| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
KD: 7.9 nM (factor B)[2] IC50: 10 nM (factor B)[2]
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在 50% 的人血清中,iptacopan (LNP023) 可有效防止补体旁路途径 (AP) 引起的膜攻击复合物 (MAC) 的形成(IC50 值:130 nM)[2]。在 41 种人类蛋白酶中,iptacopan (LNP023) 的 IC50 值 >30 μM,与其他蛋白酶(包括 AP 蛋白因子 D (>100 μM))相比具有优异的选择性 [3]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在大鼠膜性肾病实验模型中,diptacopan(LNP023;20-180 mg/kg;口服)在预防和治疗剂量下均有效,并可预防 KRN (150 μL) 诱导的小鼠关节炎 [2]。口服给药后(狗 10 mg/kg,大鼠30毫克/千克)[3]。 ?Iptacopan 是由静脉内给药(狗 1.0 mg/kg,大鼠 0.1 mg/kg)后的大分布体积(2.3 和 0.6 L/kg)和高血浆清除率(分别为 8 和 2 mL/min/kg)引起的[3]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
体外抑制试验[2]
通过使用CVF:Bb作为C3转化酶的稳定替代物和纯化的内源性C3作为底物,或者通过使用FB和Cy5标记的小分子抑制剂作为探针的竞争结合测定来测试化合物的FB抑制。通过酵母多糖A诱导的MAC形成,在50%的人血清或50%的人全血中测量AP抑制。将血清或全血与化合物预孵育30分钟,然后转移到酵母多糖A包被的平板上。通过ELISA用抗C9新表位抗体检测MAC形成。以类似的方式测量小鼠血清中的AP补体沉积,不同之处在于检测C3b沉积而不是MAC形成。SI附录中提供了有关蛋白质纯化和所有体外测定的更多详细信息。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: C57BL/6 mice with KRN-induced arthritis [2]
Doses: 20, 60 and 180 mg/kg: po (oral gavage); twice (two times) daily (bid) for 14 days Experimental Results: Blocks KRN-induced arthritis arthritis. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Following oral administration, iptacopan reached peak plasma concentrations approximately 2 hours post-dose. At the recommended dosing regimen of 200 mg twice daily, a steady state is achieved in approximately 5 days with minor accumulation (1.4-fold). Based on a food-effect study in healthy volunteers, a high-fat meal did not affect the exposure of iptacopan to a clinically meaningful degree. In a human study, following a single 100 mg oral dose of [14C]-iptacopan, the mean total excretion of radioactivity (iptacopan and metabolites) was 71.5% in the feces and 24.8% in the urine, for a total mean excretion of >96% of the dose. Specifically, 17.9% of the dose was excreted as parent iptacopan in the urine, and 16.8% of the dose was excreted as parent iptacopan in feces. After administration of iptacopan 200 mg twice daily, the apparent volume of distribution at steady state was approximately 288 L. The clearance of iptacopan at steady state is 7.96 L/h after administration of 200 mg twice daily. Metabolism / Metabolites Metabolism is a predominant elimination pathway for iptacopan with approximately 50% of the dose attributed to oxidative pathways. Metabolism of iptacopan includes N-dealkylation, O-deethylation, oxidation, and dehydrogenation, mostly driven by CYP2C8 (98%) with a small contribution from CYP2D6 (2%). Iptacopan undergoes Phase 2 metabolism through glucuronidation by UGT1A1, UGT1A3, and UGT1A8. In plasma, iptacopan was the major component, accounting for 83% of the drug-related species. Two acyl glucuronides were the only metabolites detected in plasma and were minor, accounting for 8% and 5% of the drug-related species. Iptacopan metabolites are not pharmacologically active. Biological Half-Life The half-life (t1/2) of iptacopan at steady state is approximately 25 hours after administration of 200 mg twice daily. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
Iptacopan showed concentration-dependent plasma protein binding due to binding to the target Factor B in the systemic circulation. Iptacopan was 75% to 93% protein-bound in vitro at the relevant clinical plasma concentrations. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
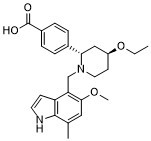
Iptacopan is a member of the class of indoles that is 1H-indole substituted by [(2S,4S)-2-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl]methyl, methoxy, and methyl groups at positions 4, 5, and 6, respectively. It is a potent inhibitor of complement factor B (IC50 = 10nM) with potential immunomodulatory activity. It has a role as a complement factor B inhibitor and an immunomodulator. It is a member of benzoic acids, a member of piperidines, an ether, a member of indoles, a diether, a monocarboxylic acid and a tertiary amino compound. It is a conjugate base of an iptacopan(1+).
Iptacopan is a small-molecule factor B inhibitor previously investigated as a potential treatment for the rare blood disease paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) by inhibiting the complement factor B. Factor B is a positive regulator of the alternative complement pathway, where it activates C3 convertase and subsequently C5 convertase. This is of particular importance to PNH, where one of the disease hallmarks is the mutation of the PIGA gene. Due to this mutation, all progeny erythrocytes will lack the glycosyl phosphatidylinositol–anchored proteins that normally anchor 2 membrane proteins, CD55 and CD59, that protect blood cells against the alternative complement pathway. Additionally, iptacopan has the benefit of targeting factor B, which only affect the alternative complement pathway, leaving the classic and lectin pathway untouched for the body to still mount adequate immune responses against pathogens. On December 6th, 2023, Iptacopan under the brand name Fabhalta was approved by the FDA for the treatment of adults with PNH. This approval was based on favorable results obtained from the phase III APPL-PNH and APPOINT-PNH studies, where 82.3% and 77.5% of patients experienced a sustained hemoglobin improvement without transfusions respectively. Iptacopan is an orally available, small-molecule inhibitor of complement factor B (FB) with potential immunomodulatory activity. Upon administration, iptacopan binds to FB and prevents the formation of the alternative pathway (AP) C3-convertase (C3bBb). This limits the cleavage of C3 to the active fragment C3b and may prevent C3b-mediated extravascular hemolysis in certain complement-driven disorders such as paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH). Drug Indication Iptacopan is indicated for the treatment of adults with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria Mechanism of Action Iptacopan binds to Factor B of the alternative complement pathway and regulates the cleavage of C3, the generation of downstream effectors, and the amplification of the terminal pathway. In paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, intravascular hemolysis (IVH) is mediated by the downstream membrane attack complex (MAC), while extravascular hemolysis (EVH) is facilitated by C3b opsonization. Iptacopan acts proximally in the alternative pathway of the complement cascade to control both C3b-mediated EVH and terminal complement-mediated IVH. Pharmacodynamics Inhibition of the alternative complement pathway biomarkers, in vitro alternative pathway assay, and plasma Bb (fragment Bb of Factor B), started approximately 2 hours after a single iptacopan dose in healthy volunteers. In paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) patients receiving concomitant anti-C5 treatment and iptacopan 200 mg twice daily, the in vitro alternative pathway assay and plasma Bb decreased from baseline by 54.1% and 56.1%, respectively, on the first observation on Day 8. In treatment-naive PNH patients, these same biomarkers decreased from baseline by 78.4% and 58.9%, respectively, on the first observation after 4 weeks of treatment with iptacopan 200 mg twice daily. In PNH patients on concomitant anti-C5 treatment and FABHALTA 200 mg twice daily, the mean PNH red blood cell (RBC) clone size was 54.8% at baseline and increased to 89.2% after 13 weeks; the proportion of PNH Type II + III RBCs with C3 deposition was 12.4% at baseline and decreased to 0.2% after 13 weeks. In treatment-naive PNH patients, the mean PNH RBC clone size was 49.1% at baseline and increased to 91.1% after 12 weeks; there were negligible PNH Type II + III RBCs with C3 deposition in this population due to the predominance of IVH. Iptacopan reduces serum LDH levels. In PNH patients previously treated with eculizumab, all patients treated with FABHALTA 200 mg twice daily achieved a reduction of LDH levels to < 1.5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) at 13 weeks. In treatment-naive PNH patients, iptacopan 200 mg twice daily reduced LDH by > 60% compared to baseline after 12 weeks and maintained the effect through the end of the study at 2 years. In a QTc clinical study in healthy volunteers, single supra-therapeutic iptacopan doses up to 1,200 mg (which provided greater than 4-fold peak concentration of the MRHD) showed no effect on cardiac repolarization or QT interval. |
| 分子式 |
C25H30N2O4
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
422.516706943512
|
| 精确质量 |
422.22
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 71.07; H, 7.16; N, 6.63; O, 15.15
|
| CAS号 |
1644670-37-0
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Iptacopan hydrochloride;1646321-63-2
|
| PubChem CID |
90467622
|
| 外观&性状 |
Off-white to gray solid powder
|
| LogP |
1.8
|
| tPSA |
74.8Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
31
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
594
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
| SMILES |
CCO[C@H]1CCN([C@@H](C1)C2=CC=C(C=C2)C(=O)O)CC3=C(C=C(C4=C3C=CN4)C)OC
|
| InChi Key |
RENRQMCACQEWFC-UGKGYDQZSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C25H30N2O4/c1-4-31-19-10-12-27(22(14-19)17-5-7-18(8-6-17)25(28)29)15-21-20-9-11-26-24(20)16(2)13-23(21)30-3/h5-9,11,13,19,22,26H,4,10,12,14-15H2,1-3H3,(H,28,29)/t19-,22-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
4-((2S,4S)-4-ethoxy-1-((5-methoxy-7-methyl-1H-indol-4-yl)methyl)piperidin-2-yl)benzoic acid
|
| 别名 |
LNP023 Iptacopan LNP-023 LNP 023; Fabhalta
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~50 mg/mL (~118.34 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 5 mg/mL (11.83 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 50.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 5 mg/mL (11.83 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 50.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 5 mg/mL (11.83 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3668 mL | 11.8338 mL | 23.6675 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4734 mL | 2.3668 mL | 4.7335 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2367 mL | 1.1834 mL | 2.3668 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Study of Efficacy and Safety of Twice Daily Oral Iptacopan (LNP023) in Adult PNH Patients Who Are Naive to Complement Inhibitor Therapy
CTID: NCT04820530
Phase: Phase 3 Status: Completed
Date: 2024-10-09