聚合酶(PARP)半胱天冬酶切割产物特异性的抗血清进行免疫印迹。 活化半胱天冬酶评估细胞凋亡的诱导作用[1] 使用Beckman Coulter CellProbe HT caspase-3/7全细胞检测系统进行胱天蛋白酶激活检测。将异步生长的细胞铺在96孔板上并使其粘附。将细胞暴露于不同浓度的Dinaciclib(SCH727965;PS-095760)或载体中24小时。随后用荧光标记的胱天蛋白酶底物孵育细胞;细胞内底物的摄取和荧光与活化的半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶的水平相关。使用Analyst AD 96.384荧光计(485nm激发和530nm发射)测定胱天蛋白酶活性。 克隆原性和alamarBlue存活率测定[1] 将细胞铺在组织培养皿上,用适当的生长培养基增殖。生长中的培养物暴露于浓度递增的Dinaciclib (SCH727965; PS-095760)或载体对照中,通常持续7天。去除培养基后,用50%甲醇/50%丙酮固定细胞5分钟,用2%乙醇中的0.2%结晶紫染色5分钟。染色后,用5至10mL水洗涤细胞。将染色细胞溶解在1%脱氧胆酸中,使用SOFTmax PRO 4.3平板读数器在600nm处测量所得溶液的吸光度。SCH 727965处理样品的吸光度以溶媒处理对照的百分比绘制,数据以相对于这些对照的IC50值报告。对于悬浮细胞系,使用alamarBlue细胞活力测定试剂盒,按照制造商推荐的方案进行细胞活力评估。 |
| 动物实验 |
Mice: Certain cell lines are grown in vitro, once they have been washed with PBS, they are resuspended in 50% Matrigel in PBS until they reach a final concentration of 4×107 to 5×107 cells per milliliter for tumor implantation. 0.1 mL of this suspension is subcutaneously injected into the flanks of naked mice. Every mouse has its tumor measured twice a week using a caliper to determine its length (L), width (W), and height (H). The tumor volume is then determined by applying the formula (L×W×H)/2. The animals are randomized to treatment groups (10 mice/group) when the tumor volume reaches 100 mm3. They are then given individual chemotherapeutic agents or Dinaciclib (8, 16, 32, and 48 mg/kg daily, i.p.) in accordance with the dosing schedule shown in the table and figure legends. Body weights and tumor volumes are measured both during and after treatment.
In vivo tumor growth assessments [1] For tumor implantation, specific cell lines were grown in vitro, washed once with PBS, and resuspended in 50% Matrigel in PBS to a final concentration of 4 × 107 to 5 × 107 cells per milliliter. Nude mice were injected with 0.1 mL of this suspension s.c. in the flank region. Tumor length (L), width (W), and height (H) were measured by a caliper twice weekly on each mouse and then used to calculate tumor volume using the formula (L × W × H)/2. When the tumor volume reached ∼100 mm3, the animals were randomized to treatment groups (10 mice/group) and treated i.p. with either Dinaciclib (SCH727965; PS-095760) or individual chemotherapeutic agents according to the dosing schedule indicated in table and figure legends. Tumor volumes and body weights were measured during and after the treatment periods. Assessments of Dinaciclib (SCH727965; PS-095760) effects on hematologic parameters [1] A daily dose of Dinaciclib (SCH727965; PS-095760) (40 mg/kg) was administered i.p. to BALB/c mice for 5 days. Blood was collected on day 6 and day 13 (1st and 7th day after the final dose, respectively), diluted 1:5 in PBS, and immediately analyzed on an Advia 120 hematology analyzer (with differential). Pharmacokinetic determinations [1] Plasma samples from mice were collected at various times after i.p. administration of Dinaciclib (SCH727965; PS-095760). At each time point, blood samples from three animals were combined and analyzed for SCH 727965 by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Pharmacokinetic variables were estimated from the plasma concentration data. Maximum plasma concentration values were taken directly from the plasma concentration time profiles, and the area under the plasma concentration versus time curve (0–24 h) was calculated using the linear trapezoidal rule. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Pharmacokinetic studies showed that SCH 727965 has a short plasma half-life in mouse. Thus, a dose of 5 mg/kg SCH 727965 given i.p. in mice was associated with a plasma half-life of ∼0.25 hour (Supplementary Table S2), perhaps suggesting a need for frequent dosing. However, previous results imply that continuous SCH 727965 exposure may not be a prerequisite for antiproliferative activity because short treatments with the drug induce long-term effects in vitro and in vivo. [1]
|
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
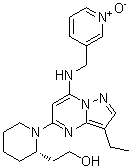
2-[(2S)-1-[3-ethyl-7-[(1-oxido-3-pyridin-1-iumyl)methylamino]-5-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidinyl]-2-piperidinyl]ethanol is a pyrazolopyrimidine.
Dinaciclib has been used in trials studying the treatment of rrMM, rrCLL, rrDLBCL, Solid Tumors, and Solid Neoplasm, among others. Dinaciclib is a pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine with potential antineoplastic activity. Dinaciclib selectively inhibits cyclin dependent kinases CDK1, CDK2, CDK5, and CDK9; inhibition of CDK1 and CDK2 may result in cell cycle repression and tumor cell apoptosis. Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK) are key positive regulators of cell cycle progression and attractive targets in oncology. SCH 727965 inhibits CDK2, CDK5, CDK1, and CDK9 activity in vitro with IC(50) values of 1, 1, 3, and 4 nmol/L, respectively. SCH 727965 was selected as a clinical candidate using a functional screen in vivo that integrated both efficacy and safety parameters. Compared with flavopiridol, SCH 727965 exhibits superior activity with an improved therapeutic index. In cell-based assays, SCH 727965 completely suppressed retinoblastoma phosphorylation, which correlated with apoptosis onset and total inhibition of bromodeoxyuridine incorporation in >100 tumor cell lines of diverse origin and background. Moreover, short exposures to SCH 727965 were sufficient for long-lasting cellular effects. SCH 727965 induced regression of established solid tumors in a range of mouse models following intermittent scheduling of doses below the maximally tolerated level. This was associated with modulation of pharmacodynamic biomarkers in skin punch biopsies and rapidly reversible, mechanism-based effects on hematologic parameters. These results suggest that SCH 727965 is a potent and selective CDK inhibitor and a novel cytotoxic agent.[1] SCH 727965 was selected for clinical development following a functional in vivo screen that integrated both efficacy and tolerability of tested compounds. This rapid and discriminatory approach identified a candidate for clinical development that was significantly more effective and better tolerated than flavopiridol. SCH 727965 has several distinct in vitro properties consistent with an improved in vivo therapeutic index. Notably, the compound exhibits strong selectivity for the CDK family. These data suggest the activated CDK conformation has unique structural aspects, not present in closely related serine/threonine kinases (such as the extracellular signal-regulated kinase and GSK3 families), thus providing a potential explanation for the observed excellent selectivity and tolerability profiles of SCH 727965. In vitro and in vivo analyses presented in this study support the conclusion that SCH 727965 has the potential to inhibit the growth of a broad spectrum of human cancers. SCH 727965 induced mechanism-based apoptosis in the vast majority of tested human tumor cell lines of diverse origin, following a single exposure. In agreement, SCH 727965 was effective at doses below the MTD level in multiple in vivo models and induced regression in several xenografts using continuous or intermittent schedules. Under similar conditions, the observed xenograft efficacy profiles of SCH 727965 were consistently superior to those achieved using approved benchmark agents, such as taxanes. Moreover, in mechanism-based biomarker studies, effective doses of the drug were sufficient to suppress phosphorylated Rb levels in surrogate tissues, such as skin and hair follicles. Likewise, active dose levels in the mouse were also associated with reversible effects on hematologic parameters. Quantitative tracking of leukocyte cell counts may offer an additional approach for tracking mechanism-based pharmacodynamic effects of SCH 727965. Interestingly, the in vivo activity of SCH 727965 observed in murine systems was readily detectable despite rapid clearance of the parent compound from mouse plasma, indicating that continual exposure to SCH 727965 was not necessary for activity in vivo. Consistent with this, short exposure to SCH 727965 can induce long-lasting pharmacodynamic effects in vitro. Thus, a 2-hour exposure to ≤500 nmol/L SCH 727965 was sufficient to suppress BrdUrd incorporation 24 hours later. Similarly, transient in vitro exposure to SCH 727965 induced suppression of Rb phosphorylation that was correlated with induction of apoptosis. Significantly, escalation of SCH 727965 exposure (≤30 μmol/L) did not augment apoptotic phenotypes, suggesting a relative lack of nonspecific or off-target cytotoxicity. Taken together, the available in vitro and in vivo data show that long-lasting therapeutic effects can be induced within sensitive cells following short exposures to SCH 727965. It is possible that selecting compounds for further development solely on the basis of pharmacokinetic parameters would not have facilitated selection of SCH 727965 for clinical development. In summary, the approach of in vivo screening in mice ultimately led to the selection of a compound with attractive biochemical and pharmacologic properties. Inhibitors of the CDK family have been proposed as attractive drug targets and pursued for oncology indications for several years, and several candidate molecules have entered clinical studies. In the case of flavopiridol, a combination of suboptimal selectivity, poor drug-like qualities, and adverse side effects may ultimately obscure any potentially desirable mechanism-based activities of this agent. In this study, we have described the novel pharmacologic properties of SCH 727965, a highly potent and selective CDK inhibitor that is differentiated from first generation CDK inhibitor compounds, such as flavopiridol. SCH 727965 is currently undergoing clinical testing against a range of solid and hematologic malignancies. The overall excellent profile of SCH 727965 suggests this molecule has the necessary properties to allow further pharmacologic exploration of the cell cycle mechanism in oncology. [1] |
| 分子式 |
C21H28N6O2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
396.49
|
|
| 精确质量 |
396.227
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 63.62; H, 7.12; N, 21.20; O, 8.07
|
|
| CAS号 |
779353-01-4
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
46926350
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.677
|
|
| LogP |
0.97
|
|
| tPSA |
91.15
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
29
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
512
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
O([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[C@]1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N1C1C([H])=C(N([H])C([H])([H])C2C([H])=C([H])C([H])=[N+](C=2[H])[O-])N2C(=C(C([H])=N2)C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])N=1
|
|
| InChi Key |
PIMQWRZWLQKKBJ-SFHVURJKSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C21H28N6O2/c1-2-17-14-23-27-19(22-13-16-6-5-9-25(29)15-16)12-20(24-21(17)27)26-10-4-3-7-18(26)8-11-28/h5-6,9,12,14-15,18,22,28H,2-4,7-8,10-11,13H2,1H3/t18-/m0/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
2-[(2S)-1-[3-ethyl-7-[(1-oxidopyridin-1-ium-3-yl)methylamino]pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-5-yl]piperidin-2-yl]ethanol
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.31 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.31 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浮液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.31 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 2% DMSO +30% PEG 300 +ddH2O: 10 mg/mL 配方 5 中的溶解度: 10 mg/mL (25.22 mM) in 20% HP-β-CD in Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5221 mL | 12.6107 mL | 25.2213 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5044 mL | 2.5221 mL | 5.0443 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2522 mL | 1.2611 mL | 2.5221 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT01434316 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Dinaciclib Drug: Veliparib |
Advanced Malignant Solid Neoplasm |
National Cancer Institute (NCI) |
November 1, 2011 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00937937 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Dinaciclib | Mucosal Melanoma Recurrent Melanoma |
National Cancer Institute (NCI) |
Phase 2 | |
| NCT01624441 | Completed | Drug: Epirubicin Hydrochloride Drug: Dinaciclib |
Male Breast Carcinoma HER2/Neu Negative |
UNational Cancer Institute (NCI) |
August 21, 2012 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00871663 | Completed | Drug: SCH 727965 | Solid Tumors Multiple Myeloma |
Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC | August 2006 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00871910 | Completed | Drug: SCH 727965 Drug: Aprepitant |
Solid Tumors Multiple Myeloma |
Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC | October 11, 2006 | Phase 1 |
 Cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor SCH727965 reduces growth, colony formation and motility of pancreatic cancer cells in vitro.Cancer Biol Ther.2011 Oct 1;12(7):598-609. |
|---|
 Spectrum of in vivo growth inhibition by SCH727965 in a panel of ten subcutaneous low-passage pancreatic cancer xenografts.Cancer Biol Ther.2011 Oct 1;12(7):598-609. |
 Combination treatment of orthotopic pancreatic cancer xenografts with SCH727965 and gemcitabine. Modified Boyden chamber assays show decreased in vitro cell motility of Pa20C cells after treatment with SCH727965 for 72 h.Cancer Biol Ther.2011 Oct 1;12(7):598-609. |