| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
ER/estrogen receptor β (Ki = 0.73 nM)
Estrogen Receptor β (ERβ): S-equol (a stereoisomer of Equol) binds to human ERβ with high affinity, Ki = 0.03 nM; binds ERα with low affinity, Ki = 1.5 nM [1] - cAMP-Protein Kinase A (PKA) Signaling Pathway: S-equol activates this pathway in pancreatic β-cells, with an EC50 of 10 μM for increasing intracellular cAMP levels [3] - Akt/FOXO3a Pathway: S-equol modulates this pathway to inhibit prostate cancer growth; [2] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
(-)-(S)-Equol 对 ERβ 的亲和力最高 (Ki=0.73±0.2 nM),但对 ERα 的亲和力较差 (Ki=6.41±1 nM) [1]。 (-)-(S)-Equol 抑制 LnCaP、DU145 和 PC3 人类前列腺癌细胞系的增殖。 (-)-(S)-Equol 通过下调细胞周期蛋白 B1 和 CDK1 并上调 CDK 抑制剂(p21 和 p27)导致 PC3 细胞中细胞周期停滞在 G2,并通过上调 Fas 配体 (FasL) 导致细胞凋亡。 /M 阶段)和促凋亡 Bim 的产生。 (-)-(S)-Equol 促进 FOXO3a 表达,抑制 p-FOXO3a 表达,并提高 FOXO3a 核稳定性。 (-)-(S)-Equol 还降低 MDM2 的表达,MDM2 充当 p-FOXO3a 的 E3 泛素连接酶,防止 p-FOXO3a 被蛋白酶体破坏。 [2]。 (-)-(S)-Equol 对映选择性地促进 INS-1 细胞活力,可能是通过激活 PKA 信号传导来实现的。 (-)-(S)-牛尿酚可用作抗 2 型糖尿病药物。在 INS-1 胰腺 β 细胞中,(-)-(S)-Equol 磷酸化 cAMP 反应元件结合蛋白 Ser 133 并促进 cAMP 反应元件介导的转录 [3]。
1. ERβ结合与选择性([1]): 重组人ERα/β结合实验显示,S-equol(0.001–100 nM)对ERβ的[³H]-雌二醇置换能力显著强于ERα。0.03 nM时可置换50% ERβ结合的[³H]-雌二醇(Ki=0.03 nM),而ERα需1.5 nM(Ki=1.5 nM)。浓度达100 nM时,不与孕酮受体或雄激素受体结合 [1] 2. 前列腺癌细胞抗增殖活性([2]): 用S-equol(1–20 μM)处理PC-3(雄激素非依赖性)和LNCaP(雄激素依赖性)前列腺癌细胞72小时,抑制增殖:IC50分别为5 μM(PC-3)和3 μM(LNCaP)(MTT实验)。10 μM时诱导凋亡:Annexin V阳性细胞比例在PC-3中增加40%,LNCaP中增加35%;蛋白质印迹法显示切割型caspase-3在PC-3中上调3倍,LNCaP中上调2.5倍。同时激活Akt/FOXO3a通路:p-Akt增加2倍,核内FOXO3a减少60% [2] 3. 胰岛β细胞保护作用([3]): INS-1胰岛β细胞用S-equol(1–50 μM)预处理1小时后,暴露于毒剂四氧嘧啶(5 mM)24小时。10 μM S-equol使四氧嘧啶诱导的细胞死亡减少55%(MTT实验),细胞内cAMP水平升高2.2倍(ELISA检测)。PKA抑制剂H-89(1 μM)可阻断该保护效应,证实依赖cAMP-PKA信号 [3] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
(-)-(S)-牛尿酚在第 33 天没有表现出明显的毒性,与对照相比,其抑制肿瘤生长的能力分别为 43.2% 和 28.4% [2]。
此外,用s -雌马酚处理可以抑制BALB/c裸鼠PC3异种移植瘤的生长。[2] 前列腺癌异种移植模型的抗肿瘤疗效([2]): 6–8周龄雌性裸鼠皮下接种5×10⁶ PC-3细胞,肿瘤体积达100 mm³后,腹腔注射S-equol(10 mg/kg/天)或溶剂,连续28天。S-equol较对照组使肿瘤体积减少65%,肿瘤重量减少60%(每周两次测量)。肿瘤组织分析:蛋白质印迹法显示p-Akt增加1.8倍,切割型caspase-3增加2.3倍;免疫组化显示增殖标志物Ki-67阳性率降低50% [2] |
| 酶活实验 |
采用手性相高效液相色谱法和质谱法,从人尿液和血浆中分离得到雌马酚,并对其对映体结构进行了鉴定。人类粪便菌群在体外培养,并与大豆黄酮一起孵育,以确定细菌产生雌马酚的立体特异性。单次口服两种对映体后,在3名健康成年人中测定了S-和R-雌马酚的药代动力学,并测量了每种雌马酚对映体对雌激素受体的亲和力[1]。
1. ERα/β竞争结合实验([1]): 1. 重组ER制备:人ERα和ERβ蛋白在Sf9昆虫细胞中表达,通过镍亲和层析纯化。 2. 反应体系:200 μL体系含50 mM Tris-HCl(pH 7.4)、10%甘油、0.5 nM [³H]-雌二醇、100 ng纯化ER(α/β)及S-equol(0.001–100 nM)。 3. 孵育与分离:4°C孵育24小时,加入葡聚糖包被活性炭(1%活性炭、0.1%葡聚糖),3000×g离心10分钟去除未结合的[³H]-雌二醇。 4. 检测与计算:液体闪烁计数器检测放射性,采用Cheng-Prusoff方程计算Ki值 [1] 2. cAMP-PKA活性实验([3]): 1. 细胞裂解液制备:S-equol(1–50 μM)处理30分钟的INS-1细胞,用RIPA缓冲液裂解。 2. cAMP检测:ELISA试剂盒检测细胞内cAMP:50 μL裂解液与cAMP抗体(1:1000)及底物混合,450 nm处测吸光度,从剂量反应曲线计算EC50。 3. PKA活性检测:激酶试剂盒检测裂解液中PKA活性:加入1 mM ATP和PKA底物肽,蛋白质印迹法(抗磷酸化肽抗体)检测磷酸化肽 [3] |
| 细胞实验 |
将PC3细胞接种在96孔培养板(约5×103个细胞/孔)中,并在37°C下培养过夜。接下来,将细胞与含有指定浓度的(-)-(S)-Equol和/或DMSO的培养基在37°C下孵育72小时。细胞活力通过MTT法测定[2]。
1. 前列腺癌细胞实验([2]): - 细胞培养:PC-3/LNCaP细胞用含10%胎牛血清的RPMI 1640培养,接种于96孔板(5×10³细胞/孔,增殖实验)或6孔板(2×10⁵细胞/孔,凋亡/蛋白检测)。 - 药物处理:细胞用S-equol(1–20 μM)处理72小时(增殖)或48小时(凋亡/蛋白);部分组联合Akt抑制剂(LY294002,10 μM)处理。 - 检测: 1. 增殖:MTT实验(570 nm吸光度)计算IC50; 2. 凋亡:Annexin V-FITC/PI染色,流式细胞术分析; 3. 蛋白:蛋白质印迹法检测p-Akt、FOXO3a、切割型caspase-3(β-肌动蛋白为内参)[2] 2. 胰岛β细胞实验([3]): - 细胞培养:INS-1细胞用含10%胎牛血清+5.6 mM葡萄糖的DMEM培养,接种于96孔板(3×10³细胞/孔,活力检测)或12孔板(1×10⁵细胞/孔,cAMP检测)。 - 药物处理:细胞用S-equol(1–50 μM)预处理1小时,再暴露于四氧嘧啶(5 mM)24小时。 - 检测: 1. 活力:MTT实验(570 nm吸光度)计算细胞存活率; 2. cAMP:细胞裂解液通过cAMP ELISA试剂盒检测 [3] |
| 动物实验 |
Mice are randomly divided into three groups of six mice each, and are treated by intragastric administration. The experimental groups are treated with 10 mg/kg or 20 mg/kg bodyweight of (-)-(S)-Equol (mice are treated everyday for 33 days). The control group is treated with an identical volume of 0.01ml sesame seed oil and 0.09 mL normal saline. The tumor size is examined every three days [2].
Prostate Cancer Xenograft Protocol ([2]): 1. Animal Selection: 6–8 weeks old female nude mice (n=6/group) randomized to control, S-equol (10 mg/kg). 2. Model Induction: 5×10⁶ PC-3 cells (suspended in 0.2 mL PBS + 50% Matrigel) subcutaneously injected into right flank. 3. Drug Preparation: S-equol dissolved in DMSO (5% v/v) + normal saline (95% v/v) to 1 mg/mL. 4. Administration: Intraperitoneal injection (10 mL/kg) once daily for 28 days; control received vehicle. 5. Detection: Tumor volume measured twice weekly (length×width²/2); mice euthanized, tumors collected for Western blot (p-Akt, cleaved caspase-3) and Ki-67 immunohistochemistry [2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Origin & Absorption: S-equol is not naturally present in soy but produced by human intestinal bacteria (e.g., Slackia isoflavoniconvertens) via daidzein metabolism. Oral bioavailability in humans is ~40%, with peak plasma concentration (Cmax) of 80 ng/mL reached 2 hours after daidzein supplementation (50 mg) [1]
- Metabolism & Excretion: S-equol is conjugated with glucuronic acid in the liver; ~70% of metabolites excreted in urine, 30% in feces. Plasma half-life is ~8 hours in humans [1] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC).
1. In Vitro Toxicity: - S-equol (1–20 μM) showed no cytotoxicity to normal prostate epithelial cells (RWPE-1) or pancreatic β-cells (viability >90% vs. control) [2][3] 2. In Vivo Toxicity: - Mice treated with S-equol (10 mg/kg/day, 28 days) had no changes in body weight, liver function (ALT/AST), or kidney function (BUN/creatinine) [2] 3. Plasma Protein Binding: S-equol has high plasma protein binding (>95%) in human plasma (bound to albumin) [1] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Equol is a member of hydroxyisoflavans.
Equol has been used in trials studying the treatment of Breast Cancer. Equol has been reported in Punica granatum with data available. S-equol is an orally bioavailable, non-steroidal estrogen naturally produced by the metabolism of the isoflavonoid daidzein by human intestinal microflora, with potential chemoprotective and estrogen receptor (ER) modulating activities. S-equol preferentially binds to and activates the beta isoform of ER in certain target tissues, while having an antagonistic effect in other tissues. This modulates the expression of ER-responsive genes in a tissue-specific manner. This agent may increase bone mineral density, affect vasomotor symptoms, and may decrease the proliferation rate of susceptible cancer cells. In addition, this agent interferes with the activity of enzymes involved in steroid biosynthesis. S-equol inhibits dihydrotestosterone (DHT) production and may inhibit the proliferation of androgen-driven prostate cancer. S-equol is the biologically active enantiomer while R-equol is essentially inactive and has a weak affinity for alpha-ER. Equol is a metabolite of daidzein, a phytoestrogen common in the human diet and abundant in soy. Intestinal bacteria in humans can reduce daidzein to equol, and can be found in normal human urine. The clinical effectiveness of soy isoflavones may be a function of the ability to biotransform soy isoflavones to the more potent estrogenic metabolite, equol, which may enhance the actions of soy isoflavones, owing to its greater affinity for estrogen receptors, unique antiandrogenic properties, and superior antioxidant activity. However, not all individuals consuming daidzein produce equol. Only approximately one-third to one-half of the population is able to metabolize daidzein to equol. This high variability in equol production is presumably attributable to interindividual differences in the composition of the intestinal microflora, which may play an important role in the mechanisms of action of isoflavones. (A3188, A3189). A non-steroidal ESTROGEN generated when soybean products are metabolized by certain bacteria in the intestines. 1. Drug Background ([1][2]): S-equol is the biologically active enantiomer of Equol, a secondary metabolite of the soy isoflavone daidzein. Only 30–50% of humans produce S-equol due to interindividual differences in intestinal flora [1][2] 2. Mechanism of Action ([1][2][3]): - ERβ Modulation: Binds ERβ to regulate estrogen-responsive genes (e.g., anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative) [1] - Prostate Cancer Inhibition: Activates Akt/FOXO3a pathway to suppress cell proliferation and induce apoptosis [2] - Pancreatic β-Cell Protection: Activates cAMP-PKA signaling to reduce oxidative stress-induced cell death [3] 3. Therapeutic Potential ([2][3]): - Potential adjuvant for prostate cancer therapy (especially androgen-independent subtypes) [2] - Candidate for preventing type 2 diabetes via protecting pancreatic β-cell function [3] |
| 分子式 |
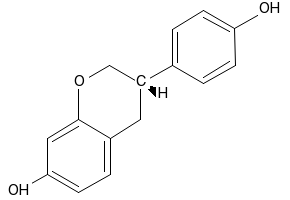
C15H14O3
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
242.27
|
|
| 精确质量 |
242.094
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 74.36; H, 5.82; O, 19.81
|
|
| CAS号 |
531-95-3
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
(±)-Equol;94105-90-5;(R)-Equol;221054-79-1
|
|
| PubChem CID |
91469
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to yellow solid
|
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
441.7±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
189-190ºC
|
|
| 闪点 |
220.9±28.7 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.645
|
|
| 来源 |
Endogenous Metabolite
|
|
| LogP |
2.98
|
|
| tPSA |
49.69
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
1
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
18
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
273
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
O1C2C([H])=C(C([H])=C([H])C=2C([H])([H])[C@@]([H])(C2C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=2[H])O[H])C1([H])[H])O[H]
|
|
| InChi Key |
ADFCQWZHKCXPAJ-GFCCVEGCSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
1S/C15H14O3/c16-13-4-1-10(2-5-13)12-7-11-3-6-14(17)8-15(11)18-9-12/h1-6,8,12,16-17H,7,9H2/t12-/m1/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (10.32 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (10.32 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (10.32 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 10 mg/mL (41.28 mM) in 50% PEG300 50% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.1276 mL | 20.6381 mL | 41.2763 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8255 mL | 4.1276 mL | 8.2553 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4128 mL | 2.0638 mL | 4.1276 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。