| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| 50g |
|
||
| 100g | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
ATP-sensitive K+ channel (KATP)
ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channels [2][5] - Voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channels [1] - Sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca²⁺-ATPase (SERCA) pumps [1] - P-glycoprotein (P-gp, MDR1) [3] - Mitochondrial membrane [4] - Autophagy-related targets in pancreatic β-cells [5] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
格列本脲(棕色脂肪细胞;10 μM;1 天)对脂肪细胞分化没有影响。格列本脲(Ucp1-2A-GFP 棕色脂肪细胞)可显着增加 UCP1 表达。格列本脲直接结合并抑制 ATP 依赖性钾通道 (KATP) 的 SUR1 亚基,从而促进胰腺 β 细胞产生胰岛素 [2]。格列本脲通过允许 Cl- 进入线粒体内膜并促进线粒体网络中的 Cl-/K+ 共转运来干扰线粒体生物能 [4]。格列本脲诱导的自噬限制了其对 β 细胞胰岛素分泌的有益作用 [5]。
在分离的大鼠胸主动脉血管平滑肌细胞(VSMCs)中,格列本脲(Glibenclamide)(1-10 μM)通过激活Kv通道和SERCA泵诱导血管舒张。5 μM浓度时,Kv通道电流幅度增加60%,SERCA泵活性提高55%,降低细胞内钙浓度并松弛VSMCs[1] - 在3T3-L1脂肪细胞和原代小鼠棕色脂肪细胞中,格列本脲(Glibenclamide)(1-20 μM)以浓度依赖方式上调解偶联蛋白1(UCP1)的mRNA和蛋白表达。10 μM浓度时,UCP1蛋白水平增加2.3倍,且该效应不依赖KATP通道阻断(在KATP通道敲低细胞中仍存在)[2] - 在过表达P-gp的LLC-PK1细胞和Caco-2细胞中,格列本脲(Glibenclamide)(1-50 μM)剂量依赖性抑制P-gp介导的药物外排。20 μM浓度时,P-gp底物的细胞内蓄积量增加75%,P-gp ATP酶活性降低62%[3] - 在分离的大鼠肝线粒体和HepG2细胞中,格列本脲(Glibenclamide)(5-50 μM)改变线粒体膜离子通透性,30 μM浓度时线粒体膜电位降低40%。它抑制线粒体呼吸速率35%,增加活性氧(ROS)生成58%,干扰线粒体生物能学[4] - 在INS-1胰岛β细胞和原代小鼠胰岛中,格列本脲(Glibenclamide)(1-10 μM)以浓度依赖方式诱导自噬。5 μM浓度时,Western blot检测显示LC3-II/LC3-I比值增加2.1倍,Beclin-1表达上调65%,同时抑制葡萄糖诱导的胰岛素分泌42%——自噬抑制剂3-MA可逆转该抑制效应[5] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
格列本脲(2 mg/kg;口服)可快速降低血糖水平并增强胰岛素的释放[2]。使用格列本脲(50 μg/kg;口服)时,体重和身体成分不会显着改变[2]。
格列本脲(是目前用于治疗2型糖尿病的美国食品药品监督管理局批准的药物之一,可以显著增强棕色和白色脂肪细胞中UCP1的表达。格列本脲喂养的小鼠对高脂饮食诱导的肥胖表现出明显的抵抗力,降低了血液甘油三酯水平,增加了棕色脂肪组织中UCP1的表达。此外,腹股沟白色脂肪组织原位注射优降糖显著增强了UCP1的表达,增加了产热。进一步的机制研究表明,格列本脲对脂肪细胞UCP1表达的影响是KATP通道无关的,但可能涉及Ca2+-钙调神经磷酸酶NFAT信号通路的调节。总的来说,我们的研究结果揭示了格列本脲/优降糖在调节脂肪细胞中UCP1表达和产热方面的显著作用,这可能被重新用于治疗肥胖。[2] |
| 酶活实验 |
众所周知,格列本脲与磺脲受体(SUR)相互作用,最近已被证明可以抑制囊性纤维化跨膜电导调节蛋白(CFTR),这两种蛋白都是ABC[腺苷5'-三磷酸(ATP)结合盒]转运蛋白的成员。研究了格列本脲和两种合成的磺酰基氰基胍衍生物(称为BM-208和BM-223)对P-糖蛋白的影响,P-糖蛋白是导致癌症细胞多药耐药性(MDR)的主要ABC转运蛋白。为此,我们采用了不同的细胞系,这些细胞系表达或不表达P-糖蛋白,如蛋白质印迹所证实的:首先,一种肿瘤细胞系(VBL600),选自急性白血病衍生的人类T细胞系(CEM);第二,来源于大鼠结肠腺癌的上皮细胞系(CC531(mdr+)),最后,来源于负鼠肾近端小管的非肿瘤上皮细胞系。格列本脲和两种相关衍生物抑制P-糖蛋白,因为首先,它们仅在P-糖蛋白表达细胞系中急性增加[3H]秋水仙碱的积累;其次,BM-223通过增强秋水仙碱、紫杉醇和长春花碱的细胞毒性逆转了MDR现象,与维拉帕米非常相似;第三,BM-208和BM-223阻断了[3H]叠氮平对P-糖蛋白的光亲和标记。此外,格列本脲本身就是P-糖蛋白的底物,因为[3H]格列本脲的细胞积累较低,并且仅在表达P-糖蛋白的细胞系中添加P-糖蛋白底物(如长春花碱和环孢菌素)会显著增加。我们得出结论,格列本脲和两种磺酰基氰基胍衍生物抑制P-糖蛋白,磺酰脲类药物似乎是ABC转运蛋白的一般抑制剂,这表明它们与一些保守的基序相互作用。[3]
通过大鼠肝线粒体在乙酸钾、硝酸钾和氯化钾介质中的被动渗透肿胀、氧气消耗和线粒体跨膜电位(Deltapsi),评估了抗糖尿病磺酰脲类药物格列本脲对线粒体生物能量学的干扰。格列本脲不会使线粒体内膜透性为H+,但会通过打开线粒体内阴离子通道(IMAC)诱导对Cl-的透性。格列本脲诱导的Cl-内流促进K+进入线粒体,从而促进Cl-/K+净共转运、Deltapsi消散和刺激状态4呼吸速率。结论是格列本脲通过使线粒体内膜对Cl-渗透并促进线粒体内Cl-/K+的净共转运来干扰大鼠肝脏的线粒体生物能量学,而膜对H+的渗透没有显著变化[4]。 P-gp ATP酶活性检测:将分离的P-gp蛋白与ATP及不同浓度的格列本脲(Glibenclamide)(1-50 μM)在37°C孵育1小时。终止ATP水解反应后,通过比色法检测释放的无机磷含量,计算P-gp ATP酶抑制率[3] - SERCA泵活性检测:从VSMCs中制备含SERCA泵的微粒体组分,将格列本脲(Glibenclamide)(1-10 μM)加入含钙和ATP的反应体系。使用荧光钙指示剂监测微粒体的钙摄取情况,根据钙摄取速率定量SERCA泵活性[1] - 线粒体膜电位检测:将分离的肝线粒体悬浮于含膜电位敏感荧光探针的缓冲液中,加入格列本脲(Glibenclamide)(5-50 μM),在探针特异性的激发/发射波长下测量荧光强度,通过与对照组对比计算线粒体膜电位变化[4] |
| 细胞实验 |
糖尿病是一种代谢性疾病,部分原因是低血糖症,影响世界8%的成年人口。众所周知,格列本脲通过靶向β细胞促进胰岛素分泌。自噬作为细胞的一种自我保护机制已被广泛研究,并在不同的组织或细胞中具有特殊的生理作用。然而,自噬和格列本脲之间的相互作用尚不清楚。在这项研究中,我们研究了自噬在格列本脲诱导的胰腺β细胞胰岛素分泌中的作用。在此,我们发现格列本脲促进胰岛素释放,并通过腺苷5'-单磷酸(AMP)激活蛋白激酶(AMPK)途径进一步激活MIN-6细胞的自噬。自噬抑制剂3-甲基腺嘌呤(3-MA)对自噬的抑制进一步增强了格列本脲的分泌功能。这些结果表明,格列本脲诱导的自噬通过激活AMPK通路而不是改变雷帕霉素(mTOR)的哺乳动物靶点,在促进胰岛素分泌方面起着抑制作用[5]。
VSMC舒张相关实验:将大鼠胸主动脉VSMCs接种到盖玻片上,加入1 μM、5 μM、10 μM的格列本脲(Glibenclamide),通过全细胞膜片钳记录Kv通道电流;使用荧光钙探针检测细胞内钙浓度,通过相差显微镜观察VSMC舒张情况[1] - 脂肪细胞UCP1表达实验:将3T3-L1细胞分化为脂肪细胞,分离原代小鼠棕色脂肪细胞,用1 μM、10 μM、20 μM的格列本脲(Glibenclamide)处理24小时。qPCR检测UCP1 mRNA水平,Western blot和免疫荧光染色分析蛋白表达[2] - P-gp外排实验:将LLC-PK1/P-gp或Caco-2细胞接种到24孔板,负载荧光P-gp底物后加入1-50 μM的格列本脲(Glibenclamide),孵育1小时。通过酶标仪检测细胞内荧光强度,评估P-gp抑制效果[3] - 线粒体生物能学实验:将HepG2细胞接种到96孔板,用5 μM、30 μM、50 μM的格列本脲(Glibenclamide)处理24小时。使用Seahorse分析仪检测线粒体呼吸速率,DCFH-DA荧光探针检测ROS生成[4] - 胰岛β细胞自噬与胰岛素分泌实验:将INS-1细胞和原代小鼠胰岛培养在含葡萄糖的培养基中,加入1 μM、5 μM、10 μM的格列本脲(Glibenclamide)(加或不加自噬抑制剂3-MA)。24小时后,Western blot分析自噬标志物(LC3-II/LC3-I、Beclin-1),葡萄糖刺激后通过ELISA检测胰岛素分泌[5] |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Mice[2]
Doses: 2 mg/kg Route of Administration: Po Experimental Results: Increased of insulin release and rapid drop of blood glucose level. Identification of safe and effective compounds to increase or activate UCP1 expression in brown or white adipocytes remains a potent therapeutic strategy to combat obesity. Here we reported that, glyburide, one of the FDA-approved drugs currently used to treat type 2 diabetes, can significantly enhance UCP1 expression in both brown and white adipocytes. Glyburide-fed mice exhibited a clear resistance to high-fat diet-induced obesity, reduced blood triglyceride level, and increased UCP1 expression in brown adipose tissue. Moreover, in situ injection of glyburide to inguinal white adipose tissue remarkably enhanced UCP1 expression and increased thermogenesis. Further mechanistic studies indicated that the glyburide effect in UCP1 expression in adipocytes was KATP channel independent but may involve the regulation of the Ca2+-Calcineurin-NFAT signal pathway. Overall, our findings revealed the significant effects of glyburide in regulating UCP1 expression and thermogenesis in adipocytes, which can be potentially repurposed to treat obesity.[2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Elderly patients taking glyburide reached a Cmax of 211-315ng/mL with a Tmax of 0.9-1.0h, while younger patients reached a Cmax of 144-302ng/mL with a Tmax of 1.3-3.0h. Patients taking glyburide have and AUC of 348ngh/mL. Unlike other sulfonylureas, glyburide is 50% excreted in the urine and 50% in the feces. Glyburide is mainly excreted as the metabolite 4-trans-hydroxyglyburide. Elderly patients have a volume of distribution of 19.3-52.6L, while younger patients have a volume of distribution of 21.5-49.3L. Elderly patients have a clearance of 2.70-3.55L/h, while younger patients have a clearance of 2.47-4.11L/h. Metabolism / Metabolites Glyburide is metabolized mainly by CYP3A4, followed by CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP3A7, and CYP3A5. These enzymes metabolize glyburide to 4-trans-hydroxycyclohexyl glyburide (M1), 4-cis-hydroxycyclohexyl glyburide (M2a), 3-cis-hydroxycyclohexyl glyburide (M2b), 3-trans-hydroxycyclohexyl glyburide (M3), 2-trans-hydroxycyclohexyl glyburide (M4), and ethylhydroxycyclohexyl glyburide (M5). The M1 and M2b metabolites are considered active, along with the parent molecule. Glyburide has known human metabolites that include 3-cis-Hydroxycyclohexyl glyburide, 3-trans-Hydroxycyclohexyl glyburide, 2-trans-hydroxycyclohexyl glyburide, and 4-cis-hydroxycyclohexyl glyburide. Biological Half-Life Elderly patients have a terminal elimination half life of 4.0-13.4h, while younger patients have a terminal elimination half life of 4.0-13.9h. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Limited data indicate that the levels of glyburide in milk are negligible. Monitor breastfed infants for signs of hypoglycemia such as jitteriness, excessive sleepiness, poor feeding, seizures cyanosis, apnea, or hypothermia. If there is concern, monitoring of the breastfed infant's blood glucose is advisable during maternal therapy with hypoglycemic agents. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants The blood glucose level was normal in one breastfed infant whose mothers was taking oral glyburide 5 mg daily. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Glyburide is 99.9% bound to protein in plasma with >98% accounted for by binding to serum albumin. Mitochondrial toxicity: Glyburide (Glibenclamide) (5-50 μM) disrupted mitochondrial bioenergetics in vitro, reducing membrane potential, inhibiting respiration, and increasing ROS generation[4] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
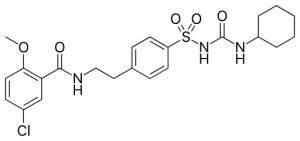
Glyburide is an N-sulfonylurea that is acetohexamide in which the acetyl group is replaced by a 2-(5-chloro-2-methoxybenzamido)ethyl group. It has a role as a hypoglycemic agent, an anti-arrhythmia drug, an EC 2.7.1.33 (pantothenate kinase) inhibitor and an EC 3.6.3.49 (channel-conductance-controlling ATPase) inhibitor. It is a N-sulfonylurea and a member of monochlorobenzenes.
Glyburide is a second generation sulfonylurea used to treat patients with diabetes mellitus type II. It is typically given to patients who cannot be managed with the standard first line therapy, [metformin]. Glyburide stimulates insulin secretion through the closure of ATP-sensitive potassium channels on beta cells, raising intracellular potassium and calcium ion concentrations. Glyburide was granted FDA approval on 1 May 1984. A formulation with metformin was granted FDA approval on on 31 July 2000. Glyburide is a Sulfonylurea. Glyburide is a sulfonamide urea derivative with antihyperglycemic activity that can potentially be used to decrease cerebral edema. Upon administration, glyburide binds to and blocks the sulfonylurea receptor type 1 (SUR1) subunit of the ATP-sensitive inwardly-rectifying potassium (K(ATP)) channels on the membranes of pancreatic beta cells. This prevents the inward current flow of positively charged potassium (K+) ions into the cell, and induces a calcium ion (Ca2+) influx through voltage-sensitive calcium channels, which triggers exocytosis of insulin-containing granules. In addition, glyburide also inhibits the SUR1-regulated nonselective cation (NC) Ca-ATP channel, melastatin 4 (transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 4; (TRPM4)), thereby preventing capillary failure and brain swelling. SUR1-TRPM4 channels are formed by co-assembly of SUR1 with TRPM4 in neurons, astrocytes, and capillary endothelium during cerebral ischemia. Upon ischemia-induced ATP depletion, channels open which results in sodium influx, cytotoxic edema formation, capillary fragmentation and necrotic cell death. SUR1-TRPM4 is not expressed in normal, uninjured tissues. An antidiabetic sulfonylurea derivative with actions like those of chlorpropamide See also: Glyburide; Metformin Hydrochloride (component of). Drug Indication Glyburide is indicated alone or as part of combination product with metformin, as an adjunct to diet and exercise, to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Amglidia is indicated for the treatment of neonatal diabetes mellitus, for use in newborns, infants and children. Sulphonylureas like Amglidia have been shown to be effective in patients with mutations in the genes coding for the β-cell ATP-sensitive potassium channel and chromosome 6q24-related transient neonatal diabetes mellitus. Treatment of large hemispheric infarction Treatment of neonatal diabetes mellitus Mechanism of Action Glyburide belongs to a class of drugs known as sulfonylureas. These drugs act by closing ATP-sensitive potassium channels on pancreatic beta cells. The ATP-sensitive potassium channels on beta cells are known as sulfonylurea receptor 1 (SUR1). Under low glucose concentrations, SUR1 remains open, allowing for potassium ion efflux to create a -70mV membrane potential. Normally SUR1 closes in response to high glucose concentrations, the membrane potential of the cells becomes less negative, the cell depolarizes, voltage gated calcium channels open, calcium ions enter the cell, and the increased intracellular calcium concentration stimulates the release of insulin containing granules. Glyburide bypasses this process by forcing SUR1 closed and stimulating increased insulin secretion. Pharmacodynamics Glyburide is a second generation sulfonylurea that stimulates insulin secretion through the closure of ATP-sensitive potassium channels on beta cells, raising intracellular potassium and calcium ion concentrations. Glibenclamide has a long duration of action as it is given once daily, and a wide therapeutic index as patients are started at doses as low as 0.75mg but that can increase as high as 10mg or more. Patients taking glyburide should be cautioned regarding an increased risk of cardiovascular mortality as seen with tolbutamide, another sulfonylurea. Glyburide (Glibenclamide) is a first-generation sulfonylurea antidiabetic drug clinically approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus[2][5] - Its classic hypoglycemic mechanism involves blocking pancreatic β-cell KATP channels to promote insulin secretion, but it also exerts multiple off-target effects[2][5] - The drug induces vasodilation via activating Kv channels and SERCA pumps in VSMCs, suggesting potential applications in vascular disorders[1] - It upregulates UCP1 expression in adipocytes independent of KATP channels, contributing to thermogenesis and energy metabolism regulation[2] - As a P-gp inhibitor, Glyburide (Glibenclamide) may alter the pharmacokinetics of P-gp substrate drugs[3] - It interferes with mitochondrial function by changing membrane ion permeability, which may be related to potential cellular toxicity[4] - In pancreatic β-cells, the drug induces autophagy that counteracts its insulin secretion-improving effect, indicating a complex regulatory role in β-cell function[5] |
| 分子式 |
C23H28CLN3O5S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
494
|
|
| 精确质量 |
493.143
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 55.92; H, 5.71; Cl, 7.18; N, 8.51; O, 16.19; S, 6.49
|
|
| CAS号 |
10238-21-8
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Glyburide-d3;1219803-02-7;Glyburide-d11;1189985-02-1; 52169-36-5 (potassium salt)
|
|
| PubChem CID |
3488
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
705.7±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
173-175°C
|
|
| 闪点 |
380.6±35.7 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.4 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.623
|
|
| LogP |
5.19
|
|
| tPSA |
121.98
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
33
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
746
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| InChi Key |
ZNNLBTZKUZBEKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C23H28ClN3O5S/c1-32-21-12-9-17(24)15-20(21)22(28)25-14-13-16-7-10-19(11-8-16)33(30,31)27-23(29)26-18-5-3-2-4-6-18/h7-12,15,18H,2-6,13-14H2,1H3,(H,25,28)(H2,26,27,29)
|
|
| 化学名 |
5-chloro-N-[2-[4-(cyclohexylcarbamoylsulfamoyl)phenyl]ethyl]-2-methoxybenzamide
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.21 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.21 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0243 mL | 10.1215 mL | 20.2429 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4049 mL | 2.0243 mL | 4.0486 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2024 mL | 1.0121 mL | 2.0243 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Spinal Cord Injury Neuroprotection With Glyburide
CTID: NCT05426681
Phase: Phase 1 Status: Recruiting
Date: 2024-10-15