| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
5-HT2A Receptor ( pIC50 = 8.7 )
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Pimavanserin (ACP-103) 竞争性拮抗 [3H]ketanserin 与异源表达的人 5-HT2A 受体的结合,膜中的平均 pKi 为 9.3,全细胞中的平均 pKi 为 9.70。 Pimavanserin 对人 5-HT2C 受体表现出较低的亲和力(膜中的平均 pKi 为 8.80,全细胞的平均 pKi 为 8.00,通过放射性配体结合测定)和作为反向激动剂的效力(R-SAT 中的平均 pIC50 7.1),并且缺乏亲和力和功能5-HT2B 受体、多巴胺 D2 受体和其他人类单胺能受体的活性[1]。 Pimavanserin (ACP-103) 对 5-HT2A 受体具有高度选择性,在包括 65 个不同分子靶标的广泛筛选中缺乏对其他受体的亲和力; Pimavanserin 表现出亲和力的唯一其他受体是 5-HT2C,根据检测结果,Pimavanserin 对 5-HT2A 受体的选择性大约是 5-HT2C 受体的 30 倍[2]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Pimavanserin (ACP-103) 是一种强效、有效、口服活性的 5-HT2A 受体反向激动剂,其行为药理学特征与抗精神病药物的用途一致。 Pimavanserin 可减轻 5-HT2A 受体激动剂 (±)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine 盐酸盐诱导的头抽搐行为 (3 mg/kg po) 和前脉冲抑制缺陷 (1-10 mg/kg sc)大鼠并减少由 N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体非竞争性拮抗剂 5H-二苯并[a,d]环庚烯-5,10-亚胺(马来酸地佐环平;MK-801)(0.1 和 0.3 mg/kg)引起的小鼠多动症sc;3 mg/kg po),与 5-HT2A 受体体内作用机制和抗精神病药样功效一致。 Pimavanserin 在大鼠中的口服生物利用度>42.6%[1]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
为了实现膜结合,使用 Polyfect 转染试剂将含有 70% 汇合度的 NIH-3T3 细胞的 15 cm2 培养皿用 10 μg 受体质粒 DNA 转染。转染两天后,将表达目标血清素受体的匀浆细胞在 4°C 下以 11,000 g 离心 30 分钟,同时在 20 mM HEPES/10 mM EDTA 中稀释。弃去上清液后,再次离心沉淀,同时重悬于 20 mM HEPES/1 mM EDTA 中。将沉淀重悬于 20 mM HEPES/0.5 mM EDTA 溶液中后,使用膜进行结合测定。为了确定总膜蛋白,使用布拉德福德分析。使用 12 点浓度实验得出 Kd 和 Bmax 值。对于 5-HT2A 受体,使用 1 nM [3H]ketanserin,对于 5-HT2B 和 5-HT 2C 受体,3 nM [3H]mesulegine。当膜在室温下用不同的测试配体浓度孵育三个小时时,存在固定浓度的放射性配体。如下文详述的全细胞结合过滤悬浮液、干燥并用冰冷的缓冲液冲洗后,使用 TopCount[1] 测量放射性。
|
| 细胞实验 |
为了进行全细胞结合,使用 Polyfect 用 5 μg 质粒 DNA 转染 600 万个人胚肾 293T 细胞,并铺板于 10 cm 培养皿中。转染两天后,使用 10 mM EDTA 收集细胞,清洗,然后在结合缓冲液(1% 牛血清白蛋白,1×DMEM)中复溶。随后,总共 100 μL 配体和 5 nM 放射性配体([3H]酮色林用于 5-HT2A 受体和 [3H ]美舒麦角 (针对 5-HT2C-INI 受体) 添加到 60,000 个转染 5-HT2A 受体的细胞或 20,000 个转染 5-HT 的细胞中2C-INI 受体,并在 37°C 下孵育 3 小时。使用 Filtermate 196 收集器,将细胞过滤到 96 孔 GF/B 过滤板上,然后用 300 mL 洗涤缓冲液(25 mM HEPES、1 mM CaCl2、5 mM MgCl2,和 0.25 M 氯化钠)。在向每个孔中添加 50 μL 闪烁液之前,将滤板在热灯下干燥。使用 TopCount 对板进行计数。在一个单独的程序中,MDS Pharma Services 使用 65 种不同受体的广泛放射性配体结合测试来评估盐酸盐形式的 pimavanserin (10 μM) 的活性[1]。
|
| 动物实验 |
Mice: For studies on locomotor activity, non-Swiss albino mice are employed. Pimavanserin is administered alone (s.c. 60 min before session start or p.o. 60 min before session start) to determine spontaneous activity. In trials involving hyperactivity, mice receive 0.3 mg/kg MK-801 (i.p.) 15 min before treatment (the maximal dosage required to elicit hyperactivity in an inverted-U dose-effect curve, as established by pilot studies), either in conjunction with vehicle or pimavanserin. Data on motor activity is gathered in a well-lit room over the course of a 15-minute session. The mice had never before been in contact with the motor cages. The mice are held by the base of their tails and their forepaws are placed in contact with a horizontal wire to assess the effects of myorelaxation/ataxia prior to their placement in the locomotor chambers. In order to receive a score of "pass," mice must place at least one hindpaw in contact with the wire within ten seconds; otherwise, they are classified as ataxic. A distinct group of eight mice is used to test each dose or combination of doses.
Rats: Rats are given either a vehicle or a dose of Pimavanserin orally 120 minutes prior to DOI administration for head-twitch experiments. Docusate Ic (2.5 mg/kg i.p.) is given right before the observation. Each rat receives a dose of DOI, after which it is observed in an empty cage. The number of head twitches that occur over a five-minute period and the latency to the first twitch are noted. Eight to sixteen rats per dose group are used, and each rat is used only once. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
The median Tmax of pimavanserin in clinical studies was 6 hours, regardless of the dose. The bioavailability of an oral tablet of pimavanserin and a solution were almost identical. Ingestion of a high-fat meal had no significant effect on the rate (Cmax) and extent (AUC) of pimavanserin exposure. Cmax decreased by about 9% while AUC increased by about 8% with a high-fat meal. The major active circulating N-desmethylated metabolite, AC-279, has a median Tmax of 6 hours. Approximately 0.55% of the 34 mg oral dose of 14C-pimavanserin was eliminated as unchanged drug in urine and 1.53% was eliminated in feces after 10 days. Less than 1% of the administered dose of pimavanserin and its active metabolite AC-279 were recovered in urine. Following administration of a single dose of 34 mg, the average apparent volume of distribution was 2173 L in clinical studies. Metabolism / Metabolites Pimavanserin is mainly metabolized CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 hepatic cytochrome enzymes, and to a lesser extent by CYP2J2, CYP2D6, and other cytochrome and flavin-containing monooxygenase enzymes. CYP3A4 metabolizes pimavanserin to its major active metabolite, AC-279. Biological Half-Life The average plasma half-lives for pimavanserin and its active metabolite (AC-279) are estimated at 57 hours and 200 hours, respectively. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Liver test abnormalities are uncommon ( Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the clinical use of pimavanserin during breastfeeding. If pimavanserin is required by the mother, it is not a reason to discontinue breastfeeding. However, an alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Pimavanserin is highly protein-bound (~95%) in human plasma. Protein binding appeared to be dose-independent and did not change significantly over dosing time from Day 1 to Day 14. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Pimavanserin is a member of the class of ureas in which three of the four hydrogens are replaced by 4-fluorobenzyl, 1-methylpiperidin-4-yl, and 4-(isopropyloxy)benzyl groups. An atypical antipsychotic that is used (in the form of its tartrate salt) for treatment of hallucinations and delusions associated with Parkinson's disease. It has a role as an antipsychotic agent, a 5-hydroxytryptamine 2A receptor inverse agonist and a serotonergic antagonist. It is a member of ureas, a member of piperidines, a member of monofluorobenzenes, an aromatic ether and a tertiary amino compound. It is a conjugate base of a pimavanserin(1+).
Pimavanserin is an atypical antipsychotic indicated for the treatment of psychiatric disorders. Although the exact mechanism of action is unknown, it is thought that pimavanserin interacts with the serotonin receptors, particularly the 5-HT2A and HT2C receptors. Unlike other atypical antipsychotics, pimavanserin lacks inherent dopaminergic activity. In fact, pimavanserin is the first antipsychotic drug without D2 blocking activity. Therefore, pimavanserin can be used to treat psychotic symptoms without causing extrapyramidal or worsening motor symptoms. Pimavanserin is marketed under the trade name NUPLAZID and developed by Acadia Pharmaceuticals. It was approved by the FDA in April 2016 for the treatment of hallucinations and delusions associated with Parkinson's disease psychosis thanks to favorable results from a pivotal six-week, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study. Pimavanserin was also under review as a potential treatment for dementia-related psychosis; however, as of April 2021, FDA approval has not been granted for this indication despite previous breakthrough designation. Pimavanserin is an Atypical Antipsychotic. Pimavanserin is an atypical antipsychotic used in the treatment of hallucinations and delusions in patients with Parkinson disease and psychosis. Use of pimavanserin is associated with a low rate of serum enzyme elevations during therapy but it has not been linked to instances of clinically apparent acute liver injury. See also: Pimavanserin Tartrate (has salt form). Drug Indication Pimavanserin is indicated for the treatment of hallucinations and delusions associated with Parkinson’s disease psychosis. Treatment of schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders Mechanism of Action Parkinson's disease psychosis (PDP) is an imbalance of serotonin and dopamine from disruption of the normal balance between the serotonergic and dopaminergic receptors and neurotransmitters in the brain. The mechanism by which pimavanserin treats hallucinations and delusions associated with Parkinson’s disease psychosis is not fully established. It is possible that pimavanserin acts via inverse agonist and antagonist activity at serotonin 5-HT2A receptors with limited effects on serotonin 5-HT2C receptors. Pimavanserin is an inverse agonist and antagonist of serotonin 5-HT2A receptors with high binding affinity, demonstrating low binding affinity to serotonin 5-HT2C receptors. In addition, this drug exhibits low affinity binding to sigma 1 receptors. Pimavanserin lacks activity at muscarinic, dopaminergic, adrenergic, and histaminergic receptors, preventing various undesirable effects typically associated with antipsychotics. Pharmacodynamics Pimavanserin's unique actions on serotonin receptors improve symptoms of hallucinations and delusions associated with Parkinson's disease. In clinical studies, 80.5% of individuals treated with pimavanserin reported improvement in symptoms. Pimavanserin does not worsen motor functioning in patients with Parkinson's disease psychosis. In vitro, pimavanserin acts as an inverse agonist and antagonist at serotonin 5-HT2A receptors with high binding affinity (Ki value 0.087 nM) and at serotonin 5-HT2C receptors with lower binding affinity (Ki value 0.44 nM). Pimavanserin shows low binding to sigma 1 receptors (Ki value 120 nM) and has no appreciable affinity (Ki value >300 nM), to serotonin 5-HT2B, dopaminergic (including D2), muscarinic, histaminergic, or adrenergic receptors, or to calcium channels. The effect of pimavanserin on the QTc interval was evaluated in a randomized placebo- and positive-controlled double-blind, multiple-dose parallel thorough QTc study in 252 healthy subjects. A central tendency analysis of the QTc data at steady-state demonstrated that the maximum mean change from baseline (upper bound of the two-sided 90% CI) was 13.5 (16.6) msec at a dose of twice the therapeutic dose. A pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic analysis with pimavanserin suggested a concentration-dependent QTc interval prolongation in the therapeutic range. In the 6-week, placebo-controlled effectiveness studies, mean increases in QTc interval of ~5-8 msec were observed in patients receiving once-daily doses of pimavanserin 34 mg. These data are consistent with the profile observed in a thorough QT study in healthy subjects. Sporadic QTcF values ≥500 msec and change from baseline values ≥60 msec were observed in subjects treated with pimavanserin 34 mg; although the incidence was generally similar for pimavanserin and placebo groups. There were no reports of torsade de pointes or any differences from placebo in the incidence of other adverse reactions associated with delayed ventricular repolarization in studies of pimavanserin, including those patients with hallucinations and delusions associated with Parkinson’s disease psychosis. |
| 分子式 |
C25H34FN3O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
427.56
|
| 精确质量 |
427.263
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 70.23; H, 8.02; F, 4.44; N, 9.83; O, 7.48
|
| CAS号 |
706779-91-1
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Pimavanserin hemitartrate; 706782-28-7
|
| PubChem CID |
10071196
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.1±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
604.2±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
117-119
|
| 闪点 |
319.2±31.5 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.576
|
| LogP |
4.67
|
| tPSA |
44.81
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
| 重原子数目 |
31
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
523
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
CC(C)COC1=CC=C(CNC(N(CC2=CC=C(F)C=C2)C3CCN(C)CC3)=O)C=C1
|
| InChi Key |
RKEWSXXUOLRFBX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C25H34FN3O2/c1-19(2)18-31-24-10-6-20(7-11-24)16-27-25(30)29(23-12-14-28(3)15-13-23)17-21-4-8-22(26)9-5-21/h4-11,19,23H,12-18H2,1-3H3,(H,27,30)
|
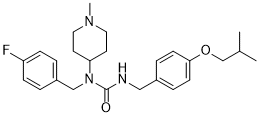
| 化学名 |
1-[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-1-(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)-3-[[4-(2-methylpropoxy)phenyl]methyl]urea
|
| 别名 |
ACP-103; BVF-036; ACP 103; BVF036; ACP103; Trade name: Nuplazid
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.85 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.85 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.85 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3389 mL | 11.6943 mL | 23.3885 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4678 mL | 2.3389 mL | 4.6777 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2339 mL | 1.1694 mL | 2.3389 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Extension Study of Pimavanserin in Irritability Associated With Autism Spectrum Disorder
CTID: NCT05555615
Phase: Phase 2/Phase 3 Status: Recruiting
Date: 2024-08-07
Anti-tremor effect of ACP-103. The number of tremulous jaw movements is shown as a function of ACP-103 dose in combination with tacrine.Pharmacol Biochem Behav.2008 Oct;90(4):540-4. |
|---|
Anti-dyskinetic effect of ACP-103. Dyskinesia severity score is shown as a function of ACP-103 dose in combination with levodopa in MPTP-treated monkeys.Pharmacol Biochem Behav.2008 Oct;90(4):540-4. |