| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) (IC50 = 4150 ± 160 nM against erythrocyte-derived AChE)[1]
Butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) (IC50 = 37 ± 5 nM)[1] Cholinesterase inhibitor (Acetylcholinesterase and Butyrylcholinesterase)[2] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
卡巴拉汀(S-卡巴拉汀;1 µM;24 小时)与卡巴胆碱 (10 µM) 联用可分别使 LPS (2.5 µg/ml) 诱导的 TNF-α 和 IL-6 降低 50% 和 46%。 %,但不会造成任何实质性影响。促炎细胞因子降低[3]。卡巴拉汀 (1 µM)、卡巴胆碱 (10 µM) 或两种药物的组合对活化细胞没有细胞毒性作用 [3]。
在离体实验中,评估了 利斯的明 对人红细胞来源的乙酰胆碱酯酶 (AChE) 和血浆来源的丁酰胆碱酯酶 (BChE) 的抑制活性。测得其对AChE的IC50值为4150 ± 160 nM,对BChE的IC50值为37 ± 5 nM。[1] 这表明 利斯的明 对BChE的抑制效力强于对AChE的抑制效力(根据报告的IC50值,对BChE的选择性约为112倍)。[1] 文献指出,利斯的明 的特殊之处在于其对脑源性AChE的活性远强于对红细胞来源的AChE。因此,测得的针对红细胞来源AChE的IC50值严重低估了其在大脑中的活性。据报道,考虑到其在大脑中的活性,该药物对AChE和BChE是非选择性的。[1] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
腹腔注射卡巴拉汀(S-卡巴拉汀;0.5-2.5 mg/kg;在测试前 60 分钟给药)可显着且剂量依赖性地减轻铝引起的行为异常[4]。在患有急性结肠炎、体重为 200-250 克的 BALB/c OlaHsd 雄性 8-9 周龄小鼠中,卡巴拉汀(0.5、1 mg/kg/天;皮下注射;持续 8 天)可使 IL-6 浓度降低约 50% 和 60%分别是,但不是 TNF-α 和 IL-1β 浓度 [3]。 1 mg/kg 的卡巴拉汀可完全止血并抑制结肠收缩,但 0.5 mg/kg 的剂量则不然。虽然卡巴拉汀 (1 mg/kg) 可减少粘膜下水肿和细胞浸润,但卡巴拉汀 (0.5 mg/kg) 治疗显示这些病理结果的变化最小。此外,还观察到了地穴结构的部分恢复。试验结束时,卡巴拉汀 (1 mg/kg) 使体重减轻了 4.7% [3]。
这项临床研究评估了将很可能患有阿尔茨海默病的患者从口服胆碱酯酶抑制剂转换为 利斯的明 透皮贴剂的疗效。治疗24周后,根据临床总体印象变化量表评分评估,82.8% (116人中的96人) 的患者整体功能表现出改善或未进一步恶化。[2] 关于通过韩国版简易精神状态检查表评估的认知功能,116名患者中有64.3%在第24周时评分较基线增加或保持稳定。然而,K-MMSE评分的平均变化为0.42 ± 0.8,无统计学显著性 (p > 0.05)。[2] 在第24周,韩国版工具性日常生活活动能力量表和临床痴呆评定量表-总分未观察到相对于基线的统计学显著变化。[2] |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Male Wistar albino rat, body weight 190–240 g (90 days old) [4]
Doses: 0.5, 1, 1.5 and 2.5 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip) injection; single dose Experimental Results: significant and dose Dependently improves aluminum-induced behavioral disturbances (100 mg/kg/day; i.p.; for 60 days) |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Rivastigmine is extensively metabolized primarily via cholinesterase-mediated hydrolysis to the decarbamylated metabolite NAP226-90. Renal excretion of the metabolites is the major route of elimination. Less than 1% of the administered dose is excreted in the feces. 1.8 to 2.7 L/kg renal cl=2.1-2.8 L/hr Metabolism / Metabolites Rivastigmine is rapidly metabolized by cholinesterase-mediated hydrolysis. Biological Half-Life 1.5 hours The rivastigmine transdermal patch delivers the drug through the skin, directly into the bloodstream, thereby avoiding first-pass effects that occur with oral administration.[2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In large placebo controlled trials, rivastigmine therapy was not associated with an increased rate of serum enzyme elevations compared to placebo treatment and no instances of clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice were reported. Nevertheless, since its introduction into clinical use, rivastigmine (administered by transdermal patch) has been implicated in at least one report of clinically apparent hepatotoxicity with mild jaundice. The time to onset was 2 months and the serum enzyme elevations had a mildly hepatocellular pattern. Mild rash and eosinophilia were also present, but autoimmune features were not. Recovery was complete within 5 weeks of drug discontinuation. Likelihood score: D (possible, rare cause of clinically apparent drug-induced liver injury). Protein Binding 40% In this 24-week study, 12.2% (20 out of 164) of enrolled patients discontinued due to adverse events. The most frequently reported adverse events were skin lesions at the application site, such as erythema or itching, occurring in 11% of patients. No serious skin problems were reported.[2] Gastrointestinal problems (e.g., nausea, vomiting, anorexia) were reported in 1.2% of patients.[2] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
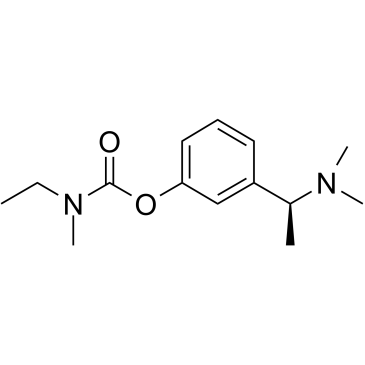
Rivastigmine is a carbamate ester obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of ethyl(methyl)carbamic acid with the phenolic OH group of 3-[(1S)-1-(dimethylamino)ethyl]phenol. A reversible cholinesterase inhibitor. It has a role as an EC 3.1.1.8 (cholinesterase) inhibitor, a neuroprotective agent and a cholinergic drug. It is a carbamate ester and a tertiary amino compound. It is a conjugate base of a rivastigmine(1+).
Rivastigmine is a parasympathomimetic or cholinergic agent for the treatment of mild to moderate dementia of the Alzheimer's type. Rivastigmine is a cholinesterase inhibitor that inhibits both butyrylcholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase. Rivastigmine is a Cholinesterase Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of rivastigmine is as a Cholinesterase Inhibitor. Rivastigmine is an oral acetylcholinesterase inhibitor used for therapy of Alzheimer disease. Rivastigmine is associated with a minimal rate of serum enzyme elevations during therapy and is a rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury. A carbamate-derived reversible CHOLINESTERASE INHIBITOR that is selective for the CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM and is used for the treatment of DEMENTIA in ALZHEIMER DISEASE and PARKINSON DISEASE. See also: Rivastigmine Tartrate (narrower). Drug Indication For the treatment of mild to moderate dementia associated with Parkinson's disease or of the Alzheimer's type. FDA Label Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's dementia. Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe dementia in patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's dementia. Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe dementia in patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's dementia. Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe dementia in patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's dementia. Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe dementia in patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's dementia. Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe dementia in patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's dementia. , , Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe dementia in patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. , Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's dementia. Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's dementia. Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe dementia in patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Treatment of dementia Treatment of dementia Mechanism of Action Rivastigmine is a carbamate derivative that is structurally related to physostigmine, but not to donepezil and tacrine. The precise mechanism of rivastigmine has not been fully determined, but it is suggested that rivastigmine binds reversibly with and inactivates chlolinesterase (eg. acetylcholinesterase, butyrylcholinesterase), preventing the hydrolysis of acetycholine, and thus leading to an increased concentration of acetylcholine at cholinergic synapses. The anticholinesterase activity of rivastigmine is relatively specific for brain acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase compared with those in peripheral tissues. Pharmacodynamics Rivastigmine is a parasympathomimetic and a reversible cholinesterase inhibitor. An early pathophysiological feature of Alzheimer's disease that is associated with memory loss and cognitive deficits is a deficiency of acetylcholine as a result of selective loss of cholinergic neurons in the cerebral cortex, nucleus basalis, and hippocampus. Tacrine is postulated to exert its therapeutic effect by enhancing cholinergic function. While the precise mechanism of rivastigmine's action is unknown, it is postulated to exert its therapeutic effect by enhancing cholinergic function. This is accomplished by increasing the concentration of acetylcholine through reversible inhibition of its hydrolysis by cholinesterase. If this proposed mechanism is correct, rivastigmine's effect may lessen as the disease progresses and fewer cholinergic neurons remain functionally intact. Rivastigmine is listed among other compounds currently in clinical assessment or approved by the FDA for use in subjects with Alzheimer's disease.[1] The activity of Rivastigmine against brain-derived AChE is noted to be far more potent than against erythrocyte-derived AChE, making its measured IC50 value against the latter a significant underestimate of its brain activity.[1] It has been reported that Rivastigmine is nonselective between AChE and BChE when considering its activity in the brain.[1] Rivastigmine is a cholinesterase inhibitor used for the symptomatic treatment of mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease.[2] This study investigated the rivastigmine transdermal patch as an alternative for patients who had a poor response or intolerance to oral cholinesterase inhibitors (donepezil, galantamine, or rivastigmine capsules).[2] The transdermal patch formulation is designed to provide smooth and continuous drug delivery, potentially improving tolerability compared to oral formulations.[2] The study concluded that immediate switching from oral cholinesterase inhibitors to the rivastigmine transdermal patch without a washout period was safe and well-tolerated in patients with probable Alzheimer's disease.[2] The starting dose was a 5 cm² patch, which could be increased to a 10 cm² patch after 4 weeks based on tolerability. The patch was applied to the upper back daily and worn for 24 hours.[2] |
| 分子式 |
C14H22N2O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
250.34
|
| 精确质量 |
250.168
|
| CAS号 |
123441-03-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Rivastigmine tartrate;129101-54-8;(rac)-Rivastigmine-d6;194930-04-6
|
| PubChem CID |
77991
|
| 外观&性状 |
Colorless to light yellow liquid
|
| 密度 |
1.0±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
316.2±34.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
145.0±25.7 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±0.7 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.518
|
| LogP |
2.14
|
| tPSA |
147.84
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
18
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
269
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
O=C(N(C)CC)OC1=CC=CC([C@H](C)N(C)C)=C1
|
| InChi Key |
XSVMFMHYUFZWBK-NSHDSACASA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C14H22N2O2/c1-6-16(5)14(17)18-13-9-7-8-12(10-13)11(2)15(3)4/h7-11H,6H2,1-5H3/t11-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
[3-[(1S)-1-(dimethylamino)ethyl]phenyl] N-ethyl-N-methylcarbamate
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ≥ 50 mg/mL (~199.73 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.99 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.99 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.99 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.9946 mL | 19.9728 mL | 39.9457 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7989 mL | 3.9946 mL | 7.9891 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3995 mL | 1.9973 mL | 3.9946 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
A Phase IV Study to Evaluate Safety, Tolerability and Effectiveness of Rivastigmine Patch 15cm2 in Patients With Severe Dementia of the Alzheimer's Type.
CTID: NCT02989402
Phase: Phase 4 Status: Completed
Date: 2024-05-31