| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
氟哌利多引起外周血管扩张和轻度 α-肾上腺素能阻断。氟哌利多已被证明可以阻断离体动物心室肌细胞心肌中的钾流出,导致复极出现剂量依赖性延迟。在分离的动物浦肯野纤维中,氟哌利多也被证明可以引起早期去极化。 [1]
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在以 60 脉冲/分钟刺激的兔浦肯野纤维中,氟哌利多 (0.01 mM-0.3 mM) 以剂量依赖性方式增加动作电位持续时间 (APD),同时保持其他参数不变。在兔浦肯野纤维中,氟哌利多 (1 mM–3 mM) 会导致延长效应逆转。在兔浦肯野纤维中,氟哌利多 (10 mM–30 mM) 除了使 APD 缩短 50% 复极化外,还导致 Vmax、动作电位振幅和静息膜电位显着降低。氟哌利多对兔浦肯野纤维复极化、低浓度下 EAD 发展的延长以及随后的触发活动具有双重作用。 [2]氟哌利多(3 mg/kg,单剂量)以剂量依赖性方式降低大鼠阿扑吗啡效应及其在开放场地中的运动和站立频率。长期给予氟哌利多(3 mg/kg)的大鼠对开放环境中观察到的所有活动参数产生显着的耐受性。戒断氟哌利多会增加对阿扑吗啡引起的刻板行为的反应性。 [3]
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Completely absorbed following intramuscular administration. Following im or iv administration, the onset of pharmacologic action of droperidol occurs within 3-10 minutes, but peak pharmacologic effects may not be apparent until 30 minutes. The sedative and tranquilizing effects of droperidol generally persist for 2-4 hours following im or iv administration of a single dose; alteration of consciousness may persist for up to 12 hours. Droperidol reportedly crosses the blood-brain barrier and is distributed into the CSF. Droperidol drug reportedly crosses the placenta, but data are limited. It is not known if droperidol is distributed into milk. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for DROPERIDOL (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Extensively metabolized. Although the exact metabolic fate of droperidol is not clearly established, the drug is metabolized in the liver. The butyrophenone moiety of droperidol is metabolized to p-fluorophenylacetic acid, which is then conjugated with glycine. The nitrogenous moiety of droperidol appears to be metabolized to benzimidazolone and p-hydroxypiperidine. Biological Half-Life Biphasic distribution. The rapid distribution phase is 1.4 ± 0.5 minutes and the slower distribution phase is 14.3 ± 6.5 minutes. Elimination half-life in adults is 134 ± 13 minutes and may be increased in geriatric patients. In children, it is 101.5 ± 26.4 minutes. ...Droperidol is rapidly absorbed after im injections, and plasma-level profiles of unchanged drug obey 2-compartment model kinetics. Plasma t1/2 is about 130 min... |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Because little information is available on the long-term use of droperidol during breastfeeding, an alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. Single-dose or short-term use during breastfeeding, such as during surgery, is unlikely to adversely affect the breastfed infant, especially if the infant is older than 2 months. When multiple doses are given to the mother, monitor the infant for drowsiness, especially in younger, exclusively breastfed infants and when using combinations of psychotropic drugs. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants A randomized study compared the breastfed infants born by cesarean section whose mothers received either morphine or morphine plus droperidol by patient-controlled analgesia postoperatively. On days 1 and 2 of life, the infants whose mothers received droperidol had a lower neonatal neurologic and adaptive capacity score (NACS) than those who received morphine only. One breastfed (extent not stated) infant whose mother was taking droperidol had a somewhat decreased intellectual development on testing, but her mother had also taken olanzapine, clonazepam, sertraline, thioridazine and valproic acid while breastfeeding. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Hyperprolactinemia has been reported in patients taking long-term droperidol and after short-term use during surgical procedures. The maternal prolactin level in a mother with established lactation may not affect her ability to breastfeed. Interactions Any drug known to have the potential to prolong the QT interval should not be used together with droperidol. Possible pharmacodynamic interactions can occur between droperidol and potentially arrhythmogenic agents such as class I or III antiarrhythmics, antihistamines that prolong the QT interval, antimalarials, calcium channel blockers, neuroleptics that prolong the QT interval, and antidepressants. Caution should be used when patients are taking concomitant drugs known to induce hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia as they may precipitate QT prolongation and interact with droperidol. These would include diuretics, laxatives and supraphysiological use of steroid hormones with mineralocorticoid potential. CNS depressant drugs (e.g. barbiturates, tranquilizers, opioids and general anesthetics) have additive or potentiating effects with droperidol. When patients have received such drugs, the dose of droperidol required will be less than usual. Following the administration of droperidol, the dose of other CNS depressant drugs should be reduced. To report a case of QT prolongation associated with concomitant cyclobenzaprine and fluoxetine administration followed by torsade de pointes potentiated by droperidol. A 59-year-old white woman who had been receiving long-term fluoxetine and cyclobenzaprine therapy was admitted for Achilles tendon repair. Baseline QTc was prolonged at 497 msec. Prior to surgery, the patient received droperidol, an agent known to prolong the QT interval. During surgery the patient developed torsade de pointes, which progressed into ventricular fibrillation. On postoperative day 1, after cyclobenzaprine discontinuation, the QTc decreased toward normal (440 msec). Cyclobenzaprine shares anticholinergic effects, tachycardia, and dysrhythmic potential with the tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs). Fluoxetine is a known inhibitor of the CYP2D6 isoenzyme (along with CYP3A4 and CYP2C) and has been shown to increase TCA serum concentrations. The combination of cyclobenzaprine and fluoxetine resulted in significant QT prolongation in our patient that progressed to torsade de pointes after preoperative droperidol administration. Resolution of QT abnormalities after cyclobenzaprine discontinuation provided further evidence of a drug-induced etiology. Other possible medical and drug-related causes of torsade de pointes are reviewed and ruled out. ... For more Interactions (Complete) data for DROPERIDOL (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Dog iv 25 mg/kg LD50 Rabbit iv 11-13 mg/kg LD50 Mouse im 195 mg/kg LD50 Rat im 104-110 mg/kg. For more Non-Human Toxicity Values (Complete) data for DROPERIDOL (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Adjuvants, Anesthesia; Antiemetics; Antipsychotic Agents; Dopamine Antagonists Droperidol Injection is indicated to reduce the incidence of nausea and vomiting associated with surgical and diagnostic procedures. /Included in US product label/ Droperidol has been used preoperatively and as an adjunct during induction and maintenance of general anesthesia and as an adjunct to regional anesthesia. /NOT included in US product labeling/ Droperidol has been used in combination with an opiate analgesic, such as fentanyl, for neuroleptanalgesia as an anxiolytic and to potentially increase the analgesic effect of the opiate. However, because of the risk of serious adverse effects, the manufacturer no longer recommends these uses. /NOT included in US product labeling/ For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for DROPERIDOL (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings /BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: Cases of QT prolongation and/or torsade de pointes have been reported in patients receiving droperidol at doses at or below recommended doses. Some cases have occurred in patients with no known risk factors for QT prolongation and some cases have been fatal. Due to its potential for serious proarrhythmic effects and death, droperidol should be reserved for use in the treatment of patients who fail to show an acceptable response to other adequate treatments, either because of insufficient effectiveness or the inability to achieve an effective dose due to intolerable adverse effects from those drugs. Cases of QT prolongation and serious arrhythmias (e.g., torsade de pointes) have been reported in patients treated with droperidol. Based on these reports, all patients should undergo a 12-lead ECG prior to administration of droperidol to determine if a prolonged QT interval (i.e., QTc greater than 440 msec for males or 450 msec for females) is present. If there is a prolonged QT interval, droperidol should NOT be administered. For patients in whom the potential benefit of droperidol treatment is felt to outweigh the risks of potentially serious arrhythmias, ECG monitoring should be performed prior to treatment and continued for 2-3 hours after completing treatment to monitor for arrhythmias. Droperidol is contraindicated in patients with known or suspected QT prolongation, including patients with congenital long QT syndrome. Droperidol should be administered with extreme caution to patients who may be at risk for development of prolonged QT syndrome (e.g., congestive heart failure, bradycardia, use of a diuretic, cardiac hypertrophy, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, or administration of other drugs known to increase the QT interval). Other risk factors may include age over 65 years, alcohol abuse, and use of agents such as benzodiazepines, volatile anesthetics, and IV opiates. Droperidol should be initiated at a low dose and adjusted upward, with caution, as needed to achieve the desired effect. Droperidol should be administered with extreme caution to patients who may be at risk for development of prolonged QT syndrome (e.g., congestive heart failure, bradycardia, use of a diuretic, cardiac hypertrophy, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, or administration of other drugs known to increase the QT interval). Other risk factors may include age over 65 years, alcohol abuse, and use of agents such as benzodiazepines, volatile anesthetics, and IV opiates. Droperidol should be initiated at a low dose and adjusted upward, with caution, as needed to achieve the desired effect. Droperidol is contraindicated in patients with known or suspected QT prolongation (i.e., QTc interval greater than 440 msec for males or 450 msec for females). This would include patients with congenital long QT syndrome. Droperidol is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for DROPERIDOL (26 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Droperidol produces marked tranquilization and sedation. It allays apprehension and provides a state of mental detachment and indifference while maintaining a state of reflex alertness. Droperidol produces an antiemetic effect as evidenced by the antagonism of apomorphine in dogs. It lowers the incidence of nausea and vomiting during surgical procedures and provides antiemetic protection in the postoperative period. Droperidol potentiates other CNS depressants. It produces mild alpha-adrenergic blockade, peripheral vascular dilatation and reduction of the pressor effect of epinephrine. It can produce hypotension and decreased peripheral vascular resistance and may decrease pulmonary arterial pressure (particularly if it is abnormally high). It may reduce the incidence of epinephrine-induced arrhythmias, but it does not prevent other cardiac arrhythmias. |
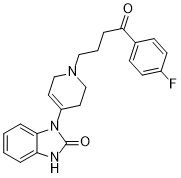
| 分子式 |
C22H22FN3O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
379.43
|
| 精确质量 |
379.169
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 69.64; H, 5.84; F, 5.01; N, 11.07; O, 8.43
|
| CAS号 |
548-73-2
|
| PubChem CID |
3168
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to light tan, amorphous or microcrystalline powder
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
616.4±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
148-149ºC
|
| 闪点 |
326.6±34.3 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.636
|
| LogP |
4.22
|
| tPSA |
58.1
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
28
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
615
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
FC1C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1[H])C(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N1C([H])([H])C([H])=C(C([H])([H])C1([H])[H])N1C(N([H])C2=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C12)=O)=O
|
| InChi Key |
RMEDXOLNCUSCGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H22FN3O2/c23-17-9-7-16(8-10-17)21(27)6-3-13-25-14-11-18(12-15-25)26-20-5-2-1-4-19(20)24-22(26)28/h1-2,4-5,7-11H,3,6,12-15H2,(H,24,28)
|
| 化学名 |
3-[1-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-oxobutyl]-3,6-dihydro-2H-pyridin-4-yl]-1H-benzimidazol-2-one
|
| 别名 |
Inapsine; Dridol; Dehydrobenzperidol; Properidol; Droperidol; Droleptan; Inapsine; Janssen Brand of Droperidol; Kern Brand of Droperidol; Taylor Brand of Droperidol;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~76 mg/mL (~200.3 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.59 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.59 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6355 mL | 13.1777 mL | 26.3553 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5271 mL | 2.6355 mL | 5.2711 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2636 mL | 1.3178 mL | 2.6355 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT05244460 | Recruiting | Drug: Diphenhydramine Drug: Droperidol Injectable Product |
Cannabis Hyperemesis Syndrome | Mercy Health Ohio | December 2, 2021 | Phase 3 |
| NCT05401058 | Recruiting | Drug: Droperidol Injection Drug: Saline |
Digestive System Disease Urologic Diseases |
RenJi Hospital | November 21, 2022 | Not Applicable |
| NCT00702442 | Completed | Drug: Droperidol Drug: Saline solution |
Vomiting | Aristotle University Of Thessaloniki |
June 2008 | Phase 4 |
| NCT04411069 | Completed | Drug: Droperidol | Postoperative Nausea Postoperative Vomiting |
Instituto do Cancer do Estado de São Paulo |
February 20, 2019 | Phase 2 |
| NCT02744495 | Completed | Drug: Betamethasone Drug: Droperidol |
Postoperative Vomiting Postoperative Nausea |
Hôpital Privé de Parly II - Le Chesnay |
February 2016 | Phase 3 |