| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Gadoxetate disodium is equally eliminated via the renal and hepatobiliary routes. The mean terminal elimination half-life of gadoxetate disodium (0.01 to 0.1 mmol/kg) has been observed in healthy volunteers of 22-39 years of age to be 0.91 to 0.95 hour. Clearance appeared to decrease slightly with increasing age. The pharmacokinetics are dose-linear up to a dose of 0.4 mL/kg (0.1 mmol/kg), which is 4 times the recommended dose. After intravenous administration, the plasma concentration time profile of gadoxetate disodium is characterized by a bi-exponential decline. The total distribution volume of gadoxetate disodium at steady state is about 0.21 L/kg (extracellular space); plasma protein binding is less than 10%. Gadoxetate disodium does not pass the intact blood-brain barrier and diffuses through the placental barrier. In lactating rats given 0.1 mmol/kg [153Gd] gadoxetate disodium, less than 0.5% of the total administered radioactivity was transferred to the neonates via maternal milk, mostly within 2 hours. Metabolism / Metabolites Gadoxetate disodium is not metabolized. Biological Half-Life The mean terminal elimination half-life of gadoxetate disodium (0.01 to 0.1 mmol/kg) has been observed in healthy volunteers of 22-39 years of age to be 0.91 to 0.95 hour. |
|---|---|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
IDENTIFICATION: Gadoxetate disodiumis a gadolinium-based contrast agent indicated for intravenous use in T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the liver to detect and characterize lesions in adults with known or suspected focal liver disease. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: The most frequent (>/=0.5%) adverse reactions associated with the use of EOVIST are nausea, headache, feeling hot, dizziness, and back pain. Patients with liver lesions received gadoxetate disodium-enhanced liver magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Adverse events (AEs) were recorded and evaluated with regard to a potential drug relationship. Subgroup analyses were run on patients with special medical history. Worldwide spontaneous AEs and adverse drug reactions (ADRs) from postmarketing safety surveillance were analyzed. A total of 1989 patients were included in the clinical development program. A total of 1581/1989 (79.5%) patients received the finally approved dose of 0.025 mmol/kg body weight. 10.1% of patients reported AEs, 4.1% were classified as related AEs. Nausea and headache were the most frequently reported related AEs, with 1.1% each. Age, history of contrast media allergy, liver cirrhosis, or impaired liver or renal function did not significantly impact the frequency and type of AEs. The postmarketing safety surveillance database encompassed more than 2.2 million patients. Nausea was the most frequent ADR, with a reporting rate of 0.00652%; all other symptoms were below 0.004%. Gadoxetate disodium for liver MRI has an excellent safety profile Gadoxetate disodium-associated transient severe respiratory motion artifact is significantly more common after 20-mL administration (2 mL/s) and occurs significantly more often in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The volume-related effect suggests a nonallergiclike mechanism. ANIMAL STUDIES: A dose-related increase in QTc which was resolved by 30 minutes post dosing was observed in dogs when given a single dose of EOVIST. The increase was noted when given in doses equal to or greater than 0.1 mmol/kg (2.2 times the human dose). Maximum increase in QTcF was equal to or less than 20 ms at doses up to 0.5 mmol/kg (11 times the human dose). Animal reproductive and developmental toxicity studies were done in rats and rabbits. Gadoxetate disodium was not teratogenic when given intravenously during organogenesis to pregnant rats at doses up to 32 times the recommended single human dose (mmol/m2 basis). However, an increase in preimplantation loss was noted at 3.2 times the human dose (mmol/m2 basis). Compared to untreated controls, rates of postimplantation loss and absorption increased and litter size decreased when pregnant rabbits received gadoxetate disodium at doses 26 times the recommended human single dose (mmol/m2 basis). This occurred without evidence of maternal toxicity. Because pregnant animals received repeated daily doses of EOVIST, their overall exposure was significantly higher than that achieved with the standard single dose administered to humans. Interactions An interaction study in healthy subjects demonstrated that the co-administration of the OATP inhibitor erythromycin did not influence efficacy and pharmacokinetics of EOVIST. No further clinical interaction studies with other medicinal products have been performed. Patients with liver lesions received gadoxetate disodium-enhanced liver magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Adverse events (AEs) were recorded and evaluated with regard to a potential drug relationship. Subgroup analyses were run on patients with special medical history. Worldwide spontaneous AEs and adverse drug reactions (ADRs) from postmarketing safety surveillance were analyzed. A total of 1989 patients were included in the clinical development program. A total of 1581/1989 (79.5%) patients received the finally approved dose of 0.025 mmol/kg body weight. 10.1% of patients reported AEs, 4.1% were classified as related AEs. Nausea and headache were the most frequently reported related AEs, with 1.1% each. Age, history of contrast media allergy, liver cirrhosis, or impaired liver or renal function did not significantly impact the frequency and type of AEs. The postmarketing safety surveillance database encompassed more than 2.2 million patients. Nausea was the most frequent ADR, with a reporting rate of 0.00652%; all other symptoms were below 0.004%. Gadoxetate disodium for liver MRI has an excellent safety profile. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
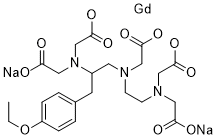
Gadoxetate Disodium is a paramagnetic contrast agent consisting of the disodium salt of the gadolinium ion chelated with the lipophilic moiety ethoxybenzyl (EOB) bound to diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid (DTPA). When placed in a magnetic field, gadolinium produces a large magnetic moment and so a large local magnetic field, which can enhance the relaxation rate of nearby protons; as a result, the signal intensity of tissue images observed with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be enhanced. Because this agent is preferentially taken up by normal functioning hepatocytes, normal hepatic tissue is enhanced with MRI while tumor tissue is unenhanced. In addition, because this agent is excreted in the bile, it may be used to visualize the biliary system using MRI.
See also: Gadoxetate Disodium (annotation moved to). Therapeutic Uses EOVIST Injection is a gadolinium-based contrast agent indicated for intravenous use in T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the liver to detect and characterize lesions in adults with known or suspected focal liver disease. Drug Warnings /BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS (NSF) Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of GBCAs in these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrasted MRI or other modalities. The risk for NSF appears highest among patients with: Chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR < 30 mL/min/1.73m2), or Acute kidney injury. Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (for example, age >60 years, hypertension or diabetes), estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through laboratory testing. Anaphylactoid and anaphylactic reactions with cardiovascular, respiratory and cutaneous manifestations, ranging from mild to severe reactions, including shock have uncommonly occurred following EOVIST administration. Before EOVIST administration, assess all patients for any history of a reaction to contrast media, a history of bronchial asthma and/or a history of allergic disorders. These patients may have an increased risk for a hypersensitivity reaction to EOVIST; weigh the benefits of EOVIST MRI carefully against the risks in these clinical settings. Administer EOVIST only in situations where trained personnel and therapies are promptly available for the treatment of hypersensitivity reactions, including personnel trained in resuscitation. Most hypersensitivity reactions to EOVIST have occurred within half an hour after administration. Delayed reactions (hours up to several days) may occur. Observe patients for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions during and following EOVIST administration. Treat these reactions with standard medications for hypersensitivity reactions. Serum iron determination using complexometric methods (for example, Ferrocine complexation method) may result in falsely high or low values for up to 24 hours after EOVIST administration. Severe renal or hepatic failure may impair EOVIST imaging performance. In patients with end-stage renal failure, hepatic contrast was markedly reduced and was attributed to elevated serum ferritin levels. In patients with abnormally high (>3 mg/dL) serum bilirubin, reduced hepatic contrast was observed. If EOVIST is used in these patients, complete MR imaging no later than 60 minutes after EOVIST administration and use a paired non-contrast and contrast MRI image set for diagnosis. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Gadoxetate disodium (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 分子式 |
C23H33N3O11.GD.2[NA+]
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
730.751220000001
|
| 精确质量 |
726.076
|
| CAS号 |
135326-22-6
|
| 相关CAS号 |
770677-60-6;135326-22-6 (sodium);
|
| PubChem CID |
91754427
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| tPSA |
220
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
14
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
40
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
746
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
CCOC1=CC=C(C=C1)CC(CN(CCN(CC(=O)[O-])CC(=O)[O-])CC(=O)[O-])N(CC(=O)[O-])CC(=O)[O-].[Gd+3].[Na+].[Na+]
|
| InChi Key |
SLYTULCOCGSBBJ-UHFFFAOYSA-I
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C23H33N3O11.Gd.2Na/c1-2-37-18-5-3-16(4-6-18)9-17(26(14-22(33)34)15-23(35)36)10-24(11-19(27)28)7-8-25(12-20(29)30)13-21(31)32;;;/h3-6,17H,2,7-15H2,1H3,(H,27,28)(H,29,30)(H,31,32)(H,33,34)(H,35,36);;;/q;+3;2*+1/p-5
|
| 化学名 |
disodium;2-[[2-[bis(carboxylatomethyl)amino]-3-(4-ethoxyphenyl)propyl]-[2-[bis(carboxylatomethyl)amino]ethyl]amino]acetate;gadolinium(3+)
|
| 别名 |
Gd EOB DTPA ZK 139834 ZK139834 GdEOBDTPA ZK-139834Gd-EOB-DTPA
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
H2O : ≥ 100 mg/mL (~137.80 mM)
DMSO : ~24 mg/mL (~33.07 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.4 mg/mL (3.31 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 24.0 mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;再向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;然后加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.4 mg/mL (3.31 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 24.0mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到900μL 20%SBE-β-CD生理盐水中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.4 mg/mL (3.31 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.3685 mL | 6.8423 mL | 13.6846 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2737 mL | 1.3685 mL | 2.7369 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1368 mL | 0.6842 mL | 1.3685 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。