| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
NADPH oxidase 4 (Nox4); The target of GLX351322 is NADPH oxidase 4 (NOX4) [1]
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
NADPH 氧化酶 4 抑制剂 GLX351322 的 IC50 为 5 μM,可防止 NOX4 过表达细胞产生过氧化氢。 GLX351322 对 hPBMC 细胞中的 NOX2 表现出很小的功效(IC50,40 μM)。
在遭受缺氧的离体跳动大鼠心房中,用GLX351322(10 μM)处理可显著阻断缺氧诱导的沉默信息调节因子2相关酶1(Sirt1)蛋白表达上调。这种抑制作用与缺氧刺激的心钠素(ANP)分泌减少相关。蛋白质印迹分析显示,GLX351322减弱了缺氧诱导的NOX4下游信号分子(包括Src、ERK1/2、Akt和GATA4)的激活。具体而言,它降低了Src、ERK1/2和Akt的磷酸化水平,以及GATA4(ANP基因表达的关键转录因子)的核转位 [2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
GLX351322(3.8 mg/kg/天,口服)可以改善HF饮食引起的大鼠高血糖[1]。
在2型糖尿病中,有人提出,NADPH氧化酶(NOX)过度活性引起的氧化应激会促进胰腺β细胞功能障碍。已经鉴定了五种不同的NOX酶(NOX1-5),其中NOX1和NOX2被认为对β细胞有负面影响,但NOX4在2型糖尿病相关β细胞功能障碍和葡萄糖不耐受中的推定作用在很大程度上尚不清楚。因此,我们目前使用新的NOX4抑制剂GLX351322,使用雄性C57BL/6小鼠研究了NOX4对高脂饮食或HFD诱导的葡萄糖不耐受的重要性,该抑制剂对NOX4的选择性相对高于NOX2。在HFD治疗的雄性C57BL/6小鼠中,用GLX351322治疗两周可以抵消非空腹高血糖和糖耐量受损。这种效应发生时,外周胰岛素敏感性没有任何变化。为了确定NOX4也对人β细胞的功能起作用,我们观察到葡萄糖和棕榈酸钠诱导的人胰岛胰岛素释放在体外对NOX4抑制剂的反应增加。在长期实验(1-3天)中,GLX351322可以预防高糖诱导的人胰岛细胞活性氧(ROS)的产生和死亡。我们提出,虽然短期NOX4产生的ROS是β细胞功能的生理要求,但持续的NOX4活性,例如在高脂肪喂养条件下,会促进ROS介导的β细胞功能障碍。因此,选择性NOX抑制可能是2型糖尿病的一种治疗策略[1]。 在高脂饮食(HFD)处理的C57BL/6小鼠中,口服给予GLX351322(30 mg/kg/天,持续12周)可对抗葡萄糖不耐受。与未使用该药物的HFD喂养小鼠相比,接受GLX351322处理的小鼠葡萄糖耐量得到改善,口服葡萄糖耐量试验(OGTT)中血糖水平更低。此外,GLX351322减少了HFD诱导的内脏脂肪量增加和血浆胰岛素水平升高。它还能使HFD诱导的白色脂肪组织(WAT)和骨骼肌中NOX4 mRNA表达上调恢复正常,并降低WAT中脂质过氧化产物(如4-羟基壬烯醛)的水平,表明氧化应激减轻 [1] |
| 酶活实验 |
酶联免疫吸附试验[3]
根据供应商的方案,用大鼠IL-1β酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)试剂盒和大鼠IL-18 ELISA试剂盒测量细胞培养基或大鼠滑液中IL-1β和IL-18的浓度。使用PowerWave XS在450nm波长下测量吸光度。 体外共免疫沉淀和泛素检测[3] 共免疫沉淀(Co-IP)用于测量USP7和NOX4的相互作用。用RIPA缓冲液提取的细胞裂解物与抗USP7、抗NOX4或正常IgG抗体在4°C下孵育过夜,然后与蛋白A/G珠在4°℃下孵育2小时。免疫复合物在磁性架上用裂解缓冲液洗涤三次,然后用抗USP7抗体、抗NOX4抗体和抗泛素抗体进行免疫印迹检测。 |
| 细胞实验 |
增殖试验[3]
按照制造商的方案,使用细胞计数试剂盒8评估软骨细胞的增殖。简而言之,将细胞接种到96孔板中,并在处理前孵育24小时。在0、24、48或72小时将对照或处理过的细胞(90μL)与CCK-8试剂(10μL)混合。孵育1小时后,使用读数器测量450 nm处的光密度(OD 450)。 制备离体大鼠心房并在含氧生理溶液中维持。稳定后,将心房分为几组:常氧组、缺氧组和缺氧 + GLX351322(10 μM)组。通过将心房暴露于低氧气体混合物特定时间来诱导缺氧。在缺氧开始前30分钟,将GLX351322加入孵育培养基中。处理结束后,收集培养基,采用放射免疫分析法测量ANP分泌。将心房组织匀浆,通过蛋白质印迹法分析蛋白提取物,检测Sirt1的表达水平以及Src、ERK1/2、Akt的磷酸化状态和GATA4的核转位情况 [2] |
| 动物实验 |
All rats were randomly divided into: control, hypoxia only, BQ123/BQ788/BQ123 + BQ788 + hypoxia/ET-1, GLX351322 + hypoxia, ET-1 only, varespladib + hypoxia/ET-1, CAY10650 + hypoxia/ET-1, NAC + hypoxia, Src inhibitor 1 + hypoxia, PD98059 + hypoxia, and LY294002 + hypoxia groups (n = 6 per group).
Each atrium was perfused for 60 min to stabilize ANP secretion and atrial dynamics parameters. After two control cycles (12-min experimental cycle), O2 was replaced with N2 and a hypoxic buffer was infused for four periods to observe changes in the atrial dynamics and ANP levels of the perfusates. Under a controlled temperature of 4°C, perfusates were collected every 2 min to measure ANP levels. Immediately after perfusion, atrial tissue was frozen and stored at –80°C for western blotting. Subsequently, another series of experiments were performed to investigate the mechanism of hypoxia-induced ANP secretion. After one control period, one treatment cycle was followed by four cycles of infusion of the treatment agent plus hypoxia. Treatment agents were as follows: BQ123 (0.3 µM), BQ788 (0.3 µM), ET-1 (3.0 nM) GLX351322 (35.0 µM), varespladib (5.0 µM), CAY10650 (120.0 nM), NAC (15.0 mM), Src inhibitor 1 (1.0 µM), PD98059 (30.0 µM), and LY294002 (30.0 µM).[2]
C57BL/6 mice are randomly divided into three groups: a control group fed a normal diet, an HFD group fed a high-fat diet, and an HFD + GLX351322 group fed a high-fat diet and administered GLX351322. GLX351322 is dissolved in drinking water at a concentration that allows a daily intake of 30 mg/kg body weight, and is administered continuously for 12 weeks. During the study, body weight is measured weekly. After 11 weeks, an OGTT is performed: mice are fasted overnight, given glucose (2 g/kg) by oral gavage, and blood glucose levels are measured at 0, 15, 30, 60, and 120 minutes. At the end of the 12-week treatment, mice are euthanized, and tissues (including WAT, skeletal muscle, liver) and blood samples are collected for further analysis [1] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
GLX351322 is a novel NADPH oxidase 4 inhibitor. By inhibiting NOX4, it reduces oxidative stress, which is associated with the improvement of glucose intolerance in HFD-induced obese mice. This suggests its potential role in managing metabolic disorders related to insulin resistance and obesity [1]
Osteoarthritis (OA), the most common form of arthritis, is a very common joint disease that often affects middle-aged to elderly people. However, current treatment options for OA are predominantly palliative. Thus, understanding its pathological process and exploring its potential therapeutic approaches are of great importance. Rat chondrocytes were isolated and exposed to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to mimic OA. The effects of H2O2 on ubiquitin-specific protease 7 (USP7) expression, reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, proliferation, inflammatory cytokine release, and pyroptosis were measured. USP7 was knocked down (KD) or overexpressed to investigate the role of USP7 in OA. Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) was used to study the interaction between USP7 and NAD(P)H oxidases (NOX)4 as well as NOX4 ubiquitination. NOX4 inhibitor was applied to study the involvement of NOX4 in USP7-mediated OA development. USP7 inhibitor was given to OA animals to further investigate the role of USP7 in OA in vivo. Moreover, H2O2 treatment significantly increased USP7 expression, enhanced ROS levels, and inhibited proliferation in rat chondrocytes. The overexpression of USP7 enhanced pyroptosis, ROS production, interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-18 levels, and the expression level of NLRP3, GSDMD-N, active caspase-1, pro-caspase-1, matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) 1, and MMP13, which was abolished by ROS inhibition. The USP7 KD protected rat chondrocytes against H2O2-induced injury. Co-IP results showed that USP7 interacted with NOX4, and USP7 KD enhanced NOX4 ubiquitinylation. The inhibition of NOX4 blocked the pro-OA effect of USP7. Moreover, the USP7 inhibitor given to OA animals suppressed OA in vivo. USP7 inhibited NOX4 ubiquitination for degradation which leads to elevated ROS production. ROS subsequently activates NLPR3 inflammasome, leading to enhanced production of IL-1β and IL-18, GSDMD-N-dependent pyroptosis, and extracellular matrix remodeling. Thus, UPS7 contributes to the progression of OA via NOX4/ROS/NLPR3 axis. [3] Osteoarthritis (OA), the most common form of arthritis, is a very common joint disease that often affects middle-aged to elderly people. However, current treatment options for OA are predominantly palliative. Thus, understanding its pathological process and exploring its potential therapeutic approaches are of great importance. Rat chondrocytes were isolated and exposed to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to mimic OA. The effects of H2O2 on ubiquitin-specific protease 7 (USP7) expression, reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, proliferation, inflammatory cytokine release, and pyroptosis were measured. USP7 was knocked down (KD) or overexpressed to investigate the role of USP7 in OA. Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) was used to study the interaction between USP7 and NAD(P)H oxidases (NOX)4 as well as NOX4 ubiquitination. NOX4 inhibitor was applied to study the involvement of NOX4 in USP7-mediated OA development. USP7 inhibitor was given to OA animals to further investigate the role of USP7 in OA in vivo. Moreover, H2O2 treatment significantly increased USP7 expression, enhanced ROS levels, and inhibited proliferation in rat chondrocytes. The overexpression of USP7 enhanced pyroptosis, ROS production, interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-18 levels, and the expression level of NLRP3, GSDMD-N, active caspase-1, pro-caspase-1, matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) 1, and MMP13, which was abolished by ROS inhibition. The USP7 KD protected rat chondrocytes against H2O2-induced injury. Co-IP results showed that USP7 interacted with NOX4, and USP7 KD enhanced NOX4 ubiquitinylation. The inhibition of NOX4 blocked the pro-OA effect of USP7. Moreover, the USP7 inhibitor given to OA animals suppressed OA in vivo. USP7 inhibited NOX4 ubiquitination for degradation which leads to elevated ROS production. ROS subsequently activates NLPR3 inflammasome, leading to enhanced production of IL-1β and IL-18, GSDMD-N-dependent pyroptosis, and extracellular matrix remodeling. Thus, UPS7 contributes to the progression of OA via NOX4/ROS/NLPR3 axis.[2] In the context of hypoxic rat atria, GLX351322 acts as a NOX4 inhibitor to suppress the NOX4/Src-mediated signaling pathway, thereby reducing ANP secretion stimulated by hypoxia. This indicates that GLX351322 can modulate NOX4-dependent cellular responses in cardiac atrial tissue under hypoxic conditions [2] |
| 分子式 |
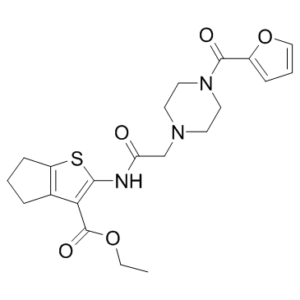
C21H25N3O5S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
431.15
|
|
| 精确质量 |
431.151
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 58.45; H, 5.84; N, 9.74; O, 18.54; S, 7.43
|
|
| CAS号 |
835598-94-2
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
2697686
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
665.5±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
356.3±31.5 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.625
|
|
| LogP |
4.1
|
|
| tPSA |
120
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
30
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
655
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| InChi Key |
KEVHLTCEMHIJTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C21H25N3O5S/c1-2-28-21(27)18-14-5-3-7-16(14)30-19(18)22-17(25)13-23-8-10-24(11-9-23)20(26)15-6-4-12-29-15/h4,6,12H,2-3,5,7-11,13H2,1H3,(H,22,25)
|
|
| 化学名 |
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 2.08 mg/mL (4.82 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浮液;超声助溶。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.82 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3194 mL | 11.5969 mL | 23.1938 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4639 mL | 2.3194 mL | 4.6388 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2319 mL | 1.1597 mL | 2.3194 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。