| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| 50g |
|
||
| 100g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
TRPV1
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Nonivamide 是一种合成辣椒素衍生物,具有很强的防污性能。对于辣椒素,恶臭假单胞菌、伊利湖细菌和纳特里氏弧菌的 4d-EC50 值为 5.5±0.5 mg/L、23±2 mg/L、6.9±0.2 mg/L 和 15.6±0.4 mg/L,并且V. parahaemolyticus,分别在静态毒性实验中。 1 mg/L Nonivamide 治疗组在 4 天内表现出显着的生长抑制 (p<0.01),第 4 天的 EC50 值为 5.1 mg/L [1]。 Nonivamide 治疗可从内质网 (ER) 释放钙,并以常见 ER 应激特征的方式修改生长停滞和 DNA 损伤诱导转录物 3 (GADD153)、GADD45α、GRP78/BiP、ATF3、CCND1 和 CCNG2) 的转录。用 2.5 μM 毒胡萝卜素预处理细胞 5 分钟后,通过添加 2.5 μM Nonivamide 测量 ER 钙流。当将 2.5 μM Nonivamide 给予 TRPV1 过表达细胞时,ER 储备中的钙被释放,导致胞质钙显着升高。 24 小时后,用 1 μM Nonivamide 处理 TRPV1 过表达细胞,导致细胞活力下降约 50%。此外,用 100 和 200 μM Nonivamide 处理的 BEAS-2B 细胞显示 GADD153 mRNA 和蛋白质表达增加,以及 EIF2α-P 相对量的变化 [2]。在每个检测浓度下,nonivamide 处理对脂质积累的影响与 CAP 处理后的减少效果相同。与未处理的对照细胞相比,Nonivamide 处理在 0.01 µM 时使脂质积累减少 5.34±1.03% (P<0.05),在 1 µM 时减少 10.4±2.47% (P<0.001) [3]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在这项研究中,研究人员调查了nonivamide(壬酸香草烯丙基酰胺,PAVA;1 mg/kg)和瑞舒伐他汀(RSV;10 mg/kg)对高脂肪饮食(HFD)诱导的肝脂肪变性的影响。雄性Sprague-Dawley大鼠喂食HFD 16周,然后再接受PAVA或RSV 4周。我们检查了肝脏的代谢参数、功能、脂肪含量、组织学改变、活性氧产生和凋亡细胞死亡,以及以下重要分子的表达:甾醇调节元件结合蛋白(pSREBP-1c/SREBP-1c)的瞬时受体电位阳离子通道亚家族V成员1(TRPV1)磷酸化、总和膜葡萄糖转运蛋白2(GLUT2)、4-羟基壬烯醛(4-HNE)和切割的半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶-3。HFD诱导的肝脂肪变性与形态学紊乱、损伤标志物、氧化应激、脂质过氧化和细胞凋亡显著增加有关。然而,RSV和PAVA治疗可减少代谢功能障碍和肝损伤。PAVA调节脂质沉积,改善胰岛素抵抗,减少氧化应激和凋亡细胞死亡。因此,PAVA代表了一种治疗NAFLD患者代谢紊乱的有前景的治疗方法。
|
| 酶活实验 |
SOD酶测定[1]
将0.1毫升的样品上清液与0.4毫升溶液1、0.04毫升溶液2、0.04摩尔溶液3和0.04毫升的溶液4混合。对于对照,将0.1ml蒸馏水与0.4ml溶液1、0.04-ml溶液2、0.04-ml溶液3和0.04-ml解决方案4混合。制备后,将两种混合物在37°C下孵育40分钟。然后向其中加入0.6毫升显色剂。反应10分钟后,记录OD550值。使用以下公式计算结果:SOD活性=(ODCONTROL–ODSAMPLE)/ODCONTROL。 POD酶测定[1] 将0.1ml的样品上清液与2.4-ml溶液1、0.3ml溶液2和0.2ml溶液3混合。对于对照,用相同体积的蒸馏水代替溶液3。制备后,将样品和对照品在37°C下浸泡30分钟。然后将0.1ml溶液4分别加入两种混合物中。通过离心获得样品和对照的上清液,并记录OD420值。使用以下公式计算结果:POD活性=ODSAMPLE–ODCONTROL。 CAT酶测定[1] 试剂盒提供的反应溶液在28°C下孵育10分钟。然后,将3 ml该反应溶液与0.5 ml样品上清液混合。制备后,以1分钟的间隔时间测量混合物的OD240值两次,分别记录为OD1和OD2。结果用以下公式计算:CAT活性=2.303×log(OD1/OD2)/60。 ALP酶测定[1] 将0.03ml的样品上清液与0.5ml缓冲溶液和0.5ml底物溶液混合。对于标准品,将0.03ml与0.5ml缓冲溶液和0.5ml底物溶液混合,底物溶液由试剂盒提供。对于标准品,将0.03-ml蒸馏水与0.5ml缓冲溶液和0.5ml底物溶液混合。制备后,将混合物在37°C下水浴15分钟。然后,向每种混合物中加入1.5ml显色剂,并测量OD520值。使用以下公式计算结果:ALP活性=ODSAMPLE/ODSTANDARD。 |
| 细胞实验 |
将细胞接种在96孔板中,并在分化开始后用1 nM–10µM CAP或nonivamide处理12天,可添加或不添加25–100µM BCH或相应的乙醇浓度(0.1–0.2%(v/v),溶剂对照)。每两天更换一次细胞培养基。在第12天,向每个孔中加入100µl MTT工作试剂(0.83mg/ml MTT在PBS/无血清培养基(1:5)中稀释),细胞在37°C下孵育约15分钟。取出MTT工作溶液,将孵育过程中形成的紫色甲赞溶解在每个孔150µl DMSO中。使用多孔板读数器在550nm处测量吸光度,以690nm为参考波长。相对于未处理的对照细胞或相应的溶剂对照(100%)计算代谢活性细胞的数量。[3]
瞬时受体电位香草酸1(TRPV1)是一种在人肺细胞中表达的钙选择性离子通道。我们发现,TRPV1细胞内亚群的激活会导致人支气管上皮细胞和肺泡细胞的内质网(ER)应激和细胞死亡。TRPV1激动剂(诺伐胺)治疗导致内质网钙释放,并以与原型内质网应激诱导剂相当的方式改变生长停滞和DNA损伤诱导转录物3(GADD153)、GADD45alpha、GRP78/BiP、ATF3、CCND1和CCNG2)的转录。TRPV1拮抗剂N-(4-叔丁基苄基)-N’-(1-[3-氟-4-(甲基磺酰氨基)-苯基]乙基)硫脲(LJO-328)抑制了mRNA反应和细胞毒性。EGTA和钌红抑制细胞表面TRPV1活性,但它们不能阻止ER应激基因反应或细胞毒性。细胞毒性与真核翻译起始因子2亚基1(EIF2alpha)磷酸化和GADD153 mRNA和蛋白质的诱导平行。GADD153的瞬时过表达导致细胞死亡,与激动剂治疗无关,选择稳定过表达GADD153显性阴性突变体的细胞表现出敏感性降低。Salubrinal是一种通过EIF2alphaK3/EIF2alpha途径抑制ER应激诱导的细胞毒性的抑制剂,或者EIF2alpha-S52A显性负突变体的稳定过表达也抑制了细胞死亡。用TRPV1激动剂治疗TRPV1缺失的人胚胎肾293细胞系不会引发ER应激反应。同样,诺伐胺的非活性类似物n-苄基壬酰胺未能引起ER钙释放、GADD153表达增加和细胞毒性。我们得出结论,通过EIF2alphaK3/EIF2alpha途径激活ER结合的TRPV1和刺激GADD153表达是细胞渗透性TRPV1激动剂细胞毒性的常见机制。这些发现在肺部炎症性疾病的背景下具有重要意义,其中内源性TRPV1激动剂的浓度升高可能会产生足够的量,导致TRPV1激活和肺细胞死亡。[2] 红辣椒及其主要刺激性成分辣椒素(CAP)已被证明是一种有效的抗肥胖药物,通过减少能量摄入、增强能量代谢、降低血清三酰甘油含量,并通过激活瞬时受体电位阳离子通道亚家族V成员1(TRPV1)抑制脂肪生成。然而,CAP与TRPV1受体的结合也是其刺激性感觉的原因,强烈限制了其饮食摄入。在这里,研究了一种刺激性较小的结构CAP类似物诺伐胺对3T3-L1细胞脂肪生成的影响及其潜在机制。发现Nonivamide可以减少平均脂质积累,这是脂肪生成的标志,与CAP的程度相似,高达10.4%(P<0.001)。用特异性抑制剂反式叔丁基环己醇阻断TRPV1受体表明,诺伐胺的抗脂肪生成活性与CAP一样,取决于TRPV1接收器的激活。此外,在脂肪生成过程中用诺伐胺处理的细胞中,促脂肪生成转录因子过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ(PPARγ)的蛋白质水平降低。miRNA微阵列和数字液滴PCR分析的结果表明,miRNA mmu-let-7d-5p的表达增加,这与PPARγ水平降低有关[3]。 |
| 动物实验 |
Male Sprague–Dawley rats (150–180 g) were were housed under a 12-h dark/light cycle with a constant temperature (25 ± 1 °C). After a 1-week acclimation period, the rats were randomly divided into normal chow diet (NCD) and high-fat diet (HFD) groups. The control group received standard rat chow, with fat representing 19.79% of total calories. This group was further divided into three groups (n = 6 per group): NCD, NCD plus 1 mg PAVA per kilogram body weight (BW) (N + PAVA), and NCD plus 10 mg rosuvastatin per kilogram BW (N + RSV). The HFD rats were fed a HFD for 20 weeks, with fat representing 65.26% of total calories. The HFD rats were divided into three groups (n = 6 per group): HFD, HFD plus PAVA (H + PAVA), and HFD plus rosuvastatin (H + RSV). After 16 weeks, the H + PAVA and H + RSV groups received PAVA or RSV for the final 4 weeks of the experimental period. Nonivamide (purity ≥ 96%) was dissolved in 10% Tween 80 and 10% ethanol in 0.9% normal saline solution. Animals in the PAVA groups were injected with 1 mg PAVA/kg/day via subcutaneous injection. Rosuvastatin was freshly dissolved in 0.5% carboxymethyl cellulose and administered by gastric gavage at a dose of 10 mg/kg/day for 4 weeks.21 The rats in the NCD and HFD control groups received the same vehicle as the treatment groups. The selected dose of PAVA was based on the results of a preliminary study, and the RSV dose was based on previous reports in rats which demonstrated its potential to improve metabolic parameters.22,23 The body weight and food and water intake of rats were recorded weekly. Metabolic parameters and oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) were performed before and after the treatments. At the end of the study, the rats were euthanized and blood and liver tissue samples were collected for subsequent experiments.[4]
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Metabolism / Metabolites
Limited information is available on pharmacokinetics and metabolism of nonivamide. For the closely related [DB06774] and other capsaicinoids, gastrointestinal absorption is rapid and almost entirely complete in studies of rats (oral dose of about 10 to 15 mg/kg of combined capsaicin and dihydrocapsaicin) with about 85% of the dose being absorbed within 3 hours. Both substances undergo first-pass metabolism in the liver and partly metabolized at the site of absorption. Biological Half-Life About 7 minutes. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
mouse LD50 intraperitoneal 8 mg/kg Journal of Medicinal Chemistry., 36(2595), 1993
|
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
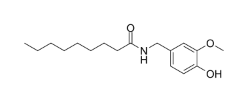
Nonivamide is a capsaicinoid that is the carboxamide resulting from the formal condensation of the amino group of 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylamine with the carboxy group of nonanoic acid. It is the active ingredient in many pepper sprays. It has a role as a lachrymator. It is a capsaicinoid and a member of phenols.
Nonivamide is found in herbs and spices. It is an alkaloid from the Capsicum species. The structures of [DB06774] and nonivamide differ only slightly with respect to the fatty acid moiety of the side chain (8-methyl nonenoic acid versus nonanoic acid). Nonivamide is a flavoring ingredient. Nonivamide is an organic compound and a capsaicinoid. It is an amide of pelargonic acid and vanillylamine. It is naturally found in chili peppers but manufactured to produce a synthetic form for various pharmacologic preparations. This drug has been studied in combination with Nicarboxil in the treatment of lower back pain. Nonivamide has also been studied for its anti-inflammatory properties, as well as in fat loss therapies and has demonstrated promising results,,,. Nonivamide has been reported in Capsicum annuum with data available. See also: Paprika (part of); Methyl salicylate; nonivamide (component of) ... View More ... Drug Indication Nonivamide is used as a topical analgesic and is also used as a flavoring ingredient,,. Mechanism of Action Nonivamide is a naturally occurring analog of [DB06774], isolated from peppers, described to produce effects similar to [DB06774]. It is an agonist of the VR1 (vanilloid/TRPV1 receptor). It serves as a transient agonist of these receptors, which are potentiated by pro-inflammatory drugs, a phenomenon that leads to thermal hyperalgesia, or increased heat sensation. Nonivamide has been shown to stimulate afferent neurons with about half the potency of [DB06774]. Agonism of the VR1 (TRPV1) (vanilloid) receptor by Nonivamide was demonstrated to induce the release of Ca2+ from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) of human lung cells, producing ER stress and cell death [MSDS]. Nonivamide, like other capsaicinoids, acts on the vanilloid receptors located in the peripheral afferent nerve fibers, providing short-acting irritant and algesic properties. Applied dermally, these substances act by stimulating sensitive chemoreceptors of the skin and by reflex, hyperemia and a local elevation in temperature. After repetitive administration, capsaicinoids have been reported to lead to desensitization to nociceptive stimuli possibly by long-acting depletion of peptide neurotransmitters (substance P) from peripheral sensory neurons. Capsaicinoids can modulate muscle tone (in bladder, bronchus etc.). Intravenous injection of nonivamide to rats (10 μg/kg) has been found to lead to bradycardia. The cardiovascular effects are partly explained by substance P release. Nonivamide given to rats subcutaneously (1 mg/kg) was found to cause body temperature decrease, vasodilatation, and increased salivation. Capsaicinoids have shown to illicit bronchospastic effects in guinea pigs. Capsaicin and its analogs were reported to increase barbiturate sleeping time in rats by interacting with hepatic metabolizing enzymes. Pharmacodynamics Relieves minor aches and pains of muscles and joints,. |
| 分子式 |
C18H27NO3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
305.4119
|
| 精确质量 |
293.199
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 66.43; H, 8.20; N, 4.56; O, 20.82
|
| CAS号 |
2444-46-4
|
| PubChem CID |
2998
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.0±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
450.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
54°C
|
| 闪点 |
226.2±31.5 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.2 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.509
|
| LogP |
4.38
|
| tPSA |
58.56
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
10
|
| 重原子数目 |
21
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
283
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
RGOVYLWUIBMPGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C17H27NO3/c1-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-17(20)18-13-14-10-11-15(19)16(12-14)21-2/h10-12,19H,3-9,13H2,1-2H3,(H,18,20)
|
| 化学名 |
N-[(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]nonanamide
|
| 别名 |
NONIVAMIDE; 2444-46-4; N-Vanillylnonanamide; Pseudocapsaicin; N-Vanillylnonamide; Pelargonic acid vanillylamide; N-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl)nonanamide; N-Vanillylpelargonamide;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~340.83 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.52 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.52 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.52 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2743 mL | 16.3714 mL | 32.7429 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6549 mL | 3.2743 mL | 6.5486 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3274 mL | 1.6371 mL | 3.2743 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。