| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
cdc2/cyclin B (IC50 = 0.65 μM); cdk2/cyclin A (IC50 = 0.7 μM); Cdk2/cyclin E2 (IC50 = 0.7 μM); CDK5/p35 (IC50 = 0.16 μM); GST-erk1 (IC50 = 30 μM); erk1 (IC50 = 34 μM); erk2 (IC50 = 14 μM); IR tyrosine kinase (IC50 = 70 μM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:Roscovitine 对一些细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶表现出高效和高选择性,对于 cdc2/cyclin B、cdk2/cyclin A、cdk2/cyclin E 和 cdk5/p53 的 IC50 分别为 0.65、0.7、0.7 和 0.16 μM。 Roscovitine 可逆性抑制海星卵母细胞和海胆胚胎微摩尔范围内的前相/中期转变,抑制非洲爪蟾卵提取物中的体外 M 相促进因子活性和体外 DNA 合成,并抑制哺乳动物细胞系的增殖,平均 IC50 16μM。在系膜细胞中,Roscovitine 导致 CDK2 活性呈剂量依赖性降低,在 7.5、12.5 和 25 mM 浓度下,Roscovitine 分别导致 CDK2 活性降低 25、50% 和 100%。最近的一项研究表明,Roscovitine 可抑制盘基网柄菌中的 cdk5 激酶活性、细胞增殖、多细胞发育和 cdk5 核转位,而不影响无菌生长期间 cdk5 蛋白的表达。激酶测定:在 30°C 的缓冲液 C 中测定激酶活性。从数据中减去空白值,并将活性计算为在 10 分钟孵育期间掺入蛋白质受体中的磷酸盐的摩尔量。使用适当稀释的 DMSO 进行对照。在少数情况下,底物的磷酸化通过 SDS/PAGE 后的放射自显影进行评估。 p34cdc2/cyclin B 通过亲和层析从 M 期海星 (M. glacialis) 卵母细胞中纯化。在终体积为 30 μL 的 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP (3000 Ci/mmol;1 mCi/mL) 存在下,用 1 mg 组蛋白 H1/mL 进行测定。在 30 °C 下孵育 10 分钟后,将 25 μL 等份上清液点样到 Whatman P81 磷酸纤维素纸片上,20 秒后,将滤膜清洗 5 次(每次至少 5 分钟)。 10mL磷酸/L水的溶液。将湿滤器转移到 6 mL 塑料闪烁瓶中,添加 5 mL ACS 闪烁液,并在 Packard 计数器中测量放射性。激酶活性表示为 10 分钟孵育期间掺入组蛋白 H1 中的磷酸盐的摩尔量或最大活性的百分比。 p33cdk2/cyclin A 和 p33cdk2/cyclinE 由感染各种杆状病毒的 sf9 昆虫细胞提取物重建。细胞周期蛋白 A 和 E 是与谷胱甘肽 S-转移酶的融合蛋白,复合物在谷胱甘肽-琼脂糖珠上纯化。如 p34cdc2/细胞周期蛋白 B 激酶所述,在 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP 存在下,用 1 mg/mL 组蛋白 H1 测定激酶活性,持续 10 分钟,最终体积为 30 μL。 p33cdk5/p35 从牛脑中纯化,不包括 Mono S 色谱步骤。将来自 Superose 12 柱的活性级分合并并浓缩至终浓度约为 25 μg 酶/mL。在 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP 存在下,用 1 mg/mL 组蛋白 HI 检测激酶,检测时间为 10 分钟,最终体积为 30 μL,如 p34cdc2/细胞周期蛋白 B 激酶所述。 p33cdk5/cyclin D1 从昆虫细胞裂解物中获得。 Cdk4 是一种与谷胱甘肽-S-转移酶的融合蛋白,活性复合物在谷胱甘肽-琼脂糖珠上纯化。在 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP 存在下,用纯化的视网膜母细胞瘤蛋白(与谷胱甘肽-S-转移酶复合)测定其激酶活性,最终体积为 30 μL。孵育 15 分钟后,添加 30 μL Laemmli 样品缓冲液。磷酸化底物通过 10% SDS/PAGE 解析,并通过 Hyperfilm MP 过夜暴露的放射自显影和光密度测定法进行分析。 p33cdk4/cyclinD 2 从昆虫细胞裂解物中获得。在终体积为 30 μL 的 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP 存在下,使用纯化的视网膜母细胞瘤蛋白(与谷胱甘肽-S-转移酶复合)进行测定。孵育 30 分钟后,添加 30 μL Laemmli 样品缓冲液。磷酸化底物通过 10% SDS/PAGE 解析,并通过 Hyperfilm MP 过夜暴露的放射自显影和光密度测定进行分析。 MAP 激酶 erkl(用谷胱甘肽-S-转移酶标记)在细菌中表达,在谷胱甘肽-琼脂糖珠上纯化,并在 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP 存在下用 1 mg 髓磷脂碱性蛋白/ml 进行测定,如上所述p34cdc2cyclin B 激酶。 His-标记的erk1和erk2在体外被丝裂原激活的蛋白激酶激酶激活、纯化(Ni亲和力和Mono Q)并如上所述在10分钟内以30μL的终体积进行测定。从杆状病毒感染的 sf9 昆虫细胞中纯化蛋白激酶 C 亚型,并在 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP 存在下用 1 mg/mL 硫酸鱼精蛋白进行测定,在 30 °C 下进行 10 分钟,最终体积为 30 μL。如 cdc2 激酶所述,在 Whatman P81 磷酸纤维素纸上回收磷酸化的硫酸鱼精蛋白。如对p34cdc2/细胞周期蛋白B激酶所述,在15μM[γ-32P]ATP存在下用1mg组蛋白H1/ml测定从牛心脏纯化的cAMP依赖性蛋白激酶的催化亚基。在 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP 存在下,如针对 p34cdc2/细胞周期蛋白 B 激酶所述,用 1 mg 组蛋白 H1/mL 测定从牛气管平滑肌纯化至同质的 cGMP 依赖性蛋白激酶。从大鼠肝细胞质中分离酪蛋白激酶 2,并用 1 mg 酪蛋白/mL 和 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP 进行测定。将底物点样在 Whatmann 3MM 过滤器上并用 10%(质量/体积)三氯乙酸洗涤。从鸡砂中纯化的肌球蛋白轻链激酶在 100 nM 钙调蛋白、100 μM CaCl2、50 mM Hepes、5 mM MgCl、1 mM 二硫苏糖醇和 0.1 mg BSA/ml 存在下在 pH 7.5 下使用基于以下的合成肽进行测定平滑肌肌球蛋白轻链磷酸化位点,并在 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP 存在下,最终体积为 50 μL。如上所述,在磷酸纤维素过滤器上监测放射性磷酸盐的掺入。 ASK-γ 是 GSK-3 的植物同源物,在大肠杆菌中表达为谷胱甘肽-S-转移酶融合蛋白,并在谷胱甘肽-琼脂糖上纯化。使用 5 μg 髓磷脂碱性蛋白,在 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP 存在下,在 30 °C 下检测 ASK-γ 激酶 10 分钟,终体积为 30 μL。如 p34cdc2/细胞周期蛋白 B 激酶所述,在 Whatman P81 磷酸纤维素纸上回收磷酸化髓磷脂碱性蛋白。胰岛素受体酪氨酸激酶结构域 (CIRK-41) 在杆状病毒系统中过表达并纯化至均质。在 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP 存在下,最终体积为 30 μL,使用 5 μg Raytide 在 30 °C 下测定其激酶活性 10 分钟。按照 p34cdc2/细胞周期蛋白 B 激酶的描述,在 Whatman P81 磷酸纤维素纸上回收磷酸化的 Raytide。 c-src 激酶从受感染的 Sf9 细胞中纯化。 v-abl 激酶在大肠杆菌中表达,并在 IgG Affigel 10 上进行亲和纯化。两种激酶均在 30 °C 下使用 5 μg Raytide、在 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP 存在下、在最终体积为 30 μL。按照 p34cdc2/细胞周期蛋白 B 激酶的描述,在 Whatman P81 磷酸纤维素纸上回收磷酸化的 Raytide。细胞测定:包含九种肿瘤类型的 60 个人类肿瘤细胞系(白血病、非小细胞肺癌、结肠癌、中枢神经系统癌症、黑色素瘤、卵巢癌、肾癌、前列腺癌、乳腺癌)提前培养 24 小时连续暴露于 0.01-100 μM roscovitine 48 小时。使用磺基罗丹明 B 蛋白测定来评估细胞毒性。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Roscovitine,剂量为 50 mg/kg,可显着抑制尤文氏肉瘤家族肿瘤 (ESFT) 异种移植物的生长。 Roscovitine 增强阿霉素的抗肿瘤作用,而不增加毒性,其机制涉及细胞周期停滞而不是荷有已建立的 MCF7 异种移植物的裸鼠的细胞凋亡。
研究人员随后通过评估药物治疗对肿瘤生长的影响,使用材料和方法中所述的A4573 ESFT细胞裸鼠异种移植物,研究了Seliciclib (Roscovitine)在体内的作用。当肿瘤体积达到约130 mm3时,按照不同的时间表,给动物腹腔注射roscovitine或单独的载体溶液,并在长达几周的时间内测量肿瘤生长。如图5A所示,与对照组动物相比,接受罗索维汀治疗的小鼠的肿瘤生长明显较慢,这反映了切除后观察到的单个肿瘤的大小明显较小(图5A,插图)。在完成第一个为期5天的治疗系列后的一天,接受roscovitine治疗的动物的肿瘤相对于治疗开始时的大小仅增长了约1.25倍,而未接受治疗的小鼠的肿瘤体积已经达到其原始大小的约14.5倍。这些值代表了肿瘤体积的约11.5倍的差异,尽管接受罗斯科维汀治疗的动物的肿瘤继续缓慢生长,但在对照动物(肿瘤已生长到其初始大小的约15倍)必须按照机构动物护理和使用指南处死时(第13天;图5A),肿瘤大小的显著差异(约7.5倍)仍然很明显。从roscovitine治疗的第1天开始计算,对照组动物的肿瘤在2天内达到原始体积的三倍,而接受治疗的动物的肿瘤需要10天才能将其初始体积增加三倍(图5A)。总的来说,这一差异表明,罗斯科维汀治疗使肿瘤生长减少了约5倍。[4] 此外,最重要的是,与未经治疗的对照组动物相比,连续5天仅以50mg/kg/d的剂量腹腔注射一次(总剂量为250mg/kg)的Seliciclib (Roscovitine)将肿瘤大小减小了约85%(第5-8天;图5A),而据报道,包括每天以100mg/kg/d的剂量腹腔内注射三次,持续5天(总剂量1500 mg/kg)的治疗计划分别仅将裸鼠体内人结肠(LoVo)和子宫(MESSA-DX5)肿瘤细胞系诱导的肿瘤生长减少了45%和62%(19)。我们的治疗在总剂量降低6倍的情况下取得了更好的抗肿瘤反应,这一事实强烈表明,与其他人类肿瘤细胞相比,罗斯科维汀对ESFT的疗效要高得多。这些结果表明,roscovitine有效地抑制了ESFT细胞在体内和培养中的生长。为了进一步阐明roscovitine在体内的作用机制,我们检查了肿瘤组织是否显示出任何凋亡的迹象。如图5B所示,TUNEL检测(图5B,,中)和切割的半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶-3的免疫组织化学检测(图5B,右)的结果表明,罗斯科维汀还通过半胱氨酸天冬氨酰蛋白酶依赖机制诱导体内ESFT肿瘤的凋亡。相比之下,在仅注射载体溶液的对照动物(图5B,上图)的肿瘤中可检测到可忽略的凋亡迹象。[4] 在MCF7异种移植物模型中,与单一药物阿霉素相比,Seliciclib(Roscovitine)+阿霉素的疗效[5] 图3显示了MCF7对照肿瘤(未经治疗或仅用载体治疗)、用阿霉素或单一药物Seliciclib(Roscovitine)治疗的肿瘤以及用Seliciclib+阿霉素治疗的肿瘤的生长情况。在治疗结束时,与seliciclib+阿霉素相比,用单一药物(阿霉素或seliciclib)治疗的肿瘤的平均相对大小分别为304 mm3和180 mm3。与溶媒对照组相比,这些分别对应于48%和70%的肿瘤生长抑制,具有统计学意义(Student t检验p<0.05)。在治疗结束时,seliciclib+阿霉素治疗组的肿瘤体积明显低于载体+阿霉素处理组(p<0.05)。未治疗组和载体治疗组的肿瘤大小倍增时间为7天,阿霉素或seliciclib治疗组为11天,seliciclib+阿霉素治疗组为23天。治疗组没有体重减轻或行为改变。 |
| 酶活实验 |
缓冲液 C 中的激酶活性在 30 °C 下测量。数据去除空白值,活性计算为在 10 分钟孵育过程中掺入蛋白质受体中的磷酸盐的摩尔量。适当的 DMSO 稀释液用于对照。 SDS/PAGE 后,有时使用放射自显影来评估底物的磷酸化。通过使用亲和层析,从 M 期海星 (M. glacialis) 卵母细胞中分离出 p34cdc2/cyclin B。在最终体积为 30 μL 的情况下,测定中使用 1 mg 组蛋白 H1/mL 以及 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP (3000 Ci/mmol;1 mCi/mL)。 30 °C 孵育 10 分钟后,将 25 μL 等份上清液点样到 Whatman P81 磷酸纤维素纸上。 20 秒后,将过滤器在 10mL 磷酸/L 水的溶液中洗涤五次(每次至少五分钟)。将湿滤器转移至 6 mL 塑料闪烁瓶中后,添加 5 mL ACS 闪烁液,并使用 Packard 计数器测量放射性。激酶活性报告为最大活性的百分比或孵育 10 分钟后掺入组蛋白 H1 中的磷酸盐的摩尔量。重组的 p33cdk2/cyclin A 和 p33cdk2/cyclin E 由杆状病毒感染的 sf9 昆虫细胞提取物制成。谷胱甘肽 S-转移酶融合蛋白、细胞周期蛋白 A 和 E 在谷胱甘肽-琼脂糖珠上纯化。与 p34cdk2/细胞周期蛋白 B 激酶一样,使用 1 mg/mL 组蛋白 H1 和 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP 在 10 分钟内测量激酶活性最终体积为 30 μL。采用牛脑纯化p33cdk5/p35;不包括 Mono S 色谱步骤。将 Superose 12 柱的活性级分合并并浓缩,直至达到约 25 μg 酶/mL 的最终浓度。与 p34cdk2/cyclin B 激酶一样,在 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP 存在下,使用 1 mg/mL 组蛋白 HI 检测该激酶,超过过程 10 分钟,最终体积为 30 μL。 p33cdk5/cyclin D1 的来源是昆虫细胞裂解物。谷胱甘肽-S-转移酶和 Cdk4 形成融合蛋白,并使用谷胱甘肽-琼脂糖珠纯化活性复合物。在最终体积为 30 μL 的情况下,在 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP 存在下,使用纯化的视网膜母细胞瘤蛋白(与谷胱甘肽-S-转移酶复合)测量其激酶活性。孵育 15 分钟后,添加 30 μL Laemmli 样品缓冲液。使用 10% SDS/PAGE 分离已磷酸化的底物,并使用放射自显影、光密度测定法和 Hyperfilm MP 过夜暴露进行检查。 p33cdk4/cyclinD 2 的来源是昆虫细胞裂解物。在终体积 30 μL 中,使用纯化的视网膜母细胞瘤蛋白(与谷胱甘肽-S-转移酶复合)和 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP 进行测试。孵育 30 分钟后,添加 30 μL Laemmli 样品缓冲液。使用 10% SDS/PAGE 分离磷酸化底物,并在暴露于 Hyperfilm MP 整夜后使用光密度测定法和放射自显影术进行检查。在谷胱甘肽-琼脂糖珠上纯化,并在 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP 存在下用 1 mg 髓磷脂碱性蛋白/ml 进行测定,MAP 激酶 erkl(用谷胱甘肽-S-转移酶标记)是在细菌中产生,如前面提到的 p34cdc2cyclin B 激酶。在体外,丝裂原激活的蛋白激酶激酶激活His标记的erk1和erk2,然后使用Ni亲和力和Mono Q进行纯化。按照前面提到的方案,在最终体积为30微升的情况下进行测定十分钟。使用受感染的 sf9 昆虫细胞分离蛋白激酶 C 亚型,然后使用 1 mg/mL 硫酸鱼精蛋白和 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP。 Whatman P81 磷酸纤维素纸用于回收磷酸化的硫酸鱼精蛋白,就像用于 CDC2 激酶一样。 cAMP 依赖性蛋白激酶的催化亚基从牛心脏中纯化出来,使用 1 mg 组蛋白 Hl/ml 和 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP 进行测量,就像 p34 cdc2/细胞周期蛋白 B 激酶。从牛气管平滑肌中匀浆和纯化后,使用 1 mg 组蛋白 Hl/mL 和 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP 测量 cGMP 依赖性蛋白激酶,就像 p34 cdc2/细胞周期蛋白 B 激酶。使用大鼠肝细胞质分离酪蛋白激酶 2,然后使用 1 mg 酪蛋白/mL 和 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP 进行测试。在 Whatmann 3MM 过滤器上点样后,用 10%(质量/体积)三氯乙酸清洁基材。基于平滑肌肌球蛋白轻链磷酸化位点的合成肽用于分析从鸡砂中纯化的肌球蛋白轻链激酶。测定的最终体积为 50 μL,条件包括 100 nM 钙调蛋白、100 μM CaCl2、50 mM Hepes、5 mM MgCl、1 mM 二硫苏糖醇和 0.1 mg BSA/ml,pH 值7.5。如前所述,在磷酸纤维素过滤器上跟踪放射性磷酸盐的掺入。 GSK-3 的植物同源物 ASK-γ 在大肠杆菌中表达为谷胱甘肽-S-转移酶融合蛋白后,在谷胱甘肽-琼脂糖上纯化。 30°C 10 分钟,将 5 μg 髓磷脂碱性蛋白添加到终体积 30 μL 的 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP 中,以测试 ASK-γ 激酶。在 Whatman P81 磷酸纤维素纸上,以与 p34cdc2/cyclin B 激酶相同的方式回收磷酸化髓磷脂碱性蛋白。在杆状病毒系统中,胰岛素受体酪氨酸激酶结构域 (CIRK-41) 过度表达并均质纯化。使用 5 μg Raytide 和 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP 在最终体积 30 μL 中在 30 °C 下测量 10 分钟,测量其激酶活性。如 p34cdc2/cyclin B 激酶所述,磷酸化的 Raytide 在 Whatman P81 磷酸纤维素纸上回收。从被感染的 Sf9 细胞中分离出 c-src 激酶。在大肠杆菌中表达后,使用 IgG Affigel 10 亲和纯化 v-abl 激酶。该测定在 30°C 下进行 10 分钟,使用 5 μg Raytide,15 μM [γ-32P]ATP,最终体积为 30 μL。如 p34cdc2/cyclin B 激酶所述,磷酸化的 Raytide 在 Whatman P81 磷酸纤维素纸上回收。
|
| 细胞实验 |
使用的细胞是大鼠肾小管上皮细胞(NRK52E)。 NRK52E 细胞的治疗涉及使用 CDK5 抑制剂 (R)-Seliciclib (Roscovitine) (Ros.;10 μM) 和激活剂 p35 (15 μM)、PPARγ 激动剂 BRL 49653 (Rosi.;50 nM) 和 ERK1/2 抑制剂U0126 (50 nm)。 72 小时治疗期后,从每组中提取细胞进行进一步分析。
细胞凋亡和细胞周期测定。[4] 通过活细胞计数和/或末端脱氧核苷酸转移酶介导的缺口末端标记(TUNEL)检测来评估细胞凋亡。细胞活力通过台盼蓝排斥法测定:将细胞悬浮在0.04%台盼蓝PBS中,置于血细胞计数器上,在显微镜下计数。使用基于红色的TMR原位死亡检测试剂盒进行TUNEL检测,以原位检测凋亡细胞。细胞在室载玻片中培养至5×104个细胞的群体密度。在Seliciclib(Roscovitine)暴露16小时后,用PBS洗涤细胞,在室温下用新鲜制备的多聚甲醛(PBS中4%)固定30分钟,在PBS中漂洗三次,用PBS中0.2%的Triton X-100渗透30分钟,并在37°C下在黑暗中的加湿气氛中与TUNEL反应混合物一起孵育1小时。用尼康E600荧光显微镜观察TUNEL阳性细胞。对于细胞周期分析,在暴露于Seliciclib(Roscovitine)后24小时收获细胞,在PBS中洗涤一次,在柠檬酸盐缓冲液(pH 7.6)中固定,在含有20μg/mL碘化丙啶的PBS中重悬,并在37°C下孵育30分钟,然后在FACScan仪器上进行流式细胞术分析,在Vincent T.Lombardi综合癌症中心的流式细胞仪/细胞分选共享资源进行。相同的原位死亡检测试剂盒用于对脱链5μm肿瘤切片进行TUNEL检测。 半胱天冬酶测定。[4] TC-71和A4573细胞的培养是通过在96孔组织培养板上每孔放置2×104个细胞(用于胱天蛋白酶活性测定)或在6孔板上每孔放置2×105个细胞(进行凋亡测定)来建立的。孵育过夜后,细胞用10μmol/L的Seliciclib (Roscovitine)、5μg/mL的顺铂(作为半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶-3依赖性凋亡的阳性诱导剂)或DMSO载体(作为阴性对照)处理24小时,每种药物都有或没有终浓度为20μmol/L的Ac-DEVD-CHO半胱氨酸天冬氨酰蛋白酶-3/7抑制剂。所有治疗均一式三份。治疗后,如上所述确定凋亡诱导的程度,并按照制造商的方案使用Apo ONE均质caspase-3/7测定法进行caspase-3/7活性测定。简而言之,一旦试剂和细胞培养板平衡到室温,将等体积的试剂直接加入细胞培养物中,以500rpm摇动培养板,在带有485/535激发/发射滤光片和增益设置为25的荧光板读数器中加入试剂8小时后测定荧光输出。 细胞毒性试验[5] 将亚流细胞胰蛋白酶消化,接种到100μl培养基中的96孔组织培养板中。孵育过夜后,从贴壁细胞中吸出培养基,并加入从储备溶液中新鲜制备的具有预定药物浓度的新鲜培养基。阿霉素储备溶液在10 mM的无菌蒸馏水中。在DMSO中制备Seliciclib (Roscovitine)。500 nM的阿霉素和20μM的seliciclib作为单一药物使用,或以24小时间隔顺序给药或联合给药。细胞暴露于药物72小时。使用MTT法在四孔中测定每种药物浓度的细胞存活率,如下所示:向每孔中加入50μl 2 mg/ml的MTT PBS溶液。将平板置于37°C、5%CO2下4小时。小心地从每孔中取出培养基,加入50μl DMSO,并使用微孔板读数器测定OD540。用培养基处理的细胞仅作为100%细胞存活的对照。 细胞周期分析[5] 对于细胞周期谱分析,将细胞接种到150毫米的平板上,并在标准条件下生长。将亚融合培养物暴露于500 nM的阿霉素和20μM的Seliciclib (Roscovitine)作为单一药物或以24小时的间隔依次给予(Seliciclib (Roscovitine),然后是阿霉素)。在48、72或96小时处理后收获细胞,并通过掺入BrdUrd(溴脱氧尿苷)然后碘化丙啶染色进行分析。在每个时间点,用稀释在DMEM(10%FCS,1%P/S)培养基中的30uM BrdUrd在37°C下标记细胞15-20分钟。保留提取的培养基,洗涤细胞,也保留上清液。将细胞胰蛋白酶化(5%胰蛋白酶,2%EDTA),与保留的培养基一起加入并洗涤。加入PBS,以1200 rpm的速度将细胞沉淀5分钟。将这些MCF7重新悬浮在1ml PBS和3ml ETOH中,在涡旋的同时逐滴加入,并在4°C下孵育过夜。通过以2500 rpm离心5分钟使细胞沉淀,加入2 ml新鲜制备的胃蛋白酶溶液(1 mg/ml,30 mM HCl pH 1.5),并在37°C下混合细胞30分钟。通过离心再次将细胞造粒,向每个样品中加入1ml 2M HCl,并在室温下孵育20分钟。将MCF7重新悬浮在200ul Becton Dickinson抗BrdUrd抗体中,该抗体在抗体缓冲液(PBS,0.5%BSA,0.5%吐温20)中稀释1:50,并在室温下孵育1小时。在PBS中洗涤后,将细胞在室温下在黑暗中在200ul FITC偶联的抗小鼠抗体中孵育30分钟,该抗体在抗体缓冲液中稀释至20ug/ml。最后,用PBS洗涤细胞,将其重新悬浮在含有25 ug/ml碘化丙啶反染剂的500 ul PBS中,并在黑暗中置于冰上,直至分析。 |
| 动物实验 |
Rats: Male Sprague Dawley rats (6–8 weeks old) receive a single intraperitoneal injection of either citrate buffer (non-diabetic) or 0.1 M citrate buffer pH 4.5 (diabetic) diluted with streptozotocin (65 mg/kg). Three days following the injection, the glucose oxidase method is used on a glucose analyzer to measure plasma glucose concentrations. The study includes rats that are classified as diabetics if their blood glucose level is greater than 16.7 mM. The level of plasma glucose is measured once a week. Seliciclib (Roscovitine) (25 mg/kg) is injected intraperitoneally into diabetic rats once a day until they are sacrificed in order to study the impact of CDK5 inhibition on renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis. As controls, DMSO is used.
Mice: Subcutaneous injections of exponentially growing UMSCC47 cells are made into the sacral region of female NUDE mice. Each mouse is inoculated with 2×105 cells in 50% matrigel and 50% PBS at a volume of 100 μL. The mice receive intraperitoneal injections of either vehicle or Seliciclib (Roscovitine) at a dose of 16.5 mg/kg once the tumors have grown to a detectable size. General behavior, tumor growth, and body weight are tracked. Every three days, tumor volumes are measured. Once the tumor grows larger than 0.5 cm3, the mice are killed. In vivo studies. [4] Mice were inoculated s.c. into the right posterior flank with 4 × 106 A4573 cells in 100 μL of Matrigel basement membrane matrix. Xenografts were grown to a mean tumor volume of 129 ± 30 mm3. Seliciclib (Roscovitine) was first dissolved in either absolute methanol or DMSO (1 volume). A carrier solution was produced by using a diluent containing 10% Tween 80, 20% N-N-dimethylacetamide, and 70% polyethylene glycol 400. Mice were randomized into two groups (six animals per group) and treatment was initiated. One group was treated with Seliciclib (Roscovitine), administered as a single daily i.p. injection, at a dose of 50 mg/kg, for either 5 days or two 5-day series with a 2-day break in between. The control group received i.p. injections of the carrier solution following identical schedules. All mice were sacrificed by asphyxiation with CO2. Seliciclib (Roscovitine)-treated mice were euthanized either 7 days after the first injection or up to 4 weeks after completion of the treatment. At those times, tumors were removed, measured, and prepared for TUNEL assays. Primary tumor volumes were calculated by the formula V = (1/2)a × b2, where a is the longest tumor axis and b is the shortest tumor axis. Data are given as mean values ± SE in quantitative experiments. Statistical analysis of differences between groups was done by a one-way ANOVA followed by an unpaired Student's t test.[4] MCF7 xenografts [5] Xenograft studies with MCF7 were carried out under license 60/3045 in accordance with the guidelines of the UKCCCR. Female nude (nu/nu) mice were implanted with 17β-estradiol pellets (0.72 mg/pellet) at least 2 days before injection of the estrogen receptor positive MCF7 cells. Mice were injected subcutaneously in both flanks with 1 × 108 MCF7 cells in DMEM and matrigel suspension. The mice were housed under aseptic conditions in individually ventilated cages in a temperature (24°C) and light-controlled (12 hr/day) environment. Doxorubicin and Seliciclib (Roscovitine) preparation for xenograft studies [5] Doxorubicin was prepared in H2O and kept at 4°C for up to 1 month. Seliciclib (Roscovitine) was dissolved in PEG400:DMSO at 90:10, sonicated for 30 min and kept at 4°C. Fresh Seliciclib (Roscovitine) preparations were made each week. Treatment regime [5] Based on previous tests, Seliciclib (Roscovitine) at a concentration of 400 mg/kg was selected for this study. When tumors were in the range 50–150 mm3, mice were divided into 4 groups of 10 animals, and the combination of Seliciclib (Roscovitine) at 400 mg/kg (administered via orogastric intubation) and doxorubicin at 1.5 mg/kg (equivalent to the clinical dose; intraperitoneal injection) was tested by 1 schedule per group (Table I) repeated every week for 3 weeks. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Pharmacokinetics [6]
Plasma samples were collected in all participants at various times during day 1, up to 12 h, and at day 5 (120 h), and stored at -80°C until LC-MS/MS determination of the concentrations of roscovitine and its M3 metabolite. Global roscovitine and M3 pharmacokinetics data are presented in Fig. 4 and Fig. 5 Large variations were observed among subjects treated with the same amounts of roscovitine. A more detailed analysis, taking cytochrome P450 polymorphism and other factors into account has been published [20]. The pharmacokinetics analysis was carried out as non-compartmental analysis using WinNonlin® software. The following parameters were determined for both roscovitine (Table S19) and M3 metabolite (Table S20): Area Under Curve (AUCt and AUCInf), maximum concentration (Cmax), time to reach Cmax (Tmax) and half-life (t1/2). Pharmacokinetics parameters are summarized by number of observations, means, standard deviation (SD) and standard deviation of the mean (SEM), median, minimum and maximum for each treatment group (Table S21). The maximum roscovitine concentrations were 10.6-344 ng/mL, 54.2-1,533 ng/mL and 307-3,783 ng/mL, for the 200, 400 and 800 mg groups, respectively. Peak concentrations were observed between 1 and 4 h for the two first groups and between 2 and 6 h for the 800 mg group. Exposures were 43.5-3,385 ng.h/mL, 344-20,210 ng.h/mL and 1,767-60,437 ng.h/mL, respectively for the three groups (Fig. 4, Table S19). The maximum M3 concentrations were 87.6-1,600 ng.h/mL, 62.2-2,811 ng.h/mL and 754-4,190 ng/mL, respectively, for the 200, 400 and 800 mg groups. Peak concentrations were observed between 1 and 2 h for the first groups and between 1 and 4 h for the 400 and 800 mg group. Exposures were 270-8,294 ng.h/mL, 262-35,114 ng.h/mL and 5,881-116,512 ng.h/mL, respectively for the three groups (Fig. 4, Table S20). For both roscovitine and M3, the increases in AUCt and Cmax strongly correlated with the administered doses (Fig. 4, Tables S19 and S20). The M3/ roscovitine ratios for median AUCt and Cmax were getting close to 1 as the dose was increased (Fig. 4, Table S21). |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Safety evaluation [6]
The primary outcome was safety evaluation (Tables 1, 2, S6–S8). All subjects presented at least one adverse event (AE) during the ROSCO-CF study. Sixty AEs were reported among the 11 subjects receiving placebo and 132 AEs for the 23 subjects receiving roscovitine (Tables 1–3, S6–S11). Median numbers of AEs were 5 (placebo), 2 (200 mg), 8 (400 mg) and 5 (800 mg). The overall AE rate was 5.46 AE/subject in the placebo group and 5.74 AE/subject in the roscovitine groups. The distribution of the highest-grade AEs per subject is presented in Table S9A. No significant difference in the prevalence of AEs between the two experimental groups was observed. Among 34 subjects, 5 presented an SAE: 0/11 (placebo), 1/8 (200 mg), 1/8 (400 mg) and 3/7 (800 mg) (Table S9B). Adverse events (serious and non-serious) [6] AEs were grouped according to clinical reaction type using the MedDRA 21.1 classification dictionary (Table 1). Gastrointestinal disorders, infections & infestations and respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders were the three most frequently reported AEs. Cardiac, eye, hepatobiliary and musculoskeletal disorders were reported more frequently in participants receiving roscovitine versus placebo. No “cardiac events” were reported in the placebo group but one in roscovitine group 2 and two in roscovitine group 3. One of them, “sinus tachycardia”, was reported as an SAE. Tachycardia and sinus tachycardia are frequent clinical reactions seen in many clinical diseases. For “eye disorders”, there was only one “non-serious AE” reported in roscovitine group 2. There were six reported “hepatobiliary disorders” events in roscovitine group 2 and three in roscovitine group 3. The observed “musculoskeletal disorders” reactions were non-specific, like myalgia, pain and arthralgia. One “renal disorder” and one dysmenorrheal (in reproductive disorders) were reported, only in roscovitine group 3. Severity of adverse events [6] The level of severity of all AEs was qualified by investigators with specific severity scales (Tables S6–S8). In the placebo group, 46 grade 1 AEs and 14 grade 2 AEs were reported. In the roscovitine groups, 95 grade 1 AEs, 35 grade 2 AEs and 2 grade 3 AEs were reported. The distribution of AEs relative to severity in the three roscovitine groups is presented in details in Tables S6-S8 and summarized in Table S9A. Expectedness of adverse events [6] The latest Seliciclib investigator brochure was used to qualify the expectedness of AEs. Some unlisted AEs were reported in the roscovitine groups: one photophobia and one visual impairment, reported as a non-serious AE. The CF status can be considered as a confounding factor for infectious diseases such as gastroenteritis, infective pulmonary exacerbation of CF, nasopharyngitis, oral herpes, pharyngitis, rhinitis tonsillitis, and viral infection. The electrocardiogram T wave inversion data was sent to health authorities as a Suspected Unexpected Serious Adverse Reaction (SUSAR). Cardiologic evaluation of pre-dose and post-dose ECG provided other episodes of T wave inversion in this subject. The case of “blood creatine phosphokinase increased” could be drawn close to unspecific musculoskeletal disorders as myalgia and arthralgia. Serious adverse reactions [6] All participants who presented at least one SAE were roscovitine-treated. Globally, 5 subjects presented a total of 8 SAEs (Table 2). Three of 5 subjects have presented 2 SAEs at the same date. The distribution of SAEs among clinical type of reaction showed that hepatobiliary events and infectious diseases were presented by more than one subject (Table 2). The distribution among roscovitine dose-escalating groups showed that subjects treated with high dosage presented more SAEs (Table 2). The independent data safety monitoring board considered that 3 of the SAEs on hepatobiliary disorders were possibly related to roscovitine treatment (2 at 400 mg and 1 at 800 mg), 1 on cardiac disorders and 1 in renal and urinary disorders were also related to roscovitine treatment (800 mg) (Table S10). |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
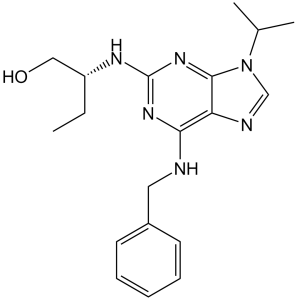
Seliciclib is 2,6-Diaminopurine carrying benzylamino, (2R)-1-hydroxybutan-2-yl and isopropyl substituents at C-6, C-2-N and N-9 respectively. It is an experimental drug candidate in the family of pharmacological cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitors. It has a role as an EC 2.7.11.22 (cyclin-dependent kinase) inhibitor and an antiviral drug.
R-roscovitine (Seliciclib or CYC202) is a cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitor that preferentially inhibits multiple enzyme targets including CDK2, CDK7 and CDK9, which alter the growth phase of treated cells. Developed by Cyclacel, seliciclib is being researched for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), leukemia, HIV infection, herpes simplex infection, and the mechanisms of chronic inflammation disorders. Seliciclib has been reported in Ophioparma ventosa with data available. Seliciclib is an orally available small molecule and cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitor with potential apoptotic and antineoplastic activity. CDKs, serine/threonine kinases that play an important role in cell cycle regulation, are overexpressed in various malignancies. Seliciclib primarily inhibits CDK 2, 7, and 9 by competing for the ATP binding sites on these kinases, leading to a disruption of cell cycle progression. In addition, this agent seems to interfere with CDK-mediated phosphorylation of the carboxy-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II, thereby inhibiting RNA polymerase II-dependent transcription. This may lead to the down-regulation of anti-apoptotic factors, such as myeloid cell leukemia sequence 1 (Mcl-1), a protein crucial for the survival of a range of tumor cell types. The down-regulation of anti-apoptotic factors may lead to an induction of apoptosis, thereby further contributing to seliciclib's antiproliferative effects. A purine derivative and competitive inhibitor of CYCLIN-DEPENDENT KINASES that has therapeutic potential as an antineoplastic and antiviral agent. Drug Indication Investigated for use/treatment in breast cancer, lung cancer, lymphoma (unspecified), multiple myeloma, leukemia (lymphoid), and cancer/tumors (unspecified). Cyclin-dependent kinases (cdk) play an essential role in the intracellular control of the cell division cycle (cdc). These kinases and their regulators are frequently deregulated in human tumours. Enzymatic screening has recently led to the discovery of specific inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases, such as butyrolactone I, flavopiridol and the purine olomoucine. Among a series of C2, N6, N9-substituted adenines tested on purified cdc2/cyclin B, 2-(1-ethyl-2-hydroxyethylamino)-6-benzylamino-9-isopropylpurine (roscovitine) displays high efficiency and high selectivity towards some cyclin-dependent kinases. The kinase specificity of roscovitine was investigated with 25 highly purified kinases (including protein kinase A, G and C isoforms, myosin light-chain kinase, casein kinase 2, insulin receptor tyrosine kinase, c-src, v-abl). Most kinases are not significantly inhibited by roscovitine. cdc2/cyclin B, cdk2/cyclin A, cdk2/cyclin E and cdk5/p35 only are substantially inhibited (IC50 values of 0.65, 0.7, 0.7 and 0.2 microM, respectively). cdk4/cyclin D1 and cdk6/cyclin D2 are very poorly inhibited by roscovitine (IC50 > 100 microM). Extracellular regulated kinases erk1 and erk2 are inhibited with an IC50 of 34 microM and 14 microM, respectively. Roscovitine reversibly arrests starfish oocytes and sea urchin embryos in late prophase. Roscovitine inhibits in vitro M-phase-promoting factor activity and in vitro DNA synthesis in Xenopus egg extracts. It blocks progesterone-induced oocyte maturation of Xenopus oocytes and in vivo phosphorylation of the elongation factor eEF-1. Roscovitine inhibits the proliferation of mammalian cell lines with an average IC50 of 16 microM. In the presence of roscovitine L1210 cells arrest in G1 and accumulate in G2. In vivo phosphorylation of vimentin on Ser55 by cdc2/cyclin B is inhibited by roscovitine. Through its unique selectivity for some cyclin-dependent kinases, roscovitine provides a useful antimitotic reagent for cell cycle studies and may prove interesting to control cells with deregulated cdc2, cdk2 or cdk5 kinase activities.[1] Glomerular injury is characterized by mesangial cell (MC) proliferation and matrix formation. We sought to determine if reducing the activity of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) with the purine analogue, Roscovitine, decreased MC proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Roscovitine (25 microM) inhibited FCS-induced proliferation (P < 0.0001) in cultured MC. Rats with experimental mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis (Thy1 model) were divided into two groups. A prevention group received daily intraperitoneal injections of Roscovitine in DMSO (2.8 mg/kg) starting at day 1. A treatment group received daily Roscovitine starting at day 3, when MC proliferation was established. Control Thy1 rats received DMSO alone. MC proliferation (PCNA +/OX7 + double immunostaining) was reduced by > 50% at days 5 and 10 in the Roscovitine prevention group, and at day 5 in the treatment group (P < 0.0001). Early administration of Roscovitine reduced immunostaining for collagen type IV, laminin, and fibronectin at days 5 and 10 (r = 0.984; P < 0.001), which was associated with improved renal function (urinary protein/creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, P < 0.05). We conclude that reducing the activity of CDK2 with Roscovitine in experimental glomerulonephritis decreases cell proliferation and matrix production, resulting in improved renal function, and may be a useful therapeutic intervention in disease characterized by proliferation. [2] Roscovitine, a cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) inhibitor, inhibited kinase activity and the axenic growth of Dictyostelium discoideum at micromolar concentrations. Growth was almost fully rescued in 50 µM and ≈ 50% rescued in 100 µM roscovitine-treated cultures by the over-expression of Cdk5-GFP. This supports the importance of Cdk5 function during cell proliferation in Dictyostelium and indicates that Cdk5 is a primary target of the drug. Roscovitine did not affect the expression of Cdk5 protein during axenic growth but did inhibit its nuclear translocation. This novel result suggests that the effects of roscovitine could be due in part to altering Cdk5 translocation in other systems as well. Kinase activity was inhibited by roscovitine in assays using AX3 whole cell lysates, but not in assays using lysates from Cdk5-GFP over-expressing cells. At higher concentrations, roscovitine impaired slug and fruiting body formation. Fruiting bodies that did form were small and produced relatively fewer spores many of which were round. However, roscovitine did not affect stalk cell differentiation. Together with previous findings, these data reveal that roscovitine inhibits Cdk5 during growth and as yet undefined Cdks during mid-late development.[3] The Ewing's sarcoma family of tumors (ESFT) comprises several well-characterized malignant neoplasms with particularly aggressive behavior. Despite recent progress in the use of multimodal therapeutic approaches and aggressive local control measures, a substantial proportion of patients die because of disease progression. Furthermore, this outcome has not changed significantly over the last 15 to 20 years. Consequently, new, more effective therapeutic options are sorely needed for the treatment of ESFT. Because ESFT cells overexpress several cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK), we explored the efficacy against ESFT of roscovitine, a CDK inhibitor shown to be surprisingly safe for humans in clinical trials of their anticancer activity. Results showed that ESFT cell lines are uniformly sensitive to roscovitine. In addition to exerting comparatively minor cell cycle effects, roscovitine treatment concomitantly caused the up-regulation of the expression of the proapoptotic protein BAX and the down-regulation of both survivin and XIAP, thus resulting in caspase-dependent apoptosis. Furthermore, in vivo experiments showed that s.c. growth of ESFT xenografts was also significantly slowed by i.p. injection of roscovitine. These results strongly suggest that roscovitine may be an effective therapeutic agent against ESFT and recommend its evaluation against ESFT in clinical trials and its inclusion in future treatment protocols.[4] We sought to determine whether seliciclib (CYC202, R-roscovitine) could increase the antitumor effects of doxorubicin, with no increase in toxicity, in an MCF7 breast cancer xenograft model. The efficacy of seliciclib combined with doxorubicin was compared with single agent doxorubicin or seliciclib administered to MCF7 cells and to nude mice bearing established MCF7 xenografts. Post-treatment cells and tumors were examined by cell cycle analysis, immunohistochemistry and real-time PCR. Seliciclib significantly enhanced the antitumor effect of doxorubicin without additional murine toxicity. MIB1 (ki67) immunohistochemistry demonstrated reduced proliferation with treatment. The levels of p21 and p27 increased after treatment with doxorubicin or seliciclib alone or in combination, compared to untreated controls. However, no changes in p53 protein (DO1, CM1), survivin or p53 phosphorylation (SER15) were observed in treated tumors compared with controls. In conclusion, the CDK inhibitor seliciclib (R-roscovitine) enhances the antitumor effect of doxorubicin in MCF7 tumors without increased toxicity with a mechanism that involves cell cycle arrest rather than apoptosis.[5] |
| 分子式 |
C19H26N6O
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
354.45
|
|
| 精确质量 |
354.216
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 64.38; H, 7.39; N, 23.71; O, 4.51
|
|
| CAS号 |
186692-46-6
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
160355
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
577.5±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
303.1±32.9 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.643
|
|
| LogP |
1.68
|
|
| tPSA |
87.89
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
26
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
417
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
O([H])C([H])([H])[C@@]([H])(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])N([H])C1=NC(=C2C(=N1)N(C([H])=N2)C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])N([H])C([H])([H])C1C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C=1[H]
|
|
| InChi Key |
BTIHMVBBUGXLCJ-OAHLLOKOSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C19H26N6O/c1-4-15(11-26)22-19-23-17(20-10-14-8-6-5-7-9-14)16-18(24-19)25(12-21-16)13(2)3/h5-9,12-13,15,26H,4,10-11H2,1-3H3,(H2,20,22,23,24)/t15-/m1/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
(2R)-2-[[6-(benzylamino)-9-propan-2-ylpurin-2-yl]amino]butan-1-ol
|
|
| 别名 |
Seliciclib; R-Roscovitine; CYC-202; roscovitine; Seliciclib; 186692-46-6; R-Roscovitine; (R)-roscovitine; Roscovitin; CYC202; Roscovitin; Roscovitine; CYC202; CYC 202
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.05 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.05 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.05 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.05 mM) (饱和度未知) in 5% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 50% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 5 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.05 mM) (饱和度未知) in 5% DMSO + 95% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 6 中的溶解度: 1% DMSO +30% polyethylene glycol+1% Tween 80 : 30 mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8213 mL | 14.1064 mL | 28.2127 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5643 mL | 2.8213 mL | 5.6425 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2821 mL | 1.4106 mL | 2.8213 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT03774446 | Recruiting | Drug: Seliciclib | Cushing Disease | Cedars-Sinai Medical Center | August 2025 | Phase 2 |
| NCT00999401 | Completed | Drug: sapacitabine and seliciclib |
Advanced Solid Tumors | Cyclacel Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | April 2009 | Phase 1 |
| NCT02649751 | Terminated | Drug: Roscovitine Drug: Placebo |
Cystic Fibrosis | University Hospital, Brest | February 22, 2016 | Phase 2 |
| NCT02160730 | Terminated | Drug: R-roscovitine | Cushings Disease | Shlomo Melmed, MD | May 2014 | Phase 2 |
| NCT00372073 | Terminated | Drug: seliciclib Drug: Placebo |
Non-small Cell Lung Cancer | Cyclacel Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | August 9, 2006 | Phase 2 |