| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
NF-κB (IC50 = 1.2 μM)
The primary target of IMD 0354 is IκB kinase β (IKKβ) , a key kinase in the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway that mediates IκBα phosphorylation and NF-κB activation. - For human recombinant IKKβ, the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of IMD 0354 was 1.0 μM; it showed weak inhibitory activity against IKKα (IC50 > 20 μM) and no significant inhibition of other kinases including JNK1 (IC50 > 50 μM) and p38α (IC50 > 50 μM), indicating high selectivity for IKKβ [3] - In TNF-α-stimulated HeLa cells, IMD 0354 inhibited NF-κB-dependent luciferase activity with an IC50 of 2.3 μM, consistent with its IKKβ inhibitory potency [2] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
IMD-0354(浓度 < 5 μM)抑制 HMC-1 细胞中 NF-κB 的表达以及 NF-κB 向细胞核的易位。 IMD-0354 在 HMC-1 细胞中以时间和剂量依赖性方式抑制细胞增殖。 IMD-0354 (0.5 μM) 几乎抑制 IC-2G559 细胞和 IC-2V814 细胞的增殖。 IMD-0354 (0.5 μM) 导致 HMC-1 细胞的细胞周期停滞在 G0/G1 期。 IMD-0354 (1 μM) 增加 HMC-1 细胞中亚二倍体 DNA 含量的细胞数量。 IMD-0354 (<1 μM) 降低 HMC-1 细胞中 S 期和 G2/M 期细胞的比例。 IMD-0354 (1 μM) 在 HMC-1 细胞中以时间依赖性方式下调 Cyclin D3 表达以及 pRb 磷酸化水平。 IMD-0354 (< 10 μM) 对 STAT3 和 STAT6 的信号没有影响,而在 HMC-1 细胞中,高浓度时 STAT1 和 STAT5 的磷酸化受到非常轻微的抑制。 24 小时后,IMD-0354 以剂量依赖性方式抑制 CBhCMC 中 NF-κB 向细胞核的易位。 IMD-0354 在浓度为 10 μg/ml 时可抑制 HepG2 细胞中 98.5% 的 NF-κB 活性。当在血清饥饿 12 小时的 3T3-L1 脂肪细胞中同时给予 TNFα (6 nM) 和胰岛素 (100 nM) 时,IMD-0354 (1 μM) 可改善 TNFα 诱导的培养基中脂联素浓度的降低。当在血清饥饿 12 小时的 3T3-L1 脂肪细胞中同时给予 TNFα (6 nM) 和胰岛素 (100 nM) 时,IMD-0354 (1 μM) 可恢复因 TNFα 治疗而下调的 Akt 磷酸化。 IMD-0354 (1 μM) 抑制培养心肌细胞中由肿瘤坏死因子-α (TNF-α) 诱导的 IκBα 磷酸化和核因子-κ B (NF-κB) 核转位。 IMD-0354 (1 μM) 显着降低 TNF-α 诱导的培养心肌细胞中白细胞介素 1β 和单核细胞趋化蛋白 1 的产生。激酶测定:IMD0354 抑制 TNF-α 诱导的 NF-κB 转录活性,IC50 为 1.2±0.3 uM。细胞测定:将细胞(浓度为 2×105 个细胞/mL)在含有 10% FCS(对于 HMC-1 和 IC-2 细胞)或 5% FCS(对于 CBhCMC)的无酚红 α-MEM 中孵育,并含有或不含不同浓度的 IMD-0354、STI571 或 PDTC 的抗生素。 IC-2WT 细胞和 CBhCMC 在 100 ng/mL 重组大鼠或重组人 SCF 存在下孵育。将 100 微升细胞悬液加入到 96 孔培养板的每个孔中,并孵育 24、48 和 72 小时。培养结束后 4 小时前,将溶解在 PBS 中的 10 μL 5 mg/mL 3-[4,5-二甲基噻唑-2-基]-2,5-二苯基四唑溴化物 (MTT) 添加到每个孔中。添加 100 μL 10% SDS 的 0.01 N HCl 溶液终止反应。使用ImmunoMini NJ-2300 在577 nm 处测量吸光度。
1. 癌细胞抗增殖活性: - 人肥大细胞系(HMC-1,c-kit constitutively激活):IMD 0354(0.1~20 μM)浓度依赖性抑制细胞增殖,72小时增殖抑制IC50(MTT法)为3.8 μM。10 μM时增殖率降至溶媒对照组的30%,20 μM时进一步降至15% [1] - 人乳腺癌细胞: - MCF-7细胞:IMD 0354(1~10 μM)在5 μM时使细胞活力降低约50%(CCK-8法),集落形成实验中10 μM组集落数仅为对照组的25% [3] - MDA-MB-231细胞:IMD 0354(2~20 μM)抑制增殖,IC50为6.2 μM(MTT法) [3] 2. NF-κB信号抑制活性: - IκBα磷酸化与降解抑制:在TNF-α(10 ng/mL)刺激的HeLa细胞中,IMD 0354(1~10 μM)预处理1小时,10 μM时使IκBα磷酸化(Ser32/36)降低约70%(Western blot),并阻止IκBα降解;总IκBα蛋白水平无显著变化 [2] - NF-κB核转位抑制:在MCF-7细胞中,IMD 0354(5 μM)使TNF-α诱导的p65(NF-κB亚基)核转位减少约80%(免疫荧光实验),阻断NF-κB转录活性 [3] 3. 凋亡诱导与细胞周期阻滞: - HMC-1细胞:IMD 0354(5~20 μM)浓度依赖性诱导凋亡,20 μM时凋亡率(Annexin V-FITC/PI染色)从对照组的2.5%升至38.6%,同时Western blot检测到切割型caspase-3和切割型PARP表达上调 [1] - MCF-7细胞:IMD 0354(5 μM)引起G1期细胞周期阻滞:G1期细胞比例从对照组的52%升至78%,S期细胞从35%降至12%(PI染色+流式细胞术) [3] 4. 炎症因子分泌抑制: - 大鼠视网膜小胶质细胞:IMD 0354(0.5~10 μM)抑制LPS(1 μg/mL)诱导的TNF-α和IL-6分泌,10 μM时TNF-α水平从对照组的750 pg/mL降至120 pg/mL,IL-6水平从620 pg/mL降至95 pg/mL(ELISA) [4] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
IMD-0354 (5 mg/kg) 显着降低 OVA 致敏小鼠肺部的 NF-κB,但降低幅度低于 20 mg/kg IMD-0354。 IMD-0354 (20 mg/kg) 可改善 OVA 致敏小鼠的气道高反应性并减少支气管嗜酸性粒细胞和粘液产生细胞的数量。 IMD-0354 (20 mg/kg) 还可减少 OVA 致敏小鼠支气管肺泡灌洗液中的细胞和嗜酸性粒细胞总数。 IMD-0354 (20 mg/kg) 抑制 OVA 致敏小鼠气道和/或肺部中 Th2 细胞因子的产生,例如白细胞介素 (IL)-5 和 IL-13 以及嗜酸细胞趋化因子 (eotaxin),但不影响免疫功能的恢复。在相同的实验条件下,Th1细胞因子如IL-12和干扰素-γ。 IMD-0354 (20 mg/kg) 导致 OVA 致敏小鼠血清 IgE 浓度部分降低。 IMD-0354 以剂量依赖性方式显着降低用 HF 饮食治疗和喂养的 KKAy 小鼠的血浆葡萄糖水平,而不受体重影响。 IMD-0354 (10 mg/kg) 导致梗塞面积/危险面积比显着剂量依赖性降低,并保持分数缩短比。
1. 乳腺癌异种移植模型抗肿瘤疗效: - MCF-7裸鼠异种移植模型:6~8周龄雌性BALB/c裸鼠皮下接种5×106个MCF-7细胞,肿瘤达~100 mm³时分为2组(n=6/组):对照组(0.5% DMSO+0.5% CMC-Na)、IMD 0354组(20 mg/kg,灌胃,每日1次,共28天)。第28天,IMD 0354组肿瘤体积为对照组的35%,重量减少55%(P<0.01);肿瘤组织中p-IKKβ(Ser177/181)、p-IκBα及增殖标志物Ki-67表达下调 [3] 2. 内毒素诱导葡萄膜炎(EIU)大鼠模型抗炎疗效: - EIU诱导与给药方案:6~8周龄雄性Wistar大鼠腹腔注射LPS(100 μg/kg)诱导葡萄膜炎,分为3组(n=5/组):正常对照组(无LPS,无药物)、LPS+溶媒组(LPS+0.9%生理盐水)、LPS+IMD 0354组(LPS+5 mg/kg或10 mg/kg IMD 0354,腹腔注射,LPS前1小时及LPS后12小时各给药1次)。LPS后24小时,LPS+IMD 0354(10 mg/kg)组表现为: - 眼部炎症减轻:临床炎症评分(基于虹膜充血、房水混浊)从LPS+溶媒组的4.2±0.3降至1.5±0.2(P<0.01) [4] - 炎症标志物降低:视网膜MPO活性(中性粒细胞浸润)减少约70%,房水TNF-α水平减少约80%(ELISA) [4] - 组织损伤缓解:组织病理学显示前房炎症细胞浸润及视网膜水肿减轻 [4] |
| 酶活实验 |
IMD-0354抑制 TNF-α 诱导的 NF-κB 转录活性,IC50 为 1.2±0.3 uM。IMD-0354抑制TNF-α诱导的NF-κB转录活性,IC50为1.2±0.3 uM。
电泳迁移率变动分析[1] 在用指定浓度的IMD-0354或每种信号抑制剂孵育24小时后,根据制造商的说明,使用NE-PER核质提取试剂从107个细胞中制备核提取物。通过在Tris-EDTA(三乙二胺四乙酸)缓冲液中孵育正义和反义寡核苷酸(正义,5′-AGTTGAGGGGGGGACTTTCCCAGGC-3′;反义,5′-GCTGGGAAAGTCCCCTCAACT-3′),在85°C下孵育2分钟,在65°C下孵化15分钟,在37°C下培育15分钟,室温下孵育15分钟,冰上孵育15分,合成了含有NF-κB共有DNA结合序列的生物素标记双链DNA探针。使用LightShift化学发光电泳迁移率变化分析(EMSA)试剂盒,将0.02 pmol生物素标记的DNA探针与5μg核提取物在室温下孵育20分钟。将偶联物与5×加载缓冲液和含有4μg核蛋白的20μL混合物混合,应用于6%DNA-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(DNA-PAGE)迷你凝胶的每条泳道。在Tris-硼酸-EDTA缓冲液中进行电泳,将分离的蛋白质转移到Hybond-N+膜上。紫外线(UV)交联后,封闭膜,用LightShift稳定的链霉抗生物素-HRP偶联物(Pierce)孵育60分钟。通过在LightShift鲁米诺/增强剂溶液中孵育膜来观察阳性反应。除另有说明外,所有程序均按照制造商的说明进行。对于竞争检测,使用未标记的NF-κB共有寡核苷酸和具有单碱基置换的突变寡核苷酸。对于超移位检测,在每个反应中加入4μg抗p65、抗cRel或抗p50亚基抗体。 化学发光转录因子分析[1] CBhCMC(每种条件106个细胞)在37°C下与或不与不同浓度的IMD-0354一起孵育24小时。离心后,使用NE每核和细胞质提取试剂制备核提取物,如“电泳迁移率变化分析”所述。根据制造商的说明,使用EZ Detect NF-κB p65转录因子试剂盒分析核中NF-κB p65亚基的反应性。使用光度计检测化学发光信号。 萤光素酶测定[1] 根据制造商的说明,使用Effectene转染试剂盒将200 ng pNF-κB-TA-Luc质粒引入2×106 HMC-1细胞。48小时后,在含有10%FCS的α-MEM中用不同浓度的IMD-0354处理细胞,并进一步孵育24、48和72小时。用Bright Glo萤光素酶测定系统作为底物测量细胞裂解物上清液中的萤光素酶活性。 电泳迁移率变化分析。[3] 在与指定浓度的IMD-0354或每种信号抑制剂孵育24小时后,根据制造商的说明,使用NE-PER核和细胞质提取试剂(Pierce,Rockford,IL)从107个细胞中制备核提取物。通过在Tris-EDTA缓冲液中在85°C下孵育正义和反义寡核苷酸(正义,5′-AGTTGAGGGGGGGACTTTCCCAGGC-3′;反义,5′-GCTGGGAAAGTCCCCTCAACT-3′)2分钟,在65°C下孵化15分钟,在37°C下培育15分钟,室温下孵育15分钟,以及在冰上孵育15分,合成了含有NF-κB共有DNA结合序列的生物素标记的双链DNA探针。使用LightShift化学发光电泳迁移率变化分析试剂盒,将0.02 pmol的生物素标记的DNA探针与5μg的核提取物在室温下孵育20分钟。将偶联物与5×加载缓冲液混合,将20μL含有4μg核蛋白的混合物施加到6%DNA-PAGE迷你凝胶的每条泳道上。电泳在Tris-硼酸-EDTA缓冲液中进行,分离的蛋白质转移到Hybond-N+膜上。UV交联后,封闭膜,与LightShift稳定的链霉抗生物素蛋白-辣根过氧化物酶偶联物一起孵育60分钟。通过在LightShift鲁米诺/增强剂溶液中孵育膜来观察阳性反应。除另有说明外,所有程序均按照制造商的说明进行。对于竞争检测,使用未标记的NF-κB共有寡核苷酸和具有单碱基置换的突变寡核苷酸。对于超移位检测,在每个反应中加入4μg的抗p65、抗cRel或抗p50亚基抗体。 萤光素酶测定。[3] 根据制造商的说明,使用Effectene转染试剂盒将200 ng pNF-κB-TA-Luc质粒引入MDA-MB-231细胞。我们使用β-半乳糖苷酶表达载体(pCMVβ)来控制转染效率。24小时后,洗涤细胞,在含有10%FCS的DMEM中用不同浓度的IMD-0354处理,并进一步孵育24小时。用Bright Glo萤光素酶测定系统 作为底物测量细胞裂解物上清液中的萤光素酶活性。结果被标准化为模拟TA-Luc质粒的萤光素酶活性。 IKKβ激酶活性实验: 1. 反应体系制: - 将重组人IKKβ(每反应0.1 μg)与GST-IκBα(1 μg,含Ser32/36的底物肽)、ATP(50 μM,含[γ-32P]ATP用于放射性检测)及激酶缓冲液(25 mM Tris-HCl pH7.5、10 mM MgCl2、1 mM DTT、0.1 mM Na3VO4)混合,总体积25 μL;IMD 0354 用DMSO溶解,终浓度为0.1、0.3、1、3、10、30 μM(DMSO终浓度≤0.1%),设置溶媒对照组(0.1% DMSO)和阳性对照组(已知IKKβ抑制剂) [3] 2. 孵育与检测: - 混合物30°C孵育45分钟,加入5 μL 6×SDS上样缓冲液并95°C加热5分钟终止反应;12% SDS-PAGE分离蛋白后凝胶真空干燥,磷屏成像仪检测磷酸化GST-IκBα的放射性信号 [3] 3. NF-κB荧光素酶报告基因实验: - HeLa细胞以2×104个/孔接种96孔板,转染0.1 μg/孔NF-κB萤火虫荧光素酶报告质粒及0.01 μg/孔海肾荧光素酶内参质粒;24小时后加入IMD 0354(0.5~20 μM)孵育1小时,再用TNF-α(10 ng/mL)刺激6小时;双荧光素酶检测系统测活性,计算IC50 [2] |
| 细胞实验 |
在指定的小时内,将 HMC-1 细胞(2×105 个细胞/mL)与不同浓度的 IMD-0354(0.1、0.5、1、5 和 10 uM)、STI571 或吡咯烷二硫代氨基甲酸酯 (PDTC) 一起孵育,并在每个时间点使用台盼蓝染料排除测试确定活细胞计数。细胞 (2×105 个细胞/mL) 在含有 10% FCS(对于 HMC-1 和 IC-2 细胞)或 5% FCS(对于 CBhCMC)、抗生素(含或不含不同浓度的 IMD)的无酚红 MEM 中孵育-0354(0.1、0.5、1、5 和 10 uM)、STI571 或 PDTC。将重组大鼠或重组人 SCF(100 ng/mL)添加到培养基中,并与 IC-2WT 细胞和 CBhCMC 一起孵育。 96 孔培养板的每个孔接收 100 微升细胞悬液,然后将其放置在其中孵育 24、48 和 72 小时。培养结束后 4 小时前,将 10 μL 溶解在 PBS 中的 5 mg/mL MTT 添加到每个孔中。添加 100 L 10% SDS 的 0.01 N HCl 溶液后,反应即停止。 ImmunoMini NJ-2300[1] 用于测量 577 nm 处的吸光度。
1. 细胞增殖实验(MTT/CCK-8法): - HMC-1细胞MTT实验:细胞以5×103个/孔接种96孔板,用含10% FBS的RPMI 1640培养基过夜培养;加入IMD 0354(0.1~20 μM),孵育72小时;加20 μL MTT(5 mg/mL PBS),4小时后用DMSO溶解甲臜,490 nm测吸光度,计算IC50 [1] - MCF-7细胞CCK-8实验:细胞以3×103个/孔接种96孔板,24小时后加入IMD 0354(1~10 μM),孵育72小时;加10 μL CCK-8溶液,2小时后450 nm测吸光度 [3] 2. 凋亡实验(Annexin V-FITC/PI染色法): - HMC-1细胞以1×106个/孔接种6孔板,用IMD 0354(5~20 μM)处理48小时;1000×g离心5分钟收集细胞,冷PBS洗涤后用Annexin V-FITC和PI染色,流式细胞仪检测凋亡细胞 [1] 3. NF-κB信号分子Western blot实验: - HeLa细胞p-IκBα检测:IMD 0354(1~10 μM)预处理细胞1小时,TNF-α(10 ng/mL)刺激15分钟;含抑制剂的RIPA缓冲液裂解细胞,SDS-PAGE分离蛋白后转膜,用抗p-IκBα(Ser32/36)和总IκBα抗体孵育 [2] - MCF-7细胞p-IKKβ检测:IMD 0354(5 μM)处理细胞24小时,制备裂解液,膜用抗p-IKKβ(Ser177/181)、p-IκBα及内参β-actin抗体孵育 [3] 4. 细胞周期分析(PI染色法): - MCF-7细胞用IMD 0354(5 μM)处理24小时;70%乙醇4°C固定过夜,用PI(50 μg/mL)和RNase A(100 μg/mL)染色30分钟,流式细胞仪分析细胞周期分布 [3] |
| 动物实验 |
Mice: Female BALB/c nude mice are injected s.c. with MDA-MB-231 cells suspended in PBS (5×106 cells/100 L mouse) when they are 4 to 5 weeks old. Following growth, the tumor is surgically removed, and at the age of 4 weeks, under ether anesthesia, 100 mg of each established tumor is transplanted to the back of additional female nude mice. Each mouse receives an intraperitoneal injection of 5 mg/kg body weight of IMD-0354 (suspended in 100 L/mouse) once daily for 28 days following the implantation. As a control, saline is injected into naked mice. Calculations are made for the estimated tumor weight (mg) and volume (mm3).
Rats: Lewis rats (180–220 g) that are eight weeks old are used. Endotoxin-induced uveitis (EIU) is brought on by injecting 200 μg of diluted Escherichia coli LPS in 200 l of PBS subcutaneously. IMD-0354, diluted in 500 μL of 0.5% CMC, is injected intraperitoneally into the rats at the same time in doses of 30, 10, or 3. 500 μL of CMC alone is intraperitoneally administered to control EIU rats. Control rats are naive rats. Five animals are used in each group for each experiment, which is carried out in triplicate. 1. MCF-7 Breast Cancer Xenograft Model: - Animal Preparation: Female BALB/c nude mice (6-8 weeks old, 18-22 g) were acclimated for 1 week. 5×106 MCF-7 cells (100 μL PBS + 100 μL Matrigel) were subcutaneously injected into the right flank [3] - Drug Formulation and Administration: When tumors reached ~100 mm³, mice were divided into 2 groups. IMD 0354 was dissolved in 0.5% DMSO + 0.5% CMC-Na to 4 mg/mL, and administered via oral gavage at 20 mg/kg once daily for 28 days. The control group received the same volume of vehicle [3] - Sample Collection: Tumor volume was measured every 3 days. At day 28, mice were euthanized; tumors were weighed and frozen for Western blot (p-IKKβ, p-IκBα, Ki-67). Serum was collected to detect ALT/AST (liver function) [3] 2. Endotoxin-Induced Uveitis (EIU) Rat Model : - Animal Preparation: Male Wistar rats (6-8 weeks old) were acclimated for 1 week. Rats were divided into 3 groups (n=5/group): Normal control, LPS + Vehicle, LPS + IMD 0354 (5 mg/kg or 10 mg/kg) [4] - EIU Induction and Dosing: LPS (100 μg/kg) was intraperitoneally injected to induce uveitis. IMD 0354 was dissolved in 0.9% saline to 1 mg/mL (5 mg/kg) or 2 mg/mL (10 mg/kg), and administered via intraperitoneal injection 1 hour before LPS and 12 hours post-LPS. The vehicle group received 0.9% saline [4] - Sample Collection: At 24 hours post-LPS, rats were euthanized. Aqueous humor was collected for TNF-α detection (ELISA). Eyes were enucleated; one eye was fixed for histopathology (HE staining), and the other was used to measure retinal MPO activity [4] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
1. In Vitro Cytotoxicity:
- In HMC-1, MCF-7, and MDA-MB-231 cells, IMD 0354 (up to 30 μM) showed no non-specific cytotoxicity. Cell viability (trypan blue exclusion) remained >80% compared to the vehicle control after 72 hours [1, 3] - In rat retinal microglial cells, 10 μM IMD 0354 had no significant effect on cell viability (>85%) [4] 2. In Vivo Safety: - In the MCF-7 xenograft model, IMD 0354 (20 mg/kg, oral gavage, 28 days) caused no significant weight loss (weight change: -4% vs. -3% in control) or abnormal behavior. Serum ALT/AST and creatinine were within normal ranges, indicating no liver/kidney toxicity [3] - In the EIU rat model, IMD 0354 (5-10 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection) did not induce additional ocular toxicity or systemic adverse effects (e.g., lethargy, reduced food intake) [4] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
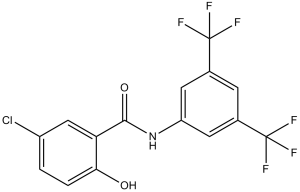
N-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzamide is a member of benzamides.
Constitutive phosphorylation of c-kit tyrosine kinase is the major cause of factor-independent proliferation of mast cells. Recently available tyrosine kinase inhibitors have shown marked activity against mast cell lines that carry wild-type c-kit, and some, but not others, carry mutant c-kit. Here we clearly demonstrated that a novel NF-kappaB inhibitor, IMD-0354, restrained factor-independent proliferation of mast cells with c-kit mutations but not of normal mast cells. In HMC-1 cells with the Asp816Val and Val560Gly mutations, we found that NF-kappaB was constitutively activated without exogenous stimulation. When the DNA-binding activity of NF-kappaB was inhibited by treatment with IMD-0354, cell proliferation was completely suppressed. We detected the expression of cyclin D2, D3, and E in HMC-1 cells and observed that cyclin D3 expression was dramatically decreased by treatment with IMD-0354. Abolishing protein kinase C or phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase pathways also inhibited NF-kappaB translocation to the nucleus, indicating the involvement of these signaling cascades in NF-kappaB activation in HMC-1 cells. Our findings indicated that autophosphorylated c-kit receptors induced NF-kappaB activation, resulting in the up-regulation of cyclin D3 expression and cell cycle progression. The observations from the current study suggest a therapeutic potential, in systemic mastocytosis, for compounds that interfere with NF-kappaB signaling.[1] Nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) is an important nuclear transcription factor which regulates pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6. Its role as immunoregulatory mediator makes it an attractive target in the development of treatments for inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. In this study, we synthesized derivatives of IMD0354, a known inhibitor for NF-κB, in attempt to understand the effect of benzanilide substitutions on its activity. The inhibition of these analogs on NF-κB activation was analyzed by luciferase assay. The inhibition of IKKβ phosphorylation and pro-inflammatory cytokines was determined by Western blot and real-time PCR. The structure activity relationships showed that the hydroxyl group on IMD0354 is a critical moiety that resulting in the inhibition of NF-κB. Derivatives 1m, 2b, and 2c were shown to inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokine production at low concentration. These newly synthesized compounds may be useful for the treatment of chronic inflammatory disorders or for cancer prevention. [2] Constitutive nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) activity plays a crucial role in the development and progression of lymphoma, leukemia, and some epithelial cancers. Given the contribution of NF-kappaB in carcinogenesis, a novel approach that interferes with its activity might have therapeutic potential against cancers that respond poorly to conventional treatments. Here, we have shown that a new IkappaB kinase beta inhibitor, IMD-0354, suppressed the growth of human breast cancer cells, MDA-MB-231, HMC1-8, and MCF-7, by arresting cell cycle and inducing apoptosis. In an electrophoretic mobility shift assay and a reporter assay, IMD-0354 abolished the NF-kappaB activity in MDA-MB-231 cells in a dose-dependent manner. In the cells incubated with IMD-0354, cell cycle arrested at the G0-G1 phase and apoptotic cells were increased. The expression of some cell cycle regulatory molecules and antiapoptotic molecules was suppressed in cells treated with IMD-0354. On the other hand, cyclin-dependent kinase suppressor p27Kip1 was up-regulated by the addition of IMD-0354. Daily administration of IMD-0354 inhibited tumor expansion in immunodeficient mice into which MDA-MB-231 cells were transplanted. These results indicate that NF-kappaB may contribute to cell proliferation through up-regulation of cell cycle progression; accordingly, inhibition of NF-kappaB activity might have a therapeutic ability in the treatment of human breast cancers.[3] 1. Mechanism of Action: - IMD 0354 exerts biological effects by selectively inhibiting IKKβ. It binds to the ATP-binding pocket of IKKβ, blocking its kinase activity and preventing IκBα phosphorylation/degradation. This traps NF-κB (p65/p50) in the cytoplasm, inhibiting transcription of NF-κB target genes (e.g., anti-apoptotic genes Bcl-2, pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α/IL-6, cell cycle regulators cyclin D1) [1, 3, 4] 2. Therapeutic Potential: - Cancer: IMD 0354 is a potential anti-cancer agent for NF-κB-overactivated cancers, including mast cell tumors and breast cancer, by inhibiting proliferation, inducing apoptosis, and arresting the cell cycle [1, 3] - Inflammatory Diseases: It shows promise for treating inflammatory ocular diseases (e.g., uveitis) and other NF-κB-driven inflammatory disorders (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis) by suppressing cytokine secretion and tissue inflammation [4] 3. Development Background: - IMD 0354 is a small-molecule IKKβ inhibitor developed as a tool compound to study NF-κB signaling. Preclinical data in cancer and inflammation models supports its potential as a therapeutic candidate, though it has not entered clinical trials [3, 4] 4. Selectivity Advantage: - Compared to non-selective NF-κB inhibitors, IMD 0354 specifically targets IKKβ (not IKKα or other kinases), reducing off-target effects and improving safety profiles [2, 3] |
| 分子式 |
C15H8CLF6NO2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
383.67
|
|
| 精确质量 |
383.015
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 46.96; H, 2.10; Cl, 9.24; F, 29.71; N, 3.65; O, 8.34
|
|
| CAS号 |
978-62-1
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
5081913
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.561g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
323.1ºC at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
149.2ºC
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.543
|
|
| LogP |
5.408
|
|
| tPSA |
49.33
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
25
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
462
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
O=C(C1C(O)=CC=C(Cl)C=1)NC1C=C(C(F)(F)F)C=C(C(F)(F)F)C=1
|
|
| InChi Key |
CHILCFMQWMQVAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C15H8ClF6NO2/c16-9-1-2-12(24)11(6-9)13(25)23-10-4-7(14(17,18)19)3-8(5-10)15(20,21)22/h1-6,24H,(H,23,25)
|
|
| 化学名 |
N-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzamide
|
|
| 别名 |
IKK2 Inhibitor V; IMD0354; N-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzamide; IKK-2 Inhibitor V; IMD0354; N-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzamide; TCMDC-125465; IMD 0354; IMD-0354
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.52 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (6.52 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: 2% DMSO+5% Tween 80+0.5% CMC Na: 3 mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6064 mL | 13.0320 mL | 26.0641 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5213 mL | 2.6064 mL | 5.2128 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2606 mL | 1.3032 mL | 2.6064 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
 |
 |
 |
|---|
 |
 |