| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
Human Endogenous Metabolite; ERK; Caspase-3/12;
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
牛磺熊去氧胆酸 (TUDCA) 通过抑制 ERK 磷酸化并通过 PKCα 诱导丝裂原激活蛋白激酶磷酸酶-1 (MKP-1) 来降低血管平滑肌细胞 (VSMC) 的活力和迁移。通过 Ca2+ 依赖性 PKC 易位阻断 ERK,牛磺熊去氧胆酸可防止 VSMC 增殖和迁移。牛磺熊去氧胆酸可防止血管损伤引起的血小板衍生生长因子 (PDGF) 和 MMP-9 表达。 Tauroursodeoxycholate (200 μM) 可降低 VSMC 活力,这表明 Tauroursodeoxycholate 抑制细胞增殖的能力取决于 MKP-1 的表达[1]。通过使用特定的 si-RNA 敲低 MKP-1 的表达,可以减少其表达。
牛磺熊去氧胆酸 (TUDCA) 通过 PKCα 激活丝裂原激活的磷酸磷酸酶 1 (MKP-1) 并抑制 ERK 磷酸化,最终降低血管平滑肌细胞 (VSMC) 的存活和迁移。牛磺熊去氧胆酸通过 Ca2+ 诱导 PKCα 易位抑制 ERK 牛磺熊去氧胆酸 (200 μM) 可以恢复牛磺熊去氧胆酸 (200 μM) 降低的 VSMC,从而限制 VSMC 的增殖和迁移 活性,这意味着牛磺熊去氧胆酸的抗应激作用取决于 MKP-1 的表达 [1]。 TUDCA转运机制及作用通路研究 [1] 通过RT-PCR和蛋白质印迹法分析了人血管平滑肌细胞(hVSMCs)摄取TUDCA的转运蛋白。特异性siRNA敲降实验证实,TUDCA通过有机阴离子转运蛋白2(OATP2)进入hVSMCs。TUDCA通过蛋白激酶Cα(PKCα)诱导丝裂原活化蛋白激酶磷酸酶-1(MKP-1),进而抑制细胞外信号调节激酶(ERK)的活性,最终降低hVSMCs的存活率。PKC抑制剂7-羟基星形孢菌素或MKP-1敲降均可逆转TUDCA的抗增殖作用。此外,TUDCA通过ERK抑制下调基质金属蛋白酶9(MMP-9)的表达,从而抑制hVSMCs迁移能力。 结论 [1] hVSMCs对TUDCA的摄取由OATP2介导。TUDCA通过PKCα/MKP-1通路抑制ERK磷酸化,从而同时抑制VSMCs的存活和迁移能力。研究还证实TUDCA可显著抑制PDGF诱导的VSMCs增殖和迁移。[1] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
采用免疫组织化学方法检测牛磺熊去氧胆酸 (TUDCA) 对体内 VSMC 增殖和凋亡的影响。 Tauroursodeoxycholate(10、50 和 100 mg/kg)以剂量依赖性方式增加受损组织的 caspase 3 活性,表明它会导致新内膜中的 VSMC 发生凋亡。损伤后 1 周,使用损伤组织与正常对照相比,对 ERK 和 MMP-9 表达的磷酸化水平进行额外测试和比较。球囊损伤后组织中 ERK 磷酸化和 MMP-9 表达均上调。 Tauroursodeoxycholate(10、50 和 100 mg/kg)以剂量依赖性方式抑制 MMP-9 和 ERK 的表达[1]。牛磺熊去氧胆酸盐 (TUDCA) 是一种亲水性胆汁酸。通过降低内质网应激和细胞凋亡,牛磺熊去氧胆酸(一种细胞保护剂)可增强肝功能并预防肝细胞癌。在 Ang II 诱导的 ApoE-/- 小鼠中,牛磺熊去氧胆酸显着降低凋亡分子的表达,如 caspase-3、caspase-12、C/EBP 同源蛋白、c-Jun N 末端激酶 (JNK)、激活转录因子 4 (ATF4) )、X-box 结合蛋白 (XBP) 和真核起始因子 2α (eIF2;p<0.05)。在 ApoE-/- 小鼠中,牛磺熊去氧胆酸可预防 Ang II 引起的腹主动脉瘤 (AAA) 的发展。牛磺熊去氧胆酸以 0.5 g/kg/天的剂量给予 ApoE-/- 小鼠(ER 应激抑制剂组)。 AAA模型组之间的总胆固醇水平(663.6±88.7 mg/dL vs 655.7±65.4 mg/dL;p>0 .05)和收缩压(141.3±5.6 mmHg vs 145.98.9 mmHg;p>0.05)具有可比性和牛磺熊去氧胆酸盐基团。此外,与AAA模型组相比,牛熊去氧胆酸盐组的最大主动脉直径显着较低(0.95±0.03 mm vs 1.79±0.04 mm;p<0.05)。牛熊去氧胆酸盐组的 AAA 病变面积也小于 AAA 模型组(0.37±0.03 mm2 vs 1.51±0.06 mm2;p<0.05)[2]。
TUDCA在体内减少新生内膜增生的作用[1] 体外实验结果表明,TUDCA可能通过PKCα介导的ERK抑制作用抑制血管损伤后的新生内膜形成。采用大鼠颈动脉损伤模型分析TUDCA对新生内膜形成的影响。球囊损伤后,口服TUDCA治疗2周能显著抑制新生内膜形成,且呈剂量依赖性(内膜/中膜比值;50 mg/kg组1.48±0.11;100 mg/kg组1.17±0.16 vs 对照组1.86±0.17,n=8,P<0.05)(图4A和B)。此外,TUDCA给药显著减少了新生内膜面积(对照组100±12.9%;TUDCA 10 mg/kg组80.0±19.7%;50 mg/kg组75.5±6.8%;100 mg/kg组56.9±20%,每组n=8)和新生内膜厚度(对照组133.5±26.7 μm;10 mg/kg组92.1±23.3 μm;50 mg/kg组78.5±15.7 μm;100 mg/kg组61.8±16.3 μm,每组n=8)(图4C和D)。同时,TUDCA以剂量依赖性方式增加了管腔面积(正常组100±5.6%;对照组63.3±7.1%;10 mg/kg组73.1±11.1%;50 mg/kg组78.7±5.8%;100 mg/kg组91.2±8.2%,每组n=8),该增加与新生内膜面积的减少呈正相关(图4E)。值得注意的是,中膜面积和中膜细胞数量未受影响(在线补充材料,图S5A和B)。 |
| 酶活实验 |
FITC-TUDCA摄取实验 [1]
人血管平滑肌细胞(hVSMCs)使用平滑肌细胞生长培养基2(Smooth Muscle Cell Growth Medium 2)培养。本研究采用4名供体来源、传代4-7次的hVSMCs。将1×10⁴个hVSMCs接种于96孔板培养后,分别加入指定浓度的FITC-TUDCA,并用预冷磷酸盐缓冲液洗涤。通过检测488 nm处吸光度评估FITC信号。竞争实验中将100 μM FITC-TUDCA与不同浓度的未标记TUDCA混合,处理hVSMCs 15分钟。具体方法详见在线补充材料。 明胶酶谱分析 [1] 细胞经TUDCA处理24小时后收集上清,上样至含1 mg/mL明胶的SDS-PAGE凝胶。电泳结束后,凝胶在反应缓冲液中孵育24小时,随后用0.15%考马斯亮蓝R250染色。具体方法详见在线补充材料。 |
| 细胞实验 |
Ez-Cytox 用于评估细胞的活力和生长。平滑肌细胞生长培养基 2 (SMCGM2) 用于在 96 孔板上接种和培养 VSMC(5×103 个细胞)。血清饥饿后,将牛磺熊去氧胆酸盐(0、50、100 和 200 μM)添加到 hVSMC,有或没有 1,2-双(邻氨基苯氧基)乙烷-N,N,N',N'-四乙酸四(乙酰氧基甲基)酯(BAPTA,10μM)和7-羟基星形孢菌素(H7,10μM)并培养24小时。将 HVSMC 接种到 96 孔板上并进行培养,以确定牛磺熊去氧胆酸对 PDGF 刺激的 hVSMC 增殖的影响。血清饥饿后,在有或没有 PDGF-BB (50 ng/mL) 的情况下,将牛磺熊去氧胆酸盐(0、50、100 和 200 μM)添加到 hVSMC,然后培养细胞。在每孔中添加 10 μL Ez-Cytox 后,450 nm 处的光密度用于评估细胞活力[1]。
划痕愈合实验 [1] 采用划痕法评估hVSMCs迁移能力。将1×10⁶个hVSMCs接种于60 mm培养皿,培养至细胞完全融合。分别用不同浓度TUDCA预处理1小时后,使用改良枪头在细胞单层中央制造划痕。划痕后用无血清SMCGM2培养基洗涤,继续含TUDCA培养36小时。由三位独立研究者对划痕边缘迁移细胞进行计数分析。 流式细胞术检测 [1] 通过流式细胞术评估TUDCA诱导的hVSMCs凋亡。血清饥饿处理24小时后,分别用浓度梯度(0、50、100及200 μM)TUDCA处理细胞。收集固定细胞后,通过DNA含量分析检测凋亡率。具体方法详见在线补充材料。 |
| 动物实验 |
Rats: Ketamine (70 mg/kg) and Xylazine (7 mg/kg) are combined to anesthetize Sprague-Dawley rats. For two weeks, tauroursodeoxycholate is given orally once daily at various concentrations (e.g., vehicle, 10, 50, and 100 mg/kg). The carotid arteries are preserved by perfusion with 4% formaldehyde, followed by paraffin embedding and H&E staining of sections (8 μm)[1].
Mice: Thirty C57BL/6 male ApoE-/- mice are divided into three groups at random, each with ten mice, and they are eight weeks old. (i) ApoE-/- mice are implanted with mini-osmotic pumps to release Ang II (1000 ng/kg/min) over the course of 28 days (AAA model group); (ii) AAA model mice are treated with Tauroursodeoxycholate daily for 4 weeks at a dosage of 0.5 g/kg/day in drinking water (Tauroursodeoxycholate group). Following a 28-day Ang II infusion, mice are sacrificed[2]. Rat carotid artery balloon injury [1] The rats were anaesthetized with a combined anaesthetic (ketamine, 70 mg/kg; xylazine, 7 mg/kg ip). Noxious stimuli were applied to a limb occasionally throughout the experiments, while monitoring changes in the end-tidal carbon dioxide, heart rate, blood pressure, and cardiac rhythm, in order to ascertain the level of anaesthesia. After the left external carotid artery was exposed, a 2 F Fogarty embolectomy catheter was introduced through an external carotid arteriotomy incision, advanced to the common carotid artery, inflated with 0.2 mL of saline, and withdrawn 10 times, with rotation.TUDCA was then administered orally once a day, in different concentrations (i.e. vehicle, 10, 50, and 100 mg/kg) for 2 weeks. The carotid arteries were fixed by perfusion with 4% formaldehyde, then the tissues were embedded in paraffin, and sections (8 μm) were stained with H&E. The detailed methods were described in Supplementary material online. Ang II induced AAA model in mice [2] Thirty ApoE−/− C57BL/6 male mice aged 8 weeks were randomly divided into three groups (n = 10 in each group): (i) sham operated and injected with physiologic (0.9%) saline as vehicle (“normal: group); (ii) mini-osmotic pumps were implanted subcutaneously into the right flank of ApoE−/− mice to release Ang II (1000 ng/kg/min) over the course of 28 days (“AAA model” group); (iii) AAA model mice treated with ER stress inhibitor (TUDCA) daily for 4 weeks at a dosage of 0.5 g/kg/day in drinking water (“ER stress inhibitor” group). Mice were sacrificed after 28 days of Ang II infusion. As described previously,22 systolic blood pressure was obtained 1 week before the implantation of the mini-osmotic pumps in mice and after 28 days of infusion, by use of a non-invasive tail cuff system. Blood was collected from the retro-orbital sinus under isoflurane anaesthesia. Serum total cholesterol levels were measured using an enzymatic method. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
There is evidence that tauroursodeoxycholic acid crosses the blood brain barrier in humans. Metabolism / Metabolites There is little biotransformation of tauroursodeoxycholic acid. It is partially deconjugated by intestinal microflora to form unconjugated bile acids. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
9848818 rat LD50 oral >5 gm/kg Japanese Kokai Tokyo Koho Patents., #92-235918
9848818 rat LD50 intravenous 300 mg/kg Japanese Kokai Tokyo Koho Patents., #92-235918 9848818 mouse LD50 oral >6 gm/kg Japanese Kokai Tokyo Koho Patents., #92-235918 9848818 mouse LD50 intravenous 350 mg/kg Japanese Kokai Tokyo Koho Patents., #92-235918 |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
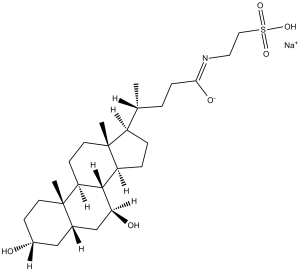
Tauroursodeoxycholic acid is a bile acid taurine conjugate derived from ursoodeoxycholic acid. It has a role as a human metabolite, an anti-inflammatory agent, a neuroprotective agent, an apoptosis inhibitor, a cardioprotective agent and a bone density conservation agent. It is functionally related to an ursodeoxycholic acid. It is a conjugate acid of a tauroursodeoxycholate.
Tauroursodeoxycholic acid, also known as ursodoxicoltaurine, is a highly hydrophilic tertiary bile acid that is produced in humans at a low concentration. It is a taurine conjugate of [ursodeoxycholic acid] with comparable therapeutic efficacy and safety, but a much higher hydrophilicity. Normally, hydrophilic bile acids regulates hydrophobic bile acids and their cytotoxic effects. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid can reduce the absorption of cholesterol in the small intestine, thereby reducing the body's intake of dietary cholesterol and the body cholesterol content. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid is currently used in Europe to treat and prevent gallstones as a bile acid derivative. Due to a range of its molecular properties - namely its anti-apoptotic effects - tauroursodeoxycholic acid has been examined in inflammatory metabolic diseases and neurodegenerative diseases. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid has been reported in Homo sapiens with data available. Drug Indication Tauroursodeoxycholic acid is used to prevent and treat gallstone formation. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid is used in combination with [phenylbutyric acid] to treat amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) in adults. Mechanism of Action About 90% of gallstones are formed by cholesterol, which may be caused by altered gut microbiota from a high-fat diet and other factors. The gut microbiota regulates bile acid metabolism; thus, altered composition in gut microbiota may significantly change the bile acid pool and alter cholesterol secretion. While the exact mechanism of action of tauroursodeoxycholic acid in reducing and preventing gallstone formation is unclear, tauroursodeoxycholic acid may achieve this effect in a number of ways. A recent mouse study suggests that tauroursodeoxycholic acid inhibits intestinal cholesterol absorption and lowers liver cholesterol levels by upregulating the bile acid excretion from the liver to the gallbladder. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid lowers the bile cholesterol saturation in the gallbladder, thereby increasing the solubility of cholesterol in bile. It can also maintain a specific gut microbiota composition to promote the synthesis of bile acids and reduce liver inflammation caused by the lipopolysaccharide in the blood. Ultimately, tauroursodeoxycholic acid enhances the synthesis of bile acids in the liver and reduces cholesterol in the serum and liver. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid inhibits cell apoptosis by disrupting the mitochondrial pathway of cell death. It works by inhibiting oxygen-radical production, ameliorating endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, and stabilizing the unfolded protein response. Other anti-apoptotic processes mediated by tauroursodeoxycholic acid include cytochrome c release, caspase activation, DNA and nuclear fragmentation, and inhibition of p53 transactivation. It is believed that tauroursodeoxycholic acid works on multiple cellular targets to inhibit apoptosis and upregulate survival pathways. TAURURSODIOL is a small molecule drug with a maximum clinical trial phase of IV (across all indications) that was first approved in 2022 and has 2 investigational indications. Aims: Hyperplasia of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) after blood vessel injury is one of the major pathophysiological mechanisms associated with neointima. Tauroursodeoxycholate (TUDCA) is a cytoprotective agent in a variety of cells including hepatocytes as well as an inducer of apoptosis in cancer cells. In this study, we investigated whether TUDCA could prevent neointimal hyperplasia by suppressing the growth and migration of VSMCs. Methods and results: Transporters of TUDCA uptake in human VSMCs (hVSMCs) were analysed by RT-PCR and western blot. A knock-down experiment using specific si-RNA revealed that TUDCA was incorporated into hVSMCs via organic anion transporter 2 (OATP2). TUDCA reduced the viability of hVSMCs, which were mediated by inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) by induction of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) via protein kinase Cα (PKCα). The anti-proliferative effect of TUDCA was reversed by treatment with 7-hydroxystaurosporine, an inhibitor of PKC, and by the knock-down of MKP-1. In addition, TUDCA suppressed hVSMC migration, which was mediated by reduced matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) expression by ERK inhibition, as well as reduced viability of hVSMCs. Rats with carotid artery balloon injury received oral administration of TUDCA; this reduced the increase in ERK and MMP-9 caused by balloon injury. TUDCA significantly decreased the ratio of intima to media by reducing proliferation and inducing apoptosis of the VSMCs. Conclusion: TUDCA inhibits neointimal hyperplasia by reducing proliferation and inducing apoptosis of smooth muscle cells by suppression of ERK via PKCα-mediated MKP-1 induction. [1] Objective/background: Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is characterised by the infiltration of smooth muscle cell (SMC) apoptosis, inflammatory cells, neovascularisation, and degradation of the extracellular matrix. Previous work has shown that endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and SMC apoptosis were increased both in a mouse model and human thoracic aortic aneurysm. However, whether the ER stress is activated in AAA formation and whether suppressing ER stress attenuates AAA is unknown. Methods: Human AAA and control aorta samples were collected. Expression of ER stress chaperones glucose-regulated protein (GRP)-78 and GRP-94 was detected by immunohistochemical staining. The effect of ER stress inhibitor tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) on AAA formation in angiotensin (Ang) II induced apolipoprotein E-/- mice was explored. Elastin staining was used to observe the rupture of elastic fragmentation. Immunohistochemistry and Western blot analysis were performed, to detect the protein expression of ER stress chaperones and apoptosis molecules. Results: There was significant upregulation of GRP-78 and GRP-94 in aneurysmal areas of human AAA and Ang II induced ApoE-/- mice (p < .05). TUDCA significantly attenuated the maximum diameters of abdominal aortas in Ang II induced ApoE-/- mice (p < .05). TUDCA significantly reduced expression of ER stress chaperones and the apoptotic cell numbers (p < .05). Furthermore, TUDCA significantly reduced expression of apoptosis molecules, such as caspase-3, caspase-12, C/EBP homologous protein, c-Jun N-terminal kinase activating transcription factor 4, X-box binding protein, and eukaryotic initiation factor 2α in Ang II induced ApoE-/- mice (p < .05). Conclusion: The results suggest that ER stress is involved in human and Ang II induced AAA formation in ApoE-/- mice. TUDCA attenuates Ang II induced AAA formation in ApoE-/- mice by inhibiting ER stress mediated apoptosis. [2] |
| 分子式 |
C26H44NNAO6S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
521.69
|
|
| 精确质量 |
521.278
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 59.86; H, 8.50; N, 2.68; Na, 4.41; O, 18.40; S, 6.15
|
|
| CAS号 |
35807-85-3
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Tauroursodeoxycholate;14605-22-2;Tauroursodeoxycholate-d4 sodium;2410279-95-5;Tauroursodeoxycholate dihydrate;117609-50-4
|
|
| PubChem CID |
46782978
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| LogP |
4.526
|
|
| tPSA |
135.14
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
35
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
864
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
10
|
|
| SMILES |
S(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N([H])C(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[C@@]([H])(C([H])([H])[H])[C@@]1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[C@@]2([H])[C@]3([H])[C@]([H])(C([H])([H])[C@]4([H])C([H])([H])[C@@]([H])(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[C@]4(C([H])([H])[H])[C@]3([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[C@@]21C([H])([H])[H])O[H])O[H])=O)(=O)(=O)[O-].[Na+]
|
|
| InChi Key |
IYPNVUSIMGAJFC-JUWYWQLMSA-M
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C26H45NO6S.Na/c1-16(4-7-23(30)27-12-13-34(31,32)33)19-5-6-20-24-21(9-11-26(19,20)3)25(2)10-8-18(28)14-17(25)15-22(24)29;/h16-22,24,28-29H,4-15H2,1-3H3,(H,27,30)(H,31,32,33);/q;+1/p-1/t16-,17+,18-,19-,20+,21+,22+,24+,25+,26-;/m1./s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
sodium;2-[[(4R)-4-[(3R,5S,7S,8R,9S,10S,13R,14S,17R)-3,7-dihydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pentanoyl]amino]ethanesulfonate
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.79 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.79 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.79 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 100 mg/mL (191.68 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9168 mL | 9.5842 mL | 19.1685 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3834 mL | 1.9168 mL | 3.8337 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1917 mL | 0.9584 mL | 1.9168 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT00771901 | Completed | Drug: tauroursodeoxycholic acid Other: placebo |
Insulin Resistance Diabetes |
Washington University School of Medicine |
February 2008 | Not Applicable |
|
|
|
|
|