| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
5-HT2A receptor (Ki = 0.54 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Lumateperone (2-30 μM) 具有抗肿瘤活性,并能以剂量依赖性方式抑制细胞增殖[1]。细胞增殖实验[1] 细胞系:RPMI-8226细胞 浓度:2-30 μM 孵育时间:48小时 结果:抑制细胞生长,IC50值为17.30 μM。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Lumateperone(腹腔注射,1-10 mg/kg)以多巴胺 D1 受体依赖性方式促进 NMDA 和 AMPA 诱导的电流,并增加大鼠 mPFC 切片中多巴胺和谷氨酸的释放 [2]。动物模型:成年雄性Sprague-Dawley大鼠[2] 剂量:1-10 mg/kg 给药方式:腹腔注射 结果:1、3和10 mg/kg浓度20分钟后回避反应受到抑制。促进 NMDA 和 AMPA 敏感电流,还显着增加大鼠 mPFC 视锥细胞中 10 mg/kg 的多巴胺和谷氨酸释放。
|
| 酶活实验 |
Lumateperone能够渗透多药耐药蛋白1(MDR1),并且在7.4的pH下是非常亲脂性的,这是允许抗精神病药物在小肠和血脑屏障中被吸收的特征。Tmax发生在口服给药后3-4小时
Lumateperone被广泛代谢。羰基侧链被酮还原酶还原,产生初级活性代谢产物。细胞色素P4503A4酶将lumateperone代谢为2种代谢产物:活性N-去甲基羰基代谢产物(IC200161)或N-去甲基醇代谢产物(IC 200565)。 |
| 动物实验 |
Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats
1-10 mg/kg Intraperitoneal injection |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Lumateperone is able to permeate multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1) and is very lipophilic at a pH of 7.4, which are characteristics that allow the antipsychotic to be absorbed in the small intestine and the blood brain barrier. Tmax occurs 3-4 hours after oral administration. Due to it's molecular weight, virtually all unchanged lumateperone is excreted in the feces. Lumateperone's metabolites are very water soluble which is a property that allows for complete elimination. Approximately 58% of a lumateperone dose can be recovered in the urine, while 29% can be recovered in the feces. The volume of distribution of lumateperone is approximately 4.1 L/Kg after intravenous administration. Lumateperone's clearance is estimated to be 27.9 L/hour. Metabolism / Metabolites Lumateperone is extensively metabolized. The carbonyl side chain is reduced by ketone reductase to produce the primary active metabolite. Cytochrome P450 3A4 enzymes metabolize lumateperone to 2 metabolites: the active N-desmethylated carbonyl metabolite (IC200161) or the N-desmethylated alcohol metabolite (IC200565). Biological Half-Life Lumateperone's half life is reported to be between 13 to 18 hours. The reported half lives of the metabolites ICI200161 and ICI200131, are 20 and 21 hours respectively. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In preregistration controlled trials, ALT elevations arose in 2% of patients receiving lumateperone compared to less than 1% of placebo controls. The elevations, however, were usually mild, transient and typically resolved without dose modification or drug discontinuation. In preregistration trials, there were no instances of severe hepatic adverse events, discontinuations because of liver related events or episodes of clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice. Since its approval and more widescale use, there have been no published reports of liver injury with symptoms or jaundice attributed to lumateperone therapy, but clinical experience with its use has been limited. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the clinical use of lumateperone during breastfeeding. However, amounts of lumateperone and its metabolites in breastmilk appear to be low and would not be expected to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants. If lumateperone is required by the mother, it is not a reason to discontinue breastfeeding ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Lumateperone is approximately 97.4% plasma protein bound. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Schizophrenia is a complex mental illness and impacts approximately 1% of the population. Although there are several antipsychotics including [aripiprazole], [paliperidone] and [clozapine] available for clinical use, they are generally accompanied by significant metabolic and/or neurological adverse effects. Lumateperone is a newly approved 2nd generation antipsychotic currently indicated for the treatment of schizophrenia. It has a unique receptor binding profile and differs from other antipsychotics in that it modulates glutamate, serotonin and dopamine, which are all neurotransmitters that contribute to the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. The data so far indicates that lumateperone can alleviate both positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Further, not only is the new antipsychotic selective for dopamine (D2) receptors in the mesolimbic and mesocortical brain regions, but it also has minimal off-target activity. Both characteristics lend to a more favourable adverse effect profile and ultimately safer drug.
Lumateperone is an Atypical Antipsychotic. Lumateperone is a second generation (atypical) antipsychotic agent that is used in the treatment of schizophrenia. Lumateperone is associated with a low rate of serum aminotransferase elevations during therapy, but has not been linked to instances of clinically apparent acute liver injury. See also: Lumateperone Tosylate (is active moiety of). Drug Indication Lumateperone is approved for the treatment of schizophrenia in adults. It is also approved for the treatment of depressive episodes associated with bipolar disorder (i.e. bipolar depression) in adults, as monotherapy and/or adjunctive therapy with lithium or valproate. Mechanism of Action There is much to learn about the pathophysiology of schizophrenia; however, dopamine abnormalities, specifically in the prefrontal and mesolimbic brain regions, are consistent in people with schizophrenia. In addition to dopamine, other neurotransmitters such as serotonin, glutamate, GABA and acetylcholine are thought to play a role. Lumateperone is unique among second generation antipsychotics based on its target profile and dopamine D2 receptor occupancy. Unlike other antipsychotics, lumateperone has partial agonist activity at presynaptic dopamine (D2) receptors, resulting in reduced presynaptic release of dopamine, and antagonistic activity at postsynaptic dopamine (D2) receptors. These characteristics allow lumateperone to efficiently reduce dopamine signaling. Lumateperone also targets dopamine (D1) receptors, and a useful secondary result of D1 activation is increased glutamatergic N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) GluN2B receptor phosphorylation. This is significant since NMDA mediated glutamate signaling appears to be impaired in patients who have schizophrenia. Finally, lumateperone is capable of modulating serotonin by inhibiting serotonin transporters (SERT), and by behaving as a 5-HT2A receptor antagonist. Pharmacodynamics Lumateperone, also known as ITI-007, is an atypical antipsychotic that has proven to be effective in the treatment of schizophrenia. Lumateperone's receptor binding profile is unique, allowing it to target schizophrenia related symptoms while minimizing adverse effects. In contrast to other second generation antipsychotics such as [lurasidone] and [brexpiprazole], lumateperone behaves as a partial agonist and as an antagonist at pre and postynaptic dopamine (D2) receptors respectively. Patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B or C) tend to have higher plasma concentrations of lumateperone than those with normal hepatic function. For this reason, patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment should receive half the recommended daily dosage. |
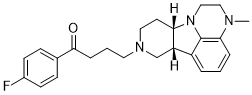
| 分子式 |
C24H28FN3O
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
393.497
|
| 精确质量 |
393.221
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 73.26; H, 7.17; F, 4.83; N, 10.68; O, 4.07
|
| CAS号 |
313368-91-1
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Lumateperone tosylate; 1187020-80-9; 313368-91-1
|
| PubChem CID |
21302490
|
| 外观&性状 |
Colorless to light yellow ointment
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.0 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
556.4±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
290.3±0.0 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±0.0 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.646
|
| LogP |
3.39
|
| tPSA |
26.8Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
29
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
593
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
| SMILES |
FC1=CC=C(C(CCCN2CC[C@H]3[C@H](C4=CC=CC5=C4N3CCN5C)C2)=O)C=C1
|
| InChi Key |
HOIIHACBCFLJET-SFTDATJTSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C24H28FN3O/c1-26-14-15-28-21-11-13-27(16-20(21)19-4-2-5-22(26)24(19)28)12-3-6-23(29)17-7-9-18(25)10-8-17/h2,4-5,7-10,20-21H,3,6,11-16H2,1H3/t20-,21-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
1-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-[(10R,15S)-4-methyl-1,4,12-triazatetracyclo[7.6.1.05,16.010,15]hexadeca-5,7,9(16)-trien-12-yl]butan-1-one
|
| 别名 |
ITI 722; ITI007; ITI722; ITI007; ITI-007; ITI-722
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~79 mg/mL (~200.8 mM)
Ethanol: ~79 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5413 mL | 12.7065 mL | 25.4130 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5083 mL | 2.5413 mL | 5.0826 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2541 mL | 1.2706 mL | 2.5413 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 4-way crossover study of ITI-007 in subjects with sleep maintenance insomnia
CTID: null
Phase: Phase 2 Status: Ongoing
Date: 2007-11-13
|
|
|