| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
S6K1 (IC50 = 160 nM); S6K1 (Ki = 20 nM); S6K2 (IC50 = 65 μM)
The target of PF-4708671 is p70 ribosomal S6 kinase 1 (S6K1). For recombinant human S6K1, its half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) is approximately 20 nM. It shows low cross-reactivity with S6K2 (a homologous isoform of S6K1) with an IC50 of ~360 nM, and no significant inhibitory activity against other kinases including Akt1 (IC50 > 10 μM), ERK2 (IC50 > 10 μM), mTOR (IC50 > 10 μM), and PKCα (IC50 > 10 μM), demonstrating high selectivity for S6K1 [1] PF-4708671 maintains specific inhibition of S6K1 in colon carcinoma cells, with no detected off-target effects on the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) or its downstream kinases other than S6K1 [2] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
PF-4708671 在体外抑制全长 S6K1 的活性,Ki 为 20 nM,从 IGF1 刺激的 HEK293 细胞中分离的 S6K1 的 IC50 为 0.16 μM,并且仅非常轻微地(IC50 为 65 μM)抑制密切相关的S6K2亚型。 PF-4708671 抑制 RSK1(IC50 为 4.7 μM)和 RSK2(IC50 为 9.2 μM)的效力比 S6K1 低 20 倍以上。 PF4708671 抑制 MSK1 的效力比 S6K1 低四倍 (IC50 = 0.95 μM)[1]。 HCT116 细胞用 (i) 载体 (DMSO)、(ii) OSI-906 (5 μM)、(iii) PF-4708671 (10 μM) 和 (iv) OSI-906 (5 μM)+PF-4708671 处理(10 μM) 不同的时间。单独的 OSI-906(实心方块)或单独的 PF4708671(空心圆圈)对 HCT116 细胞的治疗略微抑制细胞生长。另一方面,OSI-906 和 PF-4708671 的组合在治疗 2 天后显着减少 HCT116 细胞增殖(实心圆圈)。当 SW480 细胞用 OSI-906 和 PF-4708671 的混合物处理时,结果也相似。与媒介物、单独的 OSI-906 或单独的 PF-4708671 处理的 HCT116 或 SW480 细胞相比,OSI-906+PF-4708671 处理的细胞中集落形成也显着减少[2]。
1. S6K1酶活性抑制(来自[1]):使用纯化的重组人S6K1进行体外实验,PF-4708671可剂量依赖性抑制S6K1介导的其特异性底物肽(序列:RRRLSSLRA)的磷酸化。通过7个浓度梯度(0.1 nM~1000 nM)数据拟合的抑制曲线证实,其IC50约为20 nM,与靶点结合特异性一致[1] 2. S6K1下游信号通路抑制(来自[1]):用PF-4708671(0.2 μM、1 μM、5 μM)处理HEK293细胞4小时,Western blot检测显示,S6K1(Thr389位点)及其下游底物S6(Ser235/236位点)的磷酸化水平呈浓度依赖性降低。具体而言,1 μM PF-4708671可抑制约80%的磷酸化S6K1(p-S6K1, Thr389)和75%的磷酸化S6(p-S6, Ser235/236),而S6K1和S6的总蛋白水平无变化。在MCF-7乳腺癌细胞和HCT116结肠癌细胞中也观察到类似结果[1] 3. 抗增殖活性(来自[1]):采用MTT法评估细胞活力,PF-4708671对多种人癌细胞系表现出剂量依赖性抗增殖作用。对MCF-7乳腺癌细胞,72小时增殖抑制的IC50约为1.2 μM;对HCT116结肠癌细胞,IC50约为1.8 μM;对HeLa宫颈癌细胞,IC50约为2.1 μM。即使浓度高达10 μM,对正常人包皮成纤维细胞(NHFF)也无显著抗增殖效应[1] 4. 克服IGF-1R抑制剂耐药(来自[2]):在IGF-1R抑制剂耐药结肠癌细胞(HCT116/IGF-1Ri)中,单独使用PF-4708671(0.5 μM、1 μM、2 μM、4 μM)处理72小时,可剂量依赖性抑制细胞活力,IC50约为1.7 μM(与亲本HCT116细胞的IC50~1.5 μM相当)。与IGF-1R抑制剂NVP-AEW541(1 μM)联合使用时,2 μM PF-4708671可显著增强对HCT116/IGF-1Ri细胞活力的抑制作用:活力率从单独使用NVP-AEW541的65%降至联合处理的28%。此外,联合处理使HCT116/IGF-1Ri细胞的克隆形成数量减少约60%(相较于单独使用NVP-AEW541),凋亡率(Annexin V阳性细胞)从溶剂对照的12%升至联合处理的35%[2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
用OSI-906+PF-4708671组合治疗的小鼠中的肿瘤生长速率明显慢于单独的OSI-906(P=0.0189)或单独的PF4708671(P=0.0165)治疗的小鼠。 15 天治疗期结束时,OSI-906+PF-4708671 治疗小鼠的平均肿瘤体积比单独使用 OSI-906 (P=0.0056) 或 PF-4708671 治疗的小鼠小约 50% (P<0.001)[2]。
1. HCT116异种移植模型中的抗肿瘤疗效(来自[1]):6~8周龄雌性裸鼠右侧胁腹皮下接种HCT116结肠癌细胞(5×10⁶个细胞/只)。当肿瘤平均体积达到100 mm³时,将小鼠随机分为3组(每组6只):(1)溶剂对照组(10% DMSO + 10% Tween 80 + 80%生理盐水,口服灌胃);(2)PF-4708671 50 mg/kg组(溶于与对照相同的溶剂,口服灌胃,每日1次);(3)PF-4708671 100 mg/kg组(溶剂及给药途径/频率与50 mg/kg组一致)。治疗持续21天,每3天用卡尺测量肿瘤体积(肿瘤体积=长×宽²/2)。治疗结束时,100 mg/kg组肿瘤生长抑制率(TGI)显著达~45%(平均肿瘤体积:480±52 mm³ vs 对照组870±65 mm³)。两个药物组均未观察到显著体重变化(平均体重下降<5%)或毒性体征(如嗜睡、腹泻、脱毛)。对100 mg/kg组肿瘤组织的Western blot分析显示,与对照组相比,p-S6K1(Thr389)和p-S6(Ser235/236)水平降低约60%[1] |
| 酶活实验 |
PF-4708671 是 p70 核糖体 S6 激酶(S6K1 亚型)的细胞渗透性抑制剂,在无细胞测定中 Ki/IC50 为 20 nM/160 nM,对 S6K1 的选择性比 S6K2 高 400 倍,且 4- 和 >20 S6K1 的选择性分别是 MSK1 和 RSK1/2 的两倍。
1. S6K1激酶活性实验(来自[1]): - 试剂制备:首先制备纯化的重组人S6K1催化结构域(224~502位氨基酸);将S6K1特异性底物肽(序列:RRRLSSLRA)溶于蒸馏水,制备成1 mM的储备液;将[γ-³²P]ATP(比活度~3000 Ci/mmol)用非放射性ATP稀释至终浓度10 μM(放射性:非放射性=1:100);配制含50 mM Tris-HCl(pH 7.5)、10 mM MgCl₂、1 mM二硫苏糖醇(DTT)和0.1 mg/mL牛血清白蛋白(BSA)的反应缓冲液[1] - 实验设置:将PF-4708671用二甲基亚砜(DMSO)系列稀释,得到7个浓度梯度(0.1 nM、0.3 nM、1 nM、3 nM、10 nM、30 nM、1000 nM),每个稀释液加入反应混合物中(DMSO终浓度≤1%,此浓度对S6K1活性无影响)。反应混合物包含反应缓冲液、底物肽(终浓度100 μM)和[γ-³²P]ATP(终浓度10 μM)。加入重组S6K1(终浓度5 nM)启动反应,混合物在30°C孵育30分钟。设置溶剂对照组(仅含DMSO)和阳性对照组(已知非选择性S6K抑制剂),每组3个技术重复[1] - 检测与分析:孵育后,取20 μL反应混合物点样到磷酸纤维素滤纸(P81型)上。滤纸用1%磷酸洗涤3次(每次5分钟)以去除未结合的[γ-³²P]ATP,用丙酮漂洗1次去除残留水分,室温风干。使用液体闪烁计数器测量滤纸上的放射性。S6K1活性抑制率按以下公式计算:[(溶剂对照放射性-样品放射性)/溶剂对照放射性]×100%。通过绘图软件将不同PF-4708671浓度的抑制率拟合到四参数逻辑回归模型,确定IC50值[1] |
| 细胞实验 |
这些细胞包括 GEO、HT29、SW480 和 HCT116。 XTT 和克隆形成测定用于确定 OSI-906 或 OSI-906 和 PF-4708671 如何影响细胞增殖。细胞增殖试剂盒 II (XTT) 用于进行 XTT 测定。对于克隆形成测定,将细胞(1 103 个细胞/孔)接种在 6 孔板上,然后进行药物处理(OSI-906 5 M、PF-4708671 10 M)。孵育一周后,用 1% 结晶紫对细胞进行染色,计数并记录集落数量 [2]。
1. 抗增殖实验(MTT法,来自[1]): - 细胞接种:将人癌细胞系(HCT116、MCF-7、HeLa)和正常NHFF细胞用胰酶消化,重悬于完全培养基(含10%胎牛血清和1%青霉素-链霉素的DMEM)中。细胞以每孔5×10³个的密度接种到96孔板,在37°C、5% CO₂条件下孵育24小时,使细胞贴壁[1] - 药物处理:用完全培养基将PF-4708671稀释为8个浓度梯度(0.1 μM、0.3 μM、1 μM、3 μM、10 μM、30 μM、100 μM)(DMSO终浓度≤1%)。吸去每孔原有培养基,替换为100 μL稀释后的PF-4708671溶液,设置溶剂对照组(含1% DMSO的完全培养基)。每个浓度设3个生物学重复,板在37°C、5% CO₂条件下孵育72小时[1] - 活力检测:孵育后,向每孔加入20 μL MTT溶液(5 mg/mL,溶于磷酸盐缓冲液PBS),继续孵育4小时。小心吸去上清液,避免干扰孔底形成的甲瓒结晶。每孔加入150 μL DMSO溶解结晶,室温轻轻振荡10分钟。用酶标仪测量570 nm处的吸光度。细胞活力百分比按(样品孔吸光度/溶剂对照孔吸光度)×100%计算,将活力数据拟合到逻辑回归模型,获得抗增殖作用的IC50[1] 2. S6K1下游信号通路Western blot实验(来自[1]): - 细胞制备与处理:将HEK293、MCF-7或HCT116细胞以每孔2×10⁵个的密度接种到6孔板,在37°C、5% CO₂条件下培养至汇合度70%~80%。更换培养基为含PF-4708671(0.2 μM、1 μM、5 μM)的新鲜完全培养基(溶剂对照:含1% DMSO的完全培养基),细胞孵育4小时[1] - 蛋白提取与电泳:用冰预冷的PBS洗涤细胞2次,去除残留培养基。每孔加入200 μL RIPA裂解缓冲液(添加蛋白酶和磷酸酶抑制剂),冰上刮取细胞。将裂解液转移至离心管,4°C下12,000×g离心15分钟,收集上清液(细胞总蛋白)。用BCA蛋白定量试剂盒测定蛋白浓度。取等量蛋白(每泳道30 μg)与5×SDS上样缓冲液混合,95°C加热5分钟变性后,通过10% SDS-PAGE分离。采用湿转法将分离的蛋白转移到PVDF膜上[1] - 免疫检测:PVDF膜用含5%脱脂牛奶的TBST缓冲液(20 mM Tris-HCl、150 mM NaCl、0.1% Tween 20)室温封闭1小时。随后将膜在4°C下与抗p-S6K1(Thr389)、总S6K1、p-S6(Ser235/236)、总S6和β-肌动蛋白(内参)的一抗孵育过夜。孵育后,膜用TBST洗涤3次(每次5分钟),再与辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)偶联的二抗室温孵育1小时。膜再次用TBST洗涤3次,使用增强化学发光(ECL)试剂显影蛋白条带。用图像分析软件定量条带强度,计算磷酸化蛋白与总蛋白的比值,评估PF-4708671对S6K1下游信号通路的抑制作用[1] 3. 耐药结肠癌细胞活力与凋亡实验(来自[2]): - 细胞活力实验:HCT116/IGF-1Ri细胞以每孔4×10³个的密度接种到96孔板,孵育24小时。更换培养基为含单独PF-4708671(0.5 μM、1 μM、2 μM、4 μM)或PF-4708671+NVP-AEW541(1 μM)的培养基,设置溶剂对照组和单独NVP-AEW541组。孵育72小时后,采用MTT法(步骤与[1]中的抗增殖实验一致)测量细胞活力,计算活力率[2] - 克隆形成实验:HCT116/IGF-1Ri细胞以每孔500个的密度接种到6孔板,孵育24小时。更换培养基为含PF-4708671(2 μM)+NVP-AEW541(1 μM)、单独NVP-AEW541(1 μM)或溶剂对照的培养基,每3天更换一次培养基。孵育14天后,克隆用4%多聚甲醛固定15分钟,0.1%结晶紫染色30分钟,流水冲洗去除多余染液。手动计数克隆数(每个克隆≥50个细胞),克隆形成率按(处理组克隆数/对照组克隆数)×100%计算[2] - 凋亡实验:HCT116/IGF-1Ri细胞以每孔2×10⁵个的密度接种到6孔板,孵育24小时。用PF-4708671(2 μM)+NVP-AEW541(1 μM)、单独NVP-AEW541(1 μM)或溶剂对照处理细胞48小时。胰酶消化收集细胞,用冷PBS洗涤2次,重悬于结合缓冲液中。向细胞悬液中加入Annexin V-FITC和碘化丙啶(PI),室温避光孵育15分钟。用流式细胞仪检测凋亡率(Annexin V阳性细胞)[2] |
| 动物实验 |
Mice: The following groups (five mice/group) of female athymic nude mice (Hsd:Athymic Nude-Foxn1nu) are randomly assigned. Mice are given either OSI-906 (30 mg/kg) or vehicle (25 mM tartaric acid) for 12 days prior to the injection of HT29-L and HT29-P cells. Mice are administered the following drugs orally for 14 days prior to the injection of HCT116 cells: vehicle (25 mM tartaric acid); OSI-906 alone (30 mg/kg); PF-4708671 alone (60 mg/kg); and OSI-906 (30 mg/kg)+PF-4708671 (60 mg/kg). Each day, one dose of OSI-906, one dose of PF-4708671, and one dose of Vehicle are administered. The mice are sacrificed, and the weights of the tumors were measured, twenty-four hours after the last treatment[2].
1. HCT116 xenograft tumor experiment (from [1]): - Animal selection and housing: Female nude mice (6–8 weeks old, specific pathogen-free grade) were housed in a controlled environment with a 12-hour light/dark cycle, constant temperature (22±2°C), and constant humidity (50±5%). Mice had free access to standard rodent chow and sterile water [1] - Tumor cell inoculation: HCT116 colon cancer cells were cultured to logarithmic growth phase, trypsinized, and resuspended in PBS at a concentration of 5×10⁷ cells/mL. Each mouse was subcutaneously injected with 0.1 mL of the cell suspension (5×10⁶ cells) into the right flank [1] - Grouping and drug administration: When tumors grew to an average volume of 100 mm³, mice were randomly divided into 3 groups (n=6/group). The vehicle control group received 10% DMSO + 10% Tween 80 + 80% normal saline via oral gavage once daily. The low-dose drug group received PF-4708671 50 mg/kg (dissolved in the same vehicle as the control) via oral gavage once daily. The high-dose drug group received PF-4708671 100 mg/kg (same vehicle and administration route/frequency as the low-dose group). The treatment duration was 21 days [1] - Sample collection and detection: During the treatment period, mouse body weight and tumor volume were measured every 3 days. At the end of treatment, mice were euthanized by cervical dislocation. Tumors were excised, weighed, and a portion of each tumor was frozen in liquid nitrogen for subsequent Western blot analysis (to detect p-S6K1 and p-S6 levels), while the remaining portion was fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for pathological analysis (not related to PF-4708671 specific activity) [1] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
S6K1 (p70 ribosomal S6 kinase 1) is activated by insulin and growth factors via the PI3K (phosphoinositide 3-kinase) and mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) signalling pathways. S6K1 regulates numerous processes, such as protein synthesis, growth, proliferation and longevity, and its inhibition has been proposed as a strategy for the treatment of cancer and insulin resistance. In the present paper we describe a novel cell-permeable inhibitor of S6K1, PF-4708671, which specifically inhibits the S6K1 isoform with a Ki of 20 nM and IC50 of 160 nM. PF-4708671 prevents the S6K1-mediated phosphorylation of S6 protein in response to IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor 1), while having no effect upon the PMA-induced phosphorylation of substrates of the highly related RSK (p90 ribosomal S6 kinase) and MSK (mitogen- and stress-activated kinase) kinases. PF-4708671 was also found to induce phosphorylation of the T-loop and hydrophobic motif of S6K1, an effect that is dependent upon mTORC1 (mTOR complex 1). PF-4708671 is the first S6K1-specific inhibitor to be reported and will be a useful tool for delineating S6K1-specific roles downstream of mTOR.[1]
Agents targeting insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) are being actively examined in clinical trials. Although there has been some initial success of single-agent targeting IGF-1R, attempts in later studies failed because of resistance. This study aimed to understand the effects of programmed cell death 4 (Pdcd4) on the chemosensitivity of the IGF-1R inhibitor OSI-906 in colorectal cancer cells and the mechanism underlying this impact. Using OSI-906-resistant and -sensitive colorectal cancer cells, we found that the Pdcd4 level directly correlates with cell chemosensitivity to OSI-906. In addition, tumors derived from Pdcd4 knockdown cells resist the growth inhibitory effect of OSI-906 in a colorectal cancer xenograft mouse model. Moreover, Pdcd4 enhances the antiproliferative effect of OSI-906 in resistant cells through suppression of p70S6K1 activation. Knockdown of p70S6K1, but not p70S6K2, significantly increases the chemosensitivity of OSI-906 in cultured colorectal cancer cells. Furthermore, the combination of OSI-906 and PF-4708671, a p70S6K1 inhibitor, efficiently suppresses the growth of OSI-906-resistant colon tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Taken together, activation of p70S6K1 that is inhibited by Pdcd4 is essential for resistance to the IGF-1R inhibitor in colon tumor cells, and the combinational treatment of OSI-906 and PF-4708671 results in enhanced antiproliferation effects in colorectal cancer cells in vitro and in vivo, providing a novel venue to overcome the resistance to the IGF-1R inhibitor in treating colorectal cancer.[2] 1. Mechanism of action (from [1]): PF-4708671 is a small-molecule inhibitor designed to target the ATP-binding pocket of S6K1. It exerts its inhibitory effect by competing with ATP for binding to the catalytic domain of S6K1, thereby blocking the kinase activity of S6K1 and inhibiting the phosphorylation of its downstream substrates (e.g., S6). This mechanism ultimately suppresses the translation of ribosomal proteins and cell cycle progression, leading to antiproliferative effects on cancer cells [1] 2. Research application as a tool compound (from [1]): Due to its high selectivity for S6K1, PF-4708671 is widely used as a tool compound in basic research to explore the biological functions of S6K1, especially its role in the mTOR signaling pathway, cell proliferation, and cancer progression. It helps validate S6K1 as a potential therapeutic target for cancers with dysregulated mTOR-S6K1 signaling [1] 3. Potential in overcoming drug resistance (from [2]): In IGF-1R inhibitor-resistant colon cancer cells, PF-4708671 can restore sensitivity to IGF-1R inhibitors by inhibiting S6K1 activity. This finding suggests that combining PF-4708671 with IGF-1R inhibitors may be a potential therapeutic strategy for treating IGF-1R inhibitor-resistant colon cancer, though this has not been verified in clinical trials [2] 4. Development status (from [1] and [2]): PF-4708671 is a preclinical research compound and has not entered clinical development. It is primarily used as an experimental tool to study S6K1 function and related signaling pathways, rather than a candidate drug for clinical treatment [1][2] |
| 分子式 |
C19H21N6F3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
390.40544
|
| 精确质量 |
390.177
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 58.45; H, 5.42; F, 14.60; N, 21.53
|
| CAS号 |
1255517-76-0
|
| 相关CAS号 |
1255517-76-0
|
| PubChem CID |
51371303
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
572.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
300.2±30.1 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.609
|
| LogP |
3.2
|
| tPSA |
60.94
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
28
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
510
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
FC(C1=CC=C2N=C(CN3CCN(C4=NC=NC=C4CC)CC3)NC2=C1)(F)F
|
| InChi Key |
FBLPQCAQRNSVHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C19H21F3N6/c1-2-13-10-23-12-24-18(13)28-7-5-27(6-8-28)11-17-25-15-4-3-14(19(20,21)22)9-16(15)26-17/h3-4,9-10,12H,2,5-8,11H2,1H3,(H,25,26)
|
| 化学名 |
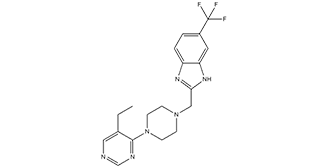
2-((4-(5-ethylpyrimidin-4-yl)piperazin-1-yl)methyl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole
|
| 别名 |
PF-4708671; PF4708671; PF 4708671
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~30 mg/mL (76.8 mM)
Water: <1 mg/mL Ethanol: 8 mg/mL (20.5 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.40 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.40 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.40 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 30% PEG400+0.5% Tween80+5% propylene glycol: 30mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5614 mL | 12.8070 mL | 25.6141 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5123 mL | 2.5614 mL | 5.1228 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2561 mL | 1.2807 mL | 2.5614 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Pdcd4 enhances cell sensitivity to OSI-906 via suppression of p70S6K1 phosphorylation.Mol Cancer Ther.2015 Mar;14(3):799-809. |
The combination of OSI-906 and PF-4708671 significantly inhibits the growth of resistant CRC cells.Mol Cancer Ther.2015 Mar;14(3):799-809. |
The combination of OSI-906 and PF-4708671 significantly inhibits the growth of HCT116-derived tumor in nude mice.Mol Cancer Ther.2015 Mar;14(3):799-809. |
Expression level of Pdcd4 correlates with cell sensitivity to OSI-906.Mol Cancer Ther.2015 Mar;14(3):799-809. |
Tumors derived from Pdcd4 knockdown cells resist to OSI-906 treatment.Mol Cancer Ther.2015 Mar;14(3):799-809. |
Knockdown of p70S6K1 but not p70S6K2 enhances cell sensitivity to OSI-906.Mol Cancer Ther.2015 Mar;14(3):799-809. |