| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
HIV
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
福沙那韦钙盐 (GW433908G)(前药的钙盐)被选择进行额外研究,因为它似乎最有希望创造新的药物制剂 [1]。
体外活性:Amprenavir 促进核受体孕烷 X 受体 (PXR) 与共激活剂 SRC-1 和 PBP 之间的特异性相互作用。 Amprenavir 与 SR12813 形成复合物,对接至人 PXR 的高分辨率晶体结构中。 Amprenavir 占据了所有四个子口袋,其羟基与位于 PXR 连接区域的 Ser247 形成氢键,有助于将药物定位在受体内的最佳方向。安普那韦与 PXR 激活功能 2 (AF-2) 表面的 αAF 上的一个残基 Phe429 形成直接接触,这可能稳定受体的活性 AF-2 构象,并有助于安普那韦对 PXR 的激动剂活性。 Amprenavir 在 HepaRG 细胞和 LS180 细胞中诱导参与 I 期 (CYP3A4)、II 期 (UGT1A1) 和 III 期 (MDR1) 代谢的真正 PXR 靶基因的表达。细胞测定:Amprenavir 在 HepaRG 肝癌细胞和 LS180 肠细胞中诱导 PXR 靶基因表达。 Fosamprenavir是一种磷酸酯前药,在溶解后,会被分解为难溶但易吸收的母体药物amprenavir。在这项研究中,设计并测试了一种新型的无细胞体外装置,该装置可准连续监测福沙普那韦的动态溶解/生物转化/渗透。它由并排的扩散池组成,供体和受体隔室由仿生屏障PermeaPad®隔开,供体隔室的取样是通过微透析探针完成的。外部添加的牛碱性磷酸酶在供体室中诱导生物转化。微透析取样允许以(几乎)实时的方式跟踪牛碱性磷酸酶将磷雷那韦酶转化为安普那韦的过程,从而消除了去除或灭活酶的需要。通过添加适量的碱性磷酸酶,建立了装置中的仿生转化率。由于在较低(500µM)浓度下的生物转化,观察到amprenavir的大量(6.5倍)和持续的过饱和,导致穿过仿生屏障的通量大幅增加,很好地反映了体内的情况。在剂量比通常人体剂量高出近10倍的条件下,一些重复实验显示过早沉淀和过饱和度崩溃,而另一些则没有。总之,所提出的新工具在深入了解生物转化/渗透相互作用的机制方面似乎非常有前景,包括磷酸酯前体药物(如福沙普那韦)的瞬时过饱和[2]。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Amprenavir 会增加 WT 小鼠中致动脉粥样硬化的 LDL 胆固醇分数,但不会增加 PXR−/− 小鼠中的水平。 Amprenavir 刺激 WT 小鼠肠道中已知 PXR 靶基因的表达,包括 CYP3A11、谷胱甘肽转移酶 A1 和 MDR1a,但在 PXR−/− 小鼠中则不然。安普那韦介导的 PXR 激活刺激 WT 小鼠肠道中 LipF 和 LipA 的表达,但在 PXR−/− 小鼠中则不然,表明肠道 PXR 在介导哺乳动物饮食脂质分解和吸收中可能发挥作用。
|
| 酶活实验 |
真实浓度与灌注液浓度的相关性:提取效率校正因子[2]
标准品是在烧杯中制备的,烧杯中含有浓度越来越高的amprenavir(0.94、2.44、9.76、24.4和48.8µM)和fosamprenavir(5.6、14.2、56.9、142和284µM)。烧杯用磁力搅拌棒搅拌,并在加热板上加热至37°C。将微透析探针连续放置在相应的烧杯中,以确定提取效率校正因子。灌注液在HBSS中含有0.2%(w/V)的维生素E TPGS,用注射泵以10µL/min的恒定速率泵送通过试管和探针。以15-20、20-25和25-30分钟的时间间隔收集样本,并用UHPLC-UV进行分析。 用于生物转化/渗透研究的并排细胞微透析提取效率校正因子[2] 将含有69.8µMfosamprenavir和53.9µM安复那韦的溶液填充到由PermeaPad®分隔的并排细胞的供体和受体隔室中。当微透析运行30分钟以达到平衡时,并排电池的水套保持在37°C。之后,按照第2.5.1节所述,通过在并排单元内进行测量来确定校正系数。 动态生物转化/渗透研究[2] 生物转化/渗透研究[2] 生物转化/渗透研究是在并排的细胞中进行的,这些细胞连接在37°C的循环水加热系统上,仿生屏障PermeaPad®的表面积为1.77 cm2,将供体和受体隔室隔开。受体隔室填充有7 mL含0.2%维生素E TPGS的HBSS,而供体体积为5.0 mL(设置1)、6.0 mL(设置2)和5.5 mL(设置3);三个重复实验之间的微小差异是由于并排细胞的几何形状存在微小差异,因为体积必须足以完全覆盖膜和微透析探针。将连接到填充有HBSS中0.2%维生素E TPGS的注射泵上的微透析探针浸入供体室(完整设置的图像可以在补充材料中找到)。通过十字型磁力搅拌棒以500rpm搅拌两个隔室。 供体隔室填充有500µM的amprenavir混悬液,该混悬液在振荡水浴中平衡过夜,或437µM的fosamrenavir溶液。在所有溶解/生物转化实验前20分钟,以10µL/min的流速启动注射泵。在福沙那韦的情况下,此时填充供体,将微透析探针浸入fosamrenavir溶液中以达到平衡。20分钟后,将牛碱性磷酸酶加入供体中,以分别对应于5.3 U/mL或53 U/mL的浓度启动实验。在安非那韦悬浮液的情况下,在加入安非那vir悬浮液后立即将微透析探针浸入供体室中以开始实验。每隔10分钟收集一次透析液样本,共180分钟。之后,用UHPLC-UV定量透析液浓度,并使用第2.5.2节中描述的探针特异性提取效率校正因子将其转换为供体浓度。在30、60、90、120和180分钟后取出常规200µL受体样品,并用UHPLC-UV定量。 人体剂量的溶解/生物转化/渗透研究[2] 在动态生物转化/渗透实验中加入溶解步骤,在供体室中加入一定量的福沙那韦,最终浓度为4500µM。这些实验的进行方式与第2.7.1节中的生物转化/渗透实验相同。然而,与安非那韦混悬液一样,微透析用供体外的探针校准了20分钟。在实验开始时添加HBSS和53U/mL酶后,立即将微透析探针添加到供体中。 |
| 细胞实验 |
MDCK wt细胞的渗透实验[2]
Marbine Darby犬肾野生型(MDCK-wt)细胞在由Dulbecco改良的Eagle培养基组成的培养基中维持,该培养基含有高葡萄糖,补充了10%胎牛血清和500U/mL青霉素/链霉素。将细胞以1.8×106个细胞/转孔的细胞密度接种在6孔转孔板(0.4µm聚碳酸酯膜)上,并在细胞培养基中分化三天。分化后,吸出细胞培养基,用HBSS洗涤细胞三次。然后,将带有MDCK wt细胞的过滤器支架转移到6孔板中,并将HBSS添加到孔的顶端(1.5 mL)和基底外侧(2.6 mL)。在生物转化/渗透实验之前,将平板在37°C的HBSS中预孵育20分钟。 生物转化/渗透实验是通过用385µMfosamprenavir溶液或80µM安那韦溶液替换顶端的HBSS来启动的。细胞在Heidolph Titramax培养箱中以400 rpm和37°C的速度培养。在10、20、30、45、60、90、120、150和180分钟时从基底外侧取出500µL的样品。取样后,将500µL HBSS添加到基底外侧作为样品的替代品。用UHPLC-UV对样品中的药物浓度进行定量。 在与MDCK-wt细胞的生物转化/渗透实验相同的条件下,在HBSS中用1:1000稀释的放射性标记的3H-甘露醇(15.9Ci/mmol)在类似的实验中研究了MDCK-wt电池的完整性。通过混合100µL受体样品和400µL闪烁介质来定量3H-甘露醇,并在放射性计数器上进行测量。 Amprenavir 在 HepaRG 肝癌细胞和 LS180 肠细胞中诱导 PXR 靶基因表达。 |
| 动物实验 |
Permeation experiments in MDCK-wt cells [2]
Marbine-Darby Canine kidney wild-type (MDCK-wt) cells were maintained in culture medium composed of Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium with high glucose supplemented with 10% foetal bovine serum and 500U/mL penicillin/streptomycin. Cells were seeded on 6 well transwell-plates (0.4 µm polycarbonate membrane) at the cell density of 1.8 × 106 cells/transwell and differentiated for three days in cell culture media. After the differentiation, the cell culture media was aspirated, and the cells were washed three times with HBSS. Then, the filter supports with MDCK-wt cells were transferred into 6-well plates, and HBSS was added to the wells’ apical (1.5 mL) and basolateral (2.6 mL) sides. Before the bioconversion/permeation experiments, the plates were pre-incubated in HBSS for 20 min at 37 °C. The bioconversion/permeation experiments were initiated by replacing the HBSS on the apical side with either 385 µM fosamprenavir solutions or 80 µM amprenavir solutions. The cells were incubated in Heidolph Titramax incubator at 400 rpm and 37 °C. Samples of 500 µL were withdrawn from the basolateral side at 10, 20, 30, 45, 60, 90, 120, 150, and 180 min. After sampling, 500 µL HBSS was added to the basolateral side as a replacement for the sample. The drug concentrations were quantified from the samples with UHPLC-UV. The ntegrity of the MDCK-wt cells was investigated in a similar experiment with 1:1000 diluted radiolabeled 3H mannitol (15.9 Ci/mmol) in HBSS under the same conditions as in the bioconversion/permeation experiments with MDCK-wt cells. The 3H mannitol was quantified by mixing a 100 µL acceptor sample and 400 µL scintillation medium and measured on a radioactivity counter. Amprenavir induced PXR target gene expression in both HepaRG hepatoma cells and LS180 intestinal cells. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
The absolute oral bioavailability of amprenavir after administration of fosamprenavir in humans has not been established. After administration of a single 1,400 mg dose in the fasted state, fosamprenavir oral suspension (50 mg/mL) and fosamprenavir tablets (700 mg) provided similar amprenavir exposures (AUC), however, the Cmax of amprenavir after administration of the suspension formulation was 14.5 % higher compared with the tablet. Excretion of unchanged amprenavir in urine and feces is minimal. The renal elimination of unchanged amprenavir represents approximately 1% of the administered dose; therefore, renal impairment is not expected to significantly impact the elimination of amprenavir. Amprenavir, the active metabolite of fosamprenavir, is metabolized in the liver by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system. Fosamprenavir is a prodrug that is rapidly hydrolyzed to amprenavir by enzymes in the gut epithelium as it is absorbed. After administration of a single dose of fosamprenavir to HIV-1-infected patients, the time to peak amprenavir concentration (Tmax) occurred between 1.5 and 4 hours (median 2.5 hours). The absolute oral bioavailability of amprenavir after administration of fosamprenavir in humans has not been established. Administration of a single 1400 mg dose of fosamprenavir in the fed state compared with the fasted state was associated with no significant changes in amprenavir Cmax, Tmax or AUC. The following are areas under the curve (AUC) values of amprenavir based on the drug therapy regimen administered: Fosamprenavir 1400 mg twice per day: 27.6 to 39.2 ug/hr/mL (median 33 ug/hr/mL; Fosamprenavir 1400 mg once per day plus ritonavir 200 mg once per day: 59.7 to 80.8 ug/hr/mL (median 69.4 ug/hr/mL);Fosamprenavir 700 mg twice per day plus ritonavir 100 mg twice per day: 69 to 90.6 ug/hr/mL (median 79.2 ug/hr/mL). Fosamprenavir may be taken with or without food. Peak plasma concentration (Cmax): The following Cmax values of amprenavir based on the drug therapy regimen administered: Fosamprenavir 1400 mg once per day plus ritonavir 200 mg once per day: 6.32 to 8.28 ug/mL (median 7.24 ug/mL); Fosamprenavir 1400 mg twice per day: 4.06 to 5.72 ug/mL (median 4.82 ug/mL); Fosamprenavir 700 mg twice per day plus ritonavir 100 mg twice per day: 5.38 to 6.86 ug/mL (median 6.08 ug/mL)... For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for FOSAMPRENAVIR (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites In the gut epithelium during absorption, fosamprenavir is rapidly and almost completely hydrolyzed to amprenavir and inorganic phosphate prior to reaching the systemic circulation. Amprenavir is metabolized in the liver by the cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) enzyme system. After oral administration, fosamprenavir is rapidly and almost completely hydrolyzed to amprenavir and inorganic phosphate prior to reaching the systemic circulation. This occurs in the gut epithelium during absorption. Amprenavir is metabolized in the liver by the cytochrome P450 and 3A4 (CYP3A4) enzyme system. The 2 major metabolites result from oxidation of the tetrahydrofuran and aniline moieties. Glucuronide conjugates of oxidized metabolites have been identified as minor metabolites in urine and feces. Biological Half-Life The plasma elimination half-life of amprenavir (the active metabolite) is approximately 7.7 hours. The plasma elimination half-life of amprenavir is approximately 7.7 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No published information is available on the use of fosamprenavir during breastfeeding. Fosamprenavir is not recommended during breastfeeding. Achieving and maintaining viral suppression with antiretroviral therapy decreases breastfeeding transmission risk to less than 1%, but not zero. Individuals with HIV who are on antiretroviral therapy with a sustained undetectable viral load and who choose to breastfeed should be supported in this decision. If a viral load is not suppressed, banked pasteurized donor milk or formula is recommended. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Gynecomastia has been reported among men receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy. Gynecomastia is unilateral initially, but progresses to bilateral in about half of cases. No alterations in serum prolactin were noted and spontaneous resolution usually occurred within one year, even with continuation of the regimen. Some case reports and in vitro studies have suggested that protease inhibitors might cause hyperprolactinemia and galactorrhea in some male patients, although this has been disputed. The relevance of these findings to nursing mothers is not known. The prolactin level in a mother with established lactation may not affect her ability to breastfeed. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Fosamprenavir (brand name: Lexiva) is a prescription medicine approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of HIV infection in adults and children. Fosamprenavir is always used in combination with other HIV medicines.
Although fosamprenavir is FDA-approved for use in adults and children, it is no longer commonly used or recommended as an HIV treatment. The Guidelines for the Use of Antiretroviral Agents in Adults and Adolescents with HIV and the Guidelines for the Use of Antiretroviral Agents in Pediatric HIV Infection no longer contain detailed or updated information on the use of fosamprenavir. Please refer to the FDA drug label for additional information regarding the use of fosamprenavir in people with HIV. HIV medicines cannot cure HIV/AIDS, but taking HIV medicines every day helps people with HIV live longer, healthier lives. HIV medicines also reduce the risk of HIV transmission. If you are taking HIV medicines, do not cut down on, skip, or stop taking them unless your health care provider tells you to. Fosamprenavir Calcium is the calcium salt form of fosamprenavir, prodrug of amprenavir, and a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) protease inhibitor with antiviral property. Fosamprenavir is converted to amprenavir by cellular phosphatases in the epithelial cells of the intestine. Then amprenavir binds to the active site of HIV-1 protease, thereby preventing the proteolytic cleavage of viral Gag-Pol polypeptide into individual functional proteins, thereby leading to the formation of immature non-infectious viral particles. See also: Amprenavir (has active moiety). Drug Indication Telzir in combination with low-dose ritonavir is indicated for the treatment of human-immunodeficiency-virus-type-1-infected adults, adolescents and children of six years and above in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products. , , In moderately antiretroviral-experienced adults, Telzir in combination with low-dose ritonavir has not been shown to be as effective as lopinavir / ritonavir. No comparative studies have been undertaken in children or adolescents. , , In heavily pretreated patients, the use of Telzir in combination with low-dose ritonavir has not been sufficiently studied. , , In protease-inhibitor-experienced patients, the choice of Telzir should be based on individual viral resistance testing and treatment history. Fosamprenavir is a sulfonamide with a structure based on that of sulfanilamide substituted on the sulfonamide nitrogen by a (2R,3S)-4-phenyl-2-(phosphonooxy)-3-({[(3S)-tetrahydrofuran-3-yloxy]carbonyl}amino)butyl group. It is a pro-drug of the HIV protease inhibitor and antiretroviral drug amprenavir. It has a role as a prodrug. It is functionally related to a sulfanilamide. Fosamprenavir is a prodrug of amprenavir, an inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) protease. Fosamprenavir is a Protease Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of fosamprenavir is as a HIV Protease Inhibitor. Fosamprenavir is a prodrug form of amprenavir. In the body fosamprenavir is metabolized to amprenavir, a synthetic derivative of hydroxyethylamine sulfonamide that selectively binds to and inhibits human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) protease. See also: Fosamprenavir Calcium (annotation moved to). Drug Indication Indicated in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) infection, as well as postexposure prophylaxis of HIV infection in individuals who have had occupational or nonoccupational exposure to potentially infectious body fluids of a person known to be infected with HIV when that exposure represents a substantial risk for HIV transmission. The use of fosamprenavir is pending revision due to a potential association between the drug and myocardial infarction and dyslipidemia in HIV infected adults. FDA Label Mechanism of Action Fosamprenavir is a prodrug that is rapidly hydrolyzed to amprenavir by cellular phosphatases in the gut epithelium as it is absorbed. Amprenavir is an inhibitor of HIV-1 protease. During HIV replication, HIV protease cleaves viral polypeptide products of the Gag and Gag-Pol genes to form structural proteins of the virion core and essential viral enzymes. Amprenavir interferes with this process by binding to the active site of HIV-1 protease, thereby preventing the processing of viral Gag and Gag-Pol polyprotein precursors, resulting in the formation of immature non-infectious viral particles. Fosamprenavir is a prodrug of amprenavir, an inhibitor of HIV protease. ...Fosamprenavir is rapidly converted to amprenavir by cellular phosphatases in vivo. Amprenavir is an inhibitor of HIV-1 protease. Amprenavir binds to the active site of HIV-1 protease and thereby prevents the processing of viral Gag and Gag-Pol polyprotein precursors, resulting in the formation of immature noninfectious viral particles. Therapeutic Uses Fosamprenavir is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of HIV infections in adults. /Included in US product labeling/ Drug Warnings Rash (usually maculopapular and of mild or moderate intensity, with or without pruritus) has been reported in about 19% of patients receiving fosamprenavir in clinical studies; manifestations occurred approximately 11 days after initiation of fosamprenavir and persisted for a median of 13 days. Severe or life-threatening skin reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, were reported in less than 1% of patients receiving fosamprenavir in clinical studies. Fosamprenavir contains a sulfonamide moiety, which may cause allergic-type reactions (e.g., rash) in certain susceptible individuals. The potential for cross-sensitivity between drugs with sulfonamide moieties and fosamprenavir is unknown. Use fosamprenavir with caution in patients with known hypersensitivity to sulfonamide-containing drugs. Patients with chronic hepatitis B or C virus infection and those with marked increases in AST or ALT concentrations prior to fosamprenavir therapy may be at increased risk for further elevations in hepatic enzyme concentrations. Liver function tests should be performed prior to initiating therapy with fosamprenavir, and patients should be monitored closely during treatment. ... Increases in serum AST (SGOT) and/or ALT (SGPT) concentrations (more than 5 times the upper limit of normal) have been reported in approximately 4-8% of patients receiving fosamprenavir in clinical studies. Possible amprenavir resistance. The possible effect of fosamprenavir therapy on subsequent therapy with other HIV protease inhibitors in unknown. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for FOSAMPRENAVIR (14 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Fosamprenavir is hydrolyzed by cellular phosphatases to the antiretroviral protease inhibitor amprenavir. This hydrolysis allows for the slow release of amprenavir, reducing the number of pills a patient must take. |
| 分子式 |
C25H34CAN3O9PS
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
623.67
|
| 精确质量 |
623.137
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 48.15; H, 5.49; Ca, 6.43; N, 6.74; O, 23.09; P, 4.97; S, 5.14
|
| CAS号 |
226700-81-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Fosamprenavir;226700-79-4; 226700-81-8; 226700-80-7
|
| PubChem CID |
131535
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 熔点 |
282-284ºC
|
| LogP |
5.449
|
| tPSA |
201.57
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
11
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
13
|
| 重原子数目 |
40
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
901
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
3
|
| SMILES |
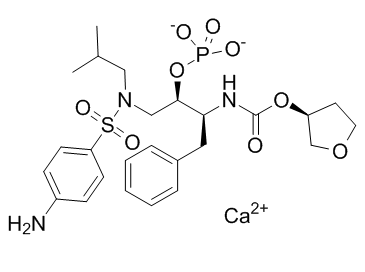
CC(C)CN(C[C@H]([C@H](CC1=CC=CC=C1)NC(=O)O[C@H]2CCOC2)OP(=O)([O-])[O-])S(=O)(=O)C3=CC=C(C=C3)N.[Ca+2]
|
| InChi Key |
PMDQGYMGQKTCSX-HQROKSDRSA-L
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C25H36N3O9PS.Ca/c1-18(2)15-28(39(33,34)22-10-8-20(26)9-11-22)16-24(37-38(30,31)32)23(14-19-6-4-3-5-7-19)27-25(29)36-21-12-13-35-17-21/h3-11,18,21,23-24H,12-17,26H2,1-2H3,(H,27,29)(H2,30,31,32)/q+2/p-2/t21-,23-,24+/m0./s1
|
| 化学名 |
calcium[(2R,3S)-1-[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl-(2-methylpropyl)amino]-3-[[(3S)-oxolan-3-yl]oxycarbonylamino]-4-phenylbutan-2-yl] phosphate
|
| 别名 |
Lexiva; GW433908G; Amprenavir phosphate calcium; UNII-ID1GU2627N; GW 433908; GW 433908G; Fosamprenavir calcium; 226700-81-8; Fosamprenavir Calcium Salt; Lexiva; Telzir; Fosamprenavir (Calcium Salt); Amprenavir phosphate calcium; Fosamprenavir calcium [USAN]; GW 908; GW-433908; GW-433908G; GW-908
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~50 mg/mL (~80.17 mM)
H2O : ~0.25 mg/mL (~0.40 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.01 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.01 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.01 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.6034 mL | 8.0171 mL | 16.0341 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3207 mL | 1.6034 mL | 3.2068 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1603 mL | 0.8017 mL | 1.6034 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
A Clinical Study Of An Investigational Regimen Including Marketed HIV Drugs In HIV-1 Pediatric Subjects Ages 2-18 Years
CTID: NCT00040664
Phase: Phase 2 Status: Completed
Date: 2017-03-03