| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| 25g |
|
||
| 50g |
|
||
| 100g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Diuretic; calcium-activated potassium (KCA) channel
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
一种噻嗪类利尿剂是氢氯噻嗪。它作用于肾脏,减少远端肾小管对钠 (Na) 的重吸收,从而降低血容量。通过争夺电中性的 Na+-Cl 协同转运蛋白上的氯离子位点,肾单位中的主要作用位点发生。氢氯噻嗪可通过阻碍远曲小管中钠离子的转运来诱导尿钠排泄并伴有失水。此时,噻嗪类药物可改善钙的重吸收,而不影响钠的转运。氢氯噻嗪还有望通过其他方法降低外周血管阻力[1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在成年雄性 Sprague Dawley 小鼠中,氢氯噻嗪(HCTZ;口服;12.5 mg/kg/d;8 周)可降低心脏组织中 AT1、TGF-β 和 Smad2 的表达,改善心脏功能,并减少心脏间质纤维化和胶原蛋白体积分数。氢氯噻嗪还可以降低血浆中醛固酮和血管紧张素 II 的水平。此外,在新生大鼠心室成纤维细胞中,氢氯噻嗪可以阻止血管紧张素 II 刺激的 TGF-β1 和 Smad2 蛋白的产生 [2]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
噻嗪和类噻嗪利尿剂是最常用的抗高血压药物之一,已有50多年的历史。然而,人们对这些药物长期降低血压的机制知之甚少。可能的机制包括直接内皮或血管平滑肌介导的血管舒张和对心输出量急性下降的间接补偿。此外,噻嗪类药物与不良代谢影响有关,尤其是高血糖,而这些影响的机制基础也鲜为人知。噻嗪诱导的低钾血症,以及解释这些代谢紊乱的其他理论,包括内脏脂肪增加、高尿酸血症、葡萄糖代谢降低和胰腺β细胞超极化,可能起到一定作用。了解对噻嗪类药物有不同反应的基因变体,可以为未来的研究揭示新的机制候选者,从而更全面地了解血压和对噻嗪利尿剂的代谢反应。[1]
|
| 动物实验 |
Aims: Our previous study indicates that hydrochlorothiazide inhibits transforming growth factor (TGF)-β/Smad signaling pathway, improves cardiac function and reduces fibrosis. We determined whether these effects were common among the diuretics and whether angiotensin II receptor type 1 (AT1) signaling pathway played a role in these effects.[2]
Methods: Heart failure was produced by ligating the left anterior descending coronary artery in adult male Sprague Dawley rats. Two weeks after the ligation, 70 rats were randomly divided into five groups: sham-operated group, control group, valsartan group (80 mg/kg/d), hydrochlorothiazide group (12.5 mg/kg/d) and furosemide group (20 mg/kg/d). In addition, neonatal rat ventricular fibroblasts were treated with angiotensin II.[2] Results: After eight-week drug treatment, hydrochlorothiazide group and valsartan group but not furosemide group had improved cardiac function (ejection fraction was 49.4±2.1%, 49.5±1.8% and 39.9±1.9%, respectively, compared with 40.1±2.2% in control group), reduced cardiac interstitial fibrosis and collagen volume fraction (9.7±1.2%, 10.0±1.3% and 14.1±0.8%, respectively, compared with 15.9±1.1% in control group), and decreased expression of AT1, TGF-β and Smad2 in the cardiac tissues. In addition, hydrochlorothiazide reduced plasma angiotensin II and aldosterone levels. Furthermore, hydrochlorothiazide inhibited angiotensin II-induced TGF-β1 and Smad2 protein expression in the neonatal rat ventricular fibroblasts.[2] Conclusions: Our study indicates that the cardiac function and remodeling improvement after ischemic heart failure may not be common among the diuretics. Hydrochlorothiazide may reduce the left ventricular wall stress and angiotensin II signaling pathway to provide these beneficial effects.[2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
An oral dose of hydrochlorothiazide is 65-75% bioavailable, with a Tmax of 1-5 hours, and a Cmax of 70-490ng/mL following doses of 12.5-100mg. When taken with a meal, bioavailability is 10% lower, Cmax is 20% lower, and Tmax increases from 1.6 to 2.9 hours. Hydrochlorothiazide is eliminated in the urine as unchanged hydrochlorothiazide. The volume of distribution varies widely from one study to another with values of 0.83-4.19L/kg. The renal clearance of hydrochlorothiazide in patients with normal renal function is 285mL/min. Patients with a creatinine clearance of 31-80mL/min have an average hydroxychlorothiazide renal clearance of 75mL/min, and patients with a creatinine clearance of ≤30mL/min have an average hydroxychlorothiazide renal clearance of 17mL/min. Hydrochlorothiazide is well absorbed from the GI tract, with an oral bioavailability of approximately 65-75%. Although the rate and extent of absorption have been reported to vary depending on the formulation administered, no studies have been performed to determine the clinical importance (if any) of variations in absorption in patients receiving chronic hydrochlorothiazide therapy. Following oral administration of hydrochlorothiazide at doses of 12.5-100 mg, peak plasma concentrations of 70-490 ng/mL are observed within 1-5 hours of dosing. Food decreases the rate and extent of absorption of hydrochlorothiazide capsules (Microzide). Bioavailability and peak plasma concentrations of the drug were decreased by about 10 and 20%, respectively, when hydrochlorothiazide capsules (Microzide) were administered with food. Times to peak plasma concentration for such capsules were delayed by 1.3 hours (from 1.6 to 2.9 hours). Absorption of hydrochlorothiazide is reduced in patients with heart failure. Approximately 40-68% of the drug is bound to plasma proteins. Hydrochlorothiazide exhibits linear pharmacokinetics. Based on determination of plasma drug concentrations over a period of at least 24 hours, the plasma half-life of hydrochlorothiazide reportedly ranges from 5.6-15 hours. Hydrochlorothiazide apparently is not metabolized and is excreted unchanged in urine. At least 61% of the drug is reportedly eliminated from the body within 24 hours. Increased hydrochlorothiazide plasma concentrations and a prolonged elimination half-life have been reported in patients with renal impairment. The effect of hemodialysis on the elimination of the drug has not been determined. Thiazides cross the placental barrier and appear in cord blood. /Thiazides/ /MILK/ Thiazides are excreted in breast milk. /Thiazides/ (14)C-hydrochlorothiazide (hct) was administered orally (n=4) and iv (n=2) to healthy subjects. The gastrointestinal absorption ranged between 60% and 80%, most of it took place in the duodenum and the upper jejunum. The radioactivity was eliminated mainly in the urine, while no sigificant biliary excretion was observed. Chromatographic analysis of the urinary radioactivity demonstrated that greater than 95% of the absorbed or injected (14)C-hct was excreted unchanged. The radioactivity in plasma during the first 10 hr after oral administration declined with a fast phase but the levels of label thereafter suggested a slow phase. The existence of such a phase was verified in 1 subject given 75 mg hct orally. His plasma levels of hct (determined with gas-liquid chromatography) declined according to a 2-compartment model, the half-lives of the alpha-and beta-phases being 1.7 and 13.1 hr, respectively. Hct accumulated in the blood cells and the ratio between the radioactivity in cells and that in plasma averaged 3.5. The fate of a single dose of (14)C-hct in 2 hypertensive patients treated with the drug chronically was similar to that in the healthy subjects. A third patient, who had slightly elevated serum creatinine, eliminated hct more slowly than the others. Like the healthy subjects, the patients eliminated hct to greater than 95% in unchanged form. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Hydrochlorothiazide (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Hydrochlorothiazide is not metabolized. Hydrochlorothiazide is not metabolized. Route of Elimination: Hydrochlorothiazide is not metabolized but is eliminated rapidly by the kidney. Hydrochlorothiazide crosses the placental but not the blood-brain barrier and is excreted in breast milk. Half Life: 5.6 and 14.8 hours Biological Half-Life The plasma half life of hydrochlorothiazide is 5.6-14.8h. Based on determination of plasma drug concentrations over a period of at least 24 hours, the plasma half-life of hydrochlorothiazide reportedly ranges from 5.6-15 hours. The bioavailability of hydrochlorothiazide from 50-mg oral tablet doses was examined in healthy male volunteers under fasting and nonfasting conditions. ... The pharmacokinetics of hydrochlorothiazide in plasma could be described in terms of a triexponential function, and the mean half-life determined from the 3 exponents were 1.0, 2.2, and 9.0 hr. The radioactivity in /human/ plasma during the first 10 hr after oral administration /of hydrochlorothiazide (hct)/ declined with a fast phase but the levels of label thereafter suggested a slow phase. The existence of such a phase was verified in 1 subject given 75 mg hct orally. His plasma levels of hct (determined with gas-liquid chromatography) declined according to a 2-compartment model, the half-lives of the alpha-and beta-phases being 1.7 and 13.1 hr, respectively. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Hydrochlorothiazide is a white or almost white crystalline odorless powder. Hydrochlorothiazide tablets are indicated as adjunctive therapy in edema associated with congestive heart failure, hepatic cirrhosis, and corticosteroid and estrogen therapy, as well as in the management of hypertension either as the sole therapeutic agent or to enhance the effectiveness of other antihypertensive drugs in the more severe forms of hypertension. They have also been found useful in edema due to various forms of renal dysfunction such as nephrotic syndrome, acute glomerulonephritis, and chronic renal failure. HUMAN STUDIES: Clinical toxicity is relatively infrequent and may result from overdosage, adverse reactions or unexpected hypersensitivity. It may cause electrolytes imbalances that may lead to cardiac arrhythmias and orthostatic hypotension, and metabolic disturbances, such as hyperglycemia and hyperuricemia. In addition it may cause aggravation of hepatic and/or renal insufficiency, hypersensitivity reactions, blood dyscrasias, acute noncardiogenic pulmonary edema, as well as gastrointestinal irritability and CNS manifestations. In general the exposure to diuretics was not associated with teratogenicity. A slight association with respiratory malformation was suggested. Other risks include fetal or neonatal jaundice, and thrombocytopenia. After two weeks of abrupt suspension of hydrochlorothiazide, 8 patients developed an intense edema. In patients, positive associations were observed for squamous cell carcinoma of the skin and lip. ANIMAL STUDIES: Available animal toxicity information comes from National Toxicology Program studies. In rats, no teratogenic, embryotoxic or fetotoxic effect was observed. Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies were conducted by feeding diets containing hydrochlorothiazide to rats and mice of each sex. The incidence of hepatocellular neoplasms was increased in high dose male mice. Changes associated with or secondary to renal injury were increased in dosed rats. These lesions included parathyroid hyperplasia, fibrous osteodystrophy of bone, and mineralization of multiple organs. Hydrochlorothiazide induced gene mutations in mouse lymphoma cells and sister chromatid exchange in Chinese hamster cells. It did not induce chromosomal aberrations in Chinese hamster cells in vitro or sex-linked recessive lethal mutations in Drosophila. Hydrochlorothiazide induced mitotic recombination and non-disjunction in Aspergillus. It was not mutagenic to Salmonella typhimurium or Escherichia coli. Hydrochlorothiazide, a thiazide diuretic, inhibits water reabsorption in the nephron by inhibiting the sodium-chloride symporter (SLC12A3) in the distal convoluted tubule, which is responsible for 5% of total sodium reabsorption. Normally, the sodium-chloride symporter transports sodium and chloride from the lumen into the epithelial cell lining the distal convoluted tubule. The energy for this is provided by a sodium gradient established by sodium-potassium ATPases on the basolateral membrane. Once sodium has entered the cell, it is transported out into the basolateral interstitium via the sodium-potassium ATPase, causing an increase in the osmolarity of the interstitium, thereby establishing an osmotic gradient for water reabsorption. By blocking the sodium-chloride symporter, hydrochlorothiazide effectively reduces the osmotic gradient and water reabsorption throughout the nephron. Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Hydrochlorothiazide doses of 50 mg daily or less are acceptable during lactation. Intense diuresis with large doses may decrease breastmilk production. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants No electrolyte abnormalities were noted in one 28-day-old infant who was breastfed since birth while his mother was taking oral hydrochlorothiazide 50 mg daily. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Hydrochlorothiazide in dosages of 100 mg daily in the morning and 50 mg in the afternoon or 50 mg twice daily have been used to successfully to suppress lactation at various times postpartum. Intense diuresis with thiazides and thiazide-like diuretics, fluid restriction and breast binding have been used to suppress postpartum lactation. The added contribution of the diuretic to these measures, which are effective in suppressing lactation, has not been studied. There are no data on the effects of diuretics on established, ongoing lactation. Protein Binding Hydrochlorothiazide is 40-68% protein bound in plasma. Hydrochlorothiazide has been shown to bind to human serum albumin. Toxicity Data The oral LD50 of hydrochlorothiazide is greater than 10 g/kg in the mouse and rat. Interactions Table: Potential Drug Interactions with Hydrochlorothiazide Tablet [Table#4429] Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Rabbit iv 461 mg/kg LD50 Dog iv 250 mg/kg LD50 Mouse sc 1470 mg/kg LD50 Mouse ip 578 mg/kg For more Non-Human Toxicity Values (Complete) data for Hydrochlorothiazide (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Crystals or white powder. (NTP, 1992)
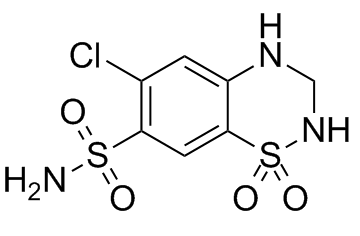
Hydrochlorothiazide is a benzothiadiazine that is 3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide substituted by a chloro group at position 6 and a sulfonamide at 7. It is diuretic used for the treatment of hypertension and congestive heart failure. It has a role as a xenobiotic, an environmental contaminant, a diuretic and an antihypertensive agent. It is a benzothiadiazine, a sulfonamide and an organochlorine compound. Hydrochlorothiazide is the most commonly prescribed thiazide diuretic. It is indicated to treat edema and hypertension. Hydrochlorothiazide use is common but declining in favour of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. Many combination products are available containing hydrochlorothiazide and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers. Hydrochlorothiazide was granted FDA approval on 12 February 1959. Hydrochlorothiazide is a Thiazide Diuretic. The physiologic effect of hydrochlorothiazide is by means of Increased Diuresis. Hydrochlorothiazide is a short acting thiazide diuretic. Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) is widely used to treat hypertension and edema. This agent's metabolite appears to preferentially bind to and accumulate in red blood cells. This agent is primarily excreted by the kidneys. A thiazide diuretic often considered the prototypical member of this class. It reduces the reabsorption of electrolytes from the renal tubules. This results in increased excretion of water and electrolytes, including sodium, potassium, chloride, and magnesium. It has been used in the treatment of several disorders including edema, hypertension, diabetes insipidus, and hypoparathyroidism. A thiazide diuretic often considered the prototypical member of this class. It reduces the reabsorption of electrolytes from the renal tubules. This results in increased excretion of water and electrolytes, including sodium, potassium, chloride, and magnesium. It is used in the treatment of several disorders including edema, hypertension, diabetes insipidus, and hypoparathyroidism. See also: Hydrochlorothiazide; Triamterene (component of); Hydralazine hydrochloride; hydrochlorothiazide (component of); Hydrochlorothiazide; methyldopa (component of) ... View More ... Drug Indication Hydrochlorothiazide is indicated alone or in combination for the management of edema associated with congestive heart failure, hepatic cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome, acute glomerulonephritis, chronic renal failure, and corticosteroid and estrogen therapy. Hydrochlorothiazide is also indicated alone or in combination for the management of hypertension. Mechanism of Action Hydrochlorothiazide is transported from the circulation into epithelial cells of the distal convoluted tubule by the organic anion transporters OAT1, OAT3, and OAT4. From these cells, hydrochlorothiazide is transported to the lumen of the tubule by multidrug resistance associated protein 4 (MRP4). Normally, sodium is reabsorbed into epithelial cells of the distal convoluted tubule and pumped into the basolateral interstitium by a sodium-potassium ATPase, creating a concentration gradient between the epithelial cell and the distal convoluted tubule that promotes the reabsorption of water. Hydrochlorothiazide acts on the proximal region of the distal convoluted tubule, inhibiting reabsorption by the sodium-chloride symporter, also known as Solute Carrier Family 12 Member 3 (SLC12A3). Inhibition of SLC12A3 reduces the magnitude of the concentration gradient between the epithelial cell and distal convoluted tubule, reducing the reabsorption of water. Therapeutic Uses Antihypertensive Agents; Diuretics; Sodium Chloride Symporter Inhibitors /CLINICAL TRIALS/ ClinicalTrials.gov is a registry and results database of publicly and privately supported clinical studies of human participants conducted around the world. The Web site is maintained by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Each ClinicalTrials.gov record presents summary information about a study protocol and includes the following: Disease or condition; Intervention (for example, the medical product, behavior, or procedure being studied); Title, description, and design of the study; Requirements for participation (eligibility criteria); Locations where the study is being conducted; Contact information for the study locations; and Links to relevant information on other health Web sites, such as NLM's MedlinePlus for patient health information and PubMed for citations and abstracts for scholarly articles in the field of medicine. Hydrochlorothiazide is included in the database. Hydrochlorothiazide tablets, USP are indicated as adjunctive therapy in edema associated with congestive heart failure, hepatic cirrhosis, and corticosteroid and estrogen therapy. /Included in US product label/ Hydrochlorothiazide tablets, USP have also been found useful in edema due to various forms of renal dysfunction such as nephrotic syndrome, acute glomerulonephritis, and chronic renal failure. /Included in US product label/ For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Hydrochlorothiazide (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings Hydrochlorothiazide shares the pharmacologic actions, uses, and toxic potentials of the thiazides, and the usual precautions of thiazide administration should be observed. Some commercially available formulations of hydrochlorothiazide contain sulfites that may cause allergic-type reactions, including anaphylaxis and life-threatening or less severe asthmatic episodes, in certain susceptible individuals. The overall prevalence of sulfite sensitivity in the general population is unknown but probably low; such sensitivity appears to occur more frequently in asthmatic than in nonasthmatic individuals. The following adverse reactions have been reported and, within each category, are listed in the order of decreasing severity. ... Whenever adverse reactions are moderate or severe, thiazide dosage should be reduced or therapy withdrawn. Table: Adverse Effects with Hydrochlorothiazide Tablet [Table#4432] Pharmacodynamics Hydrochlorothiazide prevents the reabsorption of sodium and water from the distal convoluted tubule, allowing for the increased elimination of water in the urine. Hydrochlorothiazide has a wide therapeutic window as dosing is individualized and can range from 25-100mg. Hydrochlorothiazide should be used with caution in patients with reduced kidney or liver function. |
| 分子式 |
C7H8CLN3O4S2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
297.7391
|
| 精确质量 |
296.964
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 28.24; H, 2.71; Cl, 11.91; N, 14.11; O, 21.49; S, 21.54
|
| CAS号 |
58-93-5
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Hydrochlorothiazid-d2;1219798-89-6;Hydrochlorothiazid-13C,d2;1190006-03-1;Hydrochlorothiazide-13C6;1261396-79-5; 58-93-5; 58-94-5
|
| PubChem CID |
3639
|
| 外观&性状 |
White, or practically white crystalline powder
White to off-white crystalline powder |
| 密度 |
1.7±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
577.0±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
273 °C
|
| 闪点 |
302.7±32.9 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.632
|
| LogP |
-0.07
|
| tPSA |
135.12
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
1
|
| 重原子数目 |
17
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
494
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
ClC1C([H])=C2C(=C([H])C=1S(N([H])[H])(=O)=O)S(N([H])C([H])([H])N2[H])(=O)=O
|
| InChi Key |
JZUFKLXOESDKRF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C7H8ClN3O4S2/c8-4-1-5-7(2-6(4)16(9,12)13)17(14,15)11-3-10-5/h1-2,10-11H,3H2,(H2,9,12,13)
|
| 化学名 |
6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-1lambda6,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 该产品在溶液状态不稳定,请现配现用。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~50 mg/mL (~167.93 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.40 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.40 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.40 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3586 mL | 16.7932 mL | 33.5864 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6717 mL | 3.3586 mL | 6.7173 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3359 mL | 1.6793 mL | 3.3586 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
ACES - ACE Inhibitors Combined With Exercise for Seniors With Hypertension
CTID: NCT03295734
Phase: Phase 2 Status: Completed
Date: 2024-09-24