| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
PI3Kγ (IC50 = 16 nM); PI3Kα (IC50 = 3.2 μM); PI3Kβ (IC50 = 3.5 μM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Eganelisib (IPI549) 抑制 PI3Kγ,IC50 为 16 nM,选择性是其他脂质和蛋白激酶的 100 倍以上(PI3Kα IC50=3.2 μM,PI3Kβ IC50=3.5 μM,PI3Kδ IC50>8.4 μM)。 Eganelisib 评估了所有 I 类 PI3K 同工型的活性。 eganelisib 的活性在所有 I 类 PI3K 同工型中进行评估。使用平衡荧光滴定测量 PI3K-α、β 和 δ 的各个速率常数,以确定 Eganelisib 对 PI3K-γ 的结合亲和力。 Eganelisib 是 PI3Kγ 的一种非常紧密的结合剂,Kd 为 290 pM,对其他 I 类 PI3K 同工型(PI3Kα Kd=17 nM、PI3Kβ Kd=82 nM、PI3Kδ Kd=23 M)的亲和力弱 58 倍以上。 Eganelisib 在 PI3K-α、-β、-γ 和 -δ 依赖性细胞磷酸化 AKT 测定中表现出优异的 PI3K-γ 效力 (IC50=1.2 nM) 和对其他 I 类 PI3K 同工型的选择性(>146 倍)。通过监测分别在 SKOV-3、786-O、RAW 264.7 和 RAJI 细胞中测定 I 类 PI3Kα (250 nM)、PI3Kβ (240 nM)、PI3Kγ (1.2 nM)、PI3Kδ (180 nM) 的细胞 IC50通过 ELISA 抑制 pAKT S473。此外,Eganelisib 剂量依赖性地抑制 PI3Kγ 依赖性骨髓源性巨噬细胞 (BMDM) 迁移。 Eganelisib 在 10 μM 下对一组 80 个 GPCR、离子通道和转运蛋白具有选择性[1]
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Eganelisib (IPI549) 表现出有利的药代动力学特征和有效的 PI3K 介导的中性粒细胞迁移抑制。 Eganelisib 具有优异的口服生物利用度,清除率低,体内分布到组织中的平均分布体积为 1.2 L/kg(小鼠、大鼠、狗和猴子)。总体而言,Eganelisib 具有良好的药代动力学特征,可实现有效且精确的 PI3K- 体内抑制。 IPI-549 对小鼠、大鼠、狗和猴子的 t1/2 分别为 3.2、4.4、6.7 和 4.3 小时。在此模型中,口服所有测试剂量的 eganelisib 均以剂量依赖性方式显着减少中性粒细胞迁移[1]。
基于小鼠体内的药代动力学特性和体外药理学特征,化合物26非常适合研究体内强效和选择性PI3K-γ抑制的影响。IL-8刺激的小鼠中性粒细胞向气囊的迁移先前已被证明依赖于PI3K-γ。因此,为了证明化合物26在体内的PI3K-γ依赖性活性,我们评估了口服化合物26对小鼠气囊中IL-8刺激的中性粒细胞内流的影响。7,8在所有测试剂量下口服化合物26时,在该模型中,化合物26以剂量依赖的方式显著减少了中性粒细胞的迁移(图2a)。在这些小鼠中观察到的抑制程度与化合物26的血浆浓度直接相关(图2b),清楚地表明口服化合物26可以抑制体内PI3K-γ功能。此外,化合物26(Eganelisib(IPI-549))已被证明可以通过改变肿瘤微环境中的免疫细胞来抑制小鼠同基因模型中的肿瘤生长。[1] 为了验证这一假设,我们在多种肿瘤模型中使用了选择性PI3K-γ抑制剂Eganelisib(IPI-549)19(扩展数据图2a)Eganelisib(IPI-549)单独治疗导致4T1、B16-GMCSF、MC38、CT26和LLC肿瘤模型的肿瘤生长抑制(图2a和扩展数据图2b)。具有低抑制性TAMCs的肿瘤缺乏活性(B16-F10,图2a)表明PI3K-γ抑制作用影响髓系细胞,对肿瘤细胞或其他TIL没有直接影响。我们还观察到IPI-549治疗后肺转移显著减少(图2b)。TIL定量显示,在IPI-549或载体治疗的4T1或B16-GMCSF肿瘤中,总髓系(CD11b+)或巨噬细胞(CD11b/F480+)细胞群没有一致的差异(图2c)。IPI-549对TAMC亚群的影响与p110γ-/-小鼠中的影响相当17,18。PI3K-γ抑制将巨噬细胞的激活从免疫抑制的M2样(CD11b+F4/80+CD206+)表型转变为更具炎症性的M1样(CD11b+F4/80+MHCII+)状态(图2c,扩展数据图2c)。我们进一步检测了IPI-549后4T1和B16-GMCSF肿瘤中M1和M2标志物的RNA表达。原型M2标志物(TGF-β、Arg-1、IDO)的表达降低,而经IPI-549治疗的肿瘤中M1标志物(IL-12、INOS)的表达更高(图2d)。鉴于CD11b+F4/80+巨噬细胞仅构成抑制性TAMCs的一部分,我们进一步将髓系细胞细分为粒细胞(CD11b+Ly6G+)、单核细胞(Ly6Chigh/MHCIIlow=Mono Lo)、未成熟巨噬细胞(LyC6high/MHCIIhigh=Mono Hi)、M1巨噬细胞(Ly6Clow/MHCIIhigh=TAM-M1)或M2巨噬细胞(Ly6Clow/MHCIlow=TAM-M2)20,21。当我们在4T1 TIL中使用上述门控策略分析髓系细胞时,我们还观察到Eganelisib(IPI-549)将髓系细胞向TAM-M1群体转移(扩展数据图3a)。此外,M1和M2标记物的相对mRNA表达与这些细胞的抑制功能较弱相关(扩展数据图3b)。随后,我们测试了来源于IPI-549治疗的B16-GMCSF荷瘤小鼠的髓系细胞对幼稚CD8 T细胞增殖的抑制作用(图2e)。我们发现,在IPI-549治疗的小鼠中或当IPI-549添加到培养基中时,CD8+T细胞的抑制被消除。在PBMC中的人类髓系抑制细胞中进行了类似的功能观察(扩展数据图4b),证实了其潜在的临床用途。此外,全血药效学评估证实,在人类志愿者中用PI3K-γ刺激激活后,单核细胞中的PI3H-γ受到抑制(扩展数据图4a)。为了证实抑制髓系细胞中的PI3K-γ是延缓肿瘤进展所必需的,我们在将LLC-Brei肿瘤植入小鼠之前耗尽了髓系细胞(抗CD11b)。在没有TAMCs的情况下,IPI-549治疗并没有延缓肿瘤生长(扩展数据图2e)。综上所述,这些发现表明,使用IPI-549抑制PI3K-γ主要在富含抑制性髓系细胞的肿瘤环境中有效,并允许更精确地描绘可能产生最大活性的患者。 [2] 我们在4T1和B16-GMCSF模型中测试了抗PD-1和抗CTLA4与Eganelisib(IPI-549)的组合(图4a)。单独的双检查点阻断治疗在携带4T1的小鼠中没有导致任何完全的肿瘤消退,只有20%的携带B16-GMCSF的小鼠受益于该治疗,进一步证实了这些模型中的多重检查点耐药性。值得注意的是,在抗CTLA-4+抗PD-1的组合中添加Eganelisib(IPI-549)与30%的4T1和80%的B16-GMCSF荷瘤小鼠的完全缓解有关。重要的是,无肿瘤的幸存者对肿瘤再植入具有抵抗力(扩展数据图9),表明长期持续的适应性免疫[2]。 |
| 酶活实验 |
生化检测材料:[1]
I类PI3K亚型α、β和δ提供p85α调节亚基,γ亚型单独提供。所用异构体的目录号(cat#)如下:PI3K-α:p110α/p85αcat#14-602-K,PI3K-β:p110β/p85αcat#14-603-K,PI 3K-γ:p120γcat#14-558-K,PI3O-δ:p110δ/p85αcat#14-604。II类PI3K亚型以N端6xHis标记蛋白的形式提供;PI3K-C2α氨基酸299末端:cat#14-906-K,PI3K-C1β全长:cat#14-1907-K,PI3K C2γ:cat#14-2910-K。将ATP二钠盐在水中制备至30mM的储备浓度,并用氢氧化钠(NaOH)中和至pH 7.0。使用15.4 x 103 M-1 cm-1的消光系数,通过260 nm处的紫外(UV)吸光度测定浓度。将二辛酰基磷脂酰肌醇-4,5-双磷酸盐(diC8PIP2)制成5mM的水储备溶液,并储存在-20°C下。将二辛酰基磷脂酰肌醇(diC8PIP)制成5mM的水储备溶液,并储存在-20°C下。 3 mM ATP下I类和II类PI3K生化测定的一般程序:[1] Promega ADP-Glo Max检测试剂盒用于测定人PI3激酶I类α、β、δ和γ以及II类α、α和γ亚型的IC50值。在室温下,在反应缓冲液(15 mM HEPES pH 7.4,20 mM NaCl,1 mM EGTA,0.02%吐温20,10 mM MgCl2,0.2 mg/mL牛γ-球蛋白)中,将激酶样品(20 nM PI3K-α,PI3K-C2α,PI3K C2β和PI3K C2γ或40 nM PI3Kβ和PI3K-γ)与化合物一起孵育15分钟,然后加入ATP/diC8-PP2混合物,得到3 mM ATP和500µM diC8PIP2底物(用于I类PI3K)或500µM diC8PIP底物(用于II类PI3K 3K)。反应物在室温下孵育2小时,然后加入25µL Promega试剂盒终止溶液。在室温下孵育40分钟后,加入50µL Promega检测混合物,然后在室温下温育1小时。然后在Envision印版阅读器上以发光模式读取印版。数据转换为抑制百分比,然后绘制为抑制百分比与化合物浓度的关系图,并拟合4参数逻辑方程以确定IC50值。 生化和基于细胞的检测[2] 如前所述,对I类和II类PI3K亚型进行了生化和基于细胞的检测。 |
| 细胞实验 |
以 200,000 个细胞/200 L/孔的 RPMI-1640(含 10% FBS)的密度,将 SKOV-3 细胞接种到 96 孔细胞培养级板中。细胞在 5% CO2 和 37 °C 下孵育整晚。用物质处理细胞,最终浓度为 0.5% DMSO,然后在 37°C 和 5% CO2 下孵育 30 分钟。吸出培养基后,向每个孔中添加 50 L 冰冷的裂解缓冲液。在冰上孵育 5 分钟后,将板在 4 °C 下以 3000 rpm 离心 5 分钟。
T细胞抑制试验[2] 分离来自幼稚小鼠的脾脏,并通过40μm过滤器研磨,以产生单细胞悬浮液。红细胞裂解后,根据制造商的方案,使用抗CD8(Ly-2)微珠纯化CD8+细胞,并在37°C下用预热的PBS中的1 mM CFSE标记10分钟。然后将CFSE标记的CD8+T细胞在添加了0.05 Mβ-巯基乙醇的完全RPMI培养基中,接种到涂有1μg/ml抗CD3(克隆1454-2C11)和5μg/ml抗CD28(克隆37N)抗体的圆底96孔板上(每孔25×10E3细胞)。以指定比例加入纯化的髓系细胞,并在37°C下孵育平板。48小时后,收集细胞,通过流式细胞术测量门控CD8+T细胞中的CFSE信号。对于人类MDSC抑制试验,使用Lymphoprep™从供体血液中分离PBMC。通过CD3+选择分离T细胞,并将其冷冻在Sigma冷冻培养基中以备后用。将剩余的减去T细胞的PBMCs与20 ng/ml GMCSF和20 ng/ml IL6一起孵育6天,以分化髓系细胞,并在添加或不添加Eganelisib(IPI-549)的情况下孵育。6天后,通过CD33+选择分离MDSC细胞。然后将这些MDSC细胞与自体T细胞(比例为1:4)混合,自体T细胞已用细胞微量紫预染色,并用抗CD3和抗CD28珠(Dynal)激活。72小时后,通过流式细胞术测量的细胞微量紫染料稀释来确定T细胞增殖。 IFN-γELISPOT测定[2] 治疗10天后,从Vehicle和Eganelisib(IPI-549)(15mg/kg)治疗的CT26荷瘤小鼠身上采集血液。使用Lymphoprep密度梯度培养基分离PBMC。根据制造商的说明,使用CTL小鼠免疫斑点IFN-γ单色ELISPOT试剂盒对产生IFN-γ的细胞进行定量。对于体外再刺激,将1×105 PBMC与1×105经照射(2000 rad)的CT26结肠癌靶细胞在CTL试验培养基(CTL)中共培养16小时。使用辐照(2000rad)的4T1乳腺癌靶细胞作为阴性对照靶,以评估特异性。使用CTL Immunospot S6微型分析仪和Immunospot-Professional软件(CTL)定量IFN-γ斑点。 巨噬细胞极化试验[2] 从C57Bl/6小鼠股骨和胫骨制备骨髓来源的巨噬细胞。溶解红细胞,然后将剩余的细胞接种在由DMEM、20%FBS加pen/Strep和50ng/ml M-CSF组成的骨巨噬细胞培养基(BMM)中,并孵育6天。通过添加20 ng/ml IL4和50 ng/ml M-MCSF,在添加或不添加Eganelisib(IPI-549)的情况下,细胞向M2表型极化。将细胞孵育48小时,然后从细胞中收获RNA。使用小鼠ARG1和小鼠B-actin的引物进行qRT-PCR。 PI3Kγ特异性全血PD测定[2] 用Eganelisib(IPI-549)剂量滴定预处理6名健康献血者的全血,然后用2.3 ug/ml CXCL12刺激2分钟。细胞被裂解、固定并染色。ICF批准后采集了人体血液样本。通过流式细胞术测量单核细胞(CD14+)中AKT S473的磷酸化,并将其值与未处理的对照组进行比较,从而确定对刺激的反应。计算每个供体Eganelisib(IPI-549)的IC50值,测量化合物对PI3K-γ和全血的效力。 |
| 动物实验 |
The mice used in this study are C57BL/6J and Balb/c mice, aged 6 to 8 weeks. In the first day of the experiment, tumor cells are injected intradermally (i.d.) in the right flank. Once per day, 15 mg/kg of eganelisib is given orally through gavage. Beginning on day seven after tumor implantation and lasting until day twenty-one. Transportation (5% NMP, 95% PEG) is given to the control groups. Every second or third day, tumors are calibrated with a ruler to measure their volume (length, width, and height). when the total tumor volume reaches 2500 mm3, or when there are signs of distress in the animal. Tumors are then isolated and preserved in ice until needed[2].
RNAseq [2] Mice bearing CT26 tumors were treated with vehicle or Eganelisib (IPI-549) (15 mg/kg/day, PO) for 6 or 9 days. Tumors were isolated, and frozen until needed; tumors then thawed and RNA was extracted from all cells. RNAseq was done at Expression Analysis (Q2 Solutions). Sequence reads were aligned to the mouse B38 reference genome using OmicSoft ArrayStudio and the UCSC gene model. Log2(FPKM) was calculated for each gene, and data were mean centered for display in heat maps. The analysis focused on a compilation of about 4,200 mouse genes related to cancer immunology and PI3K pathway signaling compiled from numerous sources including BioCarta pathways, GO gene ontologies, KEGG pathways, WikiPathways, and literature.5 Mice [2] C57BL/6J and Balb/c mice (6–8 weeks old) were purchased from Jackson Laboratory. Pmel-1 TCR transgenic mice have been previously reported. Ten to fifteen mice per treatment strategy were used to allow 90% power, and a 5% significance level, and detect differences in tumor-free survival from 10% to 80%. Typically, tumors grow in 100% of control animals. An additional 5 mice per group were for tissue harvest at day 7 and day 14 on treatment. Mice cage, treatment allowance were at random at day 7 after tumor implants. Tumor Challenge and Treatment Experiments [2] On day 0 of the experiments, tumor cells were injected intradermally (i.d.) in the right flank. For the B16 model, 2.5×105 B16-WT or B16-GMCSF cells were injected into C57BL/6J mice. For 4T1 model and for the CT26 model, 5×105 cells were used subcutaneously in Balb/c mice. For studies in immune compromised mice, the CT26 study was done in the Balb/c nu/nu strain and the B16-GMCSF in C57Bl.6 rag1−/− mice. Mice were obtained from Jackson Labs and Charles River Labs. Treatments were given as single agents or in combinations with the following regimen for each drug. The PI3K-γ inhibitor drug Eganelisib (IPI-549) was dissolved at 5% 1-Methyl-2-pyrrolidinone in Polyethylene Glycol 400 and administered by oral gavage once a day at 15 mg/kg . Treatment was initiated on day 7 ending on day 21 post tumor implant. Control groups received vehicle (5% NMP, 95% PEG) without the active product. Anti-CTLA-4 antibody (100 μg/mouse, clone 9H10, Bio X cell) and anti-PD-1 antibody (250 μg/mouse, clone RPM1- 14, Bio X cell) were injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) on days 7, 10, 13 and 16 for the B16, B16-GMCSF and 4T1 models and on days 10, 13 and 16 for the CT26 model. Tumors were measured every second or third day with a caliper, and the volume (length × width × height) was calculated. Mice that had no visible and palpable tumors that could be measured on consecutive measurement days were considered complete regressions. Animals were euthanized for signs of distress or when the total tumor volume reached 2500 mm3. For the re-challenge study: mice with complete responses in the anti-PD-1 treatment group and the anti-PD-1 and Eganelisib (IPI-549) combination group were re-challenged with 2.5 × 105 CT26.WT tumor cells (on day 106 of the study since original tumor implant). Additional mice with complete responses from an additional Eganelisib (IPI-549) and anti-PD-1 group were implanted with 1×105 4T1 tumor cells. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
In vitro absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) properties and pharmacokinetic parameters of compound 26/Eganelisib (IPI-549) were also determined (summarized in Table 5). In vitro, 26/Eganelisib (IPI-549) showed moderate to high cell permeability across Caco-2 cell monolayers, was slowly metabolized in cultured hepatocytes (t1/2 > 360 min), and demonstrated IC50s greater than 20 μM for the CYP isoforms tested (1A2, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 3A4). In vivo (mice, rats, dog, and monkeys), compound 26 had excellent oral bioavailability, low clearance, and distributed into tissues with a mean volume of distribution of 1.2 L/kg (Table 5). Overall, compound 26 had a favorable pharmacokinetic profile to allow potent and selective inhibition of PI3K-γ in vivo.[1]
|
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
IPI-549 is under investigation in clinical trial NCT03795610 (Window of Opportunity Study of IPI-549 in Patients With Locally Advanced HPV+ and HPV- Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma).
Eganelisib is an orally bioavailable, highly selective small molecule inhibitor of the gamma isoform of phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3K-gamma) with potential immunomodulating and antineoplastic activities. Upon administration, eganelisib prevents the activation of the PI3K-gamma-mediated signaling pathways, which may lead to a reduction in cellular proliferation in PI3K-gamma-expressing tumor cells. In addition, this agent is able to modulate anti-tumor immune responses and inhibit tumor-mediated immunosuppression. Unlike other isoforms of PI3K, the gamma isoform is overexpressed in certain tumor cell types and immune cells; its expression increases tumor cell proliferation and survival. By selectively targeting the gamma isoform, PI3K signaling in normal, non-neoplastic cells is minimally or not affected, which results in a reduced side effect profile. Optimization of isoquinolinone PI3K inhibitors led to the discovery of a potent inhibitor of PI3K-γ (26 or IPI-549) with >100-fold selectivity over other lipid and protein kinases. IPI-549 demonstrates favorable pharmacokinetic properties and robust inhibition of PI3K-γ mediated neutrophil migration in vivo and is currently in Phase 1 clinical evaluation in subjects with advanced solid tumors. [1] Recent clinical trials using immunotherapy have demonstrated its potential to control cancer by disinhibiting the immune system. Immune checkpoint blocking (ICB) antibodies against cytotoxic-T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 or programmed cell death protein 1/programmed death-ligand 1 have displayed durable clinical responses in various cancers. Although these new immunotherapies have had a notable effect on cancer treatment, multiple mechanisms of immune resistance exist in tumours. Among the key mechanisms, myeloid cells have a major role in limiting effective tumour immunity. Growing evidence suggests that high infiltration of immune-suppressive myeloid cells correlates with poor prognosis and ICB resistance. These observations suggest a need for a precision medicine approach in which the design of the immunotherapeutic combination is modified on the basis of the tumour immune landscape to overcome such resistance mechanisms. Here we employ a pre-clinical mouse model system and show that resistance to ICB is directly mediated by the suppressive activity of infiltrating myeloid cells in various tumours. Furthermore, selective pharmacologic targeting of the gamma isoform of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3Kγ), highly expressed in myeloid cells, restores sensitivity to ICB. We demonstrate that targeting PI3Kγ with a selective inhibitor, currently being evaluated in a phase 1 clinical trial (NCT02637531), can reshape the tumour immune microenvironment and promote cytotoxic-T-cell-mediated tumour regression without targeting cancer cells directly. Our results introduce opportunities for new combination strategies using a selective small molecule PI3Kγ inhibitor, such as IPI-549, to overcome resistance to ICB in patients with high levels of suppressive myeloid cell infiltration in tumours.[2] |
| 分子式 |
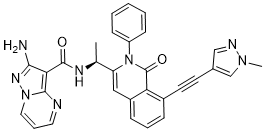
C30H24N8O2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
528.58
|
|
| 精确质量 |
528.202
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 68.17; H, 4.58; N, 21.20; O, 6.05
|
|
| CAS号 |
1693758-51-8
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
91933883
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Yellow solid powder
|
|
| LogP |
3.2
|
|
| tPSA |
123Ų
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
40
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1060
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
O=C1C2C(C#CC3C=NN(C)C=3)=CC=CC=2C=C(C(C)NC(C2C(N)=NN3C=CC=NC3=2)=O)N1C1C=CC=CC=1
|
|
| InChi Key |
XUMALORDVCFWKV-IBGZPJMESA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C30H24N8O2/c1-19(34-29(39)26-27(31)35-37-15-7-14-32-28(26)37)24-16-22-9-6-8-21(13-12-20-17-33-36(2)18-20)25(22)30(40)38(24)23-10-4-3-5-11-23/h3-11,14-19H,1-2H3,(H2,31,35)(H,34,39)/t19-/m0/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.73 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.73 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8919 mL | 9.4593 mL | 18.9186 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3784 mL | 1.8919 mL | 3.7837 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1892 mL | 0.9459 mL | 1.8919 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Status | Interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT02637531 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: IPI-549 (eganelisib) Drug: Nivolumab |
Melanoma (Part E) Mesothelioma (Part G) |
Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | December 2015 | Phase 1 |
| NCT03961698 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: IPI-549 (eganelisib) Drug: Atezolizumab |
Breast Cancer Renal Cell Carcinoma |
Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | December 17, 2019 | Phase 2 |
| NCT03980041 | Completed | Drug: IPI-549 (eganelisib) Drug: Nivolumab |
Bladder Cancer Urothelial Carcinoma |
Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | September 25, 2019 | Phase 2 |
Optimization of isoquinolinone PI3K inhibitors led to the discovery of a potent inhibitor of PI3K-γ (26or IPI-549) with >100-fold selectivity over other lipid and protein kinases.ACS Med Chem Lett.2016 Jul 22;7(9):862-7. |
|---|
Effect of compound26on migration of bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDM) in vitro.ACS Med Chem Lett.2016 Jul 22;7(9):862-7. |
(a) Effect of compound26on neutrophil migration in the mouse air pouch model.ACS Med Chem Lett.2016 Jul 22;7(9):862-7. |