| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
20alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (AKR1C1): AKR1C1 (Ki = 4 nM); AKR1C2 (Ki = 87 nM); AKR1C3 (Ki = 4.2 μM); AKR1C3 (Ki = 18.2 μM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在过度表达 AKR1C1 的 BAEC 中,AKR1C1-IN-1 可有效抑制孕酮代谢,IC50 为 460 nM [1]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
酶和活性测定[1]
重组AKR1C1、AKR1C2、AKR1C3和AKR1C4在大肠杆菌JM109中表达,并如前所述纯化至均一性。使用牛血清白蛋白作为标准品,通过双辛可宁酸蛋白质测定试剂盒测定蛋白质浓度。如前所述,通过测量25°C下NADPH荧光(在455 nm处,激发波长为340 nm)或吸光度(在340 nm处)的变化率来测定酶的NADP+连接的S-四氢萘脱氢酶活性。在抑制试验中,抑制剂的IC50值最初是使用软件ED50和分级反应版本1.2的IC50用S-四氢萘浓度(AKR1C1为0.1 mM,其他酶为1 mM)确定的。在抑制剂浓度(0-0.5×IC50)存在的情况下,使用五种底物浓度(AKR1C3为0.2-2×Km,其他酶为0.5-5×Km)将初始速度拟合到Lineweaver−Burk和Dixon图中,从而确定抑制模式。Ki值是通过使用ENZFITTER的适当程序计算的,并表示为至少三次测定的平均值±标准误差。 |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞中抑制剂的评价[1]
在37°C、5%CO2培养箱中,在添加了10%胎牛血清、青霉素(100 U/mL)和链霉素(100μg/mL)的Dulbecco改良Eagle培养基中培养BAEC。在所有实验中,细胞在第4-8代使用,使用前通过显微镜确认内皮鹅卵石形态。根据先前报道的方法构建具有AKR1C1 cDNA的表达载体。首先通过PCR从细菌表达载体pGEX/AKR1C1中扩增cDNA,使用由正向引物(5′-GAGTCGACGACgccaccATGGATTCGAAATATCAGTG-3′)和反向引物(5’-AGTCGACTTAATACATCAAAATGGA-3′)组成的引物对,其中SalI位点、Kozak序列和起始密码子分别以斜体、小写和下划线表示。通过自动DNA测序验证PCR产物,并在真核表达载体pGW1的SalI位点进行亚克隆。然后使用Lipofectamine 2000将带有插入物的表达载体转染到亚融合的BAEC中。将转染的细胞在含有2%胎牛血清的培养基中保持24小时,然后用于评估3,5-二溴水杨酸和化合物4和9对细胞中孕酮代谢的抑制作用。细胞在无血清生长培养基中用不同浓度的抑制剂预处理2小时,然后用30μM孕酮孵育6小时。通过离心收集培养基,用乙酸乙酯提取培养基的脂质部分两次。代谢物20α-羟基孕酮在LC-MS上使用Chiralcel OJ-H 5μm柱进行定量,如前所述。 |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. El-Kabbani O, et al. Structure-guided design, synthesis, and evaluation of salicylic acid-based inhibitors targeting a selectivity pocket in the active site of human 20alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (AKR1C1). J Med Chem. 2009 May 28;52(10):3259-64.
|
| 其他信息 |
The first design, synthesis, and evaluation of human 20alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (AKR1C1) inhibitors based on the recently published crystal structure of its ternary complex with inhibitor are reported. While the enzyme-inhibitor interactions observed in the crystal structure remain conserved with the newly designed inhibitors, the additional phenyl group of the most potent compound, 3-bromo-5-phenylsalicylic acid, targets a nonconserved hydrophobic pocket in the active site of AKR1C1 resulting in 21-fold improved potency (K(i) = 4 nM) over the structurally similar 3alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase isoform (AKR1C2). The compound is hydrogen bonded to Tyr55, His117, and His222, and the phenyl ring forms additional van der Waals interactions with residues Leu308, Phe311, and the nonconserved Leu54 (Val in AKR1C2). Additionally, the metabolism of progesterone in AKR1C1-overexpressed cells was potently inhibited by 3-bromo-5-phenylsalicylic acid, which was effective from 10 nM with an IC(50) value equal to 460 nM.[1]
In summary, the use of the recently determined crystal structure of AKR1C1 complexed with an inhibitor in conjunction with a GRID analysis of the inhibitor-binding site has allowed the design of a new salicylic acid-based inhibitor (compound 4) with improved potency (Ki = 4 nM) and selectivity (21-fold) over that of AKR1C2. Moreover, compound 4 significantly decreased the metabolism of progesterone in the cells with an IC50 value of 460 nM, which is comparable or superior to the IC50 values of the previously known two most potent inhibitors of AKR1C1, benzbromarone and 3′,3′′,5′,5′′-tetrabromophenolphthalein. Compound 4 was designed to target a selectivity pocket in the active site of AKR1C1 lined by the three apolar residues Leu54, Leu308, and Phe311. Leu308 is one of two nonconserved C-terminal residues (the other residue is Leu306) responsible for the greater than 4000-fold difference in inhibitor potency between AKR1C1 and the two isoforms AKR1C3 and AKR1C4. Since the active sites of AKR1C1 and AKR1C2 differ only by one amino acid residue, which is Leu54 in AKR1C1 and is Val54 in AKR1C2, and the current inhibitors show similar potency for the two enzymes, newly designed inhibitors that capture the maximum interactions with Leu54 in AKR1C1 are needed in order to improve their selectivity over AKR1C2. Thus, future developments of new derivatives of compound 4 are likely to improve on the selectivity of the currently known AKR1C1 inhibitors. We have also illustrated that while large chemical database searches are useful in discovering new enzyme inhibitors, the use of the high resolution crystal structure of an enzyme−inhibitor complex is an effective tool in optimizing the enzyme−inhibitor interaction by exploiting the small structural differences between the different enzyme isoforms.[1] |
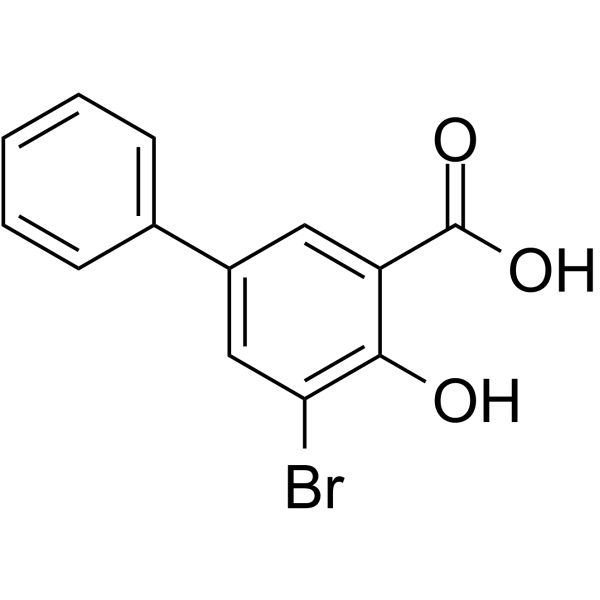
| 分子式 |
C13H9BRO3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
293.12
|
| 精确质量 |
291.974
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 53.27; H, 3.10; Br, 27.26; O, 16.37
|
| CAS号 |
4906-68-7
|
| PubChem CID |
268734
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as White to pink solids at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.6±0.0 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
439.2±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
219.4±0.0 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±0.0 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.663
|
| LogP |
4.43
|
| tPSA |
57.53
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
| 重原子数目 |
17
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
276
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
C1=CC=C(C=C1)C2=CC(=C(C(=C2)Br)O)C(=O)O
|
| InChi Key |
XVZSXNULHSIRCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C13H9BrO3/c14-11-7-9(8-4-2-1-3-5-8)6-10(12(11)15)13(16)17/h1-7,15H,(H,16,17)
|
| 化学名 |
3-bromo-2-hydroxy-5-phenylbenzoic acid
|
| 别名 |
NSC-109116; NSC 109116; NSC109116; 5-Bromo-4-hydroxy-[1,1'-biphenyl]-3-carboxylic acid; 3-Bromo-5-phenyl salicylic acid; AKR1C1-IN-1; 3-bromo-5-phenylsalicylic acid; 3-bromo-2-hydroxy-5-phenylbenzoic acid; NSC-109116; CHEMBL387536;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~341.17 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.53 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.53 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.53 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4116 mL | 17.0579 mL | 34.1157 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6823 mL | 3.4116 mL | 6.8231 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3412 mL | 1.7058 mL | 3.4116 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。