| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
PD1-PDL1 (IC50 = 6 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在三阴性乳腺癌 (TNBC) 中,PD-1/PD-L1 抑制剂 1 在较低浓度下会导致细胞活力减半,激活 MDA-MB-231 和 MCF7 中的 ERK,显着增加 MDA-MB 中 IL-8 的表达-231 和 HCC1806,并有效地将 MDA-MB-231 中的 IL-8 表达下调至一半水平。 [2]
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
NP19[[BMS-1的类似物]]在H22肝癌小鼠模型中的体内抗肿瘤活性[5]
受NP19对黑色素瘤B16-F10肿瘤模型的出色体内抗肿瘤疗效的鼓舞,以及PD-1/PD-L1抑制剂具有广谱抗肿瘤活性的事实,我们使用BALB/c小鼠H22肝癌模型进一步评估了化合物NP19的体内抗肿瘤功效。每只小鼠的右侧腹部皮下注射了80万个H22细胞。在肿瘤体积达到约100mm3后,将小鼠随机分组,通过腹膜内(i.p.)注射NP19或载体溶液治疗14天。如图8所示,NP19在25mg/kg剂量下表现出显著的体内抗肿瘤疗效,TGI为76.5%(图8A、8B、8C)。此外,NP19没有引起明显的体重减轻(图8D),表明该化合物具有良好的耐受性。 NP19[[BMS-1的类似物]]在B16-F10小鼠黑色素瘤模型中的体内抗肿瘤活性[5] 为了确定新合成化合物的体外抗PD-1/PD-L1活性是否可以转化为体内疗效,我们在小鼠黑色素瘤B16-F10肿瘤模型上测试了化合物NP19的抗肿瘤活性。由于与更有效的化合物NP2或同等有效的化合物NPT12相比,NP19易于合成且细胞毒性较小(表9),因此选择NP19进行体内疗效研究。我们用载体对照和NP19(25mg/kg、50mg/kg、100mg/kg)治疗携带黑色素瘤肿瘤的BALB/c小鼠,每天灌胃一次,持续15天。如图6所示,治疗15天后,NP19治疗后黑色素瘤肿瘤的生长受到显著抑制。 NP19的体内药代动力学特性[[BMS-1的类似物]][5] 由于化合物NP19在体外显示出高效力,接下来通过静脉和口服给药在雄性Sprague-Dawley大鼠中评估了药代动力学(PK)特征。表8总结了口服和静脉注射给药的关键PK参数。单次静脉注射1mg/kg化合物NP19后,NP19的半衰期(t1/2)、清除率(CL)和表观分布体积(Vss)分别为1.5±0.5h、0.9±0.2L/h/kg和2.1±0.5L/kg。当NP19以10mg/kg的剂量口服给药时,观察到口服吸收(Tmax=0.6±0.2小时)、长半衰期(t1/2=10.9±7.7小时)和口服生物利用度(F=5%)。此外,在大鼠身上没有观察到明显的不良反应。与静脉注射半衰期(1.5小时)相比,口服灌胃后NP19的半衰期(10.9小时)要长得多;这可能是由于NP19的高亲脂性(logP=7.9)或较差的水溶性。因此,NP19表现出触发器药代动力学。这种翻转药代动力学有时会发生在水溶性较差的化合物中,如雷巴匹德,由于水溶性差(7.6μg/mL),其t1/2(口服)/t1/2(静脉注射)比为13.5。另一个例子是李建明等人报道的亲脂性化合物IAT(一种水溶性为19μg/mL的抗结核药物),其t1/2(口服)/t1/2(静脉注射)比值约为5,与NP19[t1/2(p.o.)/t1/2(静脉注射液)=7.1]相似。由于化合物NP19的口服生物利用度较低,我们推测需要高剂量才能提供足够的药物浓度以显示抗肿瘤功效。因此,我们进一步研究了化合物NP19的体内活性。 当PD-1/PD-L1抑制剂1与解毒三根汤(JSD)联合使用时,PI3K/AKT信号通路显着抑制和逆转上皮间质转化(EMT)。 [3] |
| 酶活实验 |
体外PD-1/PD-L1结合试验[5]
使用PD-1/PD-L1均相时间分辨荧光(HTRF)结合分析研究了化合物抑制PD-1/PD-L1相互作用的能力。PD-1/PD-L1结合分析试剂盒购自Cisbio。实验根据说明书进行,说明书可在以下网址下载https://www.cisbio.com/usa/drug-discovery/human-pd1pd-l1-biochemical-interaction-assay. BMS最近披露了第一种针对PD-1/PD-L1途径的非肽小分子抑制剂,该抑制剂在均相时间分辨荧光(HTRF)结合分析中显示出活性;然而,没有提供进一步的数据来支持他们的活动 核磁共振测量[4] 通过在含有15NH4Cl作为唯一氮源的M9最低培养基中表达蛋白质,获得了均匀的15N标记。对于NMR测量,通过凝胶过滤将缓冲液交换至pH 7.4的PBS(PD-L1)或含有100 mM NaCl pH 6.4的25 mM磷酸钠(PD-1)。将10%(v/v)的D2O添加到样品中以提供锁定信号。使用Bruker Avance III 600 MHz光谱仪在300K下记录所有光谱。通过监测化合物滴定后1H-15N 2D HMQC中NMR共振化学位移的扰动来评估化合物与PD-L1的相互作用。使用拮抗剂诱导解离试验评估受试化合物解离PD-L1/PD-1的能力。简而言之,15N标记的PD-1(0.2 mM)与未标记的PD-L1略微过滴定。将化合物等分到所得混合物中。在实验期间,HMQC监测1H-15N信号。 PD1/PD-L1检查点测定[4] 在测定前24小时,将aAPC以每孔10000的密度接种在培养基中的白色96孔板中。在测定当天,在含有1%FBS的RPMI 1640中制备3.5倍系列稀释的抗体。在DMSO中制备BMS化合物[BMS-1]的系列稀释液,并在含有1%FBS的RPMI 1640中配制。通过这种方式,所有样品中DMSO的浓度保持恒定。从孔中取出95μl培养基,用40μl化合物稀释液覆盖细胞。将20000个EC加入到含有1%FBS的40μl RPMI 1640中的每个孔中。在37°C下孵育6小时后,将平板在室温下平衡10分钟,并向每个孔中加入80μl Bio-Glo试剂。孵育10分钟后,使用FlexStation 3定量发光。通过将Hill方程拟合到实验数据来确定半最大有效浓度(EC50)和最大发光值(RLUmax)。 PD-1/sPD-L1效应物测定[4] 为了评估BMS对可溶性PD-L1抑制T细胞的影响,在重组人sPD-L1存在的情况下,用抗CD3抗体刺激EC。为此,将96孔白色平底板在4°C下用5μg/ml的抗CD3抗体或PBS中的同种型对照溶液涂覆过夜。去除抗体溶液,用PBS洗涤板3次并干燥。在BMS化合物[BMS-1]或相应体积的DMSO存在下,将sPD-L1(aa 18-134)在补充有青霉素/链霉素溶液(每种终浓度为100 U/ml)的PBS中稀释。然后,将15μl溶液加入抗体包被板的每个孔中。将EC离心并稀释至每毫升50000,并向每个孔中加入60μl细胞溶液。sPD-L1的终浓度为10μg/ml(0.6μM)。BMS化合物[BMS-1]的最终浓度为:0.12、0.3、1.2和3μM,得出以下BMS:sPD-L1摩尔比:1:5、1:2、2:1和5:1。将细胞培养24小时,并根据制造商的说明使用Bio-Glo萤光素酶测定系统进行萤光素酶活性测定。 |
| 细胞实验 |
MTS 测定测定细胞增殖。在 96 孔板的每个孔中,将 1-2×103 个细胞置于 100 μl 培养基中。 24小时后,将PD-1/PD-L1抑制剂1和ERK1/2抑制剂作为单一或联合治疗一式三份添加到测试培养基(含有1%胎牛血清的DMEM)中72小时,稀释至所需浓度。
细胞系[4] 为了验证BMS化合物[BMS-1]在抑制PD-1/PD-L1相互作用方面的效力,使用了基于细胞的PD-1/PD-L1免疫检查点阻断模型。在该试验中,使用了两种模型细胞系:过表达TCR配体和PD-L1的人工抗原呈递细胞(PD-L1+aAPC/CHO-K1细胞,称为aAPC),以及T细胞替代物,一种过表达PD-1并在NFAT启动子控制下携带萤光素酶报告子的改良Jurkat T细胞系(PD-1效应细胞,称称为EC)。细胞购自Promega,在添加了10%胎牛血清、100 U/ml青霉素和100 U/ml链霉素的RPMI 1640培养基中培养。此外,细胞在潮霉素B(50μg/ml)和G418(250μg/ml)的持续存在下增殖,以提供引入的遗传构建体的稳定表达。实验中省略了后两种抗生素。通过流式细胞术(未显示)验证EC上PD-1和aAPC上PD-L1的过表达,并通过监测抗CD3抗体刺激后的萤光素酶活性来验证萤光素酶表达基因的存在。抗生素选择、流式细胞术和报告基因表达作为细胞系鉴定方法。定期检测细胞,使用基于PCR的方法发现支原体污染呈阴性。 细胞毒性试验[4] 将5000个EC接种在透明的96孔板上,并在浓度逐渐增加的BMS化合物[BMS-1]或DMSO作为对照的情况下培养48小时(DMSO的浓度在所有样品中保持恒定)。治疗后,根据制造商的说明,使用Biolog Redox Dye Mix MB进行代谢活性测试。 流式细胞术测量[4] 通过流式细胞术评估sPD-L1(aa 18-134)与EC的结合。His标记的PD-L1蛋白或其突变体在22°C下以8:1的摩尔比(蛋白:染料)用NTA Atto 647 N荧光染料染色2小时。PD-L1-Atto与受试化合物或抗体在150μl PBS中配制。样品在4°C的黑暗中孵育30分钟。同时,将EC离心,用PBS洗涤,悬浮在浓度为1×106个细胞/ml的新鲜PBS中。向每个样品中加入50μl EC,并在冰上再孵育60分钟。成分的最终浓度为:25μg/ml PD-L1(1.5μM),125μg/ml抗PD-L1抗体和对照抗体以及1μM BMS化合物[BMS-1]。使用BD FACS Verse流式细胞仪和BD FACSuite v1.0.6软件对样本进行分析。 |
| 动物实验 |
Pharmacokinetic Study in Male Sprague–Dawley Rats[5]
Male Sprague–Dawley rats (200–220 g) were used to study the pharmacokinetics of compound NP19 [an analog of BMS-1]. Diet was prohibited for 12 h before the experiment, but water was freely available. Blood samples (0.3 mL) were collected from the tail vein into heparinized 1.5 mL polythene tubes at 0.0833, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, and 24 h after oral (10 mg/kg) or intravenous (1 mg/kg) administration of compound NP19. The compound was dissolved in 5% DMSO and 95% PEG-300 for intravenous administration or suspended in 0.5% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC-Na) for oral administration. The samples were immediately centrifuged at 3000g for 10 min. The plasma as-obtained (100 μL) was stored at −20 °C until analysis. PK parameters were determined from individual animal data using noncompartmental analysis in DAS (Drug and statistics) software. Instruments and analytical conditions for PK studies: A UPLC-MS/MS system with ACQUITY I-Class UPLC and a XEVO TQD triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (Waters Corp., Milford, MA, USA), equipped with an electrospray ionization (ESI) interface, was used to analyze the blood samples. The UPLC system was comprised of a Binary Solvent Manager (BSM) and a Sample Manager with Flow-Through Needle (SM-FTN). Masslynx 4.1 software (Waters Corp.) was used for data acquisition and instrument control. Multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) modes of m/z 555.35 → 181.03 for NP19 and m/z 237 → 194.1 for carbamazepine were utilized to conduct quantitative analysis. In Vivo Efficacy Study in Mouse B16F10 Melanoma Model[5] BALB/c mice, aged 6–8 weeks old, were used to study the inhibition effect of NP19 [an analog of BMS-1]on subcutaneous transplanted model of melanoma cells. Murine B16F10 melanoma cells growing in a logarithmic growth phase were suspended in PBS at a density of 2 × 106 per mL. Each mouse was inoculated subcutaneously with 200 μL containing 4 × 105 cells. After tumors reached approximately 100 mm3 in volume, mice were divided into four groups randomly (n = 10) and treated with NP19 (25, 50, 100 mg/kg) and vehicle, respectively. The drugs were administered via intragastric gavage once a day for 15 days. The vehicle group was administered with 0.5% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC-Na). Animal activity and body weight were monitored during the entire experiment period to assess acute toxicity. Mice were sacrificed 16 days after the initiation of the treatment, and the tumor tissue and major organ (liver, spleen, thymus, and kidney) samples were collected. The harvested tumor tissue and organs (liver, kidney) were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, processed into paraffin routinely, stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), and captured by microscope. Tumor growth inhibition value (TGI) was calculated using the formula: TGI(%) = [1 – Wt/Wv] × 100%, where Wt and Wv are the mean tumor weight of treatment group and vehicle control. In Vivo Efficacy Study in Mouse H22 Hepatoma Tumor Model[5] 6–8 weeks old male BALB/c mice were used. A total of 8 × 105 H22 cells were inoculated into the right flank of each mouse according to protocols of tumor transplant research. NP19 [an analog of BMS-1]was dissolved in 5% DMSO, 40% PEG-200 and 55% saline solution to produce desired concentrations. Mice in control groups were injected intraperitoneally with 200 μL of vehicle solution only. Tumor volume was measured every 2 days with a traceable electronic digital caliper and calculated using the formula a × b2 × 0.5, where a and b represented the larger and smaller diameters, respectively. The mice were sacrificed after the treatments and tumors were excised and weighed. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Purpose
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is characterized by an unfavorable prognosis and missing systemic therapeutic approaches beside chemotherapy. Targeting the immune checkpoint PD-1/PD-L1 showed promising results in breast cancer and especially in TNBC. The extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) is an important driver of carcinogenesis. Here, the effect of combined PD-1/PD-L1 and ERK1/2 inhibitor treatment is investigated of cell growth and intracellular impact of breast cancer cell lines.
Methods
The IC50 values of each inhibitor and the effect of combined treatment were determined in three TNBC cell lines of different subtypes and one non-TNBC cell line. Phospho-specific antibodies were used in western blot analyses to investigate an effect on ERK1/2 activation. Expressions of immune modulatory and cell cycle-associated genes were examined by quantitative reverse transcription PCR.
Results
Both inhibitors PD-1/PD-L1 and ERK1/2 impeded the proliferation of TNBC to a higher extent than of non-TNBC. By combined treatment, cell lines were inhibited either synergistically or additively. ERK1/2 and S6 phosphorylation were reduced and expressions of c-Fos and FosL were diminished after ERK1/2 inhibitor as single and combined treatment. Between genes involved in immune modulation, IL-8 was upregulated in TNBC cells after combined treatment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, combination of PD-1/PD-L1 and ERK1/2 inhibitors showed favorable effects for a new therapy strategy, with better results in TNBC cell lines than in non-TNBC cells. The effects have to be validated in models that can reflect the interaction between immune and tumor cells like the situation in the tumor micro-environment.[2]
Intraluminal bacteria, food intake, and bile play important roles in indomethacin-induced small intestinal inflammation in rats. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) and ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) inhibit hydrophobic bile acid-induced damage in various types of cells. We investigated the effects of these bile acids along with the possible influence of other bile acids on this model of inflammation. Clinical and intestinal inflammatory parameters and bile secretion were assessed after 7-day dietary bile acid pretreatments and subsequent indomethacin injections. UDCA significantly enhanced indomethacin-associated reductions in food intake and body weight, increases in gross inflammatory scores and myeloperoxidase activity, and the shortening of small intestinal length. Taurochenodeoxycholic acid (TCDCA) significantly normalized the clinical inflammatory parameters, prevented indomethacin-induced increases in the biliary contents of secondary bile acids and hydrophobicity index, and tended to attenuate the intestinal inflammation. Although elevated biliary levels of muricholic acids and a decreased hydrophobicity index were evident before indomethacin injection in the TCDCA case, these alterations could not explain the TCDCA-mediated protection. Dietary TCDCA attenuates whereas UDCA exacerbates intestinal inflammation in this model. Alterations in the bile composition (increases in UDCA and chenodeoxycholic acid) may explain the observed modification effects.[3] |
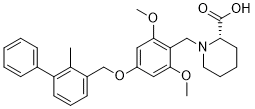
| 分子式 |
C29H33NO5
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
475.58
|
|
| 精确质量 |
475.235
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 73.24; H, 6.99; N, 2.95; O, 16.82
|
|
| CAS号 |
1675201-83-8
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
91663303
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white crystalline solid
|
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
630.2±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
334.9±31.5 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.9 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.590
|
|
| LogP |
5.18
|
|
| tPSA |
68.2
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
9
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
35
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
639
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
O([H])C([C@]1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N1C([H])([H])C1C(=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1OC([H])([H])[H])OC([H])([H])C1C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C(C2C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C=2[H])C=1C([H])([H])[H])OC([H])([H])[H])=O
|
|
| InChi Key |
ZBOYJODMIAUJHH-SANMLTNESA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C29H33NO5/c1-20-22(12-9-13-24(20)21-10-5-4-6-11-21)19-35-23-16-27(33-2)25(28(17-23)34-3)18-30-15-8-7-14-26(30)29(31)32/h4-6,9-13,16-17,26H,7-8,14-15,18-19H2,1-3H3,(H,31,32)/t26-/m0/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
(2S)-1-[[2,6-dimethoxy-4-[(2-methyl-3-phenylphenyl)methoxy]phenyl]methyl]piperidine-2-carboxylic acid
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 1 mg/mL (2.10 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 10.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 1 mg/mL (2.10 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 10.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 1 mg/mL (2.10 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 10 mg/mL (21.03 mM) in 50% PEG300 50% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1027 mL | 10.5135 mL | 21.0270 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4205 mL | 2.1027 mL | 4.2054 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2103 mL | 1.0513 mL | 2.1027 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。