| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
GR/glucagon receptor (IC50 = 6.6 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
MK 0893 对金丝桃素受体具有选择性,GIPR 的 IC50 值为 1020 nM,PAC1 的 IC50 值为 9200 nM,GLP-1R、VPAC1 和 VPAC2 的 IC50 > 10000 nM。它还具有抗恒河猴 GCGR 活性,在表达恒河猴 GCGR 的 CHO 细胞中进行的 cAMP 实验中,其 IC50 为 56 nM [1]。通过优化先前鉴定的先导物,发现了一种强效的选择性胰高血糖素受体拮抗剂9m,N-[(4-{(1S)-1-[3-(3,5-二氯苯基)-5-(6-甲氧基萘-2-基)-1H-吡唑-1-基]乙基}苯基)羰基]-β-丙氨酸。化合物9m/MK-0893是一种可逆的竞争性拮抗剂,具有高结合亲和力(IC(50)为6.6 nM)和功能性cAMP活性(IC(50中)为15.7 nM)。相对于其他B家族GPCR,它对胰高血糖素受体具有选择性,GIPR的IC(50)值为1020 nM,PAC1为9200 nM,GLP-1R、VPAC1和VPAC2的IC(50中)值>10000 nM[1]。
化合物9m/MK-0893是一种竞争性、可逆的GCGR拮抗剂,表达hGCGR的CHO细胞中的Schild分析证明了这一点(图1)。它剂量依赖性地右移胰高血糖素的EC50,而不改变胰高血糖激素的最大作用。9m的结合在测定中使用的平衡期的30分钟内是完全可逆的。数据的线性变换(插入图1)产生了一条斜率为1的直线(希尔系数,nh),KB为8.5 nM[1]。 化合物9m/MK-0893对恒河猴GCGR具有活性,在表达恒河猴GCGRCHO细胞的cAMP测定中显示IC50为56 nM。该化合物在恒河猴胰高血糖素挑战模型中进行了体内评估,该模型类似于hGCGR小鼠中使用的模型。在肌肉注射胰高血糖素(15μg/kg)前4小时,通过鼻胃管以0.3、1和3 mpk的速度将化合物9m施用于椅子束缚的恒河猴,显著降低了1和3 mpk时胰高血糖激素诱导的葡萄糖水平,对载体反应的校正率为59%和55%。在0.3 mpk时观察到非统计有效剂量(减少29%)。在0.3、1.0和3.0 mpk时,胰高血糖素给药时的平均血浆水平分别为0.1、0.3和0.7μM[1]。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
MK 0893 消除 hGCGR 电极和恒河猴中胰高血糖素诱导的糖尿病增加。它还降低了急性和慢性电极模型中的环境电极水平:在 hGCGR ob/ob 电极中,单剂量 3 和 10 mpk 的补充(AUC 0-6 小时)分别降低了 32% 和 39%。在高脂肪饮食的 hGCGR 小鼠中,与载体对照和瘦 hGCGR 小鼠之间的差异相比,饮食中 3 和 10 mpk po 的 MK 0893 在第 10 天分别降低了 89% 和 94% 的血压水平 [1 ]。
化合物9m/MK-0893减弱了hGCGR小鼠和恒河猴中胰高血糖素诱导的葡萄糖升高。它还降低了急性和慢性小鼠模型中的环境葡萄糖水平:在hGCGR ob/ob小鼠中,单次剂量为3和10 mpk时,其葡萄糖(AUC 0-6 h)分别降低了32%和39%。在高脂肪饮食的hGCGR小鼠中,与赋形剂对照组和瘦hGCGR鼠之间的差异相比,饲料中3和10 mpk po的化合物9m在第10天分别将血糖水平降低了89%和94%。基于其良好的生物学和DMPK特性,选择化合物9m(MK-0893)进行进一步的临床前和临床评估。
在急性模型中,化合物9m/MK-0893在hGCGR-ob/ob小鼠中显示出降低血糖的功效,图4s,支持信息。与赋形剂对照组相比,口服10和3 mpk剂量的化合物9m分别将血糖水平(给药后0-6小时的AUC)降低了39%和32%。在1 mpk时,化合物9m在给药后1和3小时降低了葡萄糖,但在6小时没有降低。在0.3 mpk时,在1、3和6小时的时间点没有影响。化合物9m在使用饮食诱导的肥胖hGCGR小鼠的慢性环境中也能有效降低环境葡萄糖水平。这组高脂肪饮食的hGCGR小鼠出现了轻度非致死性高血糖症、高胰岛素血症和高胰高血糖症,为评估GCGR拮抗剂在降低环境血糖方面的疗效提供了很好的机会。当以每天3和10 mpk的剂量在饲料中给药(Bio-Serv的高脂肪饮食S3282)时,化合物9m在第3天显示出降糖作用,并在整个研究期间保持治疗组的较低葡萄糖水平,见图4。在第3天,相对于赋形剂对照组和瘦肉组之间的差异,3和10 mpk组的葡萄糖水平分别降低了70%和105%。在第10天,3和10 mpk组的相应葡萄糖减少分别为89%和94%。在这10天的慢性治疗中,胰高血糖素和GLP-1水平也相对于赋形剂对照组升高,这是胰高血糖蛋白原表达反馈上调的结果。胰高血糖素水平在3和10 mpk组分别升高了1.5倍和2.6倍。3和10mpk组的GLP-1总量也分别增加了2.1倍和4.0倍。请注意,胰高血糖素的这些增加远低于GCGR敲除小鼠中观察到的报告增加(>100×)。与之前报告的数据一致,没有观察到胰腺组织的明显形态学变化。 |
| 酶活实验 |
胰高血糖素结合试验[1]
维持表达人胰高血糖素受体(CHO-hGCGR)的CHO细胞系,并按照Chicchi等人的描述制备膜。将膜(2-5μg)在含有50 mM Tris、pH 7.5、5 mM MgCl2、2 mM EDTA、1%牛血清白蛋白、12%甘油、0.2 mg麦胚凝集素包被的聚乙烯甲苯闪烁邻近测定珠、增加化合物浓度(在100%DMSO中稀释并以2.5%的终浓度加入测定中)和50 pM 125I胰高血糖蛋白的缓冲液中孵育。该测定在室温下孵育3小时,用Wallac Microbeta计数器测量总结合放射性。使用1μM未标记的胰高血糖素测定非特异性计数。使用非线性回归分析软件GraphPad Prism,v4对数据进行分析。 cAMP测定[1] CHO-hGCGR细胞在Iscove改良的Dulbecco培养基(IMDM)、10%FBS、1 mM l-谷氨酰胺、青霉素-链霉素(100 u/mL)和500 ug G418/mL中生长3-4天,然后使用无酶解离培养基收获。细胞以低速离心并重新悬浮在刺激缓冲液中。将化合物从DMSO储备中稀释,并以5%DMSO的终浓度加入到测定中。将细胞与化合物或DMSO对照物预孵育30分钟。加入胰高血糖素(250 pM),并在室温下再孵育样品30分钟。通过加入FlashPlate试剂盒检测缓冲液终止测定。然后将该测定在室温下再孵育3小时,并使用液体闪烁计数器测量结合放射性。按照制造商的说明测定cAMP水平。对于Schild Plot分析,在添加0.001-1000 nM胰高血糖素以启动测定之前,将细胞等分试样在室温下与56、100、178、300、560和1000 nMMK-0893/9m预孵育30分钟。使用线性和非线性回归分析软件GraphPad Prism,v4对数据进行分析。 |
| 动物实验 |
hGCGR Mice were anesthetized (Nembutal IP, 50 mg/kg) at approximately the middle of the dark cycle. The portal vein was then cannulated and tied off and the liver was excised and perfused with a pre-oxygenated Krebs-Bicarbonate buffered solution for 5-10 minutes which initially was not recirculated to wash out any endogenous substrates. The liver was then excised and put into an NMR tube and the initial Krebs solution was exchanged for a BSA-Krebs perfusate (approx. 72ml) which was recirculated. 31P-NMR spectroscopy was performed initially to examine the ATP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) levels in the liver which can be used to assess the viability of the liver. A 13C-NMRvisible pool of glycogen was then created by the addition of the gluconeogenic substrate [2-13C]Pyruvate + NH4Cl. The amount of glycogen contained in the liver was monitored via the C1 resonance of the glucosyl units in the glycogen chain in real time until a suitable level was reached. At this time a novel glucagon receptor (GCGR) antagonist or DMSO was infused followed 20 minutes later by a glucagon challenge. The response of glycogen levels to the glucagon challenge was used to assess the efficacy of the GCGR antagonist.
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Upon incubation with human hepatocytes at 1 and 10 μM for 48 h, compound 9m/MK-0893 did not increase CYP3A4 mRNA expression or CYP3A4-mediated testosterone 6β-hydroxylase activity, and thus it was not an inducer of CYP3A4. Furthermore, compound 9m produced no treatment-related changes in assays evaluating cardiovascular effect in anesthetized dogs (up to 10 mpk IV, reaching drug exposure of 125 μM) and central nervous system effect in conscious mice (100 mpk PO).[1]
Concern over potential metabolic instability of compound 9mMK-0893/ due to the 6-methoxynaphthalene group was quickly dispelled by the results of pharmacokinetic studies in several species, as shown in Table 4. Compound 9m was characterized by low clearance, with a Clp of 7.5, 0.18, and 2.5 mL/min/kg, in rat, dog, and rhesus monkey, respectively. The elimination half-life was species-dependent, varying from 5.9 h (rat) to 17 h (dog). The oral bioavailability (F) of 9m was ∼43% in rat, 43% in dog, and 57% in rhesus. Further studies indicated that compound 9m was metabolically very stable, undergoing only minor metabolism in vitro and in vivo. In vivo disposition studies in bile duct cannulated rats and dogs using tritium-labeled 9m indicated that elimination occurred almost exclusively via biliary excretion of the parent compound (Figure 1s, Supporting Information) and that compound 9m was the only radioactive plasma component in both rat and dog at all the time points sampled (Figures 2s, 3s, Supporting Information). In vitro metabolism studies in liver microsomes and hepatocytes from rat, dog, monkey, and human using tritium-labeled 9m revealed minor amounts of O-demethylation (M1), acyl glucuronide (M2) of 9m, and acyl glucuronide of the benzoic acid (M3) derived from hydrolysis of the amide bond of 9m (Figure 1s, Supporting Information). In all cases, the total metabolites represented <2% turnover in the in vitro incubations. [1] Plasma protein binding was also determined in vitro with the tritium-labeled 9mMK-0893. Compound 9m was highly bound (>99%) to rat, dog, monkey, and human plasma proteins, and the unbound fraction could not be accurately determined. In an acute glucagon challenge model in hGCGR mice, compound 9m was found to be active in blunting glucagon-induced glucose excursion, Figure 2. When dosed orally at 3, 10, and 30 mpk one hour prior to a glucagon challenge (IP, 15 ug/kg), compound 9m reduced glucose elevation relative to vehicle control by 30%, 56%, and 81%, respectively, as determined by AUC over a 0–24 min period (all with p < 0.05 vs the glucagon group). The drug levels were found to be 0.26, 1.15, and 2.88 μM for 3, 10, and 30 mpk dose groups, respectively. In an ex vivo study using an hGCGR mouse perfused liver model, the glucagon-induced glycogenolysis (determined by following the 13C NMR signal of glycogen derived from [2-13C]pyruvate in perfusate) was effectively inhibited by 9m added to the perfusate (Figure 5s, Supporting Information). Compound 9m inhibited glucagon-induced glycogenolysis by 12/44/66% at 0.1/0.3/1.0 μM initial concentration in perfusate and completely blocked glucagon-induced glycogenolysis at 3 μM. This experiment confirmed that compound 9m acted in the liver by inhibiting hepatic glucose production.[1] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Compound 9m/MK-0893 was well-tolerated in a five-week safety study in rat, with no treatment-related antemortem or postmortem findings at doses ≤100 mpk daily (Cmax reached 21.3 ± 1.4 μM). On the basis of the efficacy and good selectivity profile, compound 9m was selected for further evaluation in preclinical safety species and entered into clinical studies for type II diabetes treatment. In a phase IIa study in diabetic patients, compound 9m, at 200 and 1000 mg single doses, achieved ∼59% and near maximal blockade of glucagon-induced glucose excursions, respectively. In a 12-week phase IIb clinical study in type II diabetic patients, compound 9m demonstrated robust reduction from baseline level in fasting plasma glucose (−53 and −63 mg/dL) and HbA1c (−1.1 and −1.5%) at 60 and 80 mg qd doses, respectively (p < 0.001), surpassing metformin at 1000 mg bid. [1]
|
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
MK0893 has been used in trials studying the treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2. MK-0893 is a small molecule drug with a maximum clinical trial phase of II and has 1 investigational indication.
In summary, the development of a modular synthesis of 1,3,5-trisubstituted pyrazoles allowed thorough investigation of the SAR around the pyrazole 3- and 5- positions. Two key findings of the SAR studies in this pyrazole GCGR antagonist series were the potency enhancing effect of 6-substituted naphth-2-yl groups at the pyrazole 5-position, and the incorporation of a chiral methyl group at the benzylic position off the pyrazole-N-1. Consequently a large number of potent GCGR antagonists were synthesized; among them, compound 9m was further profiled due to its balanced potency and selectivity profile. Compared with the initial lead compound 2 in this pyrazole series, compound 9m showed increased potency on the GCGR (13-fold in binding, 7-fold in functional assay) and improved off-target selectivity profile, particularly in hERG channel binding activity (IC50 >10 μM for 9m vs 5.1 μM for 2). It is interesting to note that incorporation of CF3 group in the para (or pseudo para) position in pharmacophore Z was associated with hERG channel activity: IC50 in hERG channel binding was <1.2 μM for compound 9p and 9r. Compound 9m showed an improved selectivity in reversible binding to CYP3A4 but had moderate reversible inhibition of CYP2C8. Compound 9m is a reversible, competitive human GCGR antagonist with KB of 8.5 nM. It is moderately active against the mouse, dog, and rhesus GCGRs but significantly less active at the rat GCGR. Compound 9m is selective for the glucagon receptor relative to other family B GPCRs tested, GIPR (IC50, 1020 nM), PAC1 (IC50, 9200 nM), and GLP-1R/VPAC1/VPAC2 (IC50 >10000 nM). Compound 9m demonstrated acute efficacy in blunting glucagon-induced glucose elevation in hGCGR mouse and rhesus monkey models. In a hGCGR mice PD study, it reduced glucose levels (AUC 0–1 h post dose) by 56%, and 81% at 10 and 30 mpk oral doses, respectively. In a rhesus monkey PD study, it demonstrated 59% and 55% reduction in glucose level relative to vehicle group at 1 and 3 mpk oral doses, respectively. Compound 9m was also efficacious in lowering ambient glucose levels in hGCGR mice models. In a hGCGR ob/ob mice acute model, it reduced glucose level (AUC 0–6 h post dosing) by 32% and 39% at 3 and 10 mpk oral doses, respectively. In a subchronic study in hGCGR mice on a high fat diet, it reduced ambient glucose levels by 89% and 94% at 3 and 10 mpk doses, respectively, in feed at day 10. In spite of having a 6-methoxynaphthalene group on the periphery, compound 9m is actually very stable metabolically in vitro and in vivo. It has low clearance in preclinical species tested (Clp of 7.5, 0.2, and 2.5 mL/min/kg, in rats, dogs, and rhesus monkeys, respectively), and the major clearance route of compound 9m is via biliary excretion as the parent compound. Except for moderate inhibition of CYP2C8 (IC50 2700 nM), compound 9m does not inhibit major CYPs nor is it a CYP3A4 inducer. [1] |
| 分子式 |
C₃₂H₂₇CL₂N₃O₄
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
588.48
|
| 精确质量 |
587.137
|
| CAS号 |
870823-12-4
|
| 相关CAS号 |
870823-19-1
|
| PubChem CID |
11570626
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
814.0±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
446.1±34.3 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±3.1 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.649
|
| LogP |
6.97
|
| tPSA |
93.45
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
9
|
| 重原子数目 |
41
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
877
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
[C@H](C1C=CC(C(=O)NCCC(=O)O)=CC=1)(N1N=C(C2C=C(Cl)C=C(Cl)C=2)C=C1C1C=CC2C=C(C=CC=2C=1)OC)C
|
| InChi Key |
DNTVJEMGHBIUMW-IBGZPJMESA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C32H27Cl2N3O4/c1-19(20-3-5-21(6-4-20)32(40)35-12-11-31(38)39)37-30(18-29(36-37)25-14-26(33)17-27(34)15-25)24-8-7-23-16-28(41-2)10-9-22(23)13-24/h3-10,13-19H,11-12H2,1-2H3,(H,35,40)(H,38,39)/t19-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
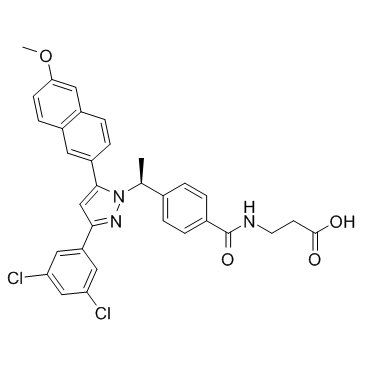
3-[[4-[(1S)-1-[3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-5-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)pyrazol-1-yl]ethyl]benzoyl]amino]propanoic acid
|
| 别名 |
MK-0893; 870823-12-4; MK 0893; MK-0893; MK0893; (S)-3-(4-(1-(3-(3,5-Dichlorophenyl)-5-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)ethyl)benzamido)propanoic acid; CID 11570626; CCP2U6LWTP; compound 9m [PMID: 22708876]; MK0893; MK 0893
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~33.33 mg/mL (~56.64 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.25 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入900 μL 玉米油中,混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.6993 mL | 8.4965 mL | 16.9929 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3399 mL | 1.6993 mL | 3.3986 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1699 mL | 0.8496 mL | 1.6993 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。