| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
c-Met (IC50 = 9 nM); RON (IC50 = 68 nM); Flk1 (IC50 = 200 nM)
The primary target of PHA-665752 is mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (c-MET) tyrosine kinase, with high selectivity for c-MET over other kinases. Specific IC50 values: - Recombinant human c-MET kinase: IC50 = 8 nM [1] - c-MET (cellular activity, H441 lung adenocarcinoma cells): IC50 = 120 nM [1] - c-MET (cellular activity, MKN-45 gastric cancer cells): IC50 = 150 nM [2] It shows no significant inhibition (IC50 > 1000 nM) against non-target kinases (e.g., EGFR, VEGFR2, PDGFRα, c-Kit) [2] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
PHA-665752 显着抑制 c-Met 激酶活性,Ki 为 4 nM,与各种酪氨酸和丝氨酸-苏氨酸激酶相比,对 c-Met 的选择性高出 50 倍以上。 PHA-665752 有效抑制 HGF 刺激的 c-Met 自磷酸化,IC50 为 25-50 nM。 PHA-665752 还显着阻断 HGF 和 c-Met 依赖性功能,例如细胞运动和细胞增殖,IC50 分别为 40-50 nM 和 18-42 nM。此外,PHA-665752 还可有效抑制多种肿瘤细胞系中 HGF 刺激的 c-Met 下游介质(例如 Gab-1、ERK、Akt、STAT3、PLC-γ 和 FAK)的组成型磷酸化。 PHA-665752 抑制 TPR-MET 转化的 BaF3 细胞的细胞生长,IC50 <60 nM,并在 0.2 μM 时抑制组成型细胞运动和迁移达 92.5%。 PHA665752 (0.2 μM) 抑制 c-Met 还会诱导 33.1% 的细胞凋亡和 G1 细胞周期停滞,处于 G1 期的细胞从 42.4% 增加到 77.0%。 PHA665752可以与雷帕霉素配合抑制TPR-MET转化的BaF3细胞和非小细胞肺癌H441细胞的细胞生长。激酶测定:c-Met 激酶结构域 GST 融合蛋白用于 c-Met 测定。 PHA-665752 抑制 c-Met 的 IC50 值基于 ATP 和二价阳离子(MgCl2 或 MnCl2 10-20 mM)存在下激酶肽底物或聚谷氨酸的磷酸化。确定c-Met的线性范围(即速率保持等于初始速率的时间段),并在此范围内进行动力学测量和IC50测定。细胞测定:对于增殖测定,细胞(S114、GTL-16、NCI-H441 和 BxPC-3)在含有 0.1% FBS 的培养基中生长 48 小时,然后用不同浓度的 HGF 中的 PHA-665752 处理( 50 ng/mL)在含有 2% FBS 的培养基中。 18小时后,将细胞与BrdUrd一起孵育1小时,固定,并用抗BrdUrd过氧化物酶缀合抗体染色,并在630 nm处读取板的读数。对于细胞凋亡测定,细胞在存在和不存在 HGF (50 ng/mL) 和不同浓度的 PHA-665752 的情况下在含有 2% FBS 的培养基中生长 72 小时。 72小时后,加入含有溴化乙锭和吖啶橙的混合物,通过荧光显微镜对凋亡细胞(亮橙色细胞或细胞碎片)进行计数。
c-Met受体酪氨酸激酶及其配体肝细胞生长因子(HGF)与多种人类癌症的发展和进展有关,是癌症治疗的有吸引力的靶点。PHA-665752被鉴定为c-Met激酶(K(i)4 nM)催化活性的小分子ATP竞争性活性位点抑制剂。与一组不同的酪氨酸和丝氨酸苏氨酸激酶相比,PHA-665752对c-Met的选择性也超过50倍。在细胞研究中,PHA-665752能有效抑制HGF刺激和组成型c-Met磷酸化,以及HGF和c-Met驱动的表型,如细胞生长(增殖和存活)、细胞运动、侵袭和/或各种肿瘤细胞的形态。此外,PHA-665752以与给定肿瘤细胞的表型反应相关的模式抑制多个肿瘤细胞系中HGF刺激的c-Met下游信号转导介体的组成性磷酸化,包括Gab-1、细胞外调节激酶、Akt、信号转导子和转录激活子3、磷脂酶cγ和粘着斑激酶。[1] PHA665752特异性抑制BaF3中的细胞生长。TPR-MET细胞(IC(50)<0.06微摩尔/升)诱导凋亡和细胞周期阻滞。BaF3的组成细胞运动和迁移。TPR-MET细胞也受到抑制。PHA665752抑制TPR-MET的特异性磷酸化以及雷帕霉素途径哺乳动物靶点下游靶点的磷酸化。当与PHA665752结合时,雷帕霉素显示出协同抑制BaF3生长的作用。TPR-MET和c-MET表达的H441 NSCLC细胞。 结论:PHA665752是一种有效的小分子选择性c-MET抑制剂,对TPR MET转化的细胞具有高度的生物活性和生化活性。PHA665752对H441 NSCLC细胞也有活性。c-MET抑制剂可以与雷帕霉素协同治疗非小细胞肺癌,这种组合对表达c-MET的癌症的体内研究是值得的。[2] 1. 对c-MET驱动肿瘤的抗增殖活性: - PHA-665752抑制c-MET过表达肺腺癌细胞:H441(IC50 = 120 nM)、EBC-1(IC50 = 180 nM)[1] - 对c-MET扩增胃癌细胞:MKN-45(IC50 = 150 nM)、NCI-N87(IC50 = 165 nM)[2] - 对c-MET低表达细胞(A549肺癌、MCF-7乳腺癌),IC50 > 1000 nM [1] 2. 信号通路抑制: - 用PHA-665752(500 nM,处理2小时)处理H441细胞后,c-MET磷酸化水平(p-c-MET)降低93%,下游p-AKT和p-ERK1/2的抑制率分别为89%和85%(通过Western blot检测)[1] - 在MKN-45细胞中,300 nM PHA-665752阻断c-MET介导的p-STAT3达87% [2] 3. 诱导凋亡: - 在MKN-45细胞中,PHA-665752(200 nM,处理48小时)使凋亡率(Annexin V阳性细胞)从对照组的3.2%升至58.6%,切割型caspase-3上调4.3倍 [1] 4. 抑制集落形成: - 在H441细胞软琼脂集落形成实验中,PHA-665752(100 nM)使集落数量较对照组减少82%;500 nM浓度下集落减少95% [1] 5. 抗血管生成活性: - 在c-MET配体(HGF)刺激的人脐静脉内皮细胞(HUVECs)中,200 nM PHA-665752使管腔形成减少76%,细胞迁移减少72% [1] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
PHA-665752 的给药剂量为 7.5、15 和 30 mg/kg/天时,可分别诱导 S114 异种移植物剂量依赖性肿瘤生长抑制 20%、39% 和 68%。 PHA665752 治疗可显着降低小鼠异种移植物中 NCI-H69、NCI-H441 和 A549 的肿瘤生长,分别达 99%、75% 和 59%。由于减少血管内皮生长因子的产生并增加血管生成抑制剂血小板反应蛋白-1 的产生,PHA665752 还可显着抑制血管生成 >85%。
c-Met受体酪氨酸激酶正在成为包括癌症在内的许多实体瘤的新靶点。PHA-665752被鉴定为c-Met激酶催化活性的ATP竞争性小分子抑制剂。在此,我们发现用PHA666552治疗小鼠异种移植物中的NCI-H69(小细胞肺癌癌症)和NCI-H441(非小细胞肺癌癌症)致瘤性分别降低了99%和75%。通过小鼠肿瘤的磁共振成像也观察到肿瘤大小的减小。PHA6665752抑制来源于非小细胞肺癌癌症细胞系(NCI-H441和A549)和小细胞肺癌癌症细胞系(NC I-H69)的小鼠异种移植物中自磷酸化和c-Cbl结合位点的c-Met磷酸化。PHA665752在所有上述细胞系中也抑制了血管生成>85%,并引起了血管生成转换,导致血管内皮生长因子的产生减少,血管生成抑制剂凝血酶敏感蛋白-1的产生增加。这些研究表明了用ATP竞争性小分子抑制剂选择性靶向c-Met的可行性,并表明PHA6665752可能为癌症提供一种新的治疗方法。[3] 在体内研究中,单剂量PHA-665752抑制肿瘤异种移植物中的c-Met磷酸化长达12小时。在耐受良好的剂量下,c-Met磷酸化的抑制与重复给药方案中剂量依赖性的肿瘤生长抑制/生长延迟有关。有趣的是,在胃癌异种移植物模型中证明了强大的细胞还原活性。总的来说,这些结果证明了用ATP竞争性小分子选择性靶向c-Met的可行性,并表明了靶向c-Met在人类癌症中的治疗潜力[1]。 1. c-MET驱动肺癌异种移植模型(H441): - 6~8周龄雌性裸鼠口服PHA-665752(50 mg/kg、100 mg/kg,每日1次,连续21天)。 - 50 mg/kg组肿瘤体积较溶媒组减少68%;100 mg/kg组减少89%,中位生存期从26天延长至54天 [1] 2. c-MET扩增胃癌异种移植模型(MKN-45): - 裸鼠口服PHA-665752(100 mg/kg,每日1次,连续18天),肿瘤重量较对照组减少83%;肿瘤增殖标志物Ki-67表达降低78% [2] 3. 体内增殖标志物调控: - 在H441异种移植瘤中,PHA-665752(100 mg/kg,连续14天口服)使肿瘤 3 H-胸苷掺入量(细胞增殖指数)较对照组减少75% [3] |
| 酶活实验 |
c-Met 测定使用含有 c-Met 激酶结构域的 GST 融合蛋白。基于 ATP 和二价阳离子(MgCl2 或 MnCl2 10–20 mM)存在下激酶肽底物或聚谷氨酸的磷酸化,PHA-测定了 665752 抑制 c-Met 的 IC50 值。对于c-Met,建立线性范围(即速率保持等于初始速率的持续时间),并在此范围内进行动力学测量和IC50计算。
c-MET激酶活性实验: 1. 制备反应体系:含重组人c-MET激酶结构域、PHA-665752(浓度:0.1~1000 nM)、10 μM [γ-³²P]ATP及合成肽底物(对应c-MET Tyr1234/1235自身磷酸化位点),溶于50 mM Tris-HCl缓冲液(pH 7.5,含10 mM MgCl₂和1 mM DTT)。 2. 30°C孵育60分钟,启动激酶反应。 3. 加入50 μL 20%三氯乙酸(TCA)终止反应,沉淀磷酸化肽。 4. 将反应混合物转移至P81磷酸纤维素滤板,用0.5% TCA洗涤滤板3次,去除未结合的ATP和底物。 5. 采用液体闪烁计数器测定结合的磷酸化肽的放射性强度。 6. 计算PHA-665752对c-MET激酶活性的抑制率,将数据拟合四参数逻辑模型,获得IC50 [1] 激酶选择性实验: 1. 采用与c-MET激酶实验相同的反应体系,将c-MET替换为其他激酶(EGFR、VEGFR2、PDGFRα、c-Kit)。 2. 测试1000 nM浓度的PHA-665752;计算每种激酶的抑制率,仅c-MET的抑制率>90% [2] |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞在 0.1% FBS 培养基中生长 48 小时以进行增殖测定。然后,在含有 2% FBS 的培养基中用不同浓度的 HGF 中的 PHA-665752 (50 ng/mL) 处理细胞。 18 小时后,固定细胞,用抗 BrdUrd 过氧化物酶偶联抗体染色,然后与 BrdUrd 一起孵育 1 小时。然后在 630 nm 处读取板。细胞在含有或不含 HGF (50 ng/mL) 和不同浓度的 PHA-665752 的 2% FBS 培养基中生长 72 小时,以进行细胞凋亡测定。 72小时后,加入含有吖啶橙和溴化乙锭的混合物,用荧光显微镜计数凋亡细胞(亮橙色细胞或细胞碎片)的数量。
测定PHA665752处理对TPR MET转化细胞的细胞生长、运动和迁移、凋亡和细胞周期阻滞的影响。此外,还测定了PHA665752对MET及其下游效应器p-AKT和p-S6K磷酸化的影响。最后,在PHA665752和雷帕霉素存在下测试TPR-MET转化细胞的生长。H441非小细胞癌症(NSCLC)细胞(具有活化的c-Met)也针对PHA666552和雷帕霉素进行了测试[2]。 1. 细胞增殖实验(MTT法): - 将肿瘤细胞(H441、MKN-45、A549)以5×10³细胞/孔接种于96孔板,在含10%胎牛血清的RPMI 1640培养基中过夜孵育。 - 加入PHA-665752(0.1~1000 nM),培养72小时。 - 每孔加入10 μL MTT(5 mg/mL),孵育4小时;去除培养基,加入150 μL DMSO溶解甲臜结晶,570 nm处测吸光度。 - 计算抑制增殖50%的浓度作为IC50 [1] 2. Western blot实验: - PHA-665752(100~500 nM)处理H441/MKN-45细胞2~4小时,含蛋白酶/磷酸酶抑制剂的RIPA裂解液裂解细胞。 - BCA法测定蛋白浓度,30 μg蛋白进行10% SDS-PAGE电泳,转移至PVDF膜。 - 膜用5%脱脂牛奶封闭后,4°C过夜孵育一抗(抗p-c-MET、c-MET、p-AKT、p-ERK1/2、切割型caspase-3、GAPDH)。 - 辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)标记二抗孵育后,ECL试剂检测信号 [1] 3. 凋亡实验(Annexin V/PI染色法): - PHA-665752(200 nM)处理MKN-45细胞24/48小时,收集细胞并用冷PBS洗涤。 - 细胞重悬于结合缓冲液,加入Annexin V-FITC和PI,避光孵育15分钟,流式细胞仪分析凋亡率 [1] 4. 管腔形成实验: - 24孔板包被基质胶,加入HUVECs(2×10⁴细胞/孔)+ HGF(50 ng/mL)+ PHA-665752(200 nM)。 - 37°C孵育6小时,拍摄图像并计数管腔分支数,计算较仅HGF刺激组的抑制率 [1] |
| 动物实验 |
Female athymic mice (nu/nu) bearing S114 or GTL-16 tumor xenografts
~30 mg/kg/day Injection via bolus i.v. Treatment of Nude Mice for Studying the Effect of c-Met Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors on Tumorigenicity and Immunohistochemistry of Tumors[3] NCI-H441, A549, and NCI-H69 cells were cultured and harvested with trypsin/EDTA. The viability of these cells was determined by trypan blue and only cell populations with 90% or greater viability were used for this investigation. The tumorigenicity of these lung cancer cells was determined by intradermally injecting 5 × 106 viable cells in balanced salt solution into the flank or leg region of nude mice to produce s.c. tumors. Once daily intratumoral injections of PHA665752, were given 8 days after the lung cancer cells were injected when tumors were visible. One group of animals was given PHA665752 (16.5 μg in 100 μL of 2% DMSO) and group 2 was injected with diluent (2% DMSO) alone. The mice were euthanized at the indicated times and tumors were measured with calipers, fixed in 4% formalin, embedded in paraffin, and stained with H&E.[3] Immunohistochemical staining of tumors was done using monoclonal antibodies against CD31, VEGF, TSP-1, and phosphospecific antibodies to c-Met pY1230/1234/1235 and pY1003. The immunostaining procedures used have been previously described by Ma et al. Appropriate negative controls for the immunostaining were prepared by omitting the primary antibody step and substituting it with nonimmune rabbit serum. To estimate the number of blood vessels in tumors before and after treatment, 10 microscopic fields were counted at 20× magnification and the number of blood vessels were evaluated. All of the slides were reviewed and scored by two investigators independently.[3] 1. H441 lung cancer xenograft model: - Animals: Female nude mice (6–8 weeks old), n=6/group. - Tumor induction: Subcutaneous injection of 5×10⁶ H441 cells (0.2 mL PBS/Matrigel 1:1) into right flank. - Drug formulation: PHA-665752 dissolved in DMSO + normal saline (1:9 v/v). - Administration: Oral gavage at 50 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg once daily for 21 days; control receives vehicle. - Monitoring: Measure tumor volume (length×width²/2) every 2 days; record survival time; weigh mice weekly [1] 2. MKN-45 gastric cancer xenograft model: - Animals: Female nude mice (6–8 weeks old), n=6/group. - Tumor induction: Subcutaneous injection of 4×10⁶ MKN-45 cells (0.2 mL PBS/Matrigel 1:1). - Administration: PHA-665752 (100 mg/kg, oral, daily for 18 days); control receives vehicle. - Endpoint: Excise tumors at sacrifice; weigh tumors; detect Ki-67 via immunohistochemistry [2] 3. 3 H-thymidine incorporation assay (in vivo): - Animals: Female nude mice bearing H441 xenografts, n=5/group. - Administration: PHA-665752 (100 mg/kg, oral, daily for 14 days); control receives vehicle. - Assay: Inject 3 H-thymidine (1 μCi/g body weight) intraperitoneally 2 hours before sacrifice; homogenize tumors; measure radioactivity via liquid scintillation counting [3] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
1. Oral pharmacokinetics in mice:
- Male C57BL/6 mice (n=3/time point) receive PHA-665752 (100 mg/kg, oral). - Plasma samples collected at 0.25–24 hours; analyzed via HPLC-UV. - Key parameters: Cmax = 1850 ng/mL, Tmax = 1.2 hours, AUC0-24h = 12600 ng·h/mL, t1/2 = 5.6 hours, oral bioavailability = 32% [2] 2. Tissue distribution: - At 2 hours post-dosing (100 mg/kg), PHA-665752 concentrations (ng/g): liver (3250), tumor (2980), kidneys (2650), spleen (2120), brain (158) [2] 3. Plasma protein binding: - Ultrafiltration assay shows >98% protein binding in mouse, rat, and human plasma (10–1000 ng/mL concentrations) [2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
1. Acute toxicity in mice:
- Male/female C57BL/6 mice (n=3/sex/dose) receive PHA-665752 (oral, 150–600 mg/kg). No mortality at 150/300 mg/kg; 600 mg/kg causes 1/6 deaths, transient weight loss (max 11% day 3, recovered day 7) [2] 2. Subacute toxicity (28-day, mice): - Doses: 50 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg (oral, daily). - 50 mg/kg group: No changes in body weight, serum biochemistry (ALT, AST, creatinine), or hematology (WBC, platelets). - 100 mg/kg group: Mild elevation of ALT (1.3× control); no histopathological damage to liver/kidneys [2] 3. Local toxicity: - Intraperitoneal injection of 100 mg/kg PHA-665752 causes no peritoneal inflammation (no increase in TNF-α/IL-6 in peritoneal fluid) [2] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
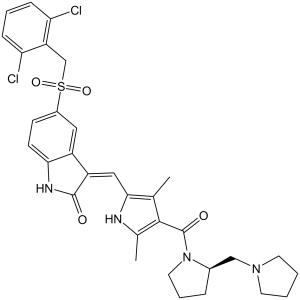
PHA-665752 is a member of the class of indolones that is 1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one which is substituted by a (2,6-dichlorobenzyl)sulfonyl group at position 5 and by a (1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylidene group at position 2, the pyrrole ring of which is substituted by methyl groups at positions 3 and 5, and by a [2-(pyrrolidin-1-ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl]carbonyl group at position 4 (the Z,R isomer). It has a role as a c-Met tyrosine kinase inhibitor and an antineoplastic agent. It is a member of indolones, a pyrrolecarboxamide, a N-acylpyrrolidine, a sulfone, a dichlorobenzene, an enamide, a secondary carboxamide and a tertiary carboxamide.
1. Therapeutic background: PHA-665752 is one of the first selective c-MET tyrosine kinase inhibitors, developed to target c-MET-driven solid tumors (lung adenocarcinoma, gastric cancer) [1] 2. Mechanism of action: It competitively binds to the ATP-binding pocket of c-MET, inhibiting c-MET autophosphorylation and downstream signaling pathways (PI3K-AKT, RAS-ERK1/2). It also suppresses tumor angiogenesis by blocking c-MET-mediated endothelial cell activation [1] 3. Research significance: PHA-665752 is widely used as a tool compound to validate c-MET as a therapeutic target in preclinical studies, laying the foundation for later c-MET inhibitors (e.g., crizotinib) [3] 4. Limitation: Due to suboptimal oral bioavailability (32%) and mild liver toxicity at high doses, PHA-665752 was not advanced to clinical trials [2] |
| 分子式 |
C32H34CL2N4O4S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
641.61
|
|
| 精确质量 |
640.167
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 59.90; H, 5.34; Cl, 11.05; N, 8.73; O, 9.97; S, 5.00
|
|
| CAS号 |
477575-56-7
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
10461815
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Yellow to orange solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
890.2±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
492.2±34.3 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.656
|
|
| LogP |
4
|
|
| tPSA |
110.96
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
43
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1180
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
ClC1C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C(C=1C([H])([H])S(C1C([H])=C([H])C2=C(C=1[H])/C(/C(N2[H])=O)=C(\[H])/C1=C(C([H])([H])[H])C(=C(C([H])([H])[H])N1[H])C(N1C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[C@]1([H])C([H])([H])N1C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C1([H])[H])=O)(=O)=O)Cl
|
|
| InChi Key |
OYONTEXKYJZFHA-SSHUPFPWSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C32H34Cl2N4O4S/c1-19-29(35-20(2)30(19)32(40)38-14-6-7-21(38)17-37-12-3-4-13-37)16-24-23-15-22(10-11-28(23)36-31(24)39)43(41,42)18-25-26(33)8-5-9-27(25)34/h5,8-11,15-16,21,35H,3-4,6-7,12-14,17-18H2,1-2H3,(H,36,39)/b24-16-/t21-/m1/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
(3Z)-5-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)methylsulfonyl]-3-[[3,5-dimethyl-4-[(2R)-2-(pyrrolidin-1-ylmethyl)pyrrolidine-1-carbonyl]-1H-pyrrol-2-yl]methylidene]-1H-indol-2-one
|
|
| 别名 |
PHA-665752; PHA665752; PHA-665752 hydrate; TCMDC-125885; UNII-0VXU5T5R3J; (R,Z)-5-((2,6-dichlorobenzyl)sulfonyl)-3-((3,5-dimethyl-4-(2-(pyrrolidin-1-ylmethyl)pyrrolidine-1-carbonyl)-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)indolin-2-one; PHA 665752
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.90 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (3.90 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.90 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 2% DMSO+castor oil: 5 mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.5586 mL | 7.7929 mL | 15.5858 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3117 mL | 1.5586 mL | 3.1172 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1559 mL | 0.7793 mL | 1.5586 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
|
 |
 |