| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
Sunitinib metabolite; VEGFR; PDGFRβ; KIT
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
此外,舒尼替尼还能有效抑制FLT-3和Kit[1]。舒尼替尼是一种强效 ATP 竞争性抑制剂,PDGFRβ 的 Ki 值为 8 nM,VEGFR2 (Flk1) 的 Ki 值为 9 nM。与 FGFR-1、EGFR、Cdk2、Met 和 IGFR 相比,它对 VEGFR2 和 PDGFR 的选择性高出十倍。多于。 1.Src 和 Abl。在表达 VEGFR2 或 PDGFRβ 的血清饥饿 NIH-3T3 细胞中,Sunitinib 抑制 VEGF 依赖性 VEGFR2 磷酸化和 PDGF 依赖性 PDGFRβ 磷酸化,IC50 值分别为 10 nM 和 10 nM。舒尼替尼对 VEGF 的 IC50 为 40 nM,可防止血清饥饿的 HUVEC 增殖,对 PDGF 的 IC50 为 39 nM 和 69 nM,可防止过度表达 PDGFRβ 或 PDGFRβ 的 NIH-3T3 细胞增殖 [2]。对于野生型 FLT3、FLT3-ITD 和 FLT3-Asp835,舒尼替尼抑制磷酸化,IC50 值分别为 250 nM、50 nM 和 30 nM。 Sunitinib 以剂量依赖性方式引起 MV4;11 和 OC1-AML5 细胞凋亡,并抑制其生长,IC50 值分别为 8 nM 和 14 nM [3]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
跨多种肿瘤异种移植模型,例如 HT-29、A431、Colo205、H-460、SF763T、C6、A375 或 MB-435 的 MDA 依赖性抗肿瘤活性、舒尼替尼(20–80 mg/kg/天)表现出广泛而有效的剂量范围,与体内 VEGFR2 或 PDGFR 磷酸化和信号转导的显着且选择性抑制一致。在八只小鼠中,有六只连续 21 天服用舒尼替尼(80 毫克/公斤/天),导致肿瘤总体缩小;治疗结束后 110 天的观察期内没有发生肿瘤再生。对于第一轮治疗期间肿瘤未完全消退的情况,第二轮舒尼替尼仍然有效。舒尼替尼治疗大大降低了肿瘤 MVD,SF763T 神经胶质瘤肿瘤的 MVD 降低了 40%。尽管肿瘤大小没有减小,但 SU11248 疗法完全阻止了表达荧光素酶的 PC-3M 异种移植物中肿瘤的进一步生长 [2]。在 FLT3-ITD 骨髓移植范例中,舒尼替尼疗法(20 mg/kg/天)有效减少了皮下 MV4;11 (FLT3-ITD) 异种移植物的生长并延长了生存期 [3]。
为了预测在小鼠异种移植模型中获得抗肿瘤活性所需的目标SU11248暴露,我们直接测量了SU11248治疗前后肿瘤异种移植的靶磷酸化水平,并将其与血浆抑制剂水平相关联。在体内靶标调节研究中,当血浆抑制剂浓度达到或超过50-100 ng/ml时,SU11248选择性抑制Flk-1/KDR (VEGF受体2)和PDGF受体β磷酸化(以时间和剂量依赖的方式)。在vegf诱导的血管通透性的体内功能测定中也获得了类似的结果。持续抑制VEGFR2和PDGF受体β磷酸化并不需要有效;在高效剂量下,抑制持续12小时(24小时给药间隔)。在这些临床前研究中,SU11248建立了药代动力学/药效学关系[2]。 |
| 酶活实验 |
舒尼替尼对VEGFR2 (Flk-1)和PDGFRβ的IC50值是用含有RTK完整细胞质结构域的谷胱甘肽s -转移酶融合蛋白来测定的。生化酪氨酸激酶测定定量VEGFR2 (Flk-1)和PDGFRβ的反式磷酸化活性在96孔微滴板上进行(20 μg/孔PBS;在4°C下孵育过夜),肽底物poly-Glu,Tyr(4:1)。在PBS中加入1-5% (w/v)的BSA可以阻断多余的蛋白质结合位点。纯化的gst融合蛋白在杆状病毒感染的昆虫细胞中产生。然后将GST-VEGFR2和GST-PDGFRβ加入到2倍浓度的激酶稀释缓冲液中,该缓冲液由100 mM HEPES, 50 mM NaCl, 40 μM NaVO4和0.02% (w/v) BSA组成。GST-VEGFR2或GST-PDGFRβ的最终酶浓度为50 ng/mL。随后在每个反应孔中加入25 μL稀释的舒尼替尼,以产生适合每种酶的抑制剂浓度范围。在MnCl2溶液中加入不同浓度的ATP,使酶的最终ATP浓度跨越Km, MnCl2的最终浓度为10 mM,从而启动激酶反应。在室温下培养5-15分钟,然后加入EDTA停止反应。然后用TBST洗三次盘子。兔多克隆抗磷酸酪氨酸抗血清加入含有0.5% (w/v) BSA、0.025% (w/v)脱脂干乳和100 μM NaVO4的TBST中,按1:10万稀释至孔中,在37℃下孵育1小时。然后用TBST洗涤三次,然后加入山辣根过氧化物酶偶联的山羊抗兔抗血清(TBST中1:10 000稀释)。37℃孵育1小时,用TBST洗涤3次。在加入2,2′-氮基-二-[3-乙基苯并噻唑啉磺酸盐]作为底物后,定量测定每孔中磷酸酪氨酸的含量。[1]
|
| 细胞实验 |
在加入舒尼替尼和FL (50 ng/mL)之前,将细胞在含有0.1% FBS的培养基中饥饿过夜;FLT3-WT细胞)。培养48小时后,用Alamar蓝法或台盼蓝细胞活力法测定细胞增殖。加入舒尼替尼24小时后,通过Western blotting检测细胞凋亡,以检测聚(adp -核糖)聚合酶(PARP)的裂解或caspase-3的水平。[3]
|
| 动物实验 |
To predict the target SU11248 exposure required to achieve antitumor activity in mouse xenograft models, we directly measured target phosphorylation in tumor xenografts before and after SU11248 treatment and correlated this with plasma inhibitor levels. In target modulation studies in vivo, SU11248 selectively inhibited Flk-1/KDR (VEGF receptor 2) and PDGF receptor beta phosphorylation (in a time- and dose-dependent manner) when plasma concentrations of inhibitor reached or exceeded 50-100 ng/ml. Similar results were obtained in a functional assay of VEGF-induced vascular permeability in vivo. Constant inhibition of VEGFR2 and PDGF receptor beta phosphorylation was not required for efficacy; at highly efficacious doses, inhibition was sustained for 12 h of a 24-h dosing interval. The pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship established for SU11248 in these preclinical studies[2].
|
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
To improve the antitumor properties and optimize the pharmaceutical properties including solubility and protein binding of indolin-2-ones, a number of different basic and weakly basic analogues were designed and synthesized. 5-[5-Fluoro-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroindol-(3Z)-ylidenemethyl]-2,4-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylic acid (2-diethylaminoethyl)amide (12b or SU11248) has been found to show the best overall profile in terms of potency for the VEGF-R2 and PDGF-Rbeta tyrosine kinase at biochemical and cellular levels, solubility, protein binding, and bioavailability. 12b is currently in phase I clinical trials for the treatment of cancers.[1]
One challenging aspect in the clinical development of molecularly targeted therapies, which represent a new and promising approach to treating cancers, has been the identification of a biologically active dose rather than a maximum tolerated dose. The goal of the present study was to identify a pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship in preclinical models that could be used to help guide selection of a clinical dose. SU11248, a novel small molecule receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor with direct antitumor as well as antiangiogenic activity via targeting the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), KIT, and FLT3 receptor tyrosine kinases, was used as the pharmacological agent in these studies. In mouse xenograft models, SU11248 exhibited broad and potent antitumor activity causing regression, growth arrest, or substantially reduced growth of various established xenografts derived from human or rat tumor cell lines. To predict the target SU11248 exposure required to achieve antitumor activity in mouse xenograft models, we directly measured target phosphorylation in tumor xenografts before and after SU11248 treatment and correlated this with plasma inhibitor levels. In target modulation studies in vivo, SU11248 selectively inhibited Flk-1/KDR (VEGF receptor 2) and PDGF receptor beta phosphorylation (in a time- and dose-dependent manner) when plasma concentrations of inhibitor reached or exceeded 50-100 ng/ml. Similar results were obtained in a functional assay of VEGF-induced vascular permeability in vivo. Constant inhibition of VEGFR2 and PDGF receptor beta phosphorylation was not required for efficacy; at highly efficacious doses, inhibition was sustained for 12 h of a 24-h dosing interval. The pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship established for SU11248 in these preclinical studies has aided in the design, selection, and evaluation of dosing regimens being tested in human trials.[2] FLT3 (fms-related tyrosine kinase/Flk2/Stk-2) is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) primarily expressed on hematopoietic cells. In blasts from acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) patients, 2 classes of FLT3 activating mutations have been identified: internal tandem duplication (ITD) mutations in the juxtamembrane domain (25%-30% of patients) and point mutations in the kinase domain activation loop (7%-8% of patients). FLT3-ITD mutations are the most common molecular defect identified in AML and have been shown to be an independent prognostic factor for decreased survival. FLT3-ITD is therefore an attractive molecular target for therapy. SU11248 is a recently described selective inhibitor with selectivity for split kinase domain RTKs, including platelet-derived growth factor receptors, vascular endothelial growth factor receptors, and KIT. We show that SU11248 also has potent activity against wild-type FLT3 (FLT3-WT), FLT3-ITD, and FLT3 activation loop (FLT3-Asp835) mutants in phosphorylation assays. SU11248 inhibits FLT3-driven phosphorylation and induces apoptosis in vitro. In addition, SU11248 inhibits FLT3-induced VEGF production. The in vivo efficacy of SU11248 was investigated in 2 FLT3-ITD models: a subcutaneous tumor xenograft model and a bone marrow engraftment model. We show that SU11248 (20 mg/kg/d) dramatically regresses FLT3-ITD tumors in the subcutaneous tumor xenograft model and prolongs survival in the bone marrow engraftment model. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analysis in subcutaneous tumors showed that a single administration of an efficacious drug dose potently inhibits FLT3-ITD phosphorylation for up to 16 hours following a single dose. These results suggest that further exploration of SU11248 activity in AML patients is warranted.[3] |
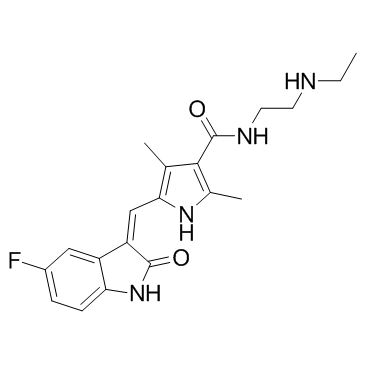
| 分子式 |
C₂₀H₂₃FN₄O₂
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
370.42
|
| 精确质量 |
370.181
|
| CAS号 |
356068-97-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
N-Desethyl Sunitinib-d5;1217247-62-5;N-Desethyl Sunitinib hydrochloride
|
| PubChem CID |
10292573
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to orange solid powder
|
| LogP |
3.522
|
| tPSA |
86.02
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
27
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
597
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
CCNCCNC(=O)C1=C(NC(=C1C)/C=C\2/C3=C(C=CC(=C3)F)NC2=O)C
|
| InChi Key |
LIZNIAKSBJKPQC-GDNBJRDFSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C20H23FN4O2/c1-4-22-7-8-23-20(27)18-11(2)17(24-12(18)3)10-15-14-9-13(21)5-6-16(14)25-19(15)26/h5-6,9-10,22,24H,4,7-8H2,1-3H3,(H,23,27)(H,25,26)/b15-10-
|
| 化学名 |
N-[2-(ethylamino)ethyl]-5-[(Z)-(5-fluoro-2-oxo-1H-indol-3-ylidene)methyl]-2,4-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxamide
|
| 别名 |
SU-11662; SU11662; N-Desethyl Sunitinib; 356068-97-8; N-DesethylSunitinib; SU-12662; N-[2-(ethylamino)ethyl]-5-[(Z)-(5-fluoro-2-oxo-1H-indol-3-ylidene)methyl]-2,4-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxamide; CHEMBL3542344; 42LJ35612R; UNII-42LJ35612R; SU 11662
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~6.25 mg/mL (~16.87 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.75 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入900 μL 玉米油中,混合均匀。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 0.62 mg/mL (1.67 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 6.2 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: 0.62 mg/mL (1.67 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6996 mL | 13.4982 mL | 26.9964 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5399 mL | 2.6996 mL | 5.3993 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2700 mL | 1.3498 mL | 2.6996 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。