| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| 25g |
|
||
| 50g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
α adrenergic receptor
α1-adrenoceptor (agonist, Ki = 0.1 μM) [1][2] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
去氧肾上腺素导致 PKC-ε 快速易位 (EC50 = 0.9 mM),但可溶性部分损失的比例小于 ET-1。 pCa 7 的去氧肾上腺素会导致高通透性细胞的收缩力出现剂量依赖性增加,添加酚妥拉明后这种现象是可逆的。去氧肾上腺素还可以保护心肌细胞免受随后 24 小时缺氧和血清剥夺处理的影响。去氧肾上腺素可防止 Bcl-2 和 Bcl-X mRNA/蛋白的下调并诱导肥大生长。去氧肾上腺素介导的保护可被磷脂酰肌醇 3 激酶 (PI 3 激酶) 抑制剂渥曼青霉素消除,并被 caspase-9 肽抑制剂 LEHD-fmk 模拟。去氧肾上腺素可刺激磷酸肌醇 (PI) 水解、细胞生长和一些通常与心脏肥大相关的基因 [例如心房钠尿因子 (ANF)] 的表达。 Phenylephrine 显着增强 HGF 诱导的肝细胞 DNA 合成和增殖。去氧肾上腺素 (10 mM) 可逆地增加 I(Ca,L) (51.3%;n = 40) 并将峰值 I(Ca,L) 激活电压移动 -10 mV。去氧肾上腺素还通过 IP3 依赖性信号传导增加局部肌膜下 SR Ca2+ 的释放。去氧肾上腺素诱导的 NOi 释放需要刺激 PI-3K/Akt 和 IP3 依赖性 Ca2+ 信号传导。去氧肾上腺素诱导的 NOi 释放可被 1 mM 哌佐星、10 mM L-NIO、10 mM W-7、10 mM LY294002、2 mM H-89、10 mM ryanodine、5 mM 毒胡萝卜素、2 mM 2-APB 或10 mM 硬海绵素 C.
盐酸去氧肾上腺素(Phenylephrine HCl)通过激活α1-肾上腺素受体诱导兔离体主动脉平滑肌浓度依赖收缩。0.01-1 μM浓度下,最大收缩幅度达氯化钾(60 mM)诱导收缩的90%,EC50为0.08 μM[2][4] 它刺激大鼠肝细胞中磷脂酶C(PLC)激活和1,4,5-三磷酸肌醇(IP3)生成。1-10 μM处理30分钟,IP3水平升高约2.5倍,介导细胞内钙释放[1] 在人脐静脉内皮细胞(HUVECs)中,盐酸去氧肾上腺素(Phenylephrine HCl)(10-50 μM)通过活性氧(ROS)生成诱导凋亡,50 μM时凋亡率从~5%升至~30%[3] 它增强大鼠心室肌细胞的L型钙电流(ICa,L)。1 μM时,ICa,L幅度增加约40%,促进心肌收缩[6] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
用 100 μM 去氧肾上腺素灌注心脏会导致两种 p38-MAPK 亚型快速(10 分钟内最大)激活 12 倍。 α1-肾上腺素受体激动剂如去氧肾上腺素可增加心脏的收缩力。去氧肾上腺素还可以激活新生儿心室肌细胞中的 SAPK/JNK。去氧肾上腺素可增加高潮气量通气大鼠的肺泡液清除率,加速肺水肿的吸收。
在麻醉大鼠中,静脉注射盐酸去氧肾上腺素(Phenylephrine HCl)(0.1-1 mg/kg)剂量依赖升高收缩压(15-40%)并降低心率(10-20%,反射性心动过缓)。升压效应10分钟达峰,持续约40分钟[2][5] 在清醒犬中,静脉输注盐酸去氧肾上腺素(Phenylephrine HCl)(0.5 μg/kg/分钟)减少肾血流量约25%,增加肾血管阻力约30%,不影响肾小球滤过率[4] 在大鼠失血性休克模型中,静脉注射盐酸去氧肾上腺素(Phenylephrine HCl)(0.3 mg/kg),5分钟内将平均动脉压从~60 mmHg恢复至~95 mmHg,改善组织灌注[5] |
| 酶活实验 |
α1-肾上腺素受体放射性配体结合实验:从大鼠大脑皮层(富含α1-肾上腺素受体)制备膜匀浆,将匀浆与[3H]-哌唑嗪(0.5 nM)及不同浓度的盐酸去氧肾上腺素(Phenylephrine HCl)(0.001-10 μM)在25°C孵育90分钟。通过玻璃纤维滤膜快速过滤分离结合态和游离态配体,用冰浴缓冲液洗涤滤膜后,通过闪烁计数器测定放射性强度,基于竞争结合曲线计算Ki值[1][2]
|
| 细胞实验 |
兔主动脉平滑肌收缩实验:分离兔主动脉片段,切成2 mm宽环,置于含含氧克雷布斯-林格溶液的器官浴中,37°C孵育1小时后,累积加入盐酸去氧肾上腺素(Phenylephrine HCl)(0.001-10 μM)。等长换能器记录张力变化,计算相对于氯化钾诱导收缩的收缩百分比[2][4]
大鼠肝细胞IP3生成实验:分离大鼠肝细胞,在Williams’ E培养基中培养,用盐酸去氧肾上腺素(Phenylephrine HCl)(1-10 μM)处理30分钟。酸化甲醇提取IP3,放射免疫法定量[1] HUVEC凋亡实验:HUVECs在血管内皮细胞生长培养基中培养至汇合,用盐酸去氧肾上腺素(Phenylephrine HCl)(10-50 μM)处理24小时。膜联蛋白V-FITC/PI双染色结合流式细胞术检测凋亡,荧光探针测定ROS水平[3] |
| 动物实验 |
Random number tables are used to randomly assign 170 male Wistar rats into 17 groups (n=10). Induce lung injury, impair active Na+ transport, and reduce lung liquid clearance in rats by administering short-term (40 minutes) high-tidal volume mechanical ventilation. Control rats are those that are not ventilated. A variety of phenylephrine concentrations (10, 1, 0.1, 0.01, and 0.001 μM) are injected into the alveolar space of rats on HVT ventilation in order to show how the drug affects alveolar fluid clearance.
Rats Anesthetized rat hemodynamic assay: Adult male rats are anesthetized with urethane, implanted with femoral artery catheters for blood pressure monitoring, and jugular vein catheters for drug administration. Phenylephrine HCl is dissolved in physiological saline and administered intravenously at 0.1, 0.5, or 1 mg/kg. Systolic/diastolic blood pressure and heart rate are recorded continuously for 1 hour [2][5] Conscious dog renal function assay: Adult dogs are instrumented with renal artery flow probes and arterial catheters. After recovery, Phenylephrine HCl is infused intravenously at 0.5 μg/kg/min for 30 minutes. Renal blood flow, renal vascular resistance, and glomerular filtration rate are measured at baseline and during infusion [4] Rat hemorrhagic shock model: Adult rats are anesthetized, and hemorrhagic shock is induced by withdrawing 30% of blood volume. Phenylephrine HCl (0.3 mg/kg) is administered intravenously, and mean arterial pressure is monitored for 60 minutes to assess hemodynamic recovery [5] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption: Phenylephrine HCl has low oral bioavailability (~4-10% in humans) due to first-pass metabolism by monoamine oxidase (MAO) [5]
Distribution: It distributes rapidly into tissues, with a volume of distribution (Vdss) of ~2-3 L/kg in humans [5] Metabolism: Primarily metabolized in the liver and gut by MAO and sulfotransferases, producing inactive metabolites [5] Excretion: The plasma elimination half-life is ~2-3 hours in humans. Approximately 70-80% of the dose is excreted in urine within 24 hours, with ~10-15% as unchanged drug [5] Plasma protein binding: Phenylephrine HCl has a plasma protein binding rate of ~10-15% in humans [5] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Acute intravenous LD50 in mice is ~20 mg/kg; lethal doses induce severe hypertension, ventricular arrhythmias, and cerebral hemorrhage [5]
Common adverse effects in humans include hypertension (incidence ~25%), headache (~18%), reflex bradycardia (~12%), and nasal irritation (for topical use, ~10%) [2][5] Subchronic toxicity study (28 days) in rats at oral doses up to 50 mg/kg/day showed no significant hepatotoxicity or nephrotoxicity, but mild myocardial hypertrophy at 50 mg/kg/day [3] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Phenylephrine hydrochloride is an odorless white microcrystalline powder. Bitter taste. pH (1% aqueous solution) about 5. (NTP, 1992)
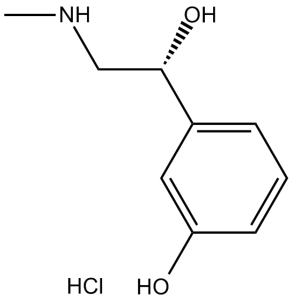
Phenylephrine Hydrochloride is the hydrochloride salt form of phenylephrine, a direct-acting sympathomimetic amine chemically related to adrenaline and ephedrine with potent vasoconstrictor property. Phenylephrine is a post-synaptic alpha-adrenergic receptor agonist that causes vasoconstriction, increases systolic/diastolic pressures, reflex bradycardia, and stroke output. An alpha-1 adrenergic agonist used as a mydriatic, nasal decongestant, and cardiotonic agent. See also: Phenylephrine (has active moiety); Ibuprofen; PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE (component of); Phenylephrine Hydrochloride; Tropicamide (component of) ... View More ... Phenylephrine HCl is a selective α1-adrenoceptor agonist with peripheral vasoconstrictive activity [1][2][4][5] Its mechanism involves activating α1-adrenoceptors to induce smooth muscle contraction (vascular, visceral), stimulate PLC-IP3-calcium signaling, and regulate myocardial calcium currents [1][2][6] Clinically indicated for the treatment of acute hypotension, hemorrhagic shock, and nasal congestion (topical formulations), based on its vasoconstrictive effects [2][5] High concentrations induce endothelial cell apoptosis via ROS generation, suggesting potential vascular toxicity at supraphysiological doses [3] Due to low oral bioavailability, intravenous or topical administration is preferred for therapeutic efficacy; oral formulations require higher doses [5] |
| 分子式 |
C9H14CLNO2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
203.67
|
|
| 精确质量 |
203.071
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 53.08; H, 6.93; Cl, 17.41; N, 6.88; O, 15.71
|
|
| CAS号 |
61-76-7
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Phenylephrine-2,4,6-d3 hydrochloride; 1276197-50-2; Phenylephrine; 59-42-7; Phenylephrine-d3 hydrochloride; 1217858-50-8; (S)-Phenylephrine-d6 hydrochloride; Phenylephrine-d6 hydrochloride; 1089675-56-8
|
|
| PubChem CID |
5284443
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 沸点 |
341.1ºC at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
143-145 °C(lit.)
|
|
| 闪点 |
163.4ºC
|
|
| 折射率 |
-45.5 ° (C=1, H2O)
|
|
| LogP |
1.837
|
|
| tPSA |
52.49
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
13
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
130
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
Cl[H].O([H])[C@]([H])(C1C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C(C=1[H])O[H])C([H])([H])N([H])C([H])([H])[H]
|
|
| InChi Key |
OCYSGIYOVXAGKQ-FVGYRXGTSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C9H13NO2.ClH/c1-10-6-9(12)7-3-2-4-8(11)5-7;/h2-5,9-12H,6H2,1H3;1H/t9-;/m0./s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
3-[(1R)-1-hydroxy-2-(methylamino)ethyl]phenol;hydrochloride
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮和光照。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (10.21 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (10.21 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (10.21 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.9099 mL | 24.5495 mL | 49.0990 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.9820 mL | 4.9099 mL | 9.8198 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4910 mL | 2.4550 mL | 4.9099 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT01791816 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Phenylephrine Drug: L-Ng-monomethyl Arginine (L-NMMA) |
Vasovagal Syncope Postural Tachycardia Syndrome |
New York Medical College | February 2013 | Early Phase 1 |
| NCT03620942 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Phenylephrine Drug: Ephedrine |
Hypotension Anesthesia |
KK Women's and Children's Hospital |
November 7, 2018 | Not Applicable |
| NCT05011357 | Recruiting | Drug: Phenylephrine Drug: Saline Control |
Intraoperative Hypotension | University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center |
September 10, 2021 | Early Phase 1 |
| NCT02630121 | Recruiting | Drug: Oxymetazoline Hydrochloride Drug: Placebo |
Sleep Apnea Chronic Nasal Congestion |
University of South Florida | April 2023 | Phase 4 |
| NCT04602767 | Recruiting | Drug: Vasopressin Drug: Phenylephrine |
Acute Kidney Injury | Thomas Jefferson University | October 15, 2020 | Phase 4 |
|
|
|
|