| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
MEK1 (IC50 = 5.2 nM); MEK2 (IC50 = 5.2 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
RO4987655 有效抑制丝裂原激活蛋白激酶信号通路激活和肿瘤细胞生长,抑制 MEK1/2 的体外 IC50 为 5.2 nM[1]。 RO4987655 以剂量依赖性方式抑制 NCI-H2122 细胞的增殖,IC50 值为 0.0065 μM。在 0.1 至 1.0 μM 的剂量范围内,RO4987655 最早在治疗后 2 小时即可抑制 pERK1/2[2]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在异种移植模型中,RO4987655 (CH4987655) 作为单一药物口服给药可完全根除肿瘤。 RO4987655 的 tmax 不到一小时,会被迅速吸收。 0.5 至 4 mg 的暴露量与剂量成正比。终末 t1/2 小于 25 小时,该处置是双相的。观察到较低的受试者间变异性; Cmax 和曲线下面积 (AUC) 的范围分别为 9%–23% 和 14%–25%。在较高剂量下,pERK 抑制率超过 80%,并且具有暴露依赖性。抑制性 Emax 模型(Emax ~100%;IC50 40.6 ng/mL)用于非线性混合效应模型来描述药代动力学-药效关系[1]。随机分配的研究组由雌性无胸腺裸鼠组成。使用数字卡尺,在第 0、1 和 3 天,使用剂量为 1.0、2.5 和 5.0 mg/kg RO4987655 来估计肿瘤大小。在此期间,载体治疗不会阻止 NCI-H2122 肿瘤异种移植物的生长。另一方面,RO4987655 治疗第 3 天,1.0 mg/kg 时的肿瘤生长抑制 (TGI) 为 119%,2.5 mg/kg 时为 145%,5.0 mg/kg 时为 150%。PET 成像表明[18F ] RO4987655 给药后 24 小时(第 1 天),异种移植物中的 FDG 摄取减少[2]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
RO4987655(也称为 CH-4987655)是一种新型、口服生物可利用的、特异性的 MEK 激酶小分子抑制剂,对 MEK1/MEK2 的 IC50 为 5.2 nM。丝裂原激活蛋白激酶激酶 1 (MAP2K1/MEK1) 可能具有抗肿瘤活性,是该药物的靶标。 MEK1/2抑制的体外IC50为5.2 nmol/L,可有效阻止丝裂原激活蛋白激酶信号通路的激活和肿瘤细胞的生长。
|
| 细胞实验 |
将热灭活的胎牛血清和 L-谷氨酰胺在人肺腺癌细胞系 NCI-H2122 的指定培养基中维持在指定浓度。在 37 摄氏度和 5% 二氧化碳的条件下,细胞会发育。将细胞在 96 孔板中暴露于不同浓度(0.00001、0.001、0.1 和 10 μM)的 RO4987655 72 小时后,使用 Cell Counting Kit-8 对活细胞进行计数 [2]。
|
| 动物实验 |
Mice: Mice that are athymic and naked in females It uses balb nu/nu that are 5 to 6 weeks old (18 to 22 g). Balb-nu/nu mice receive a subcutaneous injection of NCI-H2122 cells ((4×106/mouse). Mice are randomized into groups with comparable mean tumor volumes at the beginning of the study once tumors are established (100 to 200 mm3). On days 0, 1, and 3 with doses of 1.0, 2.5, and 5.0 mg/kg RO4987655, PET scans are used to estimate the tumor size. Days 0 (baseline), 1, 2, 3, and 9 of [18F] FDG-PET imaging are used to measure tumor volume and body weight. Calculations are made to determine tumor growth inhibition[2].
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Purpose: CH4987655 (RO4987655) is an orally active and highly selective small-molecule MEK inhibitor. It potently inhibits mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway activation and tumor cell growth, with an in vitro IC(50) of 5.2 nmol/L for inhibition of MEK1/2. Single-agent oral administration of CH4987655 resulted in complete tumor regressions in xenograft models.
[1]
Experimental design: All 40 subjects received a single oral dose followed by 72 hrs of pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic, and safety/tolerability assessments. The pharmacodynamics were measured by changes in phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (pERK) levels in a surrogate tissue peripheral blood mononuclear cells ex vivo stimulated by PMA. [1] Results: Doses of 0.5, 1, 2, 3, and 4 mg were safe and well tolerated. No clinically significant safety event was observed. A total of 26 adverse events (n = 15) were reported: 21 mild, 5 moderate, and none severe. Moderate adverse events were experienced by one subject at 1 mg (autonomic nervous system imbalance) and three subjects at 4 mg (diarrhea, abdominal pain, autonomic nervous system and acne). CH4987655 was rapidly absorbed with a t(max) of approximately 1 h. Exposures were dose proportional from 0.5 to 4 mg. The disposition was biphasic with a terminal t(1/2) of approximately 25 hr. Intersubject variability was low, 9% to 23% for C(max) and 14% to 25% for area-under-the-curve (AUC). pERK inhibition was exposure dependent and was greater than 80% inhibition at higher doses. The pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic relationship was characterized by an inhibitory E(max) model (E(max) approximately 100%; IC(50) 40.6 ng/mL) using nonlinear mixed-effect modeling. [1] Conclusions: A significant extent of pERK inhibition was achieved for a single dose that was considered to be safe and well tolerated in healthy volunteers. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
RO4987655 has been used in trials studying the treatment of Neoplasms.
MEK Inhibitor RO4987655 is an orally active small molecule, targeting mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 (MAP2K1 or MEK1), with potential antineoplastic activity. MEK inhibitor RO4987655 binds to and inhibits MEK, which may result in the inhibition of MEK-dependent cell signaling and the inhibition of tumor cell proliferation. MEK, a dual specificity threonine/tyrosine kinase, is a key component of the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway that regulates cell growth; constitutive activation of this pathway has been implicated in many cancers. Inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MEK, also known as MAPK2, MAPKK), a key molecule of the Ras/MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) pathway, has shown promising effects on B-raf-mutated and some RAS (rat sarcoma)-activated tumors in clinical trials. The objective of this study is to examine the efficacy of a novel allosteric MEK inhibitor RO4987655 in K-ras-mutated human tumor xenograft models using [(18)F] FDG-PET imaging and proteomics technology. Methods: [(18)F] FDG uptake was studied in human lung carcinoma xenografts from day 0 to day 9 of RO4987655 therapy using microPET Focus 120 (CTI Concorde Microsystems, Knoxville, TN, USA). The expression levels of GLUT1 and hexokinase 1 were examined using semi-quantitative fluorescent immunohistochemistry (fIHC). The in vivo effects of RO4987655 on MAPK/PI3K pathway components were assessed by reverse phase protein arrays (RPPA). Results: We have observed modest metabolic decreases in tumor [(18)F] FDG uptake after MEK inhibition by RO4987655 as early as 2 h post-treatment. The greatest [(18)F] FDG decreases were found on day 1, followed by a rebound in [(18)F] FDG uptake on day 3 in parallel with decreasing tumor volumes. Molecular analysis of the tumors by fIHC did not reveal statistically significant correlations of GLUT1 and hexokinase 1 expressions with the [(18)F] FDG changes. RPPA signaling response profiling revealed not only down-regulation of pERK1/2, pMKK4, and pmTOR on day 1 after RO4987655 treatment but also significant up-regulation of pMEK1/2, pMEK2, pC-RAF, and pAKT on day 3. The up-regulation of these markers is interpreted to be indicative of a reactivation of the MAPK and activation of the compensatory PI3K pathway, which can also explain the rebound in [(18)F] FDG uptake following MEK inhibition with RO4987655 in the K-ras-mutated human tumor xenografts. Conclusions: We have performed the first preclinical evaluation of a new MEK inhibitor, RO4987655, using a combination of [(18)F] FDG-PET imaging and molecular proteomics. These results provide support for using preclinical [(18)F] FDG-PET imaging in early, non-invasive monitoring of the effects of MEK and perhaps other Ras/MAPK signaling pathway inhibitors, which should facilitate a wider implementation of clinical [(18)F] FDG-PET to optimize their clinical use.[2] |
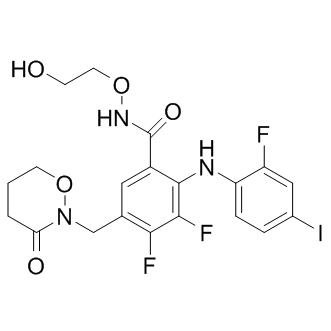
| 分子式 |
C20H19F3IN3O5
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
565.28
|
|
| 精确质量 |
565.032
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 42.49; H, 3.39; F, 10.08; I, 22.45; N, 7.43; O, 14.15
|
|
| CAS号 |
874101-00-5
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
11548630
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.7±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.638
|
|
| LogP |
5.49
|
|
| tPSA |
103.62
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
9
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
32
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
652
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
O=C(C1C(NC2C(F)=CC(I)=CC=2)=C(F)C(F)=C(CN2C(=O)CCCO2)C=1)NOCCO
|
|
| InChi Key |
FIMYFEGKMOCQKT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C20H19F3IN3O5/c21-14-9-12(24)3-4-15(14)25-19-13(20(30)26-31-7-5-28)8-11(17(22)18(19)23)10-27-16(29)2-1-6-32-27/h3-4,8-9,25,28H,1-2,5-7,10H2,(H,26,30)
|
|
| 化学名 |
3,4-difluoro-2-(2-fluoro-4-iodoanilino)-N-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5-[(3-oxooxazinan-2-yl)methyl]benzamide
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.42 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.42 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.42 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 10% DMSO+ 40% PEG300+ 5% Tween-80+ 45% saline: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7690 mL | 8.8452 mL | 17.6903 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3538 mL | 1.7690 mL | 3.5381 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1769 mL | 0.8845 mL | 1.7690 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT00817518 | Completed | Drug: RO4987655 | Neoplasms | Hoffmann-La Roche | January 2009 | Phase 1 |
|
|---|
|
|