| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在 SARS-CoV-2 感染的 VeroE6/TMPRSS2 细胞的细胞病变效应 (cpe) 抑制测定中,Ensitrelvir 显示野生型病毒以及 Alpha、Beta、Gamma 和 Delta 变体的 EC50 值约为 0.4 μM。 SARS-CoV 和 MERS-CoV 的 EC50 值分别为 0.21 和 1.4 μM[1]。根据其对 SARS-CoV-2 感染的 VeroE6/TMPRSS2 细胞中引起的细胞病变效应的抑制能力来评估抗病毒活性。 S-217622 对所有测试的 SARS-CoV-2 变体(包括导致当前这一波大流行的 Omicron 菌株)表现出类似的抗病毒活性,表明其作为治疗 COVID-19 的治疗剂具有潜在的广泛用途(半数)。最大有效浓度 [EC50] = 0.29–0.50 μM。S-217622 对 SARS-CoV 的抗病毒活性(EC50 = 0.21 μM)也与针对 SARS-CoV-2 的抗病毒活性相当,其中 3CLpro 与 SARS-CoV 之间的序列同源性CoV-2 和 SARS-CoV 高度保守。S-217622 还对 MERS-CoV (EC50 = 1.4 μM)、HCoV-OC43 (EC90 = 0.074 μM) 和 HCoV-229E (EC50 = 5.5 μM) 表现出有效的抗病毒活性。 )。S-217622 在浓度高达 100 μM 时对宿主细胞蛋白酶(如 caspase-2、糜蛋白酶、组织蛋白酶 B/D/G/L 和凝血酶)没有抑制活性,表明其对冠状病毒蛋白酶具有高选择性。在涉及 ether-a-go-go 相关基因抑制、致突变性/致畸性和光毒性的研究中,217622 没有表现出体外安全性问题。 [3]
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Ensitrelvir 剂量依赖性地抑制小鼠 SARS-CoV-2 的肺内复制[2]。在感染 SARS-CoV-2 Gamma 株的小鼠体内评估了 S-217622 的抗病毒功效。五周大的 BALB/c 小鼠鼻内接种 SARS-CoV-2 Gamma 株(hCoV-19/Japan/TY7-501/2021),并立即以 0.5% 甲基纤维素悬浮液形式口服 S-217622,12感染后数小时。 S-217622 治疗可剂量依赖性地降低肺内病毒滴度。 S-217622 治疗组的平均病毒滴度显着低于媒介物治疗组(2 mg/kg 与媒介物相比,p = 0.0289;8、16 和 32 mg/kg 与媒介物相比,p < 0.0001)。在 S-217622 治疗组中,16 和 32 mg/kg 的病毒滴度接近定量下限(1.80 – log10 50% 组织培养感染剂量 [TCID50]/mL)。虽然该小鼠模型采用每日两次治疗,但每日一次治疗模型也可适用于临床治疗,因为 S-217622 在非啮齿动物中的清除率比啮齿动物低得多,消除半衰期更长。 [3]
|
| 酶活实验 |
3CL蛋白酶抑制测定[3]
在384孔板中进行3CL蛋白酶抑制测定。将物质溶液(10mM二甲基亚砜[DMSO]溶液)逐步稀释至250μmol/L,用DMSO稀释三倍。最后,将溶液与作为化合物溶液的20mmol/L Tris-HCl(pH 7.5)混合。将10微升化合物溶液手动添加到每个孔中,然后添加5微升在抑制缓冲液(2mM EDTA、20mM DTT、0.02%BSA和20mM Tris-HCl,pH 7.5)中的16μM底物。通过在抑制缓冲液中加入5μL的12nM 3CL蛋白酶)并在室温下孵育3小时来启动反应。以下操作与生物筛选中所述的操作相同。 生物筛选[3] 在384孔板中进行化合物筛选测定。通过ECHO 555分配器将不同浓度的测试化合物(159nL)添加到每个孔中。接下来,使用Multidrop Combi分配7.5μL的8μM底物(Dabcyl KTSAVLQSGFRKME[Edans]-NH2,3249-v.)在测定缓冲液(100 mM NaCl、1 mM乙二胺四乙酸[EDTA]、10 mM dl二硫苏糖醇(DTT)、0.01%牛血清白蛋白[BSA]和20 mM Tris-HCl,pH 7.5)中。通过在测定缓冲溶液中加入7.5μL 6或0.6 nM 3CL蛋白酶开始反应,并在室温下孵育3小时。孵育后,通过加入45μL含有0.1%甲酸和10%乙腈的水溶液停止反应。和0.05μmol/L内标肽(Dabcyl KTSAVLeu[136,15N]-Q)。使用连接到iFunnel Agilent 6550精确质量四极飞行时间质谱仪的RapidFire 360高通量采样机器人,使用MS分析反应。使用RapidFire Integrator采集并分析峰值面积。从m/z 499.27获得反应产物峰面积;从m/z 502.78获得IS峰面积。IC50值是通过绘制化合物浓度与抑制的关系并用四参数逻辑拟合数据来确定的。 人蛋白酶测定法[3] 由Eurofins Panlabs Discovery Services台湾有限公司代表Shionogi Co.&有限公司按照既定方案进行针对多种宿主蛋白酶活性的选择性测试。S-217622在一组七种蛋白酶(胱天蛋白酶-2、糜蛋白酶、组织蛋白酶B/D/G/L和凝血酶)上以100μM进行测试。 |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞抗病毒活性[3]
通过监测细胞活力来评估对严重急性呼吸系统综合征冠状病毒2型、严重急性呼吸综合征冠状病毒、MERS-CoV和HCoV-229E的抗病毒活性;通过监测细胞悬浮液中的病毒RNA来评估对抗HCoV-OC43的效果。EC50值是通过绘制化合物浓度与抑制的关系并用四参数逻辑拟合数据来确定的。根据产生的剂量-反应曲线确定针对HCoV-OC43的EC90值,并用两点法计算。 使用VeroE6/TMPRSS2细胞评估针对严重急性呼吸系统综合征冠状病毒2型的抗病毒活性。将悬浮在补充有热灭活的2%FBS的最低必需培养基(MEM)中的VeroE6/TMPRSS2细胞(1.5×104/孔)接种到96孔板中,每个孔中都有稀释的化合物。细胞以30-3000 TCID50/孔感染每种严重急性呼吸系统综合征冠状病毒2型,并在37°C和5%CO2下培养3天或4天。使用CellTiter Glo 2.0测定法评估细胞活力。在培养3天后,在没有病毒的情况下评估CC50。 如前所述,北海道大学使用VeroE6/TMPRSS2细胞评估了对SARS-CoV和MERS-CoV的抗病毒活性。23将悬浮在含2%FBS的MEM中的VeroE6/TMPRSS2(1.5×104/孔)接种到96孔板中,每个孔中都有稀释的化合物。用每种SARS CoV以1000 TCID50/孔或MERS CoV 2500 TCID 50/孔感染细胞,并在37°C和5%CO2下培养3天。如前所述,通过(3-[4,5-二甲基-2-噻唑基]-2,5-二苯基-2H-四唑溴(MTT)测定法评估细胞活力。 使用MRC-5细胞评估针对HCoV-229E的抗病毒活性。将悬浮在含2%FBS的MEM中的MRC-5细胞(2.0×104/孔)接种到96孔板中,并在37°C下与5%CO2孵育过夜。第二天,用1000 TCID50/孔的HCoV-229E感染细胞,并在37°C下用5%CO2孵育1小时,然后去除接种物并加入含有2%FBS的MEM和稀释的化合物。感染HCoV-229E的细胞在37°C和5%CO2下孵育3天。使用CellTiter Glo 2.0测定法评估细胞活力。 使用MRC-5细胞评估针对HCoV-OC43的抗病毒活性。将悬浮在含2%FBS的MEM中的MRC-5细胞(2.0×104/孔)接种到96孔板中,并在37°C下与5%CO2孵育过夜。第二天,用100 TCID50/孔的HCoV-OC43感染细胞,并在37°C下用5%CO2孵育1小时,然后去除接种物并加入含有2%FBS的MEM和稀释的化合物。将感染HCoV-OC43的细胞在37°C和5%CO2下孵育42小时,并使用Quick RNA病毒试剂盒从上清液中提取病毒RNA。使用特异性引物和探针通过实时PCR对病毒RNA进行定量,用于HCoV-OC43检测。 小鼠血清存在下的细胞抗病毒活性[3] 通过监测细胞活力来评估在小鼠血清存在的情况下对严重急性呼吸系统综合征冠状病毒2型的抗病毒活性。S-217622用3.125%、6.25%、12.5%和25%的小鼠血清在补充有热灭活的2%FBS的MEM中稀释。将100微升连续稀释的化合物溶液添加到96孔板中,并在室温下孵育约1小时。用补充有热失活的2%FB的MEM将每个50μL/孔的VeroE6/TMPRSS2细胞调节至3.0×105个细胞/mL,并分配到板上。以10000 TCID50/孔的速度加入每50μL/孔的严重急性呼吸系统综合征冠状病毒2,并在37°C和5%CO2下培养3天。使用CellTiter Glo 2.0测定法评估细胞活力,然后根据细胞活力测定EC50值。使用每种血清浓度的EC50值通过线性回归计算外推到100%血清的PA-EC50。通过将PA-EC50(100%小鼠血清的外推值)除以EC50(在存在小鼠血清的情况下)来计算外推到100%血清的PS。 |
| 动物实验 |
In Vivo SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Treatment Studies[3]
In vivo SARS-CoV-2 infection experiments were conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care (AAALAC). The animal study protocol was approved by the director of the institute based on the report of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Shionogi Research Laboratories. Mouse in vivo SARS-CoV-2 infection studies were done at Shionogi Pharmaceutical Research Center. Five-week-old female BALB/cAJcl mice (n = 5 or 10 per group) were intranasally inoculated with SARS-CoV-2 Gamma strain (hCoV-19/Japan/TY7-501/2021) (10000 TCID50/mouse) under anesthesia. Immediately after infection, the mice were orally administered S-217622 fumaric acid (2, 8, 16, or 32 mg/kg q12h; n = 5 per group) or vehicle (0.5 w/v% methyl cellulose in aqueous solution q12h; n = 10 per group) for 1 day. Twenty-four hours postinfection, the mice were euthanized via cervical dislocation under anesthesia; their lungs were removed, and the viral titers in the lung homogenates were determined using VeroE6/TMPRSS2 cells. Viral titers are expressed as log10 TCID50/mL. PK Study in Infected Mice[3] View More
PK experiments in infected mice were conducted in accordance with the guidelines provided by AAALAC and were approved by IACUC of Shionogi Research Laboratories. Rat PK Studies[3] The animal study protocol was approved by the director of the institute after reviewing the protocol by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee in terms of the 3R (Replacement/Reduction/Refinement) principles. Rat PK studies were done at Shionogi Pharmaceutical Research Center. Eight-week-old male Sprague–Dawley rats were purchased from Charles River Laboratories. For oral administration, the dosing vehicle was dimethyl sulfoxide/0.5% methylcellulose (400 cP) = 1:4. The compound was orally administered at 1–2 μmol/5 mL/kg (n = 2) under nonfasted conditions. Blood samples (0.2 mL) were collected with 1 mL syringes containing anticoagulants (EDTA-2K and heparin) at 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, and 24 h after dosing. For intravenous administration, compounds were formulated as solutions in dimethyl sulfoxide/propylene glycol (1:1, v/v) and intravenously administered via the tail vein at 0.5–1.0 μmol/mL/kg (n = 2) under isoflurane anesthesia under nonfasted conditions. Blood samples (0.2 mL) were collected with 1 mL syringes containing anticoagulants (EDTA-2K and heparin) at 3, 10, 30, 60, 120, 240, and 360 min after dosing. Blood samples were centrifuged to obtain plasma samples, which were transferred to each tube and stored in a freezer until analysis. Plasma concentrations were determined by LC/MS/MS after protein precipitation with MeOH or MeCN. LC/MS/MS analysis was performed using a SCIEX Triple Quad 5500 or SCIEX API5000 or SCIEX Triple Quad 5500. PK parameters were calculated by noncompartmental analysis. Dog/Monkey PK Studies[3] PK experiments in dogs and monkeys were conducted in accordance with the guidelines provided by AAALAC. The animal study protocol was approved by the director of the institute after reviewing the protocol by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee in terms of the 3R (Replacement/Reduction/Refinement) principles. Dog and Monkey PK studies were done at Shionogi Aburahi Research Center. Male beagles were purchased from Marshall BioResources. Female cynomolgus monkeys were purchased from Shin Nippon Biomedical Laboratories, Ltd. or Hamri Co., Ltd. For oral administration, dosing vehicles were 0.5% methylcellulose (400 cP). The compound was orally administered at 3 mg/2 mL/kg (n = 3) under nonfasted conditions. Blood samples (0.3 mL) were collected with 1 mL syringes containing anticoagulants (EDTA-2K and heparin) at 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, and 24 h after dosing. For intravenous administration, compounds were formulated as solutions in dimethyl acetamide/ethanol/20% HP-β-CD in carbonate buffer (pH 9.0) (2:3:5, by volume) and intravenously administered via a forelimb or hind limb vein at 0.1 mg/0.2 mL/kg (n = 2) under nonfasted conditions. Blood samples (0.2 mL) were collected with 1 mL syringes containing anticoagulants (EDTA-2K and heparin) at 2, 5, 15, 30, 60, 120, 240, 480, and 1440 min after dosing. Blood samples were centrifuged to obtain plasma samples, which were transferred to each tube and stored in a freezer until analysis. Plasma concentrations were determined by LC/MS/MS after protein precipitation with MeOH or MeCN. LC/MS/MS analysis was performed using a SCIEX API5000 or SCIEX Triple Quad 6500 or Triple Quad 6500+ (Sciex, Framingham, MA). PK parameters were calculated by noncompartmental analysis. |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Discovery of S-217622, a Non-Covalent Oral SARS-CoV-2 3CL Protease Inhibitor Clinical Candidate for Treating COVID-19. bioRxiv 2022.01.26.477782.
[2]. COVID-19, Influenza and RSV: Surveillance-informed prevention and treatment - Meeting report from an isirv-WHO virtual conference. Antiviral Res. 2022;197:105227. [3]. Discovery of S-217622, a Noncovalent Oral SARS-CoV-2 3CL Protease Inhibitor Clinical Candidate for Treating COVID-19. J Med Chem. 2022 May 12;65(9):6499-6512. |
| 其他信息 |
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has resulted in millions of deaths and threatens public health and safety. Despite the rapid global spread of COVID-19 vaccines, effective oral antiviral drugs are urgently needed. Here, we describe the discovery of S-217622, the first oral noncovalent, nonpeptidic SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease inhibitor clinical candidate. S-217622 was discovered via virtual screening followed by biological screening of an in-house compound library, and optimization of the hit compound using a structure-based drug design strategy. S-217622 exhibited antiviral activity in vitro against current outbreaking SARS-CoV-2 variants and showed favorable pharmacokinetic profiles in vivo for once-daily oral dosing. Furthermore, S-217622 dose-dependently inhibited intrapulmonary replication of SARS-CoV-2 in mice, indicating that this novel noncovalent inhibitor could be a potential oral agent for treating COVID-19.[3]
|
| 分子式 |
C22H17CLF3N9O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
531.884
|
| 精确质量 |
531.11
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 49.68; H, 3.22; Cl, 6.66; F, 10.72; N, 23.70; O, 6.02
|
| CAS号 |
2647530-73-0
|
| 相关CAS号 |
2647530-73-0;2757470-18-9 (fumarate);
|
| PubChem CID |
162533924
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to light yellow solid powder
|
| LogP |
2.5
|
| tPSA |
114Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
37
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
919
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
QMPBBNUOBOFBFS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H17ClF3N9O2/c1-32-7-12-4-18(13(23)5-17(12)30-32)28-20-29-21(36)35(9-19-27-10-33(2)31-19)22(37)34(20)8-11-3-15(25)16(26)6-14(11)24/h3-7,10H,8-9H2,1-2H3,(H,28,29,36)
|
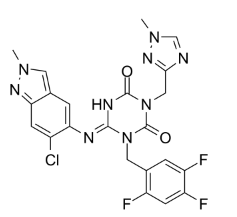
| 化学名 |
(E)-6-((6-chloro-2-methyl-2H-indazol-5-yl)imino)-3-((1-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)methyl)-1-(2,4,5-trifluorobenzyl)-1,3,5-triazinane-2,4-dione
|
| 别名 |
Ensitrelvir; S-217622; S 217622; S217622; Xocova; S-217622; Ensitrelvir [INN]; PX665RAA3H; Ensitrelvir (S-217622); (E)-6-((6-chloro-2-methyl-2H-indazol-5-yl)imino)-3-((1-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)methyl)-1-(2,4,5-trifluorobenzyl)-1,3,5-triazinane-2,4-dione; 1,3,5-Triazine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione, 6-[(6-chloro-2-methyl-2H-indazol-5-yl)imino]dihydro-3-[(1-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)methyl]-1-[(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)methyl]-, (6E)-;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~50 mg/mL (~94.01 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.70 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.70 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.70 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.70 mM) 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8801 mL | 9.4006 mL | 18.8012 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3760 mL | 1.8801 mL | 3.7602 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1880 mL | 0.9401 mL | 1.8801 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
|
|
|
|
|
|