| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
纯度: ≥98%
| 靶点 |
MCL-1 (Kd = 0.19 nM by SPR; Ki < 0.2 nM by FP assay)[2]
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
S63845 诱导已知依赖 MCL-1 的癌细胞系死亡,显示出依赖于半胱天冬酶和 BAX/BAK 介导的线粒体外膜透化的经典细胞凋亡特征。与小鼠 MCL-1 相比,它对人类 MCL-1 的亲和力高出 6 倍[1]。 S63845 在体外、体内以及对 AML 样本以及血液癌衍生细胞系均有效,但对正常人类造血祖细胞不是很有效[2]。
S63845 在78%的MCL-1依赖性癌细胞系中诱导凋亡(EC₅₀:12-190 nM),而MCL-1非依赖性细胞系无响应。与venetoclax在AML细胞系中显示协同作用(CI<0.3)。[2] 抑制12/13多发性骨髓瘤细胞系活力(EC₅₀<100 nM)。MV4-11细胞中4小时内激活caspase-3。[2] 30分钟内解除MCL-1对BIM的结合(免疫共沉淀验证)。[2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在体内,S63845 对多种癌症表现出强大的抗肿瘤活性,并具有可容忍的安全范围。小鼠对 S63845 的耐受性良好,没有观察到明显的体重减轻。一些实体瘤模型对 S63845 单一疗法反应良好,但许多其他模型仅对 S63845 和致癌激酶抑制剂的组合有反应[2]。
建立小鼠造血损伤模型,通过血常规和流式细胞术观察抑制剂对小鼠造血系统的影响。结果表明,S63845在作用早期影响了各种谱系的造血功能,引起髓系和巨核细胞谱系的髓外代偿性造血。髓内和髓外段红系的成熟受到不同程度的阻断,髓内和髓外淋巴系均受到抑制。本研究完整地描述了MCL-1抑制剂对髓内和髓外造血谱系的影响,这对于抗肿瘤药物组合的选择和预防造血相关不良反应具有重要意义。https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37111571/ S63845 在78%的MCL-1依赖性癌细胞系中诱导凋亡(EC₅₀:12-190 nM),而MCL-1非依赖性细胞系无响应。与venetoclax在AML细胞系中显示协同作用(CI<0.3)。[2] 抑制12/13多发性骨髓瘤细胞系活力(EC₅₀<100 nM)。MV4-11细胞中4小时内激活caspase-3。[2] 30分钟内解除MCL-1对BIM的结合(免疫共沉淀验证)。[2] |
| 酶活实验 |
运行缓冲液由 10 mM HEPES pH 7.4、175 mM NaCl、25 μM EDTA、1 mM TCEP、0.01% P20 和 1% DMSO 组成。带有双组氨酸标签的蛋白质用于创建配体表面。该化合物在缓冲液中连续稀释并注射到蛋白质表面。所有样品测量使用的流速为每分钟 30 μL(进样时间:120 秒,解离时间:360 秒)。通过重复注入 0.35 M EDTA pH 8.0 和 0.1 mg/mL 胰蛋白酶、0.5 M 咪唑和 45% DMSO(60 秒,每分钟 15 μL),传感器表面得以恢复。
SPR结合:重组人MCL-1固定于CM5芯片。梯度浓度S63845(0.1-1000 nM)在HBS-EP缓冲液中以30 μL/min流速进样。稳态亲和力计算Kd。[2] 荧光偏振:FITC标记的BIM SAHB肽(25聚体,20 nM)与MCL-1(10 nM)及化合物孵育1小时测定IC₅₀。[2] HTRF竞争:生物素化MCL-1与链霉亲和素-XL665及铽标记抗GST抗体孵育。生成剂量效应曲线。[2] |
| 细胞实验 |
在使用抗 FLAG 抗体进行免疫沉淀之前,将用 Flag-BCL-XL、Flag-BCL-2 或 Flag-MCL1 表达构建体转导的 HeLa 细胞用浓度递增的 S63845 处理 4 小时。免疫印迹用于检查 FLAG 标记蛋白以及相关 BAK 和 BAX 蛋白的免疫沉淀和总输入。
凋亡检测:细胞经S63845(0.1-1000 nM)处理48小时。发光底物测定caspase-3/7活性(四参数拟合计算EC₅₀)。[2] 免疫印迹:处理后裂解细胞(RIPA缓冲液),30 μg蛋白经SDS-PAGE分离,转印至PVDF膜,用抗MCL-1/BAK/cleaved PARP抗体检测。[2] 原代细胞活力:AML患者骨髓样本与S63845培养7天,流式细胞术评估活力。[2] |
| 动物实验 |
Human multiple myeloma (H929 and AMO1) xenografted mice; Intravenously injected (i.v.), 25 mg/kg
Xenograft efficacy: 5×10⁶ tumor cells implanted subcutaneously in NSG mice. Treatment started at 100-200 mm³ tumor volume. S63845 in 10% DMSO/40% PEG300/50% PBS administered i.p. daily (25-50 mg/kg) for 14-21 days.[2] PDX models: Primary patient AML cells engrafted in mice. Treatment initiated at 1% human CD45+ cells in blood.[2] Tolerability: Dose escalation (12.5-75 mg/kg i.p. daily). MTD defined as ≤20% body weight loss.[2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Xenograft efficacy: 5×10⁶ tumor cells implanted subcutaneously in NSG mice. Treatment started at 100-200 mm³ tumor volume. S63845 in 10% DMSO/40% PEG300/50% PBS administered i.p. daily (25-50 mg/kg) for 14-21 days.[2]
PDX models: Primary patient AML cells engrafted in mice. Treatment initiated at 1% human CD45+ cells in blood.[2] Tolerability: Dose escalation (12.5-75 mg/kg i.p. daily). MTD defined as ≤20% body weight loss.[2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
MTD: 50 mg/kg i.p. daily (reversible ≤10% weight loss).[2]
No hepatotoxicity (ALT/AST unchanged) or nephrotoxicity (normal BUN/creatinine).[2] hERG IC₅₀ >30 μM; CYP450 inhibition IC₅₀ >10 μM for major isoforms.[2] Myeloid hyperplasia in bone marrow at efficacious doses.[2] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Defects in apoptotic machinery have long been recognised as both a significant contributor to cancer development, and as an important mechanism by which tumour cells develop chemotherapeutic resistance. The resistance of multiple malignancies to apoptosis has been attributed to increases in a number of pro-survival BCL-2 family members (e.g., BCL-2, BCL-XL, MCL-1, BCL-W, BFL-1 and BCL-B), which prevent BAX/BAK-mediated mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilisation. Inhibitors targeting these BCL-2 family members have garnered significant interest with the most promising lead being the BH3 mimetic venetoclax (also known as ABT-199, and marketed as Venclexta™ and Venclyxto™), a selective inhibitor of the BCL-2 protein recently approved for 17p deletion chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). In a phase I trial in relapsed or refractory CLL, venetoclax induced a 79% response rate (1) which has subsequently prompted further trials in other haematological malignancies. Despite this success in CLL, venetoclax used as a monotherapy in other haematological malignancies have shown poor response rates (2), mainly due to the reliance of other BCL-2 family members such as MCL-1 for cell survival in these cancers. Indeed, studies using genetic knockout models and RNA interference have demonstrated MCL-1 to be crucial for disease development and progression in acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) (3), MYC-driven lymphomas (4), and multiple myeloma (5), and a mechanism of venetoclax resistance in these cancers (6). Indirect approaches to target MCL-1 through transcriptional repression (7,8) or post-translational degradation (9) have recently been developed. However, direct targeting strategies with obatoclax, an inhibitor of MCL-1 and also BCL-2 and BCL-XL, induced neuronal toxicity (10,11). More recently, a reported MCL-1-selective inhibitor termed A-1210477 (12) displayed in vitro activity against multiple myeloma cells (13); however, these anti-cancer effects appear likely to result from combination of both targeting MCL-1 and off-target effects (14).[1]
Avoidance of apoptosis is critical for the development and sustained growth of tumours. The pro-survival protein myeloid cell leukemia 1 (MCL1) is overexpressed in many cancers, but the development of small molecules targeting this protein that are amenable for clinical testing has been challenging. Here we describe S63845, a small molecule that specifically binds with high affinity to the BH3-binding groove of MCL1. Our mechanistic studies demonstrate that S63845 potently kills MCL1-dependent cancer cells, including multiple myeloma, leukaemia and lymphoma cells, by activating the BAX/BAK-dependent mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. In vivo, S63845 shows potent anti-tumour activity with an acceptable safety margin as a single agent in several cancers. Moreover, MCL1 inhibition, either alone or in combination with other anti-cancer drugs, proved effective against several solid cancer-derived cell lines. These results point towards MCL1 as a target for the treatment of a wide range of tumours.[2] Conventional chemotherapy for killing cancer cells using cytotoxic drugs suffers from low selectivity, significant toxicity, and a narrow therapeutic index. Hyper-specific targeted drugs achieve precise destruction of tumors by inhibiting molecular pathways that are critical to tumor growth. Myeloid cell leukemia 1 (MCL-1), an important pro-survival protein in the BCL-2 family, is a promising antitumor target. In this study, we chose to investigate the effects of S63845, a small-molecule inhibitor that targets MCL-1, on the normal hematopoietic system.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37111571/ |
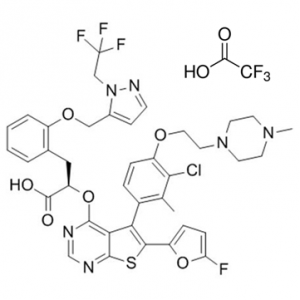
| 分子式 |
C39H37CLF4N6O6S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
829.2593
|
| 精确质量 |
828.212
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 56.49; H, 4.50; Cl, 4.27; F, 9.16; N, 10.13; O, 11.58; S, 3.87
|
| CAS号 |
1799633-27-4
|
| 相关CAS号 |
(S,R)-S63845;(R,R)-S63845
|
| PubChem CID |
122197581
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| LogP |
5.7
|
| tPSA |
156
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
16
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
15
|
| 重原子数目 |
57
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1300
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| InChi Key |
ZFBHXVOCZBPADE-SSEXGKCCSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C39H37ClF4N6O6S/c1-23-26(7-8-28(34(23)40)53-18-17-49-15-13-48(2)14-16-49)32-33-36(45-22-46-37(33)57-35(32)29-9-10-31(41)55-29)56-30(38(51)52)19-24-5-3-4-6-27(24)54-20-25-11-12-47-50(25)21-39(42,43)44/h3-12,22,30H,13-21H2,1-2H3,(H,51,52)/t30-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(2R)-2-[5-[3-chloro-2-methyl-4-[2-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-6-(5-fluorofuran-2-yl)thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]oxy-3-[2-[[2-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)pyrazol-3-yl]methoxy]phenyl]propanoic acid
|
| 别名 |
S63845 Trifluoroacetic acid; S-63845 TFA; S 63845
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: (1). 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 (2). 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: >41.45mg/mL
Water: >10mg/mL Methanol: >20mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (2.51 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (2.51 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: 5 mg/mL (6.03 mM) in 50% PEG300 50% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.2059 mL | 6.0295 mL | 12.0589 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2412 mL | 1.2059 mL | 2.4118 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1206 mL | 0.6029 mL | 1.2059 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
|
|---|
|
|