| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
ERα (IC50 = 48 nM), ERβ (IC50 = 870 nM)[1]
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
使用 elacestrant 二盐酸盐(RAD1901;0.5 nM-10 µM;48 小时)观察到 MCF-7 细胞中 ERα 表达的浓度依赖性抑制(EC50 = 0.6 nM)[1]。二盐酸盐 (0–1 µM) 48 小时。显示对雌二醇 (E2) 触发的 ER 急性 MCF-7 细胞具有浓度依赖性抗增殖作用 (EC50 = 4 pM) [1]。 MCF7 和 T47D 细胞系中的孕酮受体(PGR、PR 和 ER)会被 elacestrant diHCl(0–1 µM;24 或 48 小时)减少。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Eeleestrant diHCle 以剂量依赖性方式多重抗 E2 介导的增殖促进作用(0.3-120 mg/kg;口服;每日一次,持续 40 天)[1]。即使完全停止使用 elacestrant diHCl,肿瘤生长抑制也可能持续[2]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
体外结合试验[2]
根据制造商的说明,在PolarScreen ERα竞争对手分析中,使用野生型和突变型ERα的纯化配体结合结构域测定依拉司琼的体外结合亲和力。 |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞增殖测定 [1]
细胞类型: ER 阳性 MCF-7 细胞(雌二醇 (E2) 刺激) 测试浓度: 0-1 μM 孵育持续时间:48小时 实验结果:显示出抗增殖活性。细胞。 蛋白质印迹分析[1] 细胞类型: MCF-7 细胞 测试浓度: 0.5 nM-10 µM 孵育持续时间:48小时 实验结果:以剂量依赖性方式抑制ERα表达(EC50为0.6 nM)。 蛋白质印迹分析[2] 细胞类型: MCF7、T47D 和 HCC1428 细胞 测试浓度: 0-1 µM 孵化持续时间:24或48小时 实验结果:雌激素受体蛋白表达减少。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Mouse MCF7 cell line xenograft model [2].
Doses: 30, 60 mg/kg Route of Administration: Oral; one time/day for 4 weeks Experimental Results: Inhibition of tumor growth. In vivo xenograft experiments[2] Female athymic nude mice (NU(NCr)-Foxn1nu or BALB/cAnNCrl-Foxn1nu) were acclimated for 3 to 7 days prior to implantation. Mice were given water (reverse osmosis, 1 ppm Cl) and fed a daily complete diet ad libitum, and were housed on irradiated bedding on a 12- to 14-hour light cycle under controlled temperature and humidity. Preformulated, clinical-grade fulvestrant (Faslodex) was obtained through third party vendors and administered by subcutaneous injection once weekly. Elacestrant, palbociclib and everolimus were administered daily by oral gavage. In the ST941 study, groups receiving palbociclib were initially administered 100 mg/kg and dose reduced to 75 mg/kg on day 14 of treatment. At the end of this study, average body weight loss for all treatment groups did not exceed 15%. MCF-7 xenografts.[2] Twenty-four hours prior to implantation of MCF-7 cells, estrogen pellets (0. 18 mg/pellet 17β−estradiol, 90-day release) were implanted subcutaneously between the scapulae of female athymic nude mice using a sterilized trochar. MCF7 cells (5 × 106 per mouse) in 50:50 Matrigel:MEM were implanted in the rear flank. When mean tumor volumes reached approximately 150 to 200 mm3, mice were randomized to treatment groups based on tumor size. For pharmacodynamic analyses, MCF7 xenograft-bearing mice were treated daily for seven days, animals were euthanized, and tumors collected 4 and 24 hours post-last dose. Patient-derived xenograft models.[2] HBCx-21, HBCx-3 and HBCx-19 patient-derived tumor xenografts (PDX) were derived at and studies run at XenTech. The ST986, ST941, and ST2177 PDX models were derived at and studies run at South Texas Accelerated Research Therapeutics. MAXF-713 was derived at and studies run at Charles River Discovery. All animals were subcutaneously implanted with PDX models and began receiving estrogen supplementation in the drinking water from the date of tumor implant to the end of the study. The HBCx-19, HBCx-3, and HBCx-21 models were supplemented with 8.5 milligrams of 17β-estradiol to each liter of drinking water. The MAXF-713 model was supplemented with 10 milligrams of 17β-estradiol to each liter of drinking water. When tumors grew to 150–200 mm3, mice were randomized on the basis of tumor volume and administered the indicated treatments. At the end of study, tumors were harvested 4 hours post-last dose unless otherwise indicated. In vivo pharmacokinetic analyses[2] Terminal plasma was collected via heart puncture and nonterminal plasma was collected via orbital bleeding. For all mice, blood samples were collected in potassium-EDTA–containing tubes and processed for pharmacokinetic analysis. Analysis of fulvestrant in mouse plasma samples was carried out using high-performance liquid chromatography on a Pursuit XRs 3 Diphenyl 100 × 2.0 mm column. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption
With the recommended dosage of 345 mg once daily, elacestrant has a steady-state Cmax of 119 ng/mL and an AUC0-24h of 2440 ng⋅h/mL. The Cmax and AUC of elacestrant increase more than dose-proportional between 43 mg and 862 mg once daily (0.125 to 2.5 times the approved recommended dosage). By day 6, elacestrant reaches steady-state and has a 2-fold mean accumulation ratio based on AUC0-24h. The tmax of elacestrant goes from 1 to 4 hr, and its oral bioavailability is approximately 10%. Compared to a fasted state, the Cmax and AUC of elacestrant (345 mg) were 42% and 22% higher, respectively, when administered with a high-fat meal (800 to 1000 calories, 50% fat). Route of Elimination Elacestrant is mainly eliminated through feces and urine. Approximately 82% was recovered in feces (34% unchanged), and 7.5% was recovered in urine (< 1% unchanged) following a single radiolabeled oral dose of 345 mg. Volume of Distribution Elacestrant has an apparent volume of distribution of 5800 L. Clearance Elacestrant has an estimated clearance of 186 L/hr and a renal clearance of ≤ 0.14 L/hr. Metabolism / Metabolites Elacestrant is metabolized in the liver, mainly by CYP3A4 and, to a lesser extent, by CYP2A6 and CYP2C9. Biological Half-Life The elimination half-life of elacestrant is 30 to 50 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
Elacestrant has a protein plasma binding higher than 99% and independent of concentration. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Elacestrant Hydrochloride is the hydrochloride salt form of elacestrant, an orally available, selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD), with antineoplastic activity. Upon oral administration, elacestrant acts as a SERD, which binds to the estrogen receptor (ER) and induces a conformational change that results in the proteosomal degradation of the receptor. This prevents ER-mediated signaling and inhibits proliferation of ER-expressing cancer cells.
See also: Elacestrant (annotation moved to); Elacestrant dihydrochloride (annotation moved to). |
| 分子式 |
C30H40CL2N2O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
531.5568
|
| 精确质量 |
530.246
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 67.79; H, 7.59; Cl, 13.34; N, 5.27; O, 6.02
|
| CAS号 |
1349723-93-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Elacestrant;722533-56-4;Elacestrant S enantiomer dihydrochloride;2309762-30-7;Elacestrant (S enantiomer);2309762-29-4
|
| PubChem CID |
67479909
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| tPSA |
44.7
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
10
|
| 重原子数目 |
36
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
578
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
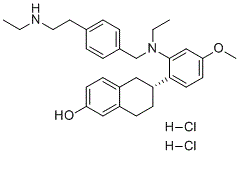
CCNCCC1=CC=C(C=C1)CN(CC)C2=C(C=CC(=C2)OC)[C@@H]3CCC4=C(C3)C=CC(=C4)O.Cl.Cl
|
| InChi Key |
XGFHYCAZOCBCRQ-FBHGDYMESA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C30H38N2O2.2ClH/c1-4-31-17-16-22-6-8-23(9-7-22)21-32(5-2)30-20-28(34-3)14-15-29(30)26-11-10-25-19-27(33)13-12-24(25)18-26/h6-9,12-15,19-20,26,31,33H,4-5,10-11,16-18,21H2,1-3H32*1H/t26-/m1../s1
|
| 化学名 |
(R)-6-(2-(ethyl(4-(2-(ethylamino)ethyl)benzyl)amino)-4-methoxyphenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-ol
dihydrochloride
|
| 别名 |
RAD1901 dihydrochloride; RAD-1901; Elacestrant dihydrochloride; 1349723-93-8; RAD1901 dihydrochloride; Elacestrant (dihydrochloride); Elacestrant hydrochloride; RAD1901 hydrochloride; 8NZT0PR8AL; ORSERDU; RAD 1901; RAD1901 HCl salt; Elacestrant
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~188.13 mM)
H2O : ~50 mg/mL (~94.06 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.87 mg/mL (5.40 mM) (饱和度未知) in 5% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 50% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
*生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.87 mg/mL (5.40 mM) (饱和度未知) in 5% DMSO + 95% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.70 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.70 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100μL 25.0mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到900μL 20%SBE-β-CD生理盐水中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 5 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.70 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 配方 6 中的溶解度: ≥ 0.57 mg/mL (1.07 mM) (饱和度未知) in 1% DMSO + 99% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加),澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8813 mL | 9.4063 mL | 18.8126 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3763 mL | 1.8813 mL | 3.7625 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1881 mL | 0.9406 mL | 1.8813 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。