| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
PKMYT1 (IC50 = 14 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在 HCC1569 乳腺癌细胞系中,RP-6306(500 nM;持续时间 24 小时)处理产生 pan-γH2AX,表明肿瘤来源的 CCNE1 也使细胞在 PKMYT1 转录后容易受到 DNA 损伤诱导 [2]。在过度表达 CCNE1 的细胞中,CDK1 突然被选择性激活,从而促进开始 DNA 合成的细胞的早期有丝分裂 [2]。
- PKMYT1抑制作用:RP-6306以2.4 nM的IC₅₀高效抑制PKMYT1激酶活性,激酶活性实验显示其对PKMYT1的选择性是EPHA1-2、EPH B2-4和WEE1的35倍以上[1] - 抗增殖活性:在CCNE1扩增的癌细胞系(如OVCAR3、HCC1569)中,RP-6306呈剂量依赖性抑制生长,GI₅₀值在低纳摩尔范围。非CCNE1扩增细胞敏感性显著降低[2] - DNA损伤诱导:RP-6306(500 nM)处理HCC1569细胞后,通过免疫荧光检测到pan-γH2AX形成,表明DNA损伤应答激活。该效应在CCNE1过表达细胞中选择性显著[2] - CDK1激活:RP-6306阻断PKMYT1对CDK1的抑制,导致S期CDK1过早激活并进入有丝分裂,引发有丝分裂灾难[2] - 克隆形成实验:长期给予RP-6306(10 nM)完全抑制CCNE1扩增卵巢癌细胞的集落形成,而非扩增细胞仍有残留集落生长[2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在 CCNE1 (OVCAR3) 产前异种移植模型中,RP-6306(15、50 和 300 ppm;口服;每天;持续 21 天)导致 OVCAR3 肿瘤生长显着剂量依赖性减少 [1]。
- 肿瘤生长抑制:口服RP-6306(3–60 mg/kg/天)在OVCAR3异种移植模型中呈剂量依赖性减少肿瘤体积。60 mg/kg剂量组肿瘤体积较对照组降低75%[1] - CDK1磷酸化:在肿瘤组织中,RP-6306抑制PKMYT1介导的CDK1 Thr14磷酸化,导致CDK1活性增加和DNA损伤标志物(γ-H2AX)升高[1] - 联合治疗:在PDX4013模型中,RP-6306(50 mg/kg)联合顺铂(3 mg/kg)实现82%肿瘤生长抑制,显著高于单药治疗(55%)。协同效应源于DNA损伤和有丝分裂缺陷增强[2] - 生存获益:CCNE1扩增子宫内膜癌模型中,RP-6306(60 mg/kg)治疗组小鼠中位生存期较对照组延长30%[2] |
| 酶活实验 |
PKMYT1酶活实验(ADP-GLO)[1]
为了测定PKMYT1抑制剂化合物的IC50,使用ADP-GLO assa。首先,将人重组PKMYT1酶在酶测定缓冲液(70 mM Hepes、3 mM MgCl2、3 mM MnCl2、50μg/mL PEG20000、3μM正钒酸钠(添加新鲜)、1.2 mM二硫苏糖醇(添加新鲜的),体积为5μL,并镀在白色384孔板上。然后,将5μL抑制剂或DMSO对照品在酶测定缓冲液中稀释并加入平板。然后将酶/化合物混合物在室温下孵育15分钟。最后,通过加入5μL ATP(在酶测定缓冲液中稀释)开始酶反应,使最终ATP浓度为10μM,最终PKMYT1酶浓度为18.5 nM。然后将酶反应在30℃的培养箱中孵育1小时。在孵育期结束时,加入15μL ADP-GLO试剂,将平板在室温下孵育40分钟。最后,加入30μL激酶检测试剂,将平板在室温下孵育30分钟,然后使用Envision平板阅读器测量发光。然后测定试验中筛选的每种化合物的IC50。本手稿中报告的IC50是至少n=3个重复的几何平均值。[1] PKMYT1/激酶NanoBret检测[1] 为了确定NanoBRET靶点结合试验中化合物的亲和力,将NanoLuc融合载体DNA(PKMYT1 NanoLuc fusion vector或其他感兴趣的激酶和转染载体DNA,使用Fugene HD转染试剂在Opti MEM无酚红缓冲液中转染HEK293 T细胞。在37°C/5%CO2培养箱中孵育过夜后,将转染的HEK293 T淋巴细胞胰蛋白酶化、计数并重新悬浮在Opti MEM无酚红缓冲剂中,浓度为200000个细胞/mL。然后将白色96孔板镀上85μL细胞(17000个细胞/孔),向其中加入5μL在示踪剂稀释缓冲液中稀释的20X示踪剂溶液。最后,加入10μL稀释在Opti-MEM无酚红缓冲液中的10X化合物,然后将平板在37°C/5%CO2培养箱中培养2小时。孵育后,向细胞中加入50μL 3X底物/抑制剂混合物溶液。然后将平板转移到Perkin-Elmer EnVision多模平板阅读器上,在那里测量受体发射(610nm)和供体发射(450nm)。本手稿中报告的IC50是至少n=3个重复的几何平均值。 - PKMYT1激酶活性实验:重组人PKMYT1与ATP及荧光标记肽底物在不同浓度RP-6306(0.1–1000 nM)存在下孵育,采用HTRF技术检测磷酸化水平,通过剂量反应曲线计算IC₅₀[1] - 选择性分析:RP-6306对450种激酶进行筛选,结果显示其对PKMYT1的选择性是脱靶激酶的35倍以上[1] |
| 细胞实验 |
PKMYT1细胞活性测定(CDK1-pThr14-AlphaLISA)[1]
为了测定化合物IC50,将FUOV1细胞以50000个细胞/孔的速度接种到96孔TC处理的培养板中,最终体积为100μL培养基。然后将平板在生物安全柜中平衡30分钟,然后放入37°C和5%CO2的加湿培养箱中过夜。第二天,使用Biomek FX液体处理器将2μL PKMYT1抑制剂或DMSO稀释在96孔块中的400μL温培养基中。将化合物混合在培养基中,然后将25μL分配到96孔细胞板的每个孔中。将板在300g下离心10秒,然后放入培养箱中2小时。与化合物孵育2小时后,使用多通道移液管通过抽吸去除培养基。向每个孔中加入30μL补充有蛋白酶和磷酸酶抑制剂以及1 mM PMSF的1X AlphaLISA裂解缓冲液(Perkin-Elmer)。将板在500g下旋转20分钟以促进裂解。然后用铝箔密封板,并在-80°C下冷冻至少1小时。将裂解物在37°C下解冻10分钟,然后将10μL的每种裂解物一式两份转移到白色384孔分析板上。在含有抗体的1X AlphaLISA测定缓冲液中制备抗体混合物(兔pThr14-CDK1和小鼠总CDK1的终浓度为5nM)。向测定板的每个孔中加入5μL抗体混合物。将分析板密封并在4°C下储存过夜。第二天,在1X AlphaLISA测定缓冲液中制备AlphaLISA珠混合物。在测定缓冲液中制备抗兔IgG受体和抗小鼠IgG供体珠,浓度为80μg/ml。向测定板的每个孔中加入5μL珠粒混合物(每个珠粒的终浓度为20μg/ml)。将板避光,在室温下孵育2小时。用珠子孵育2小时后,使用Perkin-Elmer EnVision多模平板阅读器读取平板,激发波长为680nm,发射波长为615nm。[1] 细胞增殖试验[2] 将RPE1-hTERT Cas9 TP53−/−、FT282-hERT TP53R175H及其各自的CCNE1高同源对以每孔150个细胞的密度接种在96孔板(Corning Costar目录号5595)中,用于RPE1-hTENT-Cas9 TP53−/−CCNE1(C2),或所有其他孔每孔100个细胞。24小时后,使用自动D300e数字分配器以0.15 nM至3µM的药物浓度处理细胞。每3-4天更新一次培养基和药物,并使用IncuCyte S3活细胞成像仪监测细胞融合,最多6次群体倍增。使用相对于未处理对照的汇流百分比来评估受试化合物诱导的生长抑制。使用ZIP模型,使用在线SynergyFinder v2.0工具分析RP-6306和羟基脲或吉西他滨之间的协同作用(https://synergyfinder.fimm.fi). - 增殖实验:CCNE1扩增细胞(5×10³/孔)经RP-6306(1–1000 nM)处理72小时,MTT法检测活力。CCNE1扩增细胞GI₅₀为5–20 nM,非扩增细胞GI₅₀ > 100 nM[2] - γH2AX检测:细胞经RP-6306(500 nM)处理24小时后,固定、透化并染色抗γH2AX抗体。免疫荧光显微镜显示CCNE1扩增细胞γH2AX焦点显著增加[2] - 克隆形成实验:低密度接种细胞(500细胞/孔),给予RP-6306(10 nM)处理14天。结晶紫染色显示CCNE1扩增细胞集落形成减少90%[2] |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: OVCAR3-carrying mice [1]
Doses: 15, 50, and 300 ppm (equivalent to approximately 3, 10, and 60 mg/kg/day) Route of Administration: Oral; daily; for 21 days Experimental Results: Caused OVCAR3 tumors There was a statistically significant and dose-dependent reduction in growth. OVCAR3 cells were implanted at 5×106 cells per mouse into the right flanks of female SCID-beige mice (5–7 weeks old; Charles River), in 1:1 matrigel: media. When tumors reached the target size of 100–150 mm3, (n=8) mice were randomized to treatment groups and treatment with RP-6306 was initiated. In vivo studies involving cell-derived xenografts were performed at Repare Therapeutics, in a CCAC (Canadian Council on Animal Care)-accredited vivarium with an Institutional Animal Care Committee-approved protocol. RP-6306 was formulated in chow at 15–300 ppm or in 0.5% methylcellulose and orally administered twice daily (BID, 0–8 h) for a maximum of 21 days. Chow treated mice were acclimatized to blank chow prior to drug-formulated chow for 3–5 days. Tumor volume was measured using a digital caliper and calculated using the formula 0.52×L×W2. TGI was defined as the formula: % TGI= ((TVvehicle/last – TVvehicle/day0) - (TVtreated/last – TVtreated/day0)) / (TVvehicle/last – TVvehicle/day0) x100 calculated based on the means of the treatment groups at day 0 and last day of measurement. Change in body weight (BW) was calculated using the formula: % BW change = (BWlast-BWday0/ BWday0) x100. BW change was calculated based on individual body weight changes relative to day 0. Statistical significance relative to vehicle control or other test groups was established by one-way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s LSD test for multiple groups and unpaired t-test for two group comparisons (GraphPad Prism v9.0).[1] HCC1569, OVCAR3 and SUM149PT cells were implanted at 5 × 106 cells per mouse into the right flanks of female CB17-SCID, SCID-beige and NOD-SCID mice respectively (5–7 weeks old; Charles River), in 1:1 Matrigel:medium). When tumours reached the target size of 100–150 mm3, mice (n = 8) were randomized to treatment groups according to tumour volume and body weight using the ‘stratified’ method in Studylogv4.4 software and treatment with RP-6306 was initiated.[2] Fresh primary human tumour tissue was collected and cut into small pieces (approximately 2–3 mm in diameter). These tumour fragments were inoculated subcutaneously into the right flank of female BALB/c nude mice (5–7 weeks old) for tumour development and subsequently passaged by implantation into the cohort of mice enrolled in the efficacy study. Mice were randomized according to growth rate into treatment groups (n = 6) when the mean tumour size reached approximately 150 (100–200) mm3 using the stratified method in Studylogv4.4 software. The procedures involving the care and use of animals in for the PDX model were reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of CrownBio prior to execution. During the study, the care and use of animals were conducted in accordance with the regulations of the Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care (AAALAC).[2] RP-6306 was formulated in 0.5% methylcellulose and orally administered twice daily (BID, 0–8 h) for a maximum of 21 days. Gemcitabine was administered once weekly intraperitoneally in saline. Animals were monitored for tumour volume, clinical signs and body weight three times per week. Tumour volume was measured using a digital calliper and calculated using the formula 0.52 × L × W2, where L is length and W is width. Response to treatment was evaluated for tumour growth inhibition (% TGI). Tumour growth inhibition (TGI) was defined as: TGI = ((TVvehicle/last − TVvehicle/day0) − (TVtreated/last − TVtreated/day0))/(TVvehicle/last − TVvehicle/day0) × 100% calculated based on the means of the treatment groups at day 0 and last day of measurement. TV is tumour volume and subscripts indicate treatment group and time of sampling. According to NIACC and IACUC approved animal protocols, mice were euthanized as soon as their tumour volume exceeded 2,000 mm3. Change in body weight (BW) was calculated using the formula: %BW change = (BWlast − BWday0/BWday0) × 100. BW change was calculated based on individual body weight changes relative to day 0. Statistical significance relative to vehicle control or other test groups was established by one-way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s least significant difference test for multiple groups and unpaired t-test for two group comparisons (GraphPad Prism v9.0). Investigators were not blinded during data collection and analysis.[2] - Xenograft Model: Female NSG mice bearing OVCAR3 tumors (100 mm³) were randomized to receive RP-6306 (3, 10, or 60 mg/kg) or vehicle (0.5% methylcellulose) via oral gavage daily for 21 days. Tumor volume was measured twice weekly using calipers [1] - Formulation: RP-6306 was suspended in 0.5% methylcellulose and administered at a volume of 10 mL/kg [1] - Combination Therapy: In PDX4013 models, mice received RP-6306 (50 mg/kg) + cisplatin (3 mg/kg, i.p.) weekly for 3 weeks. Tumor growth was monitored, and tissues were harvested for immunohistochemistry [2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
- Oral Bioavailability: RP-6306 demonstrated high oral bioavailability (>70%) in preclinical species, with peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) achieved within 1–2 hours [1]
- Half-Life: The terminal half-life in mice was 4.5 hours, allowing once-daily dosing [1] - Tissue Distribution: The compound exhibited broad tissue distribution, with tumor/plasma concentration ratios >2 in xenograft models [1] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
- Safety Profile: RP-6306 (up to 100 mg/kg daily) showed no significant toxicity in rodent studies. Hematology, serum chemistry, and histopathology of major organs (liver, kidney, heart) were within normal ranges [1]
- Selective Toxicity: No adverse effects were observed in normal tissues, consistent with the synthetic lethal mechanism targeting CCNE1-amplified tumors [2] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
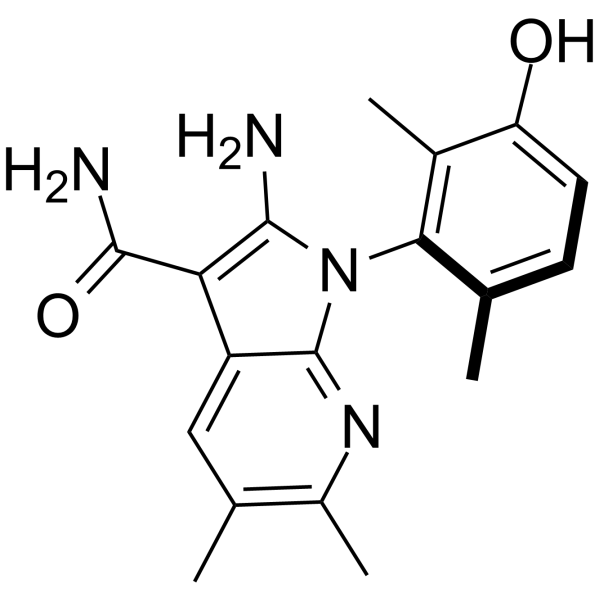
Lunresertib is an orally bioavailable inhibitor of the human membrane-associated tyrosine- and threonine-specific cdc2-inhibitory kinase (PKMYT1), with potential antineoplastic activity. Upon oral administration, lunresertib targets, binds to and inhibits the activity of PKMYT1. This results in the inhibition of CDK1 phosphorylation, which may promote both premature mitosis and a prolonged mitotic arrest, and lead to the accumulation of unrepaired DNA damage and apoptosis in susceptible tumor cells, such as CCNE1-overexpressing tumor cells. PKMYT1 phosphorylates CDK1 specifically when CDK1 is complexed to cyclins, which blocks progression from G2 into mitosis.
- Mechanism of Action: RP-6306 inhibits PKMYT1, preventing phosphorylation of CDK1 at Thr14/Tyr15. This leads to premature CDK1 activation, mitotic entry during DNA synthesis, and subsequent mitotic catastrophe [2] - Synthetic Lethality: CCNE1 amplification drives CDK2 overactivation, which sensitizes cells to PKMYT1 inhibition by exacerbating replication stress and DNA damage [2] - Clinical Potential: RP-6306 is being evaluated in phase I/II trials for CCNE1-amplified ovarian, endometrial, and bladder cancers, with preliminary data showing objective responses in heavily pretreated patients [1,2] |
| 分子式 |
C18H20N4O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
324.3770
|
| 精确质量 |
324.158625
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 66.65; H, 6.21; N, 17.27; O, 9.86
|
| CAS号 |
2719793-90-3
|
| 相关CAS号 |
(Rac)-RP-6306;2719749-28-5;(R)-RP-6306;2719793-91-4
|
| PubChem CID |
156869388
|
| 外观&性状 |
Off-white to gray solid powder
|
| LogP |
3.1
|
| tPSA |
107Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
| 重原子数目 |
24
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
488
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O([H])C1C([H])=C([H])C(C([H])([H])[H])=C(C=1C([H])([H])[H])N1C(=C(C(N([H])[H])=O)C2C([H])=C(C([H])([H])[H])C(C([H])([H])[H])=NC1=2)N([H])[H]
|
| InChi Key |
ARBRHWRTXPWZGN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H20N4O2/c1-8-5-6-13(23)10(3)15(8)22-16(19)14(17(20)24)12-7-9(2)11(4)21-18(12)22/h5-7,23H,19H2,1-4H3,(H2,20,24)
|
| 化学名 |
2-amino-1-(3-hydroxy-2,6-dimethylphenyl)-5,6-dimethylpyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine-3-carboxamide
|
| 别名 |
(Rac)-RP-6306; lunresertib; 2719793-90-3; (R)-RP-6306; 2719749-28-5; CHEMBL5199076; N95U3A7N57;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~50 mg/mL (~154.14 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 5 mg/mL (15.41 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 50.0mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到900μL 20%SBE-β-CD生理盐水中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.71 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.71 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0828 mL | 15.4140 mL | 30.8280 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6166 mL | 3.0828 mL | 6.1656 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3083 mL | 1.5414 mL | 3.0828 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。