| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Bcr-Abl kinase (wild-type, allosteric inhibitor): IC₅₀ ≈ 100 nM (recombinant human Bcr-Abl catalytic domain); Bcr-Abl kinase (T315I "gatekeeper" mutant): IC₅₀ ≈ 120 nM; no significant activity against Src (IC₅₀ > 1000 nM), EGFR (IC₅₀ > 1000 nM), or PDGFRβ (IC₅₀ > 1000 nM), showing high selectivity for Bcr-Abl [1]
- c-Abl kinase (non-oncogenic ABL1): GNF-5 inhibited c-Abl-mediated invadopodia formation in breast cancer cells without affecting Src activity [2] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
GNF-5 抑制野生型 Abl,IC50 为 0.22 µM,但不抑制肉豆蔻酸位点突变体 E505K(IC50 >10 µM)[1]。
在Bcr-Abl+白血病细胞中: 1. 增殖抑制:GNF-5(10 nM–1000 nM)浓度依赖性抑制表达Bcr-Abl野生型(IC₅₀≈150 nM)或Bcr-Abl(T315I)(IC₅₀≈180 nM)的Ba/F3细胞,以及人K562细胞(Bcr-Abl野生型,IC₅₀≈200 nM)的生长(MTT法,处理72小时)。 2. 与ATP结合位点抑制剂协同作用:GNF-5(50 nM)与伊马替尼(100 nM)或尼洛替尼(50 nM)联用,使Ba/F3-Bcr-Abl(T315I)细胞活力降低~70%(单独使用GNF-5或伊马替尼/尼洛替尼时仅降低~25%或~30%)。 3. 信号抑制:Western blot显示,GNF-5(200 nM,处理2小时)使K562细胞中Bcr-Abl自身磷酸化(Tyr412)降低~60%,总Bcr-Abl蛋白水平无变化[1] - 在人乳腺癌细胞(MDA-MB-231、BT-549;文献[2])中: 1. 侵袭伪足抑制:GNF-5(2 μM–10 μM)减少侵袭伪足形成(F-肌动蛋白/皮层肌动蛋白共染色):MDA-MB-231细胞中,5 μM处理24小时后,侵袭伪足阳性细胞比例降低~50%。 2. 侵袭抑制:Transwell实验显示,GNF-5(5 μM)使MDA-MB-231细胞侵袭率较对照组降低~65%(处理24小时)。 3. 机制:Western blot证实,GNF-5(5 μM)使c-Abl磷酸化(Tyr412)降低~55%,且不影响p-Src(Tyr416)水平,表明其对c-Abl的选择性抑制[2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
GNF-5 具有适当的药代动力学特性(5 mg/kg IV 或 20 mg/kg 口服)[1]。口服 GNF-5 在体内有效,每日两次,连续 7 天,剂量为 50 或 100 mg/kg,但可能会复发[1]。在体内,尼罗替尼与 T315I Bcr-Abl 组合可被 GNF-5 抑制(75 mg/kg,bid)[1]。
在裸鼠(nu/nu,6–8周龄)Ba/F3-Bcr-Abl(T315I)异种移植模型中: 小鼠随机分为4组(n=6/组):(1)对照组(口服溶剂:5% DMSO+10% Cremophor EL+85%生理盐水);(2)GNF-5组(100 mg/kg,口服灌胃,每日1次);(3)伊马替尼组(150 mg/kg,口服灌胃,每日1次);(4)联用组(GNF-5 100 mg/kg + 伊马替尼150 mg/kg)。肿瘤体积达~100 mm³时开始给药,持续14天。与对照组相比: - 肿瘤体积:单独GNF-5组减少~35%,单独伊马替尼组减少~40%,联用组减少~80%。 - 处死时肿瘤重量:单独GNF-5组降低~30%,单独伊马替尼组降低~35%,联用组降低~75%。 - 肿瘤裂解液:Western blot显示,单独GNF-5组p-Bcr-Abl(Tyr412)降低~40%,联用组降低~70%[1] - 在裸鼠MDA-MB-231-Luc乳腺癌肺转移模型中: 小鼠静脉注射MDA-MB-231-Luc细胞(1×10⁶个细胞/只)。1天后分为2组(n=6/组):(1)对照组(溶剂,腹腔注射,每日1次);(2)GNF-5组(50 mg/kg,腹腔注射,每日1次)。给药持续28天。 - 生物发光成像:GNF-5组肺转移信号强度较对照组降低~60%。 - 组织学:GNF-5组肺转移结节较对照组减少~55%。 - 肺组织裂解液:GNF-5组p-c-Abl(Tyr412)水平降低~50%[2] |
| 酶活实验 |
重组Bcr-Abl激酶活性测定实验:
1. 蛋白制备:在Sf9昆虫细胞中表达重组人Bcr-Abl催化结构域(野生型或T315I突变体),通过亲和层析(多组氨酸标签)纯化。 2. 反应体系:50 μL反应混合物含50 mM Tris-HCl(pH7.5)、10 mM MgCl₂、1 mM DTT、5 μM ATP(含[γ-³²P]ATP用于放射性标记)、20 μM Bcr-Abl特异性肽底物(序列:EAIYAAPFAKKK)及GNF-5(10 nM–1000 nM,溶剂为对照)。 3. 孵育与检测:混合物30℃孵育45分钟,加入25 μL 0.5 M EDTA终止反应。取40 μL反应液点样至磷酸纤维素滤纸上,用0.75%磷酸洗涤3次(每次10分钟)以去除未掺入的ATP。滤纸干燥后加入闪烁液,通过液体闪烁计数器测定放射性强度。 4. 数据分析:抑制率=(1–药物组放射性/对照组放射性)×100%,将数据拟合至四参数逻辑斯蒂曲线确定IC₅₀值[1] |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定[1]
细胞类型:表达野生型和突变型 Bcr-Abl 的 Ba/F3 细胞 测试浓度:0.2、0.8 和 1.6 μM 孵育时间:48小时 实验结果:以非ATP竞争方式抑制野生型Abl。 Bcr-Abl+细胞增殖与信号通路实验: 1. 增殖实验(MTT法):将Ba/F3-Bcr-Abl细胞(野生型/T315I)或K562细胞以5×10³个细胞/孔接种于96孔板,用GNF-5(10 nM–1000 nM)单独或与伊马替尼/尼洛替尼联用处理。37℃、5% CO₂孵育72小时后,每孔加入20 μL MTT溶液(5 mg/mL PBS配制),继续孵育4小时。吸弃上清,加入150 μL DMSO溶解甲臜结晶,测定570 nm处吸光度,计算细胞活力及IC₅₀。 2. Western blot实验:K562细胞用0.5% FBS血清饥饿过夜,用GNF-5(50 nM–200 nM)处理2小时,随后用含蛋白酶/磷酸酶抑制剂的RIPA缓冲液裂解。每泳道上样30 μg蛋白,经SDS-PAGE分离后转印至PVDF膜,用抗p-Bcr-Abl(Tyr412)、总Bcr-Abl及β-actin抗体孵育,ECL化学发光检测信号[1] - 乳腺癌侵袭伪足与侵袭实验: 1. 侵袭伪足染色:MDA-MB-231细胞接种于明胶包被的盖玻片,用GNF-5(2 μM–10 μM)处理24小时。4%多聚甲醛固定,0.1% Triton X-100透化,用抗皮层肌动蛋白抗体(侵袭伪足标志物)和鬼笔环肽(F-肌动蛋白)染色,共聚焦显微镜分析并计数侵袭伪足阳性细胞。 2. Transwell侵袭实验:将MDA-MB-231细胞(5×10⁴个细胞/孔)接种于含GNF-5(5 μM)的Transwell上室(8 μm孔径),下室加入含10% FBS的RPMI 1640培养基。24小时后,固定下室表面细胞,结晶紫染色并计数。 3. Western blot实验:MDA-MB-231细胞用GNF-5(5 μM)处理2小时,裂解后用抗p-c-Abl(Tyr412)、总c-Abl、p-Src(Tyr416)及β-actin抗体进行免疫印迹[2] |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Male balb/c (Bagg ALBino) mouse[1]
Doses: 5 mg/kg, 20 mg/kg Route of Administration: 5 mg/kg intravenously (iv)or 20 mg/kg orally Experimental Results: AUC_inf (minug/mL) 292.37 AUC_inf (hrsnM 11647 Cmax(nM) 4386.08 Tmax(hrs) 0.50 Clast (nM) 636.16 T1 /2(hrs) 2.30 Vss(L/kg) 9.18 F (%) 44.82 Animal/Disease Models: p210 xenograft model[1] Doses: 50 or 100 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage) twice (two times) daily, for 7 days Experimental Results: Could normalize blood counts and spleen size. Animal/Disease Models: Bone marrow transduction/transplantation model[1] Doses: 75 mg/kg Route of Administration: twice (two times) daily Experimental Results: demonstrated no significant response (alone). demonstrated no toxicity and had a strong and sustained inhibition of Bcr- Abl-mediated signaling combination with nilotinib. Nude mouse Ba/F3-Bcr-Abl(T315I) xenograft protocol: 1. Animal housing: Female nude mice (6–8 weeks old, 18–22 g) were housed in SPF facilities (22–25°C, 12-hour light/dark cycle) with free access to food and water. 2. Tumor implantation: Ba/F3-Bcr-Abl(T315I) cells (5×10⁶ cells/mouse) were resuspended in 100 μL PBS/matrigel (1:1) and subcutaneously injected into the right flank of mice. 3. Grouping and treatment: When tumors reached ~100 mm³ (day 0), mice were randomized into 4 groups: (1) Control: oral gavage of solvent (10 μL/g body weight); (2) GNF-5: 100 mg/kg oral gavage, once daily; (3) Imatinib: 150 mg/kg oral gavage, once daily; (4) Combination: GNF-5 + imatinib (same doses as single groups). Treatments continued for 14 days. 4. Tumor monitoring: Tumor volume was measured every 2 days with calipers (volume = length × width² / 2). On day 14, mice were euthanized via CO₂ inhalation, tumors were excised and weighed, and tumor lysates were prepared for Western blot [1] - Nude mouse breast cancer metastasis protocol: 1. Animal housing: Same as above. 2. Metastasis induction: MDA-MB-231-Luc cells (1×10⁶ cells/mouse) were resuspended in 100 μL PBS and injected into the lateral tail vein of mice. 3. Grouping and treatment: One day post-injection, mice were divided into 2 groups: (1) Control: intraperitoneal injection of solvent (5% DMSO + 95% normal saline, 10 μL/g body weight); (2) GNF-5: 50 mg/kg intraperitoneal injection, once daily. Treatments continued for 28 days. 4. Metastasis detection: Bioluminescence imaging was performed weekly to monitor lung metastasis. On day 28, mice were euthanized, lungs were excised, fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, and metastatic nodules were counted via histology. Lung lysates were prepared for Western blot [2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Oral absorption: In nude mice, oral GNF-5 (100 mg/kg) reached peak plasma concentration (Cmax) at ~2 hours, with Cmax ≈ 1.2 μg/mL and AUC₀-24h ≈ 8.5 μg·h/mL.
- Half-life: Mean terminal elimination half-life (t₁/₂) of GNF-5 in nude mice was ~6 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
In nude mice treated with GNF-5 (50 mg/kg–100 mg/kg, oral/intraperitoneal, 14–28 days) (literature [1] and [2]):
1. No significant weight loss (<5% vs. baseline) or mortality was observed. 2. Serum biochemical analysis (ALT, AST, creatinine, BUN) at sacrifice showed no significant differences between GNF-5 groups and controls, indicating no obvious hepatotoxicity or nephrotoxicity. - Plasma protein binding: ~92% (determined via equilibrium dialysis in human plasma). |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
GNF-5 is a first-in-class allosteric inhibitor of Bcr-Abl, binding to the myristate-binding pocket (a regulatory site) of Bcr-Abl instead of the ATP-binding pocket. This unique mechanism allows it to inhibit Bcr-Abl mutants (e.g., T315I) that are resistant to ATP-competitive inhibitors (imatinib, nilotinib) [1]
- In Bcr-Abl+ leukemias, GNF-5 synergizes with ATP-competitive inhibitors to overcome T315I-mediated resistance, providing a therapeutic strategy for refractory chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) [1] - In breast cancer, GNF-5 inhibits c-Abl-mediated invadopodia formation and extracellular matrix degradation, thereby suppressing metastasis. This identifies c-Abl as a potential target for anti-metastatic therapies [2] - GNF-5 is primarily used as a research tool to study allosteric regulation of Abl kinases and Abl-mediated diseases; no clinical development (phase I/II trials) or FDA approval status was mentioned in either literature [1][2] |
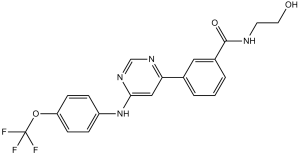
| 分子式 |
C20H17F3N4O3
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
418.37
|
|
| 精确质量 |
418.125
|
|
| CAS号 |
778277-15-9
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
44129660
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
612.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
324.2±31.5 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.9 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.600
|
|
| LogP |
3.31
|
|
| tPSA |
99.86
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
9
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
30
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
544
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| InChi Key |
IIQUYGWWHIHOCF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C20H17F3N4O3/c21-20(22,23)30-16-6-4-15(5-7-16)27-18-11-17(25-12-26-18)13-2-1-3-14(10-13)19(29)24-8-9-28/h1-7,10-12,28H,8-9H2,(H,24,29)(H,25,26,27)
|
|
| 化学名 |
N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-3-[6-[[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]amino]-4-pyrimidinyl]benzamide
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.98 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.98 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.98 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3902 mL | 11.9511 mL | 23.9023 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4780 mL | 2.3902 mL | 4.7805 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2390 mL | 1.1951 mL | 2.3902 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Cellular and enzymatic inhibition of wild-type and mutants by combination treatments.Nature.2010 Jan 28;463(7280):501-6. |
In vivo efficacy studies with GNF-5 on wild-type and T315I Bcr-Abl dependent proliferation in xenograft and bone marrow transplantation models.Nature.2010 Jan 28;463(7280):501-6. |
Hydrogen exchange mass spectrometry upon binding of GNF-5 to Abl.Nature.2010 Jan 28;463(7280):501-6. |