| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
MEK1; MEK2
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Pimasertib(5、0.5 和 0.1 μM)特异性抑制单独培养或与 BMSC 一起培养的 MM 细胞中的 ERK1/2 激活。 Pimasertib 的 IC50 值范围为 0.005 至 2 M,表明它以剂量依赖性方式抑制 MM 细胞系的生长。 Pimasertib 对于 INA-6、U266 和 H929 细胞的 IC50 值分别为 10 nM、5 nM 和 200 nM。 pimasertib 可以改变细胞凋亡和细胞周期特征。 BM微环境是pimasertib对MM细胞作用的目标[1]。在对西妥昔单抗耐药的 D-MUT 细胞中,pimasertib (10 mol/L) 抑制 ERK 通路、增殖和转化[2]。与单独使用每种药物相比,pimasertib 与 PLX4032 联合使用时显着增加 RPMI-7951 细胞发生凋亡的可能性。为了达到与 PLX4032 和 Pimasertib 联合治疗相当的结果,Pimasertib 与小干扰 RNA 介导的 BRAF 下调协同作用[3]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Pimasertib (15、30 mg/kg) 显着减缓携带人 H929 MM 异种移植物的 CB17 SCID 小鼠的肿瘤生长[1]。 Pimasertib(10 mg/kg,口服)可抑制因 K-ras 基因突变而对西妥昔单抗产生耐药性的肿瘤的生长[2]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
AS703026 溶解在 2.5% DMSO 中。激活的二磷酸化 MEK (pp-MEK) 检测包含 40 M 33P-γATP (AppKm 8.5 MμM、0.5 nM 人激活 MEK1 或 MEK2 和 1 M 激酶死亡 ERK2 (AppKm 0.73 μM)。所有测试均在含有以下成分的缓冲液中进行: 20 mM HEPES (pH 7.2)、5 mM 2-巯基乙醇、0.15 mg/mL BSA 和 10 mM MgCl2。对于所有测定,最终 33P-ATP 浓度为 0.02 μCi/μL。40 分钟后,pp-MEK 激酶反应通过将 30 μL 反应混合物转移至含有 12.5% TCA 的 Durapore 0.45-μm 过滤板来停止。将过滤器干燥,然后使用液体闪烁剂在 TopCount 上读取。对于 IC50,检查浓度响应数据。最初未磷酸化的 MEK 的 IC50 (u-MEK) 的计算方法是将 0.2 nM 重组人 MEK1 或 MEK2 与载体或 AS703026 在反应缓冲液中预孵育 40 分钟。通过添加最终浓度 20 nM B-RafV600E 和 30 μM ATP 10 分钟,磷酸化/激活然后加入B-Raf抑制剂SB590885(终浓度100 nM),猝灭B-Raf活性,并通过在反应缓冲液中添加1 μM KD-ERK2和0.02 μCi/μL 33P-ATP来测量MEK激酶活性。将 30μL 反应混合物转移至 Durapore 滤板并照常读数,90 分钟后激酶反应停止。
|
| 细胞实验 |
[3H]胸苷掺入和MTT染料吸光度测量均用于确定研究化合物对MM细胞生长和存活的抑制作用。在 96 孔板中,细胞以每孔 104 个细胞的密度一式三份以及每孔 2-5×105 个细胞的密度培养 3 天(MM 细胞系)或 5 天(患者 MM 细胞)。对于 [3H] 胸苷掺入测定,细胞用 0.5 μCi (0.0185 MBq)/孔 [3H]胸苷脉冲 6 小时(细胞系),收获到玻璃纤维过滤器上,并在 β-闪烁计数器中计数。由于患者的 MM 细胞的 DNA 合成水平较低,因此用 2 μCi/孔的 [3H]胸苷对其进行脉冲,并在培养的最后 36 小时内测量其 DNA 合成。
|
| 动物实验 |
H929 (4×106 cells) are subcutaneously injected into CB17 severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) mice in 100 μL RPMI-1640 medium. Pimasertib (15 or 30 mg/kg) or the control vehicle alone was administered orally twice daily to the mice, which had palpable tumors (about 130 mm3) by the third week after cell injection. Every other day, calipers are used to measure the tumor's size in two dimensions, and the tumor's volume is computed. When an animal's quality of life is significantly compromised, its tumors grow to a volume of 2 cm3, it becomes moribund, it exhibits paralysis, or it becomes moribund. GraphPad Prism version 4.03 for Windows is used to plot changes in tumor formation in mice treated with control medication vs. pimasertib. Utilizing specific monoclonal (m) antibodies, immunoblotting and immunochemistry analyses of tumors are performed. Abs. Leica IM50 Image Manager is used to take pictures, Leica DM LB research microscope is used for image analysis, and Adobe Photoshop Software 7.0 is used for post-processing.
|
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
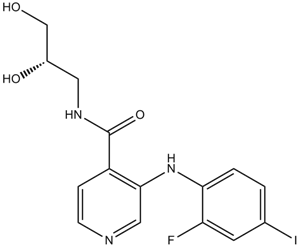
N-[(2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl]-3-(2-fluoro-4-iodoanilino)-4-pyridinecarboxamide is a pyridinecarboxamide.
Pimasertib is under investigation in clinical trial NCT01378377 (Combination Trial of Pimasertib (MSC1936369B) With Temsirolimus). Pimasertib is an orally bioavailable small-molecule inhibitor of MEK1 and MEK2 (MEK1/2) with potential antineoplastic activity. Pimasertib selectively binds to and inhibits the activity of MEK1/2, preventing the activation of MEK1/2-dependent effector proteins and transcription factors, which may result in the inhibition of growth factor-mediated cell signaling and tumor cell proliferation. MEK1/2 (MAP2K1/K2) are dual-specificity threonine/tyrosine kinases that play key roles in the activation of the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and are often upregulated in a variety of tumor cell types. We investigate cytotoxicity and mechanism of action of AS703026, a novel, selective, orally bioavailable MEK1/2 inhibitor, in human multiple myeloma (MM). AS703026, more potently (9-10 fold) than AZD6244, inhibited growth and survival of MM cells and cytokine-induced osteoclast differentiation. Inhibition of proliferation induced by AS703026 was mediated by G0-G1 cell cycle arrest and was accompanied by reduction of c-maf oncogene expression. AS703026 further induced apoptosis via caspase 3 and PARP cleavage in MM cells, both in the presence or absence of bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs). Importantly, AS703026 sensitized MM cells to a broad spectrum of conventional (dexamethasone, melphalan), novel or emerging (lenalidomide, perifosine, bortezomib, rapamycin) anti-MM therapies. Significant tumor growth reduction in AS703026- vs. vehicle-treated mice bearing H929 MM xenograft tumors correlated with downregulated pERK1/2, induced PARP cleavage, and decreased microvessels in vivo. Moreover, AS703026 (<200 nM) was cytotoxic against the majority of tumor cells tested from patients with relapsed and refractory MM (84%), regardless of mutational status of RAS and BRAF genes. Importantly, BMSC-induced viability of MM patient cells was similarly blocked within the same dose range. Our results therefore support clinical evaluation of AS703026, alone or in combination with other anti-MM agents, to improve patient outcome.[1] Background: Although inhibitors of the proto-oncogene BRAF have shown excellent antitumor activity against malignant melanoma, their efficacy is limited by the development of acquired drug resistance, a process in which reactivation of MAP kinase (MEK) is known to play an important role. In this study, we evaluated the efficacy of AS703026, a new MEK inhibitor, in BRAF inhibitor-resistant melanoma cell lines. Methods: Two melanoma cells lines, RPMI-7951 and SK-MEL5, harboring an activating mutation of BRAF (V600E) were treated with the BRAF inhibitor PLX4032 to select a BRAF inhibitor-resistant cell line for further study. Cell viability assay was determined with MTS [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium] assay and trypan blue exclusion method; apoptosis assay was performed by annexin-V staining. Knockdown of BRAF was investigated by small interfering RNA. Results: RPMI-7951 cells exhibited an increased sensitivity to combined treatment with PLX4032 and AS703026 compared to either drug alone. Consistent with this, the combination of PLX4032 and AS703026 significantly induced apoptosis, whereas each drug used alone did not, as demonstrated by a flow cytometric analysis of annexin-V/propidium iodide-stained cells and Western blot analysis of cleaved caspase-3. Notably, immunoblot analyses also showed a depletion of phosphorylated-ERK with combined drug treatment. In addition, AS703026 synergized with small interfering RNA-mediated downregulation of BRAF to produce results similar to those of combined treatment with PLX4032 and AS703026. Conclusions: Our results suggest that combined treatment with AS703026 and a BRAF inhibitor overcomes the resistance to BRAF inhibitors in malignant melanoma cells harboring a mutant form of BRAF.[2] Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) monoclonal antibodies (mAb) are used widely to treat metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) patients, but it is now clear that patients harboring K-ras mutation are resistant to EGFR mAbs such as cetuximab (Erbitux) and panitumumab (Vectibix). For this reason, current recommendations for patient care involve diagnosing the K-ras mutational status of patients prior to EGFR mAb therapy. In this study, we investigated the ability of two MEK inhibitors currently in clinical trials, AS703026 and AZD6244, to address the challenge posed by the resistance of K-ras mutated colorectal cancers to EGFR mAb. AS703026 and AZD6244 were tested in various cell-based assays and tumor xenograft studies, focusing on isogenic human colorectal tumor cell lines that expressed only WT or mutant K-Ras (D-WT or D-MUT). The EGFR mAb cetuximab inhibited the Ras-ERK pathway and proliferation of D-WT cells in vitro and in vivo, but it did not inhibit proliferation of D-MUT cells in either setting. In contrast, AS703026 and AZD6244 effectively inhibited the growth of D-MUT cells in vitro and in vivo by specific inhibition of the key MEK downstream target kinase ERK. Inhibition of MEK by AS703026 or AZD6244 also suppressed cetuximab-resistant colorectal cancer cells attributed to K-ras mutation both in vitro and in vivo. Our findings offer proof-of-concept for the use of MEK inhibitors as an effective therapy in K-ras mutated CRC.[3] |
| 分子式 |
C15H15FIN3O3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
431.20
|
| 精确质量 |
431.014
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 41.78; H, 3.51; F, 4.41; I, 29.43; N, 9.74; O, 11.13
|
| CAS号 |
1236699-92-5
|
| 相关CAS号 |
1236361-78-6 (HCl); 1236699-92-5;
|
| PubChem CID |
44187362
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to khaki solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.8±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
623.2±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
330.7±31.5 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.9 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.684
|
| LogP |
3.05
|
| tPSA |
94.48
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
23
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
391
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
FC1=C(C=CC(I)=C1)NC2=CN=CC=C2C(NC[C@@H](CO)O)=O
|
| InChi Key |
VIUAUNHCRHHYNE-JTQLQIEISA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C15H15FIN3O3/c16-12-5-9(17)1-2-13(12)20-14-7-18-4-3-11(14)15(23)19-6-10(22)8-21/h1-5,7,10,20-22H,6,8H2,(H,19,23)/t10-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
N-[(2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl]-3-(2-fluoro-4-iodoanilino)pyridine-4-carboxamide
|
| 别名 |
MSC 1936369B; SAR 245509; AS-703026; SAR245509; SAR-245509; AS703026; AS 703026
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.80 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.80 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.80 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 0.5% CMC+0.25% Tween 80: 30mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3191 mL | 11.5955 mL | 23.1911 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4638 mL | 2.3191 mL | 4.6382 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2319 mL | 1.1596 mL | 2.3191 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT04789668 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Pimasertib Drug: Bintrafusp Alfa |
Stage IV Lung Cancer AJCC v8 Metastatic Melanoma |
M.D. Anderson Cancer Center | January 15, 2021 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
| NCT04985604 | Recruiting | Drug: Tovorafenib Drug: Pimasertib |
Melanoma Solid Tumor |
Day One Biopharmaceuticals, Inc. | July 15, 2021 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
| NCT01985191 | Completed | Drug: Pimasertib Drug: SAR405838 |
Neoplasm Malignant | Sanofi | November 2013 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01992874 | Completed | Drug: Pimasertib Capsule (Part A) Drug: Pimasertib Tablet (Part A) |
Neoplasms | EMD Serono | November 30, 2013 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00982865 | Completed | Drug: MSC1936369B | Solid Tumors Cancer |
Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany | December 31, 2007 | Phase 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|