| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
DLK (Ki = 0.5 nM); p-JNK (IC50 = 30 nM); DRG (IC50 = 107 nM); MKK4 (IC50 >5000 nM); MKK7 (IC50 >5000 nM); JNK1 (IC50 = 129 nM); JNK2 (IC50 = 514 nM); JNK3 (IC50 = 364 nM); MLK1 (IC50 = 67.8 nM); MLK2 (IC50 = 767 nM); MLK3 (IC50 = 602 nM)
GNE-3511 targets dual leucine zipper kinase (DLK, MAP3K12) with an IC50 of 1.9 nM (recombinant human DLK) and a Ki value of 0.6 nM [1] GNE-3511 shows high selectivity for DLK over other MAP kinases (e.g., LZK, MLK1-4, JNK1-3) with IC50 > 1000 nM [1] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
GNE-3511 对 p-JNK 的 IC50 为 30 nM,对 DRG 的 IC50 为 107 nM,这表明具有抑制活性[1]。 GNE-3511 对 MKK4、MKK7、JNK1、JNK2、JNK3、MLK1、MLK2 和 MLK3 具有激酶选择性,IC50 值为 >5000 nM、>5000 nM、129 nM、514 nM、364 nM、67.8 nM、767 nM 和 602分别为 nM[1]。 GNE-3511 在体外表现出浓度依赖性的神经元衰老抑制作用[1]。
重组人DLK激酶实验中,GNE-3511(0.1-100 nM)剂量依赖性抑制DLK活性,IC50为1.9 nM;浓度高达1 μM时,未显著抑制其他45种激酶 [1] - 在原代大鼠皮质神经元中,GNE-3511(1-100 nM)保护神经生长因子(NGF)剥夺诱导的轴突损伤;10 nM浓度较溶媒对照组完整轴突长度增加62%(p < 0.01) [1] - GNE-3511(0.3-10 μM)剂量依赖性降低NGF剥夺神经元中c-Jun氨基末端激酶(JNK)和c-Jun(DLK下游底物)的磷酸化水平,10 μM浓度抑制p-JNK达75%(蛋白质印迹分析) [1] - 在脂多糖(LPS)刺激的小鼠膀胱上皮细胞(MBECs)中,GNE-3511(1-10 μM)降低促炎细胞因子TNF-α(10 μM时降幅48%)和IL-6(10 μM时降幅52%)的mRNA表达(p < 0.05) [2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
GNE-3511(口服灌胃;75 mg/kg;单剂量)抑制小鼠体内的 DLK,以减少 CYP 诱导的伤害性行为[2]。 GNE-3511(口服管饲;75 mg/kg;单剂量)可减少 CYP 在小鼠膀胱中引起的水肿和出血[2]。 GNE-3511(静脉注射;1 mg/kg 或口服;5 mg/kg)具有中等的体内血浆清除率、中等的分布体积、短暂的半衰期和中等的脑渗透性[2]。
在小鼠轴突损伤模型(视神经挤压伤)中,腹腔注射GNE-3511(30 mg/kg,每日两次,连续7天)维持视网膜神经节细胞(RGC)存活;RGC密度较溶媒对照组高58%(p < 0.01) [1] - 在环磷酰胺诱导的膀胱炎(CIC)小鼠中,口服GNE-3511(10、30 mg/kg,每日一次,连续7天)减轻膀胱炎症;30 mg/kg剂量组膀胱湿重降低32%,TNF-α蛋白水平降低45%(p < 0.05) [2] - GNE-3511(30 mg/kg,口服)改善CIC小鼠的痛觉反应,排尿频率减少38%,骨盆对冯·弗雷刺激的超敏反应降低42%(p < 0.01) [2] - 在视神经挤压伤模型中,GNE-3511(30 mg/kg,腹腔注射)维持轴突完整性,视神经中点处完整轴突数量较溶媒组增加47% [1] |
| 酶活实验 |
p-JNK细胞测定[1]
用dox诱导的人DLK在40 μL含10%血清的DMEM中稳定转染7500个HEK293细胞,每孔接种384孔聚赖氨酸包被板。37℃孵育20-24 h后,在DMEM中加入5 μL 60 μM强力霉素。37°C强力霉素孵育约20 h后,加入DMEM中DLK抑制剂5 μL, 37°C孵育细胞5.5 h。PBS洗涤细胞,0.1% Triton X-100渗透,SuperBlock阻断1 h,然后与一抗在4°C孵育过夜。二抗孵育2小时,PBS洗涤,然后用Hoechst 33342染料染色。在Opera成像平台上成像。 体外轴突变性细胞试验[1] 实验按照先前描述(14,64)进行,并进行以下修改。从E14.5大鼠胚胎新鲜解剖背根神经节(DRG)神经元。用50 μm筛过滤细胞悬浮液,去除剩余组织块,1000 rpm离心5分钟,重悬于DRG培养基(DMEM/F12,含1× N3, 0.18%葡萄糖,25 ng/mL NGF)中。然后将神经元以每孔1200-2000个细胞的密度置于384孔培养皿上,置于星形胶质细胞单层上。为抑制细胞增殖,第二天分别在培养液中加入200 μM尿嘧啶和100 μM 5-氟脱氧尿嘧啶。DRGs在实验前培养4天。 体外转运蛋白测定[1] 从美国国立卫生研究院获得稳定转染人MDR1 (Pgp)的Madin-Darby肾细胞(MDCK)。细胞保存在Dulbecco 's改良Eagle培养基中,培养基中添加10% FBS、80 ng/mL秋水仙碱和5 μg/mL plasmoin。用胰蛋白酶收获细胞,接种于Millipore Millicell 24孔板上,初始浓度为2.0 × 105个细胞/mL,培养5天。实验前,将细胞单层在运输缓冲液(含10 mM Hepes的Hank 's平衡盐溶液,pH 7.4)中平衡60分钟,温度37°C, CO2 5%,相对湿度95%。在传输缓冲液中制备剂量溶液,由5 μM的测试化合物和100 μM的单层完整性标记物lucifer yellow组成。给药室中加入剂量溶液,所有受药室中加入传输缓冲液。在根尖到基底外侧(A-B)和基底外侧到根尖(B-A)方向检查了转运。分别在60、120和180 min取样(50 μL),并在60和120 min后补充新鲜传输缓冲液。在实验中,路西法黄渗透性作为单层完整性的标志。采用LC-MS /MS分析测定供、受室的化合物浓度。从根尖到基底A - b和基底到根尖B-A方向的表观渗透率(Papp)计算公式如下:Papp = (dQ/dt)[1/(AC0)],其中dQ/dt =化合物在受体室出现的速率,A =插入物的表面积,C0 = T = 0时的初始底物浓度。外排比(ER)计算为Papp(B-A)/Papp(A-B) GNE-3511是一种新型、高效、选择性的拉链激酶(例如DLK、MAP3K12)抑制剂,对DLK的IC50为0.107 uM。最近,人们发现双亮氨酸拉链激酶(DLK、MAP3K12)是各种情况下神经元变性的重要调节因子。 GNE-3511在高剂量时完全抑制c-Jun的磷酸化,而在低剂量时,pc-Jun阳性细胞的比例降低至中等水平。 重组DLK激酶活性实验:将纯化的重组人DLK与GNE-3511(0.01 nM至1 μM)及荧光标记的肽底物在激酶实验缓冲液中30°C孵育60分钟;通过检测磷酸化底物的荧光偏振度评估激酶活性;从剂量-反应曲线计算IC50值 [1] - 激酶选择性实验:将GNE-3511(1 μM)对46种人激酶(包括MAP激酶、JNKs和MLKs)进行筛选;采用相同的荧光肽实验方案评估激酶活性,通过比较相对于DLK的抑制率确定选择性 [1] |
| 细胞实验 |
在 384 孔聚-d-赖氨酸包被板的每个孔中,将 hek293 细胞与 7500 个 Dox 诱导型人 DLK 转染细胞一起接种在 40 μL 含有 10% 血清的 DMEM 中。在添加 5 μL 含有 60 μM 多西环素的 DMEM 之前,将板在 37 °C 下孵育 20-24 小时。将细胞与多西环素在 37°C 下孵育大约 20 小时后,在 DMEM 中加入 5 μL DLK 抑制剂。然后将细胞再孵育5.5小时。在这个温度下。用 0.1% Triton X-100 透化并用 SuperBlock 封闭 1 小时后,用 PBS 洗涤细胞,然后在 4 °C 下与一抗一起孵育第二天。将二抗孵育 2 小时,然后进行 PBS 洗涤和 Hoechst 33342 染料染色。 Opera 成像平台用于对细胞板进行成像。
原代皮质神经元轴突保护实验:解剖胚胎18天大鼠的大脑皮质,解离后接种到聚L-赖氨酸包被的盖玻片上;神经元在含NGF的培养基中培养7天,随后去除NGF并加入GNE-3511(1-100 nM);48小时后,固定神经元,对β-微管蛋白III(轴突标志物)进行免疫染色,图像分析量化完整轴突长度 [1] - DLK下游信号蛋白质印迹实验:NGF剥夺的皮质神经元用GNE-3511(0.3-10 μM)处理24小时;裂解细胞,SDS-PAGE分离蛋白,转移至PVDF膜,用针对p-JNK、JNK、p-c-Jun、c-Jun和内参蛋白GAPDH的抗体进行孵育;光密度法量化条带强度 [1] - MBEC炎症反应实验:小鼠膀胱上皮细胞接种到24孔板培养至汇合;用GNE-3511(1-10 μM)预处理细胞1小时,再用LPS(1 μg/mL)刺激6小时;提取总RNA,逆转录为cDNA,qPCR检测TNF-α/IL-6 mRNA水平(以GAPDH为内参) [2] |
| 动物实验 |
Cystitis mouse model[1]
75 mg/kg oral gavage;75 mg/kg; single All experiments with mice were performed under animal protocols approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee at Genentech and adhere to ACS Ethical Guidelines for animal studies. For all in vivo studies, C57Bl/6 mice were dosed with GNE-3511orally as an MCT suspension. Optic nerve crush studies were conducted as described, except p-c-Jun was measured at 6 h by MSD ELISA. For MPTP studies, animals were administered four ip doses of 20 mg/kg MPTP (1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine), with each dose separated by 4 h. Twenty-five hours after the first MPTP dose, animals were sacrificed and processed essentially as described. For each animal, the p-c-Jun positive cell number/mm2 in five sections was averaged to generate a value for that animal.[1] To determine the effect of DLK inhibition in mice with cystitis, a single dose of DLK inhibitor GNE-3511 was administered at a dose of 75 mg/kg with 10 mg/kg of 7.5 mg/mL GNE-3511 solution by oral gavage at 2 h prior to CYP injection. Mice were housed in an environmentally controlled facility with a 12 h/12 h light/dark cycle and free access to water and food. [2] Mouse optic nerve crush model: 8-week-old C57BL/6 male mice were anesthetized, and the right optic nerve was crushed with forceps for 10 seconds; mice were randomly divided into 2 groups (n=10 per group): vehicle control and GNE-3511 30 mg/kg [1] - GNE-3511 was formulated in 10% DMSO, 40% polyethylene glycol 400, and 50% saline; mice were administered the drug via intraperitoneal injection twice daily for 7 consecutive days, starting 1 hour post-injury [1] - RGC survival assessment: At 7 days post-injury, mice were euthanized, retinas were isolated, and RGCs were labeled with a fluorescent tracer; RGC density was counted in retinal flat mounts under a fluorescence microscope [1] - Cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis model: 8-week-old female C57BL/6 mice were intraperitoneally injected with cyclophosphamide (150 mg/kg) to induce cystitis; 24 hours later, mice were randomly divided into 3 groups (n=8 per group): vehicle control, GNE-3511 10 mg/kg, 30 mg/kg [2] - GNE-3511 was formulated in 0.5% methylcellulose and 0.1% Tween 80 in water; mice were administered the drug via oral gavage once daily for 7 days [2] - Cystitis assessment: At study end, mice were euthanized, bladders were excised and weighed; bladder tissue was homogenized for TNF-α protein quantification by ELISA, and paraffin sections were stained with HE for histological analysis [2] - Nociception testing: Voiding frequency was recorded for 2 hours before euthanasia; pelvic hypersensitivity was assessed using von Frey filaments (0.02-4 g) to measure withdrawal threshold [2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
In rats, oral bioavailability of GNE-3511 was 42% after a 10 mg/kg dose [1]
- The terminal elimination half-life (t1/2) of GNE-3511 was 3.2 hours in rats and 4.5 hours in mice [1] - Peak plasma concentration (Cmax) in mice after 30 mg/kg oral dose was 2.8 μg/mL, with a time to peak (Tmax) of 1 hour [2] - GNE-3511 showed good tissue penetration, with brain-to-plasma concentration ratio of 0.7 in mice and bladder-to-plasma ratio of 1.2 in CIC mice [1][2] - Plasma protein binding rate of GNE-3511 was 92% in human plasma (equilibrium dialysis assay) [1] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
In 2-week repeat-dose toxicity studies in rats (doses up to 100 mg/kg/day, i.p.) and mice (up to 150 mg/kg/day, p.o.), GNE-3511 did not cause significant changes in body weight, food intake, or clinical chemistry parameters (ALT, AST, creatinine, BUN) [1][2]
- No histopathological abnormalities were observed in major organs (brain, liver, kidney, heart, bladder) of animals treated with therapeutic doses [1][2] - GNE-3511 did not induce cytotoxicity in primary cortical neurons or MBECs at concentrations up to 100 μM after 72-hour incubation [1][2] - No significant drug-drug interaction potential was identified with CYP3A4, CYP2D6, or CYP2C9 in human liver microsomes [1] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Interstitial cystitis is associated with neurogenic inflammation and neuropathic bladder pain. Dual leucine zipper kinase (DLK) expressed in sensory neurons is implicated in neuropathic pain. We hypothesized that neuronal DLK is involved in the regulation of inflammation and nociceptive behavior in cystitis. Mice deficient in DLK in sensory neurons (cKO) were generated by crossing DLK floxed mice with mice expressing Cre recombinase under Advillin promoter. Cystitis was induced by cyclophosphamide (CYP) administration in mice. Nociceptive behavior, bladder inflammation, and pathology were assessed following cystitis induction in control and cKO mice. The role of DLK in CYP-induced cystitis was further determined by pharmacological inhibition of DLK with GNE-3511. Deletion of neuronal DLK attenuated CYP-induced pain-like nociceptive behavior and suppressed histamine release from mast cells, neuronal activation in the spinal cord, and bladder pathology. Mice deficient in neuronal DLK also showed reduced inflammation induced by CYP and reduced c-Jun activation in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG). Pharmacological inhibition of DLK with GNE-3511 recapitulated the effects of neuronal DLK depletion in CYP treatment mice. Our study suggests that DLK is a potential target for the treatment of neuropathic pain and bladder pathology associated with cystitis.[2]
Dual leucine zipper kinase (DLK, MAP3K12) was recently identified as an essential regulator of neuronal degeneration in multiple contexts. Here we describe the generation of potent and selective DLK inhibitors starting from a high-throughput screening hit. Using proposed hinge-binding interactions to infer a binding mode and specific design parameters to optimize for CNS druglike molecules, we came to focus on the di(pyridin-2-yl)amines because of their combination of desirable potency and good brain penetration following oral dosing. Our lead inhibitor GNE-3511 (26) displayed concentration-dependent protection of neurons from degeneration in vitro and demonstrated dose-dependent activity in two different animal models of disease. These results suggest that specific pharmacological inhibition of DLK may have therapeutic potential in multiple indications.[1] GNE-3511 is a potent, selective, orally bioavailable DLK inhibitor developed for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases and inflammatory conditions [1][2] - Its mechanism of action involves inhibiting DLK-mediated activation of the JNK/c-Jun signaling pathway, thereby preventing axonal degeneration and reducing pro-inflammatory cytokine production [1][2] - GNE-3511 demonstrates neuroprotective activity in axonal injury models, supporting its potential for diseases involving neuronal loss (e.g., Alzheimer's disease, glaucoma) [1] - In cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis, GNE-3511 reduces bladder inflammation and nociception by inhibiting DLK-dependent inflammatory signaling, suggesting utility in inflammatory bladder disorders [2] |
| 分子式 |
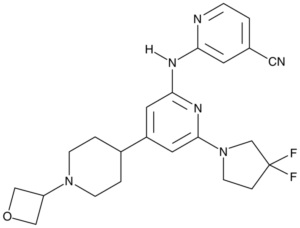
C23H26F2N6O
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
440.49
|
|
| 精确质量 |
440.213
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 62.71; H, 5.95; F, 8.63; N, 19.08; O, 3.63
|
|
| CAS号 |
1496581-76-0
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
72547959
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to yellow solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
579.0±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
304.0±30.1 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.630
|
|
| LogP |
2.01
|
|
| tPSA |
77.3
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
9
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
32
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
689
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
FC1(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N(C1([H])[H])C1=C([H])C(=C([H])C(N([H])C2C([H])=C(C#N)C([H])=C([H])N=2)=N1)C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N(C([H])([H])C1([H])[H])C1([H])C([H])([H])OC1([H])[H])F
|
|
| InChi Key |
RHFIAUKMKYHHFA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C23H26F2N6O/c24-23(25)4-8-31(15-23)22-11-18(17-2-6-30(7-3-17)19-13-32-14-19)10-21(29-22)28-20-9-16(12-26)1-5-27-20/h1,5,9-11,17,19H,2-4,6-8,13-15H2,(H,27,28,29)
|
|
| 化学名 |
2-[[6-(3,3-difluoropyrrolidin-1-yl)-4-[1-(oxetan-3-yl)piperidin-4-yl]pyridin-2-yl]amino]pyridine-4-carbonitrile
|
|
| 别名 |
GNE 3511; GNE3511; 2-((6-(3,3-difluoropyrrolidin-1-yl)-4-(1-(oxetan-3-yl)piperidin-4-yl)pyridin-2-yl)amino)isonicotinonitrile; GNE 3511; 2-[[6-[3,3-Bis(Fluoranyl)pyrrolidin-1-Yl]-4-[1-(Oxetan-3-Yl)piperidin-4-Yl]pyridin-2-Yl]amino]pyridine-4-Carbonitrile; CHEMBL3393333; GNE3511; compound 26 [PMID: 25341110]; GNE-3511
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.72 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 +5% Tween-80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80+,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2702 mL | 11.3510 mL | 22.7020 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4540 mL | 2.2702 mL | 4.5404 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2270 mL | 1.1351 mL | 2.2702 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
 |
|---|
 |
 |