| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
5-HT2A Receptor ( Ki = 0.54 nM )
Lumateperone tosylate (2-30 μM) exhibits anti-tumor activity and has the ability to dose-dependently inhibit cell proliferation[1]. |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Lumateperone (2-30 μM) 甲苯磺酸盐具有抗肿瘤活性,并能以剂量依赖性方式抑制细胞增殖[1]。细胞增殖实验[1] 细胞系:RPMI-8226 细胞 浓度:2-30 μM 孵育时间: 结果:抑制细胞生长,IC50 值为17.30 μM。
在大鼠内侧前额叶皮层(mPFC)第V/VI层锥体神经元的体外细胞内记录实验中,Lumateperone (30 nM) 显著促进了NMDA和AMPA诱导的电流。与对照相比,对NMDA诱导电流的最大增强为150.7 ± 15.7%,对AMPA诱导电流的最大增强为138.8 ± 10.0%。这种促进作用呈倒U型浓度-反应关系,并且依赖于多巴胺D1受体的激活,因为D1拮抗剂SCH23390 (1 µM) 的预处理可阻止该效应。[2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Lumateperone(腹腔注射,1-10 mg/kg)甲苯磺酸盐以多巴胺 D 1 受体依赖性方式促进 NMDA 和 AMPA 诱导的电流,并增加大鼠 mPFC 切片中多巴胺和谷氨酸的释放 [2]。动物模型:成年雄性Sprague-Dawley大鼠[2] 剂量:1-10 mg/kg 给药方式:腹腔注射 结果:1、3和10 mg/kg浓度20分钟后回避反应受到抑制。促进 NMDA 和 AMPA 敏感电流,还显着增加大鼠 mPFC 视锥细胞中 10 mg/kg 的多巴胺和谷氨酸释放。
在大鼠的条件性回避反应(CAR)测试中,全身给予 Lumateperone (3和10 mg/kg,腹腔注射) 在注射后20分钟显著抑制了回避反应,表明其具有抗精神病样效应。未观察到逃避失败,提示非特异性副作用风险较低。该效应是短暂的,行为在注射后90分钟恢复至基线水平。[2] 使用大鼠mPFC的体内微透析技术,Lumateperone (10 mg/kg, 腹腔注射) 引起细胞外多巴胺水平的强效、快速且持续的升高。较低剂量(1和3 mg/kg)未产生显著增加。[2] 使用大鼠mPFC的体内安培法技术,Lumateperone (10 mg/kg, 腹腔注射) 显著增加了细胞外谷氨酸的释放,该效应在给药后约15分钟开始,并在注射后约50分钟达到平台期。在120分钟的记录期间,增加效应持续存在。[2] |
| 酶活实验 |
Lumateperone能够渗透多药耐药蛋白1(MDR1),并且在7.4的pH下是非常亲脂性的,这是允许抗精神病药物在小肠和血脑屏障中被吸收的特征。Tmax发生在口服给药后3-4小时。
Lumateperone被广泛代谢。羰基侧链被酮还原酶还原,产生初级活性代谢产物。细胞色素P4503A4酶将lumateperone代谢为2种代谢产物:活性N-去甲基羰基代谢产物(IC200161)或N-去甲基醇代谢产物(IC 200565)。 |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞系:RPMI-8226细胞
浓度:2-30 μM 结果:抑制细胞生长,IC50值为17.30 μM。 |
| 动物实验 |
Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats
1-10 mg/kg Intraperitoneal injection Conditioned Avoidance Response (CAR) Test: Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were trained in shuttle boxes. After achieving stable avoidance performance (≥85%), they received intraperitoneal (i.p.) injections of Lumateperone (1, 3, or 10 mg/kg) or vehicle. Behavioral testing sessions (10 min) were conducted 20, 90, and 240 minutes post-injection. Avoidances, escapes, and escape failures were recorded. [2] Ex Vivo Brain Slice Electrophysiology: Brain slices containing the mPFC were prepared from male Sprague-Dawley rats. Pyramidal neurons in layers V/VI were recorded using standard intracellular techniques under voltage-clamp. NMDA (10-15 µM) or AMPA (1.5-2.5 µM) was applied via bath perfusion to induce currents. After establishing control responses, Lumateperone (concentrations ranging from 3 to 100 nM) was bath-applied, and its effect on agonist-induced currents was measured 5 and 30 minutes later. In some experiments, slices were pretreated with the D1 antagonist SCH23390 (1 µM) or phencyclidine (PCP, 1 µM) before Lumateperone application. [2] In Vivo Microdialysis: Male Wistar Han rats were implanted with custom-made microdialysis probes targeted at the mPFC. After 48 hours of recovery, probes were perfused with Ringer's solution. After establishing a stable baseline of extracellular dopamine (3 consecutive stable samples), rats received an i.p. injection of Lumateperone (1, 3, or 10 mg/kg) or vehicle. Dialysate samples were collected every 30 minutes for 270 minutes post-injection and analyzed for dopamine content by HPLC with electrochemical detection. [2] In Vivo Amperometry: Male Sprague-Dawley rats were implanted under anesthesia with a ceramic microelectrode array (MEA) coated with glutamate oxidase, targeted at the mPFC. After surgical implantation and system stabilization (≥60 min), rats received an i.p. injection of Lumateperone (10 mg/kg) or vehicle. Extracellular glutamate levels were recorded via amperometry at a frequency of 10 Hz for at least 120 minutes post-injection. The electrodes were calibrated in vitro prior to implantation against known concentrations of glutamate, ascorbic acid, dopamine, and H2O2. [2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
In the CAR test, administration of Lumateperone at doses up to 10 mg/kg did not cause escape failures, suggesting it does not induce motor impairment or sedation at these doses in this model. [2]
The article references prior studies indicating that Lumateperone did not cause forelimb catalepsy in mice at doses up to 10 mg/kg, suggesting a low risk of extrapyramidal side effects. [2] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Pharmacodynamics
Lumateperone, also known as ITI-007, is an atypical antipsychotic that has proven to be effective in the treatment of schizophrenia. Lumateperone's receptor binding profile is unique, allowing it to target schizophrenia related symptoms while minimizing adverse effects. In contrast to other second generation antipsychotics such as [lurasidone] and [brexpiprazole], lumateperone behaves as a partial agonist and as an antagonist at pre and postynaptic dopamine (D2) receptors respectively. Patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B or C) tend to have higher plasma concentrations of lumateperone than those with normal hepatic function. For this reason, patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment should receive half the recommended daily dosage. Biological Half-Life Lumateperone's half life is reported to be between 13 to 18 hours. The reported half lives of the metabolites ICI200161 and ICI200131, are 20 and 21 hours respectively. Mechanism of Action There is much to learn about the pathophysiology of schizophrenia; however, dopamine abnormalities, specifically in the prefrontal and mesolimbic brain regions, are consistent in people with schizophrenia. In addition to dopamine, other neurotransmitters such as serotonin, glutamate, GABA and acetylcholine are thought to play a role. Lumateperone is unique among second generation antipsychotics based on its target profile and dopamine D2 receptor occupancy. Unlike other antipsychotics, lumateperone has partial agonist activity at presynaptic dopamine (D2) receptors, resulting in reduced presynaptic release of dopamine, and antagonistic activity at postsynaptic dopamine (D2) receptors. These characteristics allow lumateperone to efficiently reduce dopamine signaling. Lumateperone also targets dopamine (D1) receptors, and a useful secondary result of D1 activation is increased glutamatergic N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) GluN2B receptor phosphorylation. This is significant since NMDA mediated glutamate signaling appears to be impaired in patients who have schizophrenia. Finally, lumateperone is capable of modulating serotonin by inhibiting serotonin transporters (SERT), and by behaving as a 5-HT2A receptor antagonist. Hepatotoxicity In preregistration controlled trials, ALT elevations arose in 2% of patients receiving lumateperone compared to less than 1% of placebo controls. The elevations, however, were usually mild, transient and typically resolved without dose modification or drug discontinuation. In preregistration trials, there were no instances of severe hepatic adverse events, discontinuations because of liver related events or episodes of clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice. Since its approval and more widescale use, there have been no published reports of liver injury with symptoms or jaundice attributed to lumateperone therapy, but clinical experience with its use has been limited. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Lumateperone is an FDA-approved drug for the treatment of schizophrenia in adults and for depressive episodes associated with bipolar I or II disorder (as monotherapy or adjunctive therapy). [2] It has a novel, multimodal mechanism of action, simultaneously modulating serotonin, dopamine, and glutamate neurotransmission. [2] The ability of Lumateperone to facilitate prefrontal NMDA/AMPA receptor function and increase dopamine/glutamate release via a D1 receptor-dependent mechanism may underlie its clinical efficacy in improving not only positive symptoms but also negative symptoms, depressive symptoms, and cognitive deficits associated with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. [2] The pharmacology of Lumateperone is suggested to confer a safety profile with low risk for extrapyramidal symptoms, metabolic side effects, and prolactin elevation, as observed in clinical trials. [2] |
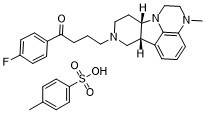
| 分子式 |
C24H28FN3O-HCL
|
|---|---|
| 精确质量 |
393.22
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 65.82; H, 6.41; F, 3.36; N, 7.43; O, 11.31; S, 5.67
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Lumateperone; 313368-91-1
|
| PubChem CID |
44241743
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to gray solid powder
|
| tPSA |
89.5Ų
|
| InChi Key |
LHAPOGAFBLSJJQ-GUTACTQSSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C24H28FN3O.C7H8O3S/c1-26-14-15-28-21-11-13-27(16-20(21)19-4-2-5-22(26)24(19)28)12-3-6-23(29)17-7-9-18(25)10-8-17;1-6-2-4-7(5-3-6)11(8,9)10/h2,4-5,7-10,20-21H,3,6,11-16H2,1H3;2-5H,1H3,(H,8,9,10)/t20-,21-;/m0./s1
|
| 化学名 |
1-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-[(10R,15S)-4-methyl-1,4,12-triazatetracyclo[7.6.1.05,16.010,15]hexadeca-5,7,9(16)-trien-12-yl]butan-1-one;4-methylbenzenesulfonic acid
|
| 别名 |
ITI722; ITI-722; ITI 722; Lumateperone toluenesulfonic acid; Lumateperone PTSA salt; ITI-007; ITI 007; ITI007; Lumateperone, Caplyta; UNII:JIE88N006O; ITI-007 tosylate
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~100 mg/mL (~176.8 mM)
H2O: < 0.1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.42 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.42 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT03249376 | Completed | Drug: Lumateperone Other: Placebo |
Bipolar Depression | Intra-Cellular Therapies, Inc. | November 27, 2017 | Phase 3 |
| NCT02600507 | Completed | Drug: Placebo Drug: Lumateperone (ITI-007) |
Bipolar Depression | Intra-Cellular Therapies, Inc. | March 7, 2016 | Phase 3 |
|
|
|