| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
The primary target of Methocarbamol is the skeletal muscle voltage-gated sodium channel subtype Nav1.4. In isolated mouse extensor digitorum longus (EDL) muscle fibers, the IC50 for inhibiting Nav1.4-mediated sodium currents (measured via voltage-clamp) was 1.2 mM [3]
. |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
美索巴莫(2 mM;持续 20 分钟)显着增加膈神经刺激产生的 EPC 和 EPP 的衰减期[3]。 Nav1.7 电流不受美索巴莫影响[3]。
1. 抑制Nav1.4钠通道:在分离的小鼠EDL肌纤维(22-24°C电压钳记录)中,Methocarbamol以剂量依赖性方式抑制Nav1.4峰值电流。0.5 mM时,电流幅度较溶媒对照组降低25%;1.2 mM(IC50)时,抑制率达50%;2.0 mM时,电流抑制率达80%。该抑制作用不依赖电压(通道激活/失活曲线无显著偏移)[3] 。 2. 降低骨骼肌等长收缩力:在分离的小鼠比目鱼肌标本(维持于氧合克雷布斯-林格溶液中)中,Methocarbamol降低电刺激(50 Hz、200 ms)诱导的等长收缩力。1.5 mM时,收缩力降低45%;2.5 mM时,降低70%;3.0 mM时,收缩力几乎完全消失(降低95%)[3] 。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
美索巴莫(200 mg/kg;腹膜内注射)的肌肉松弛活性为 88.96%[3]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
1. Nav1.4钠通道电流记录(电压钳实验):将分离的小鼠EDL肌纤维置于含细胞外液(140 mM NaCl、5 mM KCl、2 mM CaCl2、1 mM MgCl2、10 mM HEPES,pH 7.4)的记录槽中。采用双微电极电压钳技术:一根微电极(填充3 M KCl)记录膜电位,另一根注入电流。从-90 mV钳位电位给予去极化至0 mV的阶跃刺激(持续50 ms),诱发Nav1.4电流。Methocarbamol在细胞外液中系列稀释(0.1-5.0 mM)后灌流入记录槽,药物暴露5分钟后记录电流。电流幅度相对于溶媒对照组归一化,通过四参数逻辑模型拟合计算IC50 [3]
。 |
| 细胞实验 |
1. 骨骼肌等长收缩力测定:8-10周龄雄性C57BL/6小鼠安乐死后,快速分离比目鱼肌,置于氧合(95% O2/5% CO2)的克雷布斯-林格溶液(37°C)中。肌肉两端固定:一端连接玻璃钩,另一端连接张力换能器。通过铂电极给予电刺激(50 Hz、200 ms脉冲、0.2 ms持续时间),诱导等长收缩。记录稳定基线张力后,向溶液中加入Methocarbamol(0.5-3.0 mM),每5分钟记录一次张力,持续30分钟。张力值相对于基线归一化,计算降低百分比 [3]
。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Mice with weight 20-30 g[3]
Doses: 200 mg/kg Route of Administration: IP; single dose Experimental Results: Had Muscle relaxant activity of 88.96%. 1. Rodent and dog metabolism studies : - Rats: Male Sprague-Dawley rats (250-300 g, n=4/group) were fasted for 12 hours, then administered Methocarbamol orally (100 mg/kg) dissolved in 0.5% methylcellulose. Urine samples were collected at 0-24, 24-48, and 48-72 hours post-administration; blood samples were collected at 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 24 hours. Tissues (liver, kidney) were harvested at 24 hours post-euthanasia [1] . - Dogs: Male beagle dogs (10-12 kg, n=3/group) received Methocarbamol orally (50 mg/kg) dissolved in 0.5% methylcellulose. Urine and blood samples were collected at the same time points as rats; feces were collected at 0-24, 24-48, and 48-72 hours [1] . 2. Mouse muscle preparation: Male C57BL/6 mice (8-10 weeks old, n=6) were euthanized via CO2 inhalation. EDL and soleus muscles were excised immediately and placed in ice-cold Krebs-Ringer solution to maintain viability. Muscles were used within 1 hour for voltage-clamp recording or force measurement [3] . |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
The time to maximum concentration is 1.1 hours for both healthy patients and those on hemodialysis. The maximum plasma concentration is 21.3mg/L for healthy patients and 28.7mg/L in hemodialysis patients. The area under the curve for healthy patients is 52.5mg/L\\hr and 87.1mg/Lhr in hemodialysis patients. AUC% based on terminal elimination half life is 2% for healthy patients and 4% for hemodialysis patients. Older studies report maximum plasma concentrations in 0.5 hours. In humans the majority of the dose is eliminated in the urine. In dogs, 88.85% of the dose is eliminated in urine and 2.14% in the feces. In rats, 84.5-92.5% of the dose is eliminated in the urine and 0-13.3% is eliminated in the feces. Volume of distribution data in humans is scarce. In horses, the volume of distribution is 515-942mL/kg at steady state or 724-1130mL/kg. 0.2-0.8L/h/kg. Methocarbamol is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the GI tract. Blood or serum concentrations of methocarbamol required for sedative, skeletal muscle relaxant, or toxic effects are not known. Following oral administration of a single dose of methocarbamol, peak blood or serum concentrations of the drug appear to be attained in approximately 1-2 hours; the onset of action is usually within 30 minutes. Data from an unpublished study indicate that peak blood concentrations (measured as total carbamates and expressed in terms of methocarbamol) average 16.5 mcg/mL following a single 2-g oral dose, while data from a published study (using an assay relatively specific for methocarbamol) indicate that peak serum concentrations average 29.8 mcg/mL following the same dose. Data from the unpublished study also indicate that after IV administration of 1 g of methocarbamol at a rate of 300 mg/minute, blood concentrations of 19 mcg/mL are attained immediately and that the onset of action is almost immediate. In dogs, methocarbamol is widely distributed, with highest concentrations attained in the kidney and liver; lower concentrations are attained in the lungs, brain, and spleen, and low concentrations are attained in heart and skeletal muscle. The drug and/or its metabolites cross the placenta in dogs. It is not known if methocarbamol is distributed into milk in humans. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for METHOCARBAMOL (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Methocarbamol is metabolized in the liver by demethylation to 3-(2-hydroxyphenoxy)-1,2-propanediol-1-carbamate or hydroxylation to 3-(4-hydroxy-2-methoxyphenoxy)-1,2-propanediol-1-carbamate. Methocarbamol and its metabolites are conjugated through glucuronidation or sulfation. Methocarbamol is extensively metabolized, presumably in the liver, by dealkylation and hydroxylation. Based on limited data, about 10-15% of a single oral dose is excreted in urine as unchanged drug, about 40-50% as the glucuronide and sulfate conjugates of 3-(2-hydroxyphenoxy)-1,2-propanediol-1-carbamate and 3-(4-hydroxy-2-methoxyphenoxy)-1,2-propanediol-1-carbamate, and the remainder as unidentified metabolites. In dogs, rats and in man, methocarbamol gave p-hydroxymethocarbamol and o-demethylation product. All three substances were excreted in urine as glucuronic acid and ester sulfate conjugates. Permethylation and g.l.c.-mass spectrometric analysis of bile from an isolated rat liver perfusion to which methocarmol was added showed seven components not present in control bile: methocarbamol, glucuronides of methocarbamol and desmethyl-methocarbamol, and four glucuronides of hydroxylated methocarbamol metabolites. 2. An interesting rearrangement of a methyl group has been found in the mass spectrum of 3-(2-methoxyphenyloxy)-1,2-dimethoxypropane, the permethylation product from methocarbamol. Biological Half-Life The elimination half life is 1.14 hours in healthy subjects and 1.24 hours in subjects with renal insufficiency. Older studies report half lives of 1.6-2.15 hours. Methocarbamol has a serum half-life of 0.9-1.8 hours. ... Pharmacokinetics of methocarbamol were studied in eight healthy, adult horses after intravenous (iv) and oral administration of large dosages. ... Plasma methocarbamol concentration declined very rapidly during the initial or rapid disposition phase after iv administration; the terminal elimination half-life ranged from 59 to 90 mins. ... /Investigators/ determined plasma methocarbamol concentrations over 24 hr following a 1.5 g methocarbamol dose (off-dialysis day) to 8 chronic hemodialysis patients and compared these results to those from 17 healthy male volunteers. The harmonic mean elimination half-life was similar between the two groups, 1.24 and 1.14 hr, respectively. ... ... Pharmacokinetics of methocarbamol were studied in eight healthy, adult horses after intravenous (iv) and oral administration of large dosages. ... Plasma methocarbamol concentration declined very rapidly during the initial or rapid disposition phase after iv administration; the terminal elimination half-life ranged from 59 to 90 mins. ... 1. Absorption: In humans, oral Methocarbamol (500 mg) had an oral bioavailability of ~75%, with peak plasma concentration (Cmax) of 8.0 ± 1.2 μg/mL achieved at Tmax=1.0 ± 0.2 hours [2] . In rats, oral administration (100 mg/kg) resulted in Cmax=12.5 ± 1.8 μg/mL, Tmax=0.8 ± 0.1 hours [1] . 2. Distribution: Plasma protein binding rate in healthy humans was 46.0 ± 3.5% (measured via equilibrium dialysis); in patients with severe renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min), binding rate was 42.0 ± 2.8% (no significant difference vs. healthy controls) [2] . In rats, liver and kidney concentrations at 24 hours post-oral 100 mg/kg were 15.2 ± 2.1 μg/g and 10.8 ± 1.5 μg/g, respectively [1] . 3. Metabolism: Methocarbamol was primarily metabolized via glucuronidation: - Rats: 65% of the oral dose was excreted in urine as glucuronide conjugate within 72 hours; 10% as unchanged drug [1] - Dogs: 70% of the oral dose was excreted in urine as glucuronide conjugate within 72 hours; 8% as unchanged drug [1] - Humans: 68% of the oral dose was excreted in urine as glucuronide conjugate within 72 hours; 12% as unchanged drug [1] . 4. Excretion: In healthy humans, terminal elimination half-life (t1/2) was 1.1 ± 0.2 hours; in patients with severe renal insufficiency, t1/2 prolonged to 3.5 ± 0.4 hours. Renal clearance (CLR) in healthy humans was 85 ± 10 mL/min; in renal insufficiency patients, CLR decreased to 32 ± 5 mL/min [2] . In rats, 75% of the dose was excreted in urine, 15% in feces within 72 hours [1] . |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
While the product label for methocarbamol states that it can cause jaundice (including cholestatic jaundice), there is little published evidence to suggest that methocarbamol is a cause of hepatic injury or clinically apparent drug induced liver disease. During clinical trials of methocarbamol, some patients had to stop treatment because of nausea, dizziness, or other nonspecific complaints, but no serum aminotransferase levels or other laboratory results were reported. Methocarbamol appears to be well tolerated, but the lack of monitoring of serum aminotransferase levels during clinical trials with methocarbamol makes it impossible to rule out the possibility of mild liver injury occurring with treatment. Likelihood score: E (Unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Drug Class: Muscle Relaxants Protein Binding Methocarbamol is 46-50% protein bound in healthy patients and 47.3-48.9% protein bound in hemodialysis patients. Interactions Additive CNS depression may occur when methocarbamol is administered concomitantly with other CNS depressants, including alcohol. If methocarbamol is used concomitantly with other depressant drugs, caution should be used to avoid overdosage. A case is presented of a fatal drug interaction caused by ingestion of methocarbamol (Robaxin) and ethanol. ... Therapeutic concentrations of methocarbamol are reported to be 24 to 41 ug/mL. Biological fluids were screened for ethanol ... and quantitated by gas-liquid chromatography (GLC). Determination of methocarbamol concentrations in biological tissue homogenates and fluids were obtained by colorimetric analysis of diazotized methocarbamol. Blood ethanol concentration was 135 mg/dL (0.135% w/v) and urine ethanol was 249 mg/dL (0.249% w/v). Methocarbamol concentrations were: blood, 257 ug/mL; bile, 927 ug/L; urine, 255 ug/L; gastric, 3.7 g; liver, 459 ug/g; and kidney, 83 ug/g. The combination of ethanol and carbamates is contraindicated since acute alcohol intoxication combined with carbamate usage can lead to combined central nervous system depression as a result of the interactive sedative-hypnotic properties of the compound .../Methocarbamol/ is capable of inducing hepatic microsomal enzymes that metabolize warfarin in animals. Imipramine enhances CNS effect of.../methocarbamol/ in animals... Methocarbamol may inhibit the effects of pyridostigmine bromide. Use with caution in patients with myasthenia gravis receiving anticholinesterase agents. 1. Plasma protein binding-related safety: No significant difference in plasma protein binding of Methocarbamol between healthy humans and renal insufficiency patients, indicating no increased free drug concentration (a risk factor for toxicity) in renal impairment [2] . |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
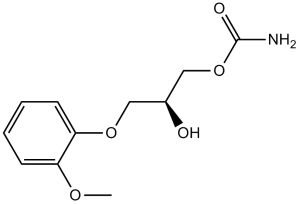
2-hydroxy-3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)propyl carbamate is a carbamate ester that is glycerol in which one of the primary alcohol groups has been converted to its 2-methoxyphenyl ether while the other has been converted to the corresponding carbamate ester. It is a carbamate ester, a secondary alcohol and an aromatic ether.
Methocarbamol was developed in the early 1950s as a treatment for muscle spasticity and the associated pain. It is a guaiacol glyceryl ether. Methocarbamol tablets and intramuscular injections are prescription medicines indicated in the United States as an adjunct to rest, physical therapy, and other measures for the relief of discomforts associated with acute, painful musculoskeletal conditions. In Canada, methocarbamol can be sold as an over the counter oral medicine at a lower dose that may be combined with [acetaminophen] or [ibuprofen]. A combination product with [acetylsalicylic acid] and [codeine] is available in Canada by prescription. Methocarbamol was FDA approved on 16 July 1957. Methocarbamol is a Muscle Relaxant. The physiologic effect of methocarbamol is by means of Centrally-mediated Muscle Relaxation. Methocarbamol is a commonly used, centrally acting muscle relaxant and has not been linked to instances of liver injury. Methocarbamol is a carbamate with centrally acting muscle relaxant properties. Though the exact mechanism of action of methocarbamol was not established, it's postulated to be via a mechanism similar of carbamate, inhibition of acetylcholinesterase at synapses in the autonomic nervous system, neuromuscular junction, and central nervous system. Methocarbamol has no direct effect on the contractile mechanism of striated muscle, the motor end plate or the nerve fiber. A centrally acting muscle relaxant whose mode of action has not been established. It is used as an adjunct in the symptomatic treatment of musculoskeletal conditions associated with painful muscle spasm. (From Martindale, The Extra Pharmacopoeia, 30th ed, p1206) See also: Aspirin; methocarbamol (component of). Drug Indication Methocarbamol tablets and intramuscular injections are indicated in the United States as an adjunct to rest, physical therapy, and other measures for the relief of discomforts associated with acute, painful musculoskeletal conditions. Oral methocarbamol in America may be given up to 1500mg 4 times daily for 2-3 days. In Canada, methocarbamol containing oral formulations are sold over the counter for pain associated with muscle spasm. However, if these combination formulations include codeine, they are prescription only. FDA Label Mechanism of Action The mechanism of action of methocarbamol is thought to be dependant on its central nervous system depressant activity. This action may be mediated through blocking spinal polysynaptic reflexes, decreasing nerve transmission in spinal and supraspinal polysynaptic pathways, and prolonging the refractory period of muscle cells. Methocarbamol has been found to have no effect on contraction of muscle fibres, motor end plates, or nerve fibres. Precise mechanism of action has not been determined. These agents act in the central nervous system (CNS) rather than directly on skeletal muscle. Several of these medications have been shown to depress polysynaptic reflexes preferentially. The muscle relaxant effects of most of these agents may be related to their CNS depressant (sedative) effects. /Skeletal Muscle Relaxants/ Therapeutic Uses Muscle Relaxants, Central Skeletal muscle relaxants are indicated as adjunts to other measures, such as rest and physical therapy, for the relief of muscle spasm associated with acute, painful musculoskeletal conditions. /Included in US product label/ Methcarbamol is also FDA-approved for control of the neuromuscular manifestations of tetanus. However it has largely been replaced in the treatment of tetanus by diazepam, or, in severe cases a neuromuscular blocking agent such as pancuronium. Such therapy is used as an adjunct to other measures, such as debridement, tetanus antitoxin, penicillin, tracheotomy, fluid and electrolyte replacement, and supportive treatment. VET: In dogs, cats, and horses, methocarbamol is indicated as adjunct therapy of acute inflammatory and traumatic conditions of skeletal muscle and to reduce muscle spasms. For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for METHOCARBAMOL (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings The most frequent adverse effects of methocarbamol are drowsiness, dizziness, and lightheadedness. Blurred vision, headache, fever, and nausea may occur after oral, IM, or IV administration of the drug. Anorexia has been reported after oral administration. Adynamic ileus occurred in one patient who received a total of 10 g of methocarbamol orally. Metallic taste, GI upset, nystagmus, diplopia, flushing, vertigo, mild muscular incoordination, syncope, hypotension, and bradycardia have occurred in patients receiving the drug IM or IV. Allergic reactions such as urticaria, pruritus, rash, skin eruptions, and conjunctivitis with nasal congestion may occur in patients receiving methocarbamol. Anaphylactic reactions have occurred following IM or IV administration of the drug. Although most patients with methocarbamol-induced syncope recover with supportive treatment, epinephrine, corticosteroids, and/or antihistamines have been used to increase the rate of recovery in some of these patients. When methocarbamol is administered IV, thrombophlebitis, sloughing, and pain at the injection site may result from extravasation. IM injection of the drug may also cause local irritation. IV injection of methocarbamol may cause a small amount of hemolysis and increased hemoglobin and red blood cells in the urine. Leukopenia may occur rarely. Parenteral dosage forms should be used with caution in patients with epilepsy. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for METHOCARBAMOL (14 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Methacarbamol is a skeletal muscle relaxant with an unknown mechanism of action. Methacarbamol has been shown to block spinal polysynaptic reflexes, decrease nerve transmission in spinal and supraspinal polysynaptic pathways, and prolong the refractory period of muscle cells. Methocarbamol does not act as a local anesthetic upon injection. In animal studies, methocarbamol also prevents convulsions after electric shock. 1. Chemical class and clinical use: Methocarbamol is a centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxant, chemically classified as a carbamate derivative. It is clinically approved for relieving acute musculoskeletal spasms (e.g., due to injury or inflammation) [3] . 2. Mechanism of action: Methocarbamol exerts muscle relaxant effects by blocking skeletal muscle Nav1.4 sodium channels, which reduces sodium influx, inhibits muscle fiber depolarization, and thereby decreases excessive muscle contraction [3] . 3. Pharmacokinetic consideration in renal impairment: Due to prolonged t1/2 and decreased CLR in patients with severe renal insufficiency, dose adjustment (e.g., 50% of the standard dose) is recommended to avoid drug accumulation [2] . 4. Metabolism characteristic: The primary metabolic pathway (glucuronidation) is not dependent on cytochrome P450 enzymes, suggesting low risk of drug-drug interactions via P450-mediated metabolism [1] . |
| 分子式 |
C11H15NO5
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
241.24
|
|
| 精确质量 |
241.095
|
|
| CAS号 |
532-03-6
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Methocarbamol-d5;1189699-70-4;Methocarbamol-d3;1346600-86-9;Methocarbamol-13C,d3;2747917-88-8
|
|
| PubChem CID |
4107
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
472.5±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
95-97ºC
|
|
| 闪点 |
239.6±27.3 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.2 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.541
|
|
| LogP |
0.55
|
|
| tPSA |
91.01
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
17
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
236
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| InChi Key |
GNXFOGHNGIVQEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C11H15NO5/c1-15-9-4-2-3-5-10(9)16-6-8(13)7-17-11(12)14/h2-5,8,13H,6-7H2,1H3,(H2,12,14)
|
|
| 化学名 |
[2-hydroxy-3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)propyl] carbamate
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 3.5 mg/mL (14.51 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 35.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 3.5 mg/mL (14.51 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 35.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 3.5 mg/mL (14.51 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 25 mg/mL (103.63 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶 (<60°C). 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.1452 mL | 20.7262 mL | 41.4525 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8290 mL | 4.1452 mL | 8.2905 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4145 mL | 2.0726 mL | 4.1452 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT05100017 | Recruiting | Drug: Methocarbamol Drug: Oxybutynin |
Kidney Calculi Kidney Diseases |
Northwestern University | September 30, 2021 | Not Applicable |
| NCT04458454 | Completed | Diagnostic Test: Relaxin ELISA Kit | Infertility Reproductive |
D.O. Ott Research Institute of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductology |
December 2, 2019 | |
| NCT05204667 | Recruiting | Drug: 380 mg/300 mg comprimidos metocarbamol/paracetamol - 4 times daily |
Low Back Pain | Aziende Chimiche Riunite Angelini Francesco S.p.A |
October 7, 2021 | Phase 4 |
| NCT05388929 | Recruiting | Drug: Methocarbamol Drug: Standard Opioid |
Ventral Hernia Inguinal Hernia |
Prisma Health-Upstate | June 23, 2022 | Phase 4 |
|
|
|