| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
S1PR2
S1P2 (Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor 2) (Ki: 0.4 nM for human S1P2 binding; Ki > 10,000 nM for human S1P1, S1P3, S1P4, S1P5 receptors) [1] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
GLPG2938(0.5~5 μM;HPF 细胞)在所有测试浓度下均显着阻止 S1P 介导的收缩[1]。
抑制S1P2介导的信号通路 GLPG2938(0.1–100 nM)以剂量依赖方式抑制表达人S1P2的HEK293细胞中S1P诱导的Gα13介导的信号传导。1 nM浓度下,Western blot检测显示S1P诱导的ERK1/2磷酸化降低78%,Akt磷酸化降低72%。HTRF实验显示,抑制S1P2介导的肌醇磷酸生成的EC50为0.8 nM[1] - 人肺成纤维细胞抗增殖活性 在原代人肺成纤维细胞(HLFs)和特发性肺纤维化(IPF)患者来源的肺成纤维细胞中,GLPG2938(1–30 μM)抑制S1P诱导的细胞增殖。MTT法检测显示,抑制HLF增殖的EC50为3.1 μM。10 μM浓度下,ELISA检测显示I型胶原蛋白分泌减少47%,Western blot显示α-SMA表达降低53%,表明成纤维细胞活化受到抑制[1] - 对S1P2的高选择性 浓度高达10 μM时,该化合物不影响S1P1介导的cAMP抑制、S1P3介导的钙动员或S1P4/S1P5依赖的信号传导,证实对S1P2的选择性较其他S1P受体亚型高>25,000倍[1] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
GLPG2938(1~10 mg/kg;口服)在所有测试剂量下均显示出显着的保护作用,导致 Ashcroft 评分在统计学上显着降低[1]。 GLPG2938在所有物种中表现出良好的药代动力学,半衰期长,清除率低,生物利用度良好,尤其是在狗中[1]。动物模型:雄性C57BL/6小鼠[1] 剂量:1~10 mg/kg 给药方式:口服 结果:在所有测试剂量下均显示出显着的保护作用,导致 Ashcroft 评分在统计学上显着降低。
改善博来霉素诱导的小鼠肺纤维化 C57BL/6小鼠气管内给予博来霉素(2.5 U/kg)诱导肺纤维化后,每日口服GLPG2938(10、30、100 mg/kg)连续21天。30 mg/kg剂量下,羟脯氨酸实验显示肺胶原含量减少52%,流式细胞术显示炎症细胞浸润(中性粒细胞和巨噬细胞)减少61%。组织学分析显示肺组织纤维化程度减轻(Ashcroft评分降低48%),flexiVent系统检测显示肺功能改善(动态顺应性提高39%)[1] - 剂量依赖性抗纤维化疗效 上述博来霉素模型中,10 mg/kg GLPG2938使肺纤维化减轻29%,100 mg/kg剂量下羟脯氨酸含量减少63%。qPCR检测显示肺组织中促纤维化基因(COL1A1、α-SMA、TGF-β1)表达下调35%–58%,ELISA显示血清纤维化标志物(PDGF-BB、CTGF)水平降低42%–49%[1] - 不影响心血管功能 麻醉大鼠静脉注射GLPG2938(1–10 mg/kg)后,平均动脉压、心率或心输出量无显著变化,与该化合物不作用于调节血管张力的S1P1一致[1] |
| 酶活实验 |
S1P2结合实验(SPR)
将重组人S1P2蛋白(胞外域和跨膜域)固定于传感器芯片,GLPG2938(0.001–100 nM)与0.1 nM [³H]-S1P(选择性S1P2配体)在25°C共孵育60分钟。洗涤去除未结合配体后,检测结合部分的放射性,通过竞争结合曲线计算Ki值,并通过检测其他S1P受体亚型评估选择性[1] - S1P2介导的Gα13信号抑制实验(HTRF) 稳定表达人S1P2和Gα13依赖性HTRF报告基因的HEK293细胞接种于384孔板,37°C下用GLPG2938(0.001–100 nM)预处理30分钟,加入100 nM S1P诱导信号。60分钟后检测HTRF信号,衡量肌醇磷酸生成(Gα13激活的下游标志物),计算抑制作用的EC50值[1] |
| 细胞实验 |
人肺成纤维细胞增殖实验
原代HLFs和IPF患者来源成纤维细胞接种于96孔板(5×10³细胞/孔),过夜培养后血清饥饿24小时。用GLPG2938(1–30 μM)处理2小时,再加入1 μM S1P刺激72小时,MTT法检测细胞活力,计算相对于S1P刺激对照组的增殖抑制率[1] - 成纤维细胞活化与胶原蛋白分泌实验 HLFs接种于6孔板(2×10⁵细胞/孔),用GLPG2938(5–20 μM)+ TGF-β1(5 ng/mL)处理48小时。细胞裂解后Western blot检测α-SMA(成纤维细胞活化标志物),收集培养上清液ELISA检测I型胶原蛋白水平[1] - S1P2介导的信号通路检测 表达人S1P2的HEK293细胞接种于6孔板(5×10⁵细胞/孔),用GLPG2938(0.1–10 nM)处理30分钟,再加入100 nM S1P刺激15分钟。细胞裂解后,通过Western blot用抗p-ERK1/2、ERK1/2、p-Akt和Akt抗体检测蛋白表达[1] |
| 动物实验 |
Male C57BL/6 mice
1~10 mg/kg P.o. Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis mouse model Female C57BL/6 mice (6–8 weeks old, 18–22 g) were acclimated for 7 days. Pulmonary fibrosis was induced by intratracheal instillation of bleomycin (2.5 U/kg in 50 μL saline) under anesthesia. Starting 7 days post-induction, GLPG2938 was suspended in 0.5% carboxymethylcellulose sodium (CMC-Na) and administered by oral gavage at 10, 30, 100 mg/kg once daily for 21 days. Vehicle group received 0.5% CMC-Na. At study end, mice were euthanized; lungs were collected for hydroxyproline assay (collagen content), histological analysis (Ashcroft scoring), and qPCR (pro-fibrotic gene expression). Lung function was measured using a flexiVent system 1 day before euthanasia [1] - Pharmacokinetic study in rats Male Sprague-Dawley rats (200–250 g) were administered GLPG2938 via oral gavage (30 mg/kg) or intravenous injection (5 mg/kg). Blood samples were collected at 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 24 hours post-dosing. Plasma was separated, and drug concentrations were measured by LC-MS/MS to calculate PK parameters (Cmax, t1/2, AUC, bioavailability) [1] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Oral bioavailability:38% in mice (30 mg/kg oral dose); 45% in rats (30 mg/kg oral dose) [1]
- Plasma half-life (t1/2):6.2 hours in mice (oral); 7.8 hours in rats (oral) [1] - Peak plasma concentration (Cmax):2.9 μM at 1.5 hours post-oral administration (30 mg/kg in mice); 3.4 μM at 2 hours (30 mg/kg in rats) [1] - Plasma protein binding rate:95.2% (in vitro human plasma); 94.7% (rat plasma) [1] - Tissue distribution:Highest concentrations in lung (4.8 μM), liver (5.2 μM), and spleen (3.9 μM) at 2 hours post-oral dose (30 mg/kg in mice); minimal distribution in brain (0.3 μM) [1] - Metabolism and excretion:Metabolized primarily via CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 in the liver; 71% excreted in feces (parent drug + metabolites), 23% in urine within 72 hours [1] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Acute toxicity:No mortality or obvious toxic signs (weight loss, respiratory distress, abnormal behavior) in mice after single oral dose up to 300 mg/kg [1]
- Chronic toxicity:In 28-day repeat-dose study (mice: 10, 30, 100 mg/kg oral daily), no significant changes in body weight, hematological parameters (WBC, RBC, platelets), or liver/kidney function markers (ALT, AST, BUN, creatinine) were observed. Histological examination of lung, liver, kidney, heart, and spleen showed no drug-related lesions [1] - Cardiovascular safety:No significant effects on blood pressure, heart rate, or electrocardiogram (ECG) parameters in anesthetized dogs at doses up to 30 mg/kg (intravenous) [1] - No off-target toxicity:Due to high selectivity for S1P2, no adverse effects related to other S1P receptor inhibition (e.g., vascular leakage, immunosuppression) were observed [1] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Mechanism of action:GLPG2938 is a selective, competitive antagonist of S1P2. It binds to the S1P2 ligand pocket, preventing S1P from activating the receptor, thereby inhibiting downstream Gα13-mediated signaling pathways. This suppresses lung fibroblast activation, proliferation, and extracellular matrix (collagen) secretion, which are key pathological processes in pulmonary fibrosis [1]
- Therapeutic potential:Indicated for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), a progressive fibrotic lung disease. It addresses the unmet medical need by targeting S1P2-mediated fibroblast dysfunction, a key driver of IPF progression [1] - Preclinical candidate status:Classified as a preclinical candidate with favorable pharmacokinetics (oral bioavailability, long half-life) and safety profile, supporting advancement into clinical trials for IPF [1] - Selectivity advantage:Highly selective for S1P2 over other S1P receptor subtypes avoids off-target effects associated with non-selective S1P modulators, such as cardiovascular or immune system disturbances [1] |
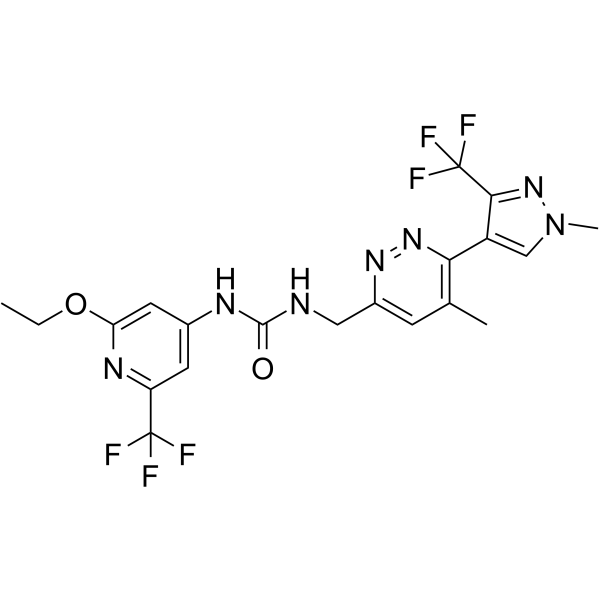
| 分子式 |
C20H19F6N7O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
503.400984048843
|
| 精确质量 |
503.15
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 47.72; H, 3.80; F, 22.64; N, 19.48; O, 6.36
|
| CAS号 |
2130996-00-6
|
| PubChem CID |
137377911
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| LogP |
2.2
|
| tPSA |
107
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
12
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
35
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
712
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
MGJMUVKYINFAQC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C20H19F6N7O2/c1-4-35-15-7-11(6-14(29-15)19(21,22)23)28-18(34)27-8-12-5-10(2)16(31-30-12)13-9-33(3)32-17(13)20(24,25)26/h5-7,9H,4,8H2,1-3H3,(H2,27,28,29,34)
|
| 化学名 |
1-[2-ethoxy-6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-4-yl]-3-[[5-methyl-6-[1-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)pyrazol-4-yl]pyridazin-3-yl]methyl]urea
|
| 别名 |
MUN-96006; MUN96006; MUN 96006; GLPG-2938; GLPG2938; GLPG 2938
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~100 mg/mL (~198.7 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.97 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入900 μL 玉米油中,混合均匀。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.13 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;再向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;然后加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9865 mL | 9.9325 mL | 19.8649 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3973 mL | 1.9865 mL | 3.9730 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1986 mL | 0.9932 mL | 1.9865 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。