| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
瑞格列奈通过促进早期胰岛素分泌并增加胰岛素分泌总量来降低餐后血糖水平[1]。
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
瑞格列奈 (AG-EE 623ZW) 的 t1/2 小于一小时,并且吸收非常快(tmax 小于一小时)。在 90% 以上的病例中,瑞格列奈也会在肝脏中失活并通过胆汁消除。瑞格列奈(1 mg/kg,口服)在 2 型糖尿病大鼠模型(低剂量链脲佐菌素)中是一种有效的(P<0.001)胰岛素释放药物。
|
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Rapidly and completely absorbed following oral administration. Peak plasma concentrations are observed within 1 hour (range 0.5-1.4 hours). The absolute bioavailability is approximately 56%. Maximal biological effect is observed within 3-3.5 hours and plasma insulin levels remain elevated for 4-6 hours. When a single 2 mg dose of repaglinide is given to healthy subjects, the area under the curve (AUC) is 18.0 - 18.7 (ng/mL/h)^3. 90% eliminated in feces (<2% as unchanged drug), 8% in urine (0.1% as unchanged drug) 31 L following IV administration in healthy individuals 33-38 L/hour following IV administration Metabolism / Metabolites Repaglinide is rapidly metabolized via oxidation and dealkylation by cytochrome P450 3A4 and 2C9 to form the major dicarboxylic acid derivative (M2). Further oxidation produces the aromatic amine derivative (M1). Glucuronidation of the carboxylic acid group of repaglinide yields an acyl glucuronide (M7). Several other unidentified metabolites have been detected. Repaglinide metabolites to not possess appreciable hypoglycemic activity. Repaglinide has known human metabolites that include Repaglinide aromatic amine, 2-ethoxy-4-[2-[[1-[2-(4-hydroxybutylamino)phenyl]-3-methylbutyl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]benzoic acid, 3'-Hydroxy Repaglinide(Mixture of Diastereomers), 2-ethoxy-4-[2-[[3-hydroxy-3-methyl-1-(2-piperidin-1-ylphenyl)butyl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]benzoic acid, and 2-Hydroxy-4-[2-[[3-methyl-1-(2-piperidin-1-ylphenyl)butyl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]benzoic acid. Biological Half-Life 1 hour |
||
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In several large clinical trials, serum aminotransferase elevations during repaglinide therapy were uncommon and similar in frequency with placebo. All serum enzyme elevations that occurred were asymptomatic and resolved rapidly with stopping therapy. Since its approval and with wide scale use, there have been a small number of reports of clinically apparent liver injury attributed to repaglinide. The time to onset ranged from 2 to 8 weeks and the pattern of serum enzyme elevations was typically cholestatic or mixed. Jaundice and pruritus were prominent. Immunoallergic features and autoantibodies were not present. All published cases have been self-limited, resolving within 1 to 2 months of stopping. Likelhood score: D (possible rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the use of repaglinide during breastfeeding. Repaglinide is a weak acid that is over 98% protein bound, so it is unlikely to pass into breastmilk in clinically important amounts. Monitor breastfed infants for signs of hypoglycemia such as jitteriness, excessive sleepiness, poor feeding, seizures cyanosis, apnea, or hypothermia. If there is concern, monitoring of the breastfed infant's blood glucose is advisable during maternal therapy with repaglinide. However, an alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding >98% (e.g. to to albumin and α1-acid glycoprotein) |
||
| 参考文献 | |||
| 其他信息 |
Pharmacodynamics
Insulin secretion by pancreatic β cells is partly controlled by cellular membrane potential. Membrane potential is regulated through an inverse relationship between the activity of cell membrane ATP-sensitive potassium channels (ABCC8) and extracellular glucose concentrations. Extracellular glucose enters the cell via GLUT2 (SLC2A2) transporters. Once inside the cell, glucose is metabolized to produce ATP. High concentrations of ATP inhibit ATP-sensitive potassium channels causing membrane depolarization. When extracellular glucose concentrations are low, ATP-sensitive potassium channels open causing membrane repolarization. High glucose concentrations cause ATP-sensitive potassium channels to close resulting in membrane depolarization and opening of L-type calcium channels. The influx of calcium ions stimulates calcium-dependent exocytosis of insulin granules. Repaglinide increases insulin release by inhibiting ATP-sensitive potassium channels in a glucose-dependent manner. |
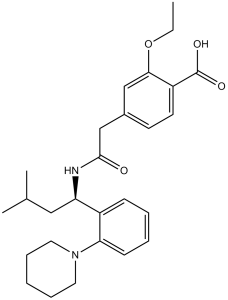
| 分子式 |
C27H36N2O4
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
452.59
|
|
| 精确质量 |
452.267
|
|
| CAS号 |
135062-02-1
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Repaglinide-d5;1217709-85-7
|
|
| PubChem CID |
65981
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.1±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
672.9±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
129-130.2 °C
|
|
| 闪点 |
360.8±31.5 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.2 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.568
|
|
| LogP |
4.69
|
|
| tPSA |
78.87
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
10
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
33
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
619
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
CCOC1=C(C=CC(=C1)CC(=O)N[C@@H](CC(C)C)C2=CC=CC=C2N3CCCCC3)C(=O)O
|
|
| InChi Key |
FAEKWTJYAYMJKF-QHCPKHFHSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C27H36N2O4/c1-4-33-25-17-20(12-13-22(25)27(31)32)18-26(30)28-23(16-19(2)3)21-10-6-7-11-24(21)29-14-8-5-9-15-29/h6-7,10-13,17,19,23H,4-5,8-9,14-16,18H2,1-3H3,(H,28,30)(H,31,32)/t23-/m0/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
2-ethoxy-4-[2-[[(1S)-3-methyl-1-(2-piperidin-1-ylphenyl)butyl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]benzoic acid
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.52 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.52 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.52 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2095 mL | 11.0475 mL | 22.0951 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4419 mL | 2.2095 mL | 4.4190 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2210 mL | 1.1048 mL | 2.2095 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
A Phase 3, 24-Week, Multi-Center, Open-Label, Randomized, Controlled Trial Comparing the Efficacy and Safety of Prandial Inhalation of Technosphere®/Insulin in Combination with Metformin or Technosphere®/Insulin Alone Versus 2 Oral Anti-Diabetic Agents (Metformin and a Secretagogue) in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Sub-Optimally Controlled on Combination Metformin and a Secretagogue
CTID: null
Phase: Phase 3 Status: Completed
Date: 2006-12-01
|
|---|
|