| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
奈非那韦 (AG1341) (1-10 μM;48) 可抑制多发性骨髓瘤细胞生长 [4]。新鲜奈非那韦(1-10 μM;17 小时)会引起多发性骨髓瘤细胞系炎症,并抑制 26S 胰凝乳蛋白酶淀粉样蛋白染色体活性,损害缺血,并导致骨髓瘤细胞系细胞破裂 [4]。 [4] 奈非那韦(5 μM;0-24 小时)可降低 AKT 磷酸化。茴香染料可增加 caspase-3 的稳定性,降低 ERK1/2、AKT 和 STAT-3 磷酸化,并激活未折叠的蛋白质反应系统 [4]。另一种 IC50 为 35.93 μM 的 SARS-CoV 3CL pro 适配器是奈非那韦。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在 NOD/SCID 小鼠中,奈非那韦 (AG1341)(75 mg/kg;腹腔注射;每周 5 天,持续 21 天)抑制多发性骨髓瘤细胞的增殖 [4]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞增殖测定 [4]
细胞类型: RPMI、LP1、U266、OPM2 和 MM1S 细胞 测试浓度: 1、2、5、10 μM 孵育持续时间:48小时 实验结果:抑制RPMI、LP1、U266增殖。 OPM2 和 MM1S 细胞系呈剂量依赖性,IC50 为 1-5 μM。 细胞凋亡分析 [4] 细胞类型: LP1 和 U266 细胞 测试浓度: 1-10 μM 孵育持续时间:17 小时 实验结果:诱导膜联蛋白 V+/碘化丙啶+ 细胞百分比出现剂量依赖性增加。 蛋白质印迹分析 [4] 细胞类型: U266 细胞 测试浓度: 5 μM 孵育时间:0-24小时 实验结果:U266细胞中AKT磷酸化水平降低。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: NOD/SCID (severe combined immunodeficient) mouse (carrying U266-luc cells) [4]
Doses: 75 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip) injection; 5 days a week for 21 days Experimental Results: MM cells in NOD/SCID (severe combined immunodeficient) mouse diminished growth. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Well absorbed following oral administration. The majority (87%) of an oral 750 mg dose containing 14C-nelfinavir was recovered in the feces; fecal radioactivity consisted of numerous oxidative metabolites (78%) and unchanged nelfinavir (22%). Only 1–2% of the dose was recovered in urine, of which unchanged nelfinavir was the major component. The apparent volume of distribution following oral administration of nelfinavir was 2-7 L/kg. Oral clearance estimates after single doses (24-33 L/h) and multiple doses (26-61 L/h) indicate that nelfinavir is a drug with medium to high hepatic bioavailability. Metabolism / Metabolites Unchanged nelfinavir comprised 82-86% of the total plasma radioactivity after a single oral 750 mg dose of 14C-nelfinavir. In vitro, multiple cytochrome P-450 enzymes including CYP3A and CYP2C19 are responsible for the metabolism of nelfinavir. One major and several minor oxidative metabolites were found in plasma. The major oxidative metabolite has in vitro antiviral activity comparable to the parent drug. Nelfinavir has known human metabolites that include 3,4-Dihydroxynelfinavir and Nelfinavir hydroxyl-t- butylamide. Biological Half-Life The terminal half-life in plasma was typically 3.5 to 5 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Some degree of serum aminotransferase elevation occurs in a high proportion of patients taking nelfinavir containing antiretroviral regimens. Moderate-to severe elevations in serum aminotransferase levels (>5 times the upper limit of normal) are found in only 3% to 10% of patients, although rates may be higher in patients with HIV-HCV coinfection. These elevations are usually asymptomatic and self-limited and can resolve even with continuation of the medication. Clinically apparent acute liver injury due to nelfinavir is rare. The few cases that have been reported have arisen after 1 to 8 weeks of starting nelfinavir, and the pattern of serum enzyme elevations has not been reported, but is likely to have been hepatocellular (Case 1). Signs of hypersensitivity (fever, rash, eosinophilia) can occur as can autoantibody formation but these features are not very prominent. The acute liver injury due to nelfinavir is usually self-limited, but it can be severe, and isolated cases of acute liver failure have been reported to the sponsor, although not in great detail. In HBV or HCV coinfected patients, some instances appear to be due to exacerbation of the underlying chronic liver disease, perhaps as a result of sudden immune reconstitution. Nelfinavir therapy has not been clearly linked to lactic acidosis and acute fatty liver that is reported in association with several nucleoside analogue reverse transcriptase inhibitors used to treat HIV infection. Likelihood score: D (possible rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Nelfinavir levels in milk are low and the drug is usually not detectable in the serum of breastfed infants. However, some evidence of nelfinavir-induced adverse reactions in breastfed infants exists. Nelfinavir is not a recommended agent during breastfeeding. Achieving and maintaining viral suppression with antiretroviral therapy decreases breastfeeding transmission risk to less than 1%, but not zero. Individuals with HIV who are on antiretroviral therapy with a sustained undetectable viral load and who choose to breastfeed should be supported in this decision. If a viral load is not suppressed, banked pasteurized donor milk or formula is recommended. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants A study compared the frequency of rash, hepatotoxicity, and hyperbilirubinemia among 464 breastfed infants whose mothers were taking either nelfinavir (n = 206) or nevirapine (n = 258) along with zidovudine and lamivudine for HIV infection during pregnancy and postpartum. Infants were examined during the first, second and sixth weeks postpartum. Moderate rash occurred in 7 (2.7%) of the infant exposed to nevirapine and one (0.5%) infant exposed to nelfinavir. Rash occurred at a median of 2 weeks postpartum. Four infants (1.9%) exposed to nelfinavir developed hepatotoxicity (3 moderate and 1 severe) and none exposed to nevirapine. Twenty-one infants (4.5%) developed high-risk hyperbilirubinemia, all prior to 48 hours of age, but there was no difference in exposure between the two drugs. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Gynecomastia has been reported among men receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy. Gynecomastia is unilateral initially, but progresses to bilateral in about half of cases. No alterations in serum prolactin were noted and spontaneous resolution usually occurred within one year, even with continuation of the regimen. Some case reports and in vitro studies have suggested that protease inhibitors might cause hyperprolactinemia and galactorrhea in some male patients, although this has been disputed. The relevance of these findings to nursing mothers is not known. The prolactin level in a mother with established lactation may not affect her ability to breastfeed. Protein Binding Nelfinavir in serum is extensively protein-bound (>98%). |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Nelfinavir is an aryl sulfide that is used (as its mesylate salt) for treatment of HIV and also exhibits some anticancer properties. It has a role as a HIV protease inhibitor and an antineoplastic agent. It is a member of benzamides, a member of phenols, an aryl sulfide, a secondary alcohol, a tertiary amino compound and an organic heterobicyclic compound. It is a conjugate base of a nelfinavir(1+).
Nelfinavir is a potent HIV-1 protease inhibitor. It is used in combination with other antiviral drugs in the treatment of HIV in both adults and children. Nelfinavir inhibits the HIV viral proteinase enzyme which prevents cleavage of the gag-pol polyprotein, resulting in noninfectious, immature viral particles. Nelfinavir is a Protease Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of nelfinavir is as a HIV Protease Inhibitor, and Cytochrome P450 3A Inhibitor. Nelfinavir is an antiretroviral protease inhibitor used in the therapy and prevention of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Nelfinavir can cause transient and usually asymptomatic elevations in serum aminotransferase levels and is a rare cause of clinically apparent, acute liver injury. In HBV or HCV coinfected patients, hepatic injury during antiretroviral therapy that includes nelfinavir may be a result of exacerbation of the underlying chronic hepatitis B or C, rather than a direct effect of the medication. Nelfinavir is a synthetic antiviral agent that selectively binds to and inhibits human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) protease. Nelfinavir has activity against HIV 1 and 2. A potent HIV protease inhibitor. It is used in combination with other antiviral drugs in the treatment of HIV in both adults and children. See also: Nelfinavir Mesylate (has salt form). Drug Indication Used in combination with other antiviral drugs in the treatment of HIV in both adults and children. FDA Label Viracept is indicated in antiretroviral combination treatment of human-immunodeficiency-virus (HIV-1)-infected adults, adolescents and children of three years of age and older. In protease-inhibitor (PI)-experienced patients, the choice of nelfinavir should be based on individual viral resistance testing and treatment history. Mechanism of Action HIV viral protease is an important enzyme for HIV maturation and pathogenicity since HIV produces its structural and key proteins in the form of a polyprotein that needs to be cleaved by a protease. HIV protease is synthesized as part of the Gag-pol polyprotein, where Gag encodes for the capsid and matrix protein to form the outer protein shell, and Pol encodes for the reverse transcriptase and integrase protein to synthesize and incorporate its genome into host cells. The Gag-pol polyprotein undergoes proteolytic cleavage by HIV protease to produce 66 molecular species which will assume conformational changes to become fully active. Inhibition of protease, therefore, prevents HIV virion from fully maturing and becoming infective. Nelfinavir is a competitive inhibitor of the HIV protease by reversibly binding to the active site of the enzyme, preventing it from interacting with its substrate to produce mature and infectious viral particles. Pharmacodynamics Nelfinavir is a protease inhibitor with activity against Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 (HIV-1). Protease inhibitors block the part of HIV called protease. HIV-1 protease is an enzyme required for the proteolytic cleavage of the viral polyprotein precursors into the individual functional proteins found in infectious HIV-1. Nelfinavir binds to the protease active site and inhibits the activity of the enzyme. This inhibition prevents cleavage of the viral polyproteins resulting in the formation of immature non-infectious viral particles. Protease inhibitors are almost always used in combination with at least two other anti-HIV drugs. |
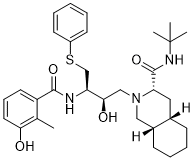
| 分子式 |
C32H45N3O4S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
567.789
|
| 精确质量 |
567.3131
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 67.69; H, 7.99; N, 7.40; O, 11.27; S, 5.65
|
| CAS号 |
159989-64-7
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Nelfinavir Mesylate;159989-65-8;Nelfinavir-d3;1217629-70-3
|
| PubChem CID |
64143
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.22g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
786.8ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
429.7ºC
|
| 蒸汽压 |
4.38E-26mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.618
|
| LogP |
6.052
|
| tPSA |
189.95
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
10
|
| 重原子数目 |
40
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
830
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
5
|
| SMILES |
S(C1C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C=1[H])C([H])([H])[C@@]([H])([C@@]([H])(C([H])([H])N1[C@]([H])(C(N([H])C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])=O)C([H])([H])[C@]2([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[C@]2([H])C1([H])[H])O[H])N([H])C(C1C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C(C=1C([H])([H])[H])O[H])=O
|
| InChi Key |
QAGYKUNXZHXKMR-HKWSIXNMSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C32H45N3O4S/c1-21-25(15-10-16-28(21)36)30(38)33-26(20-40-24-13-6-5-7-14-24)29(37)19-35-18-23-12-9-8-11-22(23)17-27(35)31(39)34-32(2,3)4/h5-7,10,13-16,22-23,26-27,29,36-37H,8-9,11-12,17-20H2,1-4H3,(H,33,38)(H,34,39)/t22-,23+,26-,27-,29+/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(3S,4aS,8aS)-N-tert-butyl-2-[(2R,3R)-2-hydroxy-3-[(3-hydroxy-2-methylbenzoyl)amino]-4-phenylsulfanylbutyl]-3,4,4a,5,6,7,8,8a-octahydro-1H-isoquinoline-3-carboxamide
|
| 别名 |
Nelfinavir free base; AG-1343; AG 1343; AG1343; Nelfinavir; Viracept.
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (176.12 mM
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.40 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.40 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.40 mM) 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7612 mL | 8.8061 mL | 17.6121 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3522 mL | 1.7612 mL | 3.5224 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1761 mL | 0.8806 mL | 1.7612 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。