| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
FGFR1 (IC50 = 0.6 nM); FGFR2 (IC50 = 1.3 nM); FGFR3 (IC50 = 4.1 nM); FGFR4 (IC50 = 19.3 nM); CSF1R (IC50 = 8.1 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:PRN1371 是 FGFR1−4 的不可逆纳摩尔抑制剂。 PRN1371 具有独特的高生化和细胞效力(FGFR1 IC50 = 0.6 nM,SNU16 IC50 = 2.6 nM)、延长的靶点参与(FGFR1 占用率 24 小时 = 96%)、<30% 1= herg= 抑制= at= 和= 良好= 预测= adme= 稳定性= with= bme= 反应性= kd=>100 μM。 PRN1371 保持了较高的 FGFR1 占有率,并具有改善的溶解度和出色的口服生物利用度。激酶测定:使用 Caliper 毛细管电泳系统测定酶抑制,该系统根据电荷分离磷酸化和非磷酸化肽。首先将不同浓度的 PRN1371 与酶预孵育 15 分钟。通过添加肽底物、ATP 和 Mg2+ 来启动反应,并在 25°C 下孵育 3 小时。为了停止反应,用 EDTA 猝灭混合物。缓冲液为 100 mM HEPES、pH 7.5、0.1% BSA、0.01% Triton X-100、1 mM DTT、10 mM MgCl2、10 mM 原钒酸钠、10 μM β-甘油磷酸盐和 1% DMSO。反应的 ATP 浓度处于 ATP 的 Km 预定值。 MCE 尚未独立证实这些方法的准确性。它们仅供参考。细胞测定:将人脐静脉内皮细胞(HUVEC)在补充有10%FBS的培养基中孵育,并以每孔30000个细胞接种在96孔板中过夜。然后在化合物处理前1小时将HUVEC转移至无血清培养基中。将化合物浓度系列添加到细胞中并在 37°C 下孵育 1 小时。然后用 50 ng/mL 的 FGF2 或 50 ng/mL 的 VEGF 刺激细胞 10 分钟。加入冰冷的PBS终止反应,洗涤细胞3次以除去培养基。测定ERK磷酸化。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
化合物 34 的大鼠静脉注射 (2 mg/kg) PK 研究显示快速清除 (Cl = 160 ml/min/kg),但口服给药 (20 mg/kg) 表现出较高的口服暴露量 (AUC = 4348 h·ng/mL) )和合理的半衰期(t1/2 = 3.8 h)。化合物 34 在大鼠、狗和食蟹猴中的 PK 研究表明,所有物种的静脉注射清除率均迅速;然而,与大鼠和狗相比,猴子的口服暴露和生物利用度存在很大的物种差异。在大鼠中,口服给药后的高暴露(例如,Cmax = 1785 ng/mL,AUC = 4348 ng·h/mL)和>100% 生物利用度(F)表明在 20 mg/kg 剂量下具有良好的吸收和清除机制部分饱和剂量。对于大鼠来说,静脉注射(t1/2 = 0.8 小时)和口服(t1/2 = 3.8 小时)给药途径之间的半衰期存在很大差异,这也表明口服清除机制可能饱和。剂量。在狗中,用于大鼠的相同甲基纤维素悬浮液制剂的口服吸收和生物利用度较低(F < 15%)。在 SNU16 胃癌异种移植小鼠模型中,化合物 34 诱导肿瘤体积呈剂量依赖性减小,并且在治疗 27 天后,在最高剂量 10 mg/kg bid 时,肿瘤生长抑制率高达 68%。所有剂量均耐受良好,没有明显的体重减轻。
|
| 酶活实验 |
激酶分析[1]< br >
使用卡钳毛细管电泳系统,根据电荷划分磷酸化和非磷酸化肽,测量酶抑制。首先,以不同浓度将PRN1371与酶预孵育15分钟。加入肽底物、ATP和Mg2+开始反应,然后在25℃下孵育3小时。EDTA用于淬火混合物以停止反应。pH 7.5、100 mM HEPES、0.1% BSA、0.01% Triton X-100、1 mM DTT、10 mM MgCl2、10 mM正钒酸钠、10 μM β-甘油磷酸钠和1% DMSO组成缓冲液。反应的ATP浓度为预先设定的ATP Km值[1]。
β-巯基乙醇测定Kd [1] 溶液中分别含有0、1.5、15、150和1500 mM β-巯基乙醇(BME),乙醇和磷酸盐缓冲盐水(pH 7.4, PBS)以1:1的比例混合。将试验化合物PRN1371 (10 μL)的10 mM DMSO原液分别加入90 μL的乙醇/PBS (0-1500 mM BME)溶液中。这些溶液在室温下放置2小时后,使用配备50 mm × 2 mm Phenomenex Luna 5 μm C18 100A柱的Agilent 1200 LCMS系统进行分析。样品用乙腈和水的梯度洗脱,两种溶剂都含有0.1%甲酸。根据母本和BME加合物的质量确定其对应的峰,通过测量母本和BME加合物对应的正离子谱中提取的质量峰的曲线下面积来确定每个样品中母本的百分比。使用GraphPad Prism绘制亲本百分比与BME浓度的对数,以确定反应的表观Kd。 HUVECs中ERK磷酸化的研究[1] 人脐静脉内皮细胞(HUVECs)在添加10%胎牛血清的培养基中孵育,以每孔30 000个细胞的速度在96孔板中孵育过夜。在复合/PRN1371处理前1 h,将huvec转移到无血清培养基中。在细胞中加入化合物浓度系列,在37℃下孵育1 h。然后用50 ng/mL的FGF2或50 ng/mL的VEGF刺激细胞10分钟。加入冰冷的PBS停止反应,细胞清洗三次以去除培养基。使用Envision多标签平板阅读器,使用pERK SureFire试剂盒测定ERK磷酸化。 基于荧光竞争的FGFR1停留时间研究[1] 采用50 mM Hepes pH 7.5、10 mM MgCl2、0.01% Triton-X 100和1 mM EGTA缓冲液,将1 μL 15 μM compound/PRN1371加入到9 μL 0.5 μM FGFR1的96孔聚丙烯板中。孵育60分钟后,将混合物在实验缓冲液中稀释100倍。将10 μL稀释后的混合物转移到格雷纳384孔黑板上。加入铕偶联抗6xhis Ab和cy5标记吡啶嘧啶酮示踪剂,最终浓度分别为15 nM和0.75 μM,体积为20 μL。数据采集使用PerkinElmer Envision平板阅读器(型号2101)包含LANCE TR-FRET兼容激发和发射滤波器。在不同时间采集665 nM和615 nM波长的荧光。在每个实验中,在没有测试化合物的情况下,获得由酶、铕偶联Anti-6XHis Ab和示踪剂信号组成的提供最大信号(max)的条件。加入1 μM浓度的PP-ir完全阻断示踪剂结合,获得背景信号(bkg)。每个试验化合物的数据以占用率报告,其计算为100 × (1 - (compd - bkg)/(max - bkg))。 FGFR1进展曲线分析[1] 获得6种浓度下FGFR1肽(5-FAM-KKKKEEIYFFF-NH2)磷酸化的进展曲线。使用气候控制的Caliper LabChip仪器获得共5小时的实时曲线。用XLfit4软件拟合得到的曲线与时间依赖性抑制方程:[P] = Vst + ((Vi - Vs)/Kobs)(1 - exp(−Kobst))。式中,Vi为初速度,Vs为稳态速度,Kobs为失活速率。对于时间依赖性抑制剂,获得的Kobs值与化合物/PRN1371浓度使用双曲线拟合或线性拟合绘制。从这些图中,确定了kinact和Ki。 |
| 细胞实验 |
为了达到 5 μM 的最终化合物浓度,首先将 SNU16 细胞接种到 384 孔板中,然后添加 PRN1371。 PRN1371 在 37°C 下在细胞中孵育 72 小时。将 Presto-Blue 细胞活力试剂添加到样品中以确定状态。 Analyst HT 在荧光模式下使用 530 nm 激发和 590 nm 发射来读取板[1]。
|
| 动物实验 |
Mice: Using a SNU16 gastric cancer xenograft mouse model with high FGFR2 overexpression, PRN1371 is assessed in pharmacodynamic and efficacy studies. pFGFR2 levels in the tumor are assessed by Western blotting eight hours after a 10 mg/kg oral dose in mice that are implanted with subcutaneous SNU16 tumors and are left naked. Compound 34's capacity to inhibit FGFR2 activity in tumor tissue was validated by low levels of pFGFR2. Tumor growth inhibition is measured in the same SNU16 xenograft model to determine efficacy[1].
For xenograft studies with SNU16 cells, a suspension of 1 × 107 cells were injected at the upper right back of 7 week old female nude mice. The care and treatment of experimental animals were in accordance with institutional guidelines. Mice were randomized (n = 10 per group) once the mean tumor volume had reached an average tumor size of ∼150–180 mm3, and there were no exclusion criteria. PRN1371 was suspended in 0.5% methylcellulose w/w in deionized water. Tumor volumes were measured three times weekly using a caliper, and the volume was expressed in mm3 using the formula V = 0.5ab2 where a and b are the long and short diameters of the tumor, respectively. Tumor weight was measured at study termination. SNU16 tumor cell lysates were evaluated for pFGFR by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotting using a rabbit anti-pFGFR2 antibody and a mouse anti-FGFR2 antibody |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
PK studies of compound 34 (PRN1371) in rat, dog, and cynomolgus monkey showed rapid iv clearance in all species; however there were large species differences in oral exposure and bioavailability for monkey compared to rat and dog (Table 8). In rat, high exposure upon oral dosing (e.g., Cmax = 1785 ng/mL, AUC = 4348 ng·h/mL) and >100% bioavailability (F) suggested good absorption and partial saturation of clearance mechanisms at the 20 mg/kg dose. Unique to the rat, there is a large difference in half-life between the iv (t1/2 = 0.8 h) and po (t1/2 = 3.8 h) routes of administration, also indicative of possible saturation of a clearance mechanism upon oral dosing. In the dog, the same methylcellulose suspension formulation used for the rat gave low oral absorption and bioavailability (F < 15%). We hypothesized that the less acidic gastric and intestinal pH of the dog may be contributing to low absorption of the free base of compound 34. (31) Coadministration of a molar equivalent of citric acid improved the oral absorption of a 10 mg/kg dose (e.g., Cmax = 1103 ng/mL, AUC = 1134 ng·h/mL, F = 94%) and brought it in line with the rat PK. Exceptionally low oral exposure in the monkey (e.g., Cmax = 96 ng/mL, AUC = 84 ng·h/mL) was initially a cause for concern. We were able to attribute this to intestinal Cyp3A4 mediated metabolism. It has been reported that the bioavailability in monkey of compounds that undergo intestinal metabolism is much lower than that of rat or human. (32) For neratinb and ibrutinib, two covalent kinase inhibitors with acrylamide Michael acceptors that undergo extensive Cyp3A4 mediated metabolism, monkey PK grossly overestimates clearance and underestimates absorption, making monkey an inappropriate species for the prediction of human absorption. (29) On this basis, we were comfortable with the preclinical PK of compound 34 as it predicted our desired profile of high oral absorption followed by rapid clearance.[1]
With good in vivo efficacy and PK, compound 34 (PRN1371)was progressed into preclinical safety evaluations including 28 day GLP toxicology studies in rats and dogs. The toxicological findings were consistent with those reported for other FGFR inhibitors, predominantly phosphorus dysregulation and concomitant soft tissue mineralization. (33) Phosphorus homeostasis is dependent upon FGF23 signaling in the kidney. As a consequence, clinical on-target mediated effects of FGFR blockade include elevated serum FGF23, phosphate, and vitamin D. (4b, 34) The combination of a clean preclinical safety profile, favorable human PK projections, and efficacy in the xenograft models gave us confidence to advance compound 34 into human clinical trials.[1] Compound 34/PRN1371 presents a unique profile of high biochemical and cellular potency (FGFR1 IC50 = 0.6 nM, SNU16 IC50 = 2.6 nM), prolonged target engagement (FGFR1 occupancy 24 h = 96%), < 30% hERG inhibition at 1 μM, and good predicted ADME stability with BME reactivity Kd > 100 μM. A rat iv (2 mg/kg) PK study of compound 34 showed rapid clearance (Cl = 160 mL min–1 kg–1), yet dosing po (20 mg/kg) demonstrated high oral exposure (AUC = 4348 h·ng/mL) and a reasonable half-life (t1/2 = 3.8 h). Broader kinome-wide biochemical profiling of 34 against 251 kinases identified only FGFR1–4 and CSF1R as being potently inhibited (e.g., IC50 < 20 nM) (Table 6 and Supporting Information Table S1). The ATP binding site of CSF1R does not have a proximal cysteine residue, and compound 34 binds noncovalently, as determined by recovery of kinase activity upon dialysis. Consistent with reversible binding, there is a large shift between the biochemical potency (8.1 nM IC50) and the cellular potency of CSF1R inhibition (>1500 nM IC50), rendering it physiologically irrelevant.[1] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
A phase 1 dose escalation study is being conducted in patients with advanced solid tumors and metastatic disease to assess pharmacokinetics, tolerability, and objective response rate, among other end points (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT02608125). Compound 34 free base (PRN1371) has been administered orally once daily as powder in a capsule on a 28-day continuous schedule. Human plasma concentrations for doses ranging from 15 to 35 mg (Figure 4A) confirm good oral exposure, rapid systemic clearance, no accumulation from day 1 to day 15, and a dose-dependent increase in AUC. Serum phosphate, a pharmacodynamic marker of FGFR inhibition, is increased for all doses studied and shows a dose-dependent increase between 20 and 35 mg, despite the administration of prophylactic phosphate binders (Figure 4B). Additional cohorts and dosing regimens are being explored in ongoing clinical studies and will be reported in due course.[1]
|
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
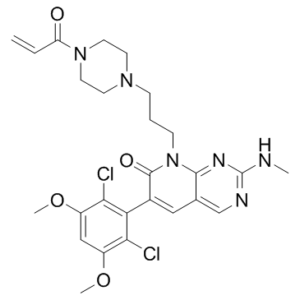
pan FGFR Inhibitor PRN1371 is a highly specific covalent inhibitor of human fibroblast growth factor receptor types 1, 2, 3 and 4 (FGFR1-4) with potential antiangiogenic and antineoplastic activities. FGFR1-4 tyrosine kinase inhibitor PRN1371 specifically binds to a conserved cysteine residue in the glycine-rich loop in FGFRs and inhibits their tyrosine kinase activity, which may result in the inhibition of both tumor angiogenesis and tumor cell proliferation, and the induction of tumor cell death. FGFRs are a family of receptor tyrosine kinases, which may be upregulated in various tumor cell types and may be involved in tumor cell differentiation, proliferation and survival, and in tumor angiogenesis. This agent potently inhibits FGFR1-4 but does not inhibit other tyrosine kinases, even those that share the conserved cysteine, which may improve therapeutic responses and decrease toxicity when compared with less selective inhibitors.
|
| 分子式 |
C26H30CL2N6O4
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
561.460203647614
|
|
| 精确质量 |
560.17
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 55.62; H, 5.39; Cl, 12.63; N, 14.97; O, 11.40
|
|
| CAS号 |
1802929-43-6
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
118295624
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| LogP |
3.5
|
|
| tPSA |
100
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
9
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
38
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
870
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
0
|
|
| InChi Key |
PUIXMSRTTHLNKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C26H30Cl2N6O4/c1-5-20(35)33-11-9-32(10-12-33)7-6-8-34-24-16(15-30-26(29-2)31-24)13-17(25(34)36)21-22(27)18(37-3)14-19(38-4)23(21)28/h5,13-15H,1,6-12H2,2-4H3,(H,29,30,31)
|
|
| 化学名 |
6-(2,6-dichloro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-(methylamino)-8-[3-(4-prop-2-enoylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl]pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-one
|
|
| 别名 |
PRN-1371; PRN 1371; PRN1371; 1802929-43-6; 8-(3-(4-acryloylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl)-6-(2,6-dichloro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-(methylamino)pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7(8H)-one; UNII-S3OPE9IA3Q; S3OPE9IA3Q; 6-(2,6-dichloro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-(methylamino)-8-[3-(4-prop-2-enoylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl]pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-one; compound 34 [PMID: 28665128]; PRN1371
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.45 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (4.45 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.45 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7811 mL | 8.9054 mL | 17.8107 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3562 mL | 1.7811 mL | 3.5621 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1781 mL | 0.8905 mL | 1.7811 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT02608125 | Terminated | Drug: PRN1371 | Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma & Renal Pelvis & Ureter Solid Tumors |
Principia Biopharma, a Sanofi Company |
October 28, 2015 | Phase 1 |
Rat in vivo inhibition of bFGF-induced CCL2 production.J Med Chem.2017 Aug 10;60(15):6516-6527. |
|---|
PK/PD and efficacy of compound34in a SNU16 mouse xenograft model.J Med Chem.2017 Aug 10;60(15):6516-6527. |
Phase I clinical data for once daily oral administration of compound34.J Med Chem.2017 Aug 10;60(15):6516-6527. |