| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
gt1b (Ki=0.01±<0.01 nM);gt1a (Ki=0.01±0.01 nM);gt2a (Ki=0.08±0.02 nM);gt2b (Ki=0.15±0.06 nM);gt3a (Ki=0.90±0.2 nM)
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:MK-5172 (Grazoprevir) 在针对常见耐药突变的主要基因型和变异体的生化检测中有效,Ki 为 0.01±<0.01 nM (gt1b)、0.01±0.01 nM (gt1a)、0.08±0.02 nM (gt2a)、0.15±0.06nM(gt2b)、0.90±0.2nM(gt3a)、0.07±0.01nM(gt1bR155K)、0.14±0.03nM(gt1bD168V)、0.30±0.04nM(gt1bD168Y)、5.3±0.9nM(gt1bD168Y) 1bA156T ) 和 12±2 nM (gt1bA156V)。在复制子测定中,MK-5172 对基因型 1a、1b 和 2a 表现出亚纳摩尔至低纳摩尔 EC50,对于 gt1bcon1、gt1a 和 gt2a 的 EC50 分别为 0.5±0.1 nM、2±1 nM 和 2±1 nM,分别。 MK-5172 对一组 HCV 复制突变体 NS5A (Y93H) (EC50=0.7±0.3 nM)、NS5B 核苷 (S282T) (EC50=0.3±0.1 nM) 和 NS5B (C316Y) (EC50=0.4±0.2) 有效。 )。 MK-5172 保持了针对 gt 3a 酶以及多种突变酶的优异功效,在复制子系统中具有优异的功效 [gt1b IC50(50% NHS)=7.4 nM; gt1a IC50(40% NHS)=7 nM],并且显示出优异的大鼠肝脏暴露。激酶测定:从大肠杆菌中表达并纯化重组 HCV NS3/4A 酶。酶序列源自基因型 1a (gt1a) H77、gt1b con1、gt2a JFH1、gt2b HCJ8 和 gt3a NZL1。在时间分辨荧光测定中测定含有 MK-5172 (Grazoprevir)、Vaniprevir 或参考化合物 Danoprevir 和 TMC435 的反应混合物中 HCV NS3/4A 蛋白酶活性的抑制。基于细胞的 HCV 复制子测定是在 10% 胎牛血清 (FBS) 或 40% 正常人血清 (NHS) 存在下,在基因型 1b (con1) 稳定细胞系 HB1 或 gt2a 细胞系 (JFH) 中进行。使用基于 TaqMan 的测定法确定针对一组基因型或突变复制子细胞系的 50% 有效浓度 (EC50)。使用 MTS 测定在 HCV 复制子细胞系中测定 50% 细胞毒性浓度 (CC50)。使用基于细胞的瞬时表型测定来确定针对临床基因型 1 NS3/4A 序列的效力。 NS3/4A 患者分离株是从感染 HCV 的人血浆中克隆出来的。 MDS Pharma Services 进行了广泛的反筛选,评估 MK-5172 在 10 μM 浓度下的抑制效力。细胞测定:将HB1细胞(每孔30,000个)按照药物浓度接种到6孔组织培养板中。第二天(第 0 天),用新鲜培养基和适当药物浓度的 MK-5172 补充培养基。在第 0、1 和 2 天从每个药物浓度的单个孔中收获细胞,洗涤并冷冻保存直至评估。第四个孔在第 3.5 天以类似方式收获,不同之处在于用新鲜培养基和适当药物浓度的 MK-5172 重新接种 30,000 个细胞。对于其他时间点,每半周传代并收获细胞,持续 2 周。第三周,对细胞进行类似处理,不同之处在于细胞接受含有0.5mg/ml G418且不含蛋白酶抑制剂的补充培养基。
|
||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
MK-5172(Grazoprevir)对慢性 HCV 感染的黑猩猩表现出高体内功效。当给狗给药时,MK-5172 在静脉给药后显示出 5 mL/min/kg 的低清除率和 3 小时的半衰期,并且在口服 1 mg/kg 剂量后具有良好的血浆暴露(AUC=0.4 μM h)。狗肝活检研究表明,口服 1 mg/kg 剂量后 MK-5172 在 24 小时时间点的肝脏浓度为 1.4 μM。与在大鼠中的行为类似,MK-5172 在狗口服给药 24 小时后表现出有效分配到肝组织中并相对于效力保持较高的肝脏浓度。
体内疗效。[1] 为了证明体内疗效,将Grazoprevir/MK-5172口服给三只慢性HCV感染的黑猩猩,剂量为每公斤1毫克,每天两次,持续7天。其中两只黑猩猩感染了野生型(WT)gt1a或gt1b,病毒滴度很高(约106IU/ml)。第三只黑猩猩的病毒滴度适中(约104IU/ml),为gt1a NS3 R155K病毒。在没有事先用HCV小分子抑制剂进行实验治疗的情况下,这只黑猩猩保持了慢性R155K病毒感染(J.Fontenot,个人通讯)。MK-5172的药效学反应如图4A所示。 所有动物的病毒滴度都立即大幅下降。gt1a(WT)感染在2天内被抑制了约4个对数,达到约100 IU/ml,并且在整个给药过程中保持了病毒抑制。gt1b感染被抑制超过5个对数,达到定量水平(20IU/ml);在给药期间或给药后都没有出现耐药性的遗传证据。 感染gt1a NS3 R155K的黑猩猩病毒滴度迅速降低了约2-log。在给药期的剩余时间里,病毒载量逐渐上升,只有在停止给药后才恢复到基线水平。在整个研究过程中,R155K突变的病毒是同质的。给药没有引起额外的突变,也没有遗传证据表明给药期间或给药后病毒滴度的波动是由于新出现的耐药变异引起的。 MK-5172/Grazoprevir浓度是从给药最后一剂后12小时收集的匹配血浆和肝活检样本中测定的(表7)。与血浆中的低纳摩尔浓度相比,肝脏中的药物浓度明显更高,范围在0.85至1.99μM之间。这导致肝脏与血浆的比率为425比785。此时,gt1a和gt1b感染的病毒载量减少大于4 log,gt1a NS3 R155K感染的病毒载荷减少大于0.8 log。虽然不能从单一药物剂量确定药代动力学-药效学关系,但病毒载量的减少更能反映肝脏中的药物浓度。 通过比较gt1b感染黑猩猩在相同给药方案下对MK-5172或瓦尼普雷韦的反应,进一步说明了Grazoprevir/MK-5172的体内疗效(图4B)。MK-5172使病毒滴度进一步降低了对数。最终剂量后12小时,MK-5172的肝脏药物浓度也高出约4倍,为1.97μM,而瓦尼普雷韦为0.54μM,表明HCV复制部位的药物暴露更好。 基于两种基因型和临床相关抗性突变体的更大效力、改善的药代动力学、临床前物种中优异的24小时肝脏浓度以及HCV感染黑猩猩的体内疗效,选择Grazoprevir/MK-5172进行临床开发。 |
||
| 酶活实验 |
重组 HCV NS3/4A 酶从大肠杆菌中表达和纯化。酶序列源自基因型 1a (gt1a) H77、gt1b con1、gt2a JFH1、gt2b HCJ8 和 gt3a NZL1。在时间分辨荧光测定中测定含有 MK-5172 (Grazoprevir)、Vaniprevir 或参考化合物 Danoprevir 和 TMC435 的反应混合物中 HCV NS3/4A 蛋白酶活性的抑制。基于细胞的 HCV 复制子测定在 10% 胎牛血清 (FBS) 或 40% 正常人血清 (NHS) 存在下,在基因型 1b (con1) 稳定细胞系 HB1 或 gt2a 细胞系 (JFH) 中进行。使用基于 TaqMan 的测定法确定针对一组基因型或突变复制子细胞系的 50% 有效浓度 (EC50)。使用 MTS 测定在 HCV 复制子细胞系中测定 50% 细胞毒性浓度 (CC50)。使用基于细胞的瞬时表型测定来确定针对临床基因型 1 NS3/4A 序列的效力。 NS3/4A 患者分离株是从感染 HCV 的人血浆中克隆出来的。 MDS Pharma Services 进行了广泛的反筛选,评估 MK-5172 在 10 μM 浓度下的抑制效力。
酶实验。[2] 使用NS3/4A蛋白酶活性的时间分辨荧光测定法测定化合物的抑制效力。NS3蛋白酶测定在最终体积为100µL的测定缓冲液中进行,该缓冲液含有50 mM 4-(2-羟乙基)哌嗪-1-乙磺酸钠盐(HEPES),pH 7.5,150 mM NaCl,15%甘油,0.15%Triton X-100,10 mM二硫苏糖醇(DTT)和0.1%PEG8000。将NS3蛋白酶与不同浓度的抑制剂在二甲亚砜(DMSO)中预孵育30分钟。通过加入时间分辨荧光(TRF)肽底物(终浓度100nM)引发反应。在室温下1小时后,用100µL 500 mM 2-(N-吗啉代)乙磺酸(MES)(pH 5.5)淬灭NS3介导的底物水解。使用Victor V2或Fusion荧光光度计检测产品荧光,激发波长为340 nm,发射波长为615 nm,延迟400µs。抑制常数是使用标准的四参数拟合数据得出的。从大肠杆菌中表达并纯化编码氨基酸突变R155K、A156T、A156V或D168V的gt1b(BK)、gt3a(NZL1)或gt1b的全长NS3/4A蛋白酶序列。26使用标准分子生物学技术将蛋白酶突变工程化到gt1b表达构建体中。 |
||
| 细胞实验 |
将 HB1 细胞(每孔 30,000 个)按照药物浓度接种到 6 孔组织培养板中。第二天(第 0 天),用新鲜培养基和适当药物浓度的 MK-5172 补充培养基。在第 0、1 和 2 天从每个药物浓度的单个孔中收获细胞,洗涤并冷冻保存直至评估。第四个孔在第 3.5 天以类似方式收获,不同之处在于用新鲜培养基和适当药物浓度的 MK-5172 重新接种 30,000 个细胞。对于其他时间点,每半周传代并收获细胞,持续 2 周。第三周,对细胞进行类似处理,不同之处在于细胞接受含有0.5mg/ml G418且不含蛋白酶抑制剂的补充培养基。
体外试验。[1] 如前所述,重组HCV NS3/4A酶从大肠杆菌中表达和纯化。酶序列来源于基因型1a(gt1a)H77(GenBank登录号AF09606)、gt1b con1(GenBank注册号AJ238799)、gt2a JFH1(GenBank登陆号AB047639)、gt2b HCJ8(GenBank登入号D10988)和gt3a NZL1(GenBank登记号D17763)。在时间分辨荧光分析中测定了含有Grazoprevir/MK-5172、vaniprevir或参考化合物danoprevir和TMC435(图1)的反应混合物中HCV NS3/4A蛋白酶活性的抑制作用。在10%胎牛血清(FBS)或40%正常人血清(NHS)存在下,在基因型1b(con1)稳定细胞系HB1或gt2a细胞系(JFH)中进行基于细胞的HCV复制子检测。使用基于TaqMan的测定法对基因型或突变复制子细胞系进行50%有效浓度(EC50s)的测定。根据制造商的方案,使用MTS测定法在HCV复制子细胞系中测定50%细胞毒性浓度(CC50)。使用基于瞬时细胞的表型测定法对临床基因型1 NS3/4A序列进行效力测定。NS3/4A患者分离株是从感染HCV的人血浆中克隆的。MDS Pharma Services进行了广泛的反筛选,其中评估了MK-5172在10μM浓度下的抑制效力。 对于体外抗性选择,将100000个HB1细胞接种到T162 Z-top烧瓶中,并在0.5mg/ml G418和所需浓度的Grazoprevir/MK-5172存在下培养。将细胞培养约3周,定期更换培养基,直到发生足够的细胞死亡以形成不同的集落。扩增后,分离总RNA,用作产生NS3/4a cDNA的模板,并使用常规分子生物学技术进行测序。通过与未经处理的细胞产生的序列进行比较,鉴定出突变。 对于2周的效力评估,每种药物浓度每6孔组织培养板的每孔接种30000个HB1细胞。第二天(第0天),用新鲜培养基和适当药物浓度的Grazoprevir补充培养基。在第0、1和2天收获每种药物浓度的单孔细胞,洗涤并冷冻储存直至评估。第四孔在第3.5天同样收获,除了用新鲜培养基和适当药物浓度的Grazoprevir/MK-5172重新接种30000个细胞。对于额外的时间点,细胞每半周传代并收获一次,持续2周。第三周,细胞接受类似的处理,除了细胞接受含有0.5mg/ml G418的补充培养基,不含蛋白酶抑制剂。 Replicon检测。[2] 使用适于使用原位杂交进行定量分析的HCV双顺反子复制子测定27确定病毒复制的抑制作用。28将稳定转染有HCV复制子RNA(gt 1b con1序列;28 gt 2a JFH序列29)的Huh-7细胞接种到96孔板中,用闪烁剂浸渍,密度为每孔20000个细胞,并在添加了50%NHS的Dulbecco改良鹰培养基(DMEM)存在下,在37°C/5%CO2下孵育24小时。将DMSO中的化合物加入1%,再孵育24小时。用10%甲醛处理细胞,用0.25%Triton X100处理细胞使其透性。加入与复制子的新霉素抗性基因杂交的放射性标记RNA探针,在50°C下杂交18小时,然后进行RNase A处理以去除未杂交的探针并清洗。然后在Topcount NXT中对平板进行计数。抑制常数是使用标准的四参数拟合数据得出的。 |
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Grazoprevir reaches peak plasma concentration 0.5-3 hours after administration. Grazoprevir has an absolute bioavailability of 27%. When taken with food the peak concentration of Grazoprevir increases 2.8 fold but this increase in exposure has not been deemed clinically relevant. Grazoprevir is mainly eliminated in the feces (90%) with very little eliminated in the urine (<1%). Grazoprevir has an estimated apparent volume of distribution of 1250 liters. It is thought to distribute primarily to the liver with its uptake facilitated by organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1/3. The clearance of Grazoprevir has not been determined. Metabolism / Metabolites Grazoprevir is partially eliminated by oxidative metabolism meditated by CYP3A. No circulating metabolites of have been detected in human plasma. Biological Half-Life The geometric mean apparent terminal half-life for Grazoprevir is 31 hours in HCV-infected subjects. The pharmacokinetic properties of the potassium salt of compound 15/Grazoprevir were evaluated in multiple species (Table 3). In rat, 15 showed a plasma clearance of 28 mL/min/kg and a plasma half-life of 1.4 h. When dosed orally at 5 mg/kg, the plasma exposure of 15 was good with an AUC of 0.7 μM h. The liver exposure of the compound is quite good (23 μM at 4 h), and 15 remains in liver 24 h after a single 5 mg/kg oral dose. At 24 h, the liver concentration of 15 is 0.2 μM, which is >25-fold higher than the IC50 in the replicon assay with 50% NHS. When dosed to dogs, compound 15/Grazoprevir shows low clearance of 5 mL/min/kg and a 3 h half-life after iv dosing and has good plasma exposure (AUC = 0.4 μM h) after a 1 mg/kg oral dose. Dog liver biopsy studies showed that the liver concentration of 15 after the 1 mg/kg oral dose is 1.4 μM at the 24 h time point. Similar to its behavior in rats, 15 demonstrates effective partitioning into liver tissue and maintains high liver concentration, relative to potency, 24 h after oral dosing in dogs. [2] |
||
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Grazoprevir has not been studied in nursing mothers being treated for hepatitis C infection. Because it is greater than 98.9% bound to maternal plasma proteins, amounts in breastmilk are likely to be very low. Some sources recommend against breastfeeding when grazoprevir is used with ribavirin. Hepatitis C is not transmitted through breastmilk and breastmilk has been shown to inactivate hepatitis C virus (HCV). However, the Centers for Disease Control recommends that mothers with HCV infection should consider abstaining from breastfeeding if their nipples are cracked or bleeding. It is not clear if this warning would apply to mothers who are being treated for hepatitis C. Infants born to mothers with HCV infection should be tested for HCV infection; because maternal antibody is present for the first 18 months of life and before the infant mounts an immunologic response, nucleic acid testing is recommended. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. |
||
| 参考文献 | |||
| 其他信息 |
HCV NS3/4a protease inhibitors are proven therapeutic agents against chronic hepatitis C virus infection, with boceprevir and telaprevir having recently received regulatory approval as add-on therapy to pegylated interferon/ribavirin for patients harboring genotype 1 infections. Overcoming antiviral resistance, broad genotype coverage, and a convenient dosing regimen are important attributes for future agents to be used in combinations without interferon. In this communication, we report the preclinical profile of MK-5172, a novel P2-P4 quinoxaline macrocyclic NS3/4a protease inhibitor currently in clinical development. The compound demonstrates subnanomolar activity against a broad enzyme panel encompassing major hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotypes as well as variants resistant to earlier protease inhibitors. In replicon selections, MK-5172 exerted high selective pressure, which yielded few resistant colonies. In both rat and dog, MK-5172 demonstrates good plasma and liver exposures, with 24-h liver levels suggestive of once-daily dosing. When administered to HCV-infected chimpanzees harboring chronic gt1a or gt1b infections, MK-5172 suppressed viral load between 4 to 5 logs at a dose of 1 mg/kg of body weight twice daily (b.i.d.) for 7 days. Based on its preclinical profile, MK-5172 is anticipated to be broadly active against multiple HCV genotypes and clinically important resistance variants and highly suited for incorporation into newer all-oral regimens.[1]
A new class of HCV NS3/4a protease inhibitors containing a P2 to P4 macrocyclic constraint was designed using a molecular modeling-derived strategy. Building on the profile of previous clinical compounds and exploring the P2 and linker regions of the series allowed for optimization of broad genotype and mutant enzyme potency, cellular activity, and rat liver exposure following oral dosing. These studies led to the identification of clinical candidate 15 (MK-5172), which is active against genotype 1-3 NS3/4a and clinically relevant mutant enzymes and has good plasma exposure and excellent liver exposure in multiple species.[2] Grazoprevir is an azamacrocyclic compound that is a hepatitis C protease inhibitor used in combination with elbasvir (under the brand name Zepatier) for treatment of chronic HCV genotypes 1 or 4 infection in adults. It has a role as an antiviral drug, a hepatoprotective agent and a hepatitis C protease inhibitor. It is an azamacrocycle, a carbamate ester, a lactam, an aromatic ether, a member of cyclopropanes, a N-sulfonylcarboxamide and a quinoxaline derivative. Grazoprevir is a direct acting antiviral medication used as part of combination therapy to treat chronic Hepatitis C, an infectious liver disease caused by infection with Hepatitis C Virus (HCV). HCV is a single-stranded RNA virus that is categorized into nine distinct genotypes, with genotype 1 being the most common in the United States, and affecting 72% of all chronic HCV patients. Treatment options for chronic Hepatitis C have advanced significantly since 2011, with the development of Direct Acting Antivirals (DAAs) such as Grazoprevir. Grazoprevir is an inhibitor of NS3/4A, a serine protease enzyme, encoded by HCV genotypes 1 and 4 [synthesis]. These enzymes are essential for viral replication and serve to cleave the virally encoded polyprotein into mature proteins like NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5A and NS5B. The barrier for develoment of resistance to NS3/4A inhibitors is lower than that of NS5B inhibitors, another class of DAAs. Subtitutions at amino acid positions 155, 156, or 168 are known to confer resistance. The substitutions of the enzyme's catalytic triad consisting of H58, D82, and S139 are also likely to alter the affinity of the drug for NS3/4A or the activity of the enzyme itself. Despite this disadvantage Grazoprevir is still effective against HCV particularly when paired with [DB11574]. In a joint recommendation published in 2016, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) and the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) recommend Grazoprevir as first line therapy in combination with [DB11574] for genotypes 1a, 1b, and 4 of Hepatitis C. Grazoprevir and [DB11574] are used with or without [DB00811] with the intent to cure, or achieve a sustained virologic response (SVR), after 12 weeks of daily therapy. SVR and eradication of HCV infection is associated with significant long-term health benefits including reduced liver-related damage, improved quality of life, reduced incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma, and reduced all-cause mortality. Grazoprevir is available as a fixed dose combination product with [DB11574] (tradename Zepatier) used for the treatment of chronic Hepatitis C. Approved in January 2016 by the FDA, Zepatier is indicated for the treatment of HCV genotypes 1 and 4 with or without [DB00811] depending on the the presence of resistance associated amino acid substitutions in the NS5A protein and previous treatment failure with [DB00811], [DB00008], [DB00022], or other NS3/4A inhibitors like [DB08873], [DB06290], or [DB05521]. When combined together, Grazoprevir and [DB11574] as the combination product Zepatier have been shown to achieve a SVR between 94% and 97% for genotype 1 and 97% and 100% for genotype 4 after 12 weeks of treatment. It can be used in patients with compensated cirrhosis, human immunodeficiency virus co-infection, or severe kidney disease. Grazoprevir anhydrous is a Hepatitis C Virus NS3/4A Protease Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of grazoprevir anhydrous is as a HCV NS3/4A Protease Inhibitor, and Breast Cancer Resistance Protein Inhibitor, and Cytochrome P450 3A Inhibitor. Drug Indication Grazoprevir is indicated in combination with [DB11574] (as the fixed dose combination product Zepatier) with or without [DB00811] for treatment of chronic HCV genotypes 1a, 1b, or 4 infection in adults. FDA Label Treatment of chronic hepatitis C Mechanism of Action Grazoprevir is a second generation NS3/4a protease inhibitor used to inhibit viral HCV replication. NS3/4a protease is an integral part of viral replication and mediates the cleavage the virally encoded polyprotein to mature proteins (NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5A and NS5B). Grazoprevir inhibits the NS3/4protease enzymes of HCV genotype 1a, 1B, and 4 with IC50 values of 7pM, 4pM, and 62pM, respectively. HCV NS3/4a protease inhibitors are proven therapeutic agents against chronic hepatitis C virus infection, with boceprevir and telaprevir having recently received regulatory approval as add-on therapy to pegylated interferon/ribavirin for patients harboring genotype 1 infections. Overcoming antiviral resistance, broad genotype coverage, and a convenient dosing regimen are important attributes for future agents to be used in combinations without interferon. In this communication, we report the preclinical profile of Grazoprevir/MK-5172, a novel P2-P4 quinoxaline macrocyclic NS3/4a protease inhibitor currently in clinical development. The compound demonstrates subnanomolar activity against a broad enzyme panel encompassing major hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotypes as well as variants resistant to earlier protease inhibitors. In replicon selections, MK-5172 exerted high selective pressure, which yielded few resistant colonies. In both rat and dog, MK-5172 demonstrates good plasma and liver exposures, with 24-h liver levels suggestive of once-daily dosing. When administered to HCV-infected chimpanzees harboring chronic gt1a or gt1b infections, MK-5172 suppressed viral load between 4 to 5 logs at a dose of 1 mg/kg of body weight twice daily (b.i.d.) for 7 days. Based on its preclinical profile, MK-5172 is anticipated to be broadly active against multiple HCV genotypes and clinically important resistance variants and highly suited for incorporation into newer all-oral regimens. [1] Phenotypic assays showed that Grazoprevir/MK-5172 maintained potency across a genetically diverse panel of genotype 1a and 1b sequences derived from plasma of HCV-infected patients. In preclinical animal species, MK-5172 demonstrated a favorable pharmacokinetic profile with good plasma concentrations while maintaining the high liver concentrations as previously described with vaniprevir. Importantly, moderate oral doses achieved 24-h liver concentrations in preclinical species that were well above the in vitro EC50s. Resistance selections demonstrated that MK-5172 elicited few colonies even at low concentrations of the inhibitor. MK-5172 proved highly efficacious in vivo at moderate doses against chronic-HCV-infected chimpanzees, including greater viral load suppression than vaniprevir when dosed alternatively to the same animal at an otherwise identical dose and frequency. Collectively, these properties identified MK-5172 as an inhibitor of greater potency than current developmental HCV protease inhibitors with the potential to improve HCV treatment options. Indeed, early phase I studies in both healthy volunteers and HCV-infected patients showed that MK-5172 has a favorable preclinical profile that translates into a clinically efficacious drug, is broadly active across multiple HCV genotypes, and possesses favorable pharmacokinetics suggestive of once-daily (QD) dosing [1] A new class of HCV NS3/4a protease inhibitors containing a P2 to P4 macrocyclic constraint was designed using a molecular modeling-derived strategy. Building on the profile of previous clinical compounds and exploring the P2 and linker regions of the series allowed for optimization of broad genotype and mutant enzyme potency, cellular activity, and rat liver exposure following oral dosing. These studies led to the identification of clinical candidate 15 (Grazoprevir), which is active against genotype 1-3 NS3/4a and clinically relevant mutant enzymes and has good plasma exposure and excellent liver exposure in multiple species.[2] In summary, initial screening for gt 3a activity along with molecular modeling has led to the discovery of a series of P2 quinoline macrocycles with excellent broad activity vs NS3/4a genoytpes and clinically observed gt 1b mutant enzymes. This series was optimized for enzyme activity and liver exposure in preclinical species. Compound 15 emerged from this series via the introduction of a mildly basic quinoxaline P2 heterocycle to deal with disproportionation issues with the more basic quinoline P2 heterocycle. We believe the combination of good PK, and broad enzyme potency gives compound 15 the potential to be an important second generation NS3/4a protease inhibitor that could be a cornerstone of an all-oral treatment for hepatitis C. Further studies of 15 (Grazoprevir), including clinical investigations of the pharmacokinetic and efficacy profile, are ongoing.[2] |
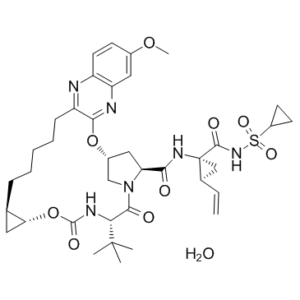
| 分子式 |
C38H52N6O10S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
784.93
|
| 精确质量 |
784.347
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 58.15; H, 6.68; N, 10.71; O, 20.38; S, 4.08
|
| CAS号 |
1350462-55-3
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Grazoprevir;1350514-68-9;Grazoprevir potassium salt;1206524-86-8;Grazoprevir sodium salt;1425038-27-2
|
| PubChem CID |
71576667
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder.
|
| LogP |
5.576
|
| tPSA |
223.3
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
12
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
| 重原子数目 |
55
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1580
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
7
|
| SMILES |
S(C1([H])C([H])([H])C1([H])[H])(N([H])C([C@]1(C([H])([H])[C@@]1([H])C([H])=C([H])[H])N([H])C([C@]1([H])C([H])([H])[C@]2([H])C([H])([H])N1C([C@]([H])(C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])N([H])C(=O)O[C@]1([H])C([H])([H])[C@@]1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C1C(=NC3C([H])=C(C([H])=C([H])C=3N=1)OC([H])([H])[H])O2)=O)=O)=O)(=O)=O.O([H])[H]
|
| InChi Key |
RXSARIJMSJWJLZ-CIAYNJNFSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C38H50N6O9S.H2O/c1-6-22-19-38(22,35(47)43-54(49,50)25-13-14-25)42-32(45)29-18-24-20-44(29)34(46)31(37(2,3)4)41-36(48)53-30-16-21(30)10-8-7-9-11-27-33(52-24)40-28-17-23(51-5)12-15-26(28)39-27;/h6,12,15,17,21-22,24-25,29-31H,1,7-11,13-14,16,18-20H2,2-5H3,(H,41,48)(H,42,45)(H,43,47);1H2/t21-,22-,24-,29+,30-,31-,38-;/m1./s1
|
| 化学名 |
(33R,35S,91R,92R,5S)-5-(tert-butyl)-N-((1R,2S)-1-((cyclopropylsulfonyl)carbamoyl)-2-vinylcyclopropyl)-17-methoxy-4,7-dioxo-2,8-dioxa-6-aza-1(2,3)-quinoxalina-3(3,1)-pyrrolidina-9(1,2)-cyclopropanacyclotetradecaphane-35-carboxamide hydrate
|
| 别名 |
MK5172 hydrate; MK 5172; MK-5172 hydrate; 1350462-55-3; MK-5172 (hydrate); MK-5172 hydrate; Grazoprevir [USAN]; Grazoprevir monohydrate; 4O2AB118LA; Grazoprevir (USAN); Trade name: Zepatier.
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~50 mg/mL (~63.70 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.19 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.19 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.19 mM) 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.2740 mL | 6.3700 mL | 12.7400 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2548 mL | 1.2740 mL | 2.5480 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1274 mL | 0.6370 mL | 1.2740 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Two-weekin vitropotency of MK-5172 against gt1b replicon cells.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2012 Aug;56(8):4161-7. |
|---|
MK-5172 demonstrates efficacyin vivoagainst chronic-HCV-infected chimpanzees.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2012 Aug;56(8):4161-7. |
Compounds3(A),4(B), and5(C) docked in the gt 1b NS3/4a active site. Cyan = areas of diversity between the gt 1b and gt 3a enzymes. White = conserved areas.ACS Med Chem Lett.2012 Mar 2;3(4):332-6. |
Comparison of the energy-minimized conformations of compounds12(magenta) and14(green) docked in the gt 1b NS3/4a active site.ACS Med Chem Lett.2012 Mar 2;3(4):332-6. |
|---|
Synthesis of Compound15(MK-5172).ACS Med Chem Lett.2012 Mar 2;3(4):332-6. |