| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Human angiotensin II ( Ki = 0.8 nM ); Human endothelin A ( Ki = 9.3 nM ); Rat angiotensin II ( Ki = 0.4 nM )
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Sparsentan 剂量依赖性地抑制血管紧张素 II 诱导的升压反应,ED50 值为 0.8 µmol/kg iv 和 3.6 µmol/kg po。 Sparsentan 还在大型 ET-1 诱导升压模型中表现出长效和有效的特性。在自发性高血压大鼠中,sparsentan 在最低测试剂量(10 µmol/kg/天)下可显着降低血压。 Sparsentan 在大鼠、狗和猴子中显示出良好的口服生物利用度,平均分别为 40%、86% 和 21% F。在药物的药代动力学持续时间内,Sparsentan 以 100 µmol/kg/天的剂量将血压从 170 mmHg 降低至 100 mmHg 以下。在其药代动力学持续时间内,100 µmol/kg/天的sparsentan 可有效地将自发性高血压大鼠转变为血压正常的大鼠[1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Sparsentan 剂量依赖性地拮抗血管紧张素 II 诱导的升压反应,ED50 值为 0.8 µmol/kg iv 和 3.6 µmol/kg po。 Sparsentan 在大 ET-1 诱导的升压模型中也显示出有效且长效的作用。 Sparsentan 在最低测试剂量(10 µmol/kg/天)下可显着降低自发性高血压大鼠的血压。 Sparsentan 在大鼠、狗和猴子中显示出良好的口服生物利用度,平均分别为 40%、86% 和 21% F。剂量为 100 µmol/kg/天时,Sparsentan 在药物药代动力学期间可将血压从 170 mmHg 降低至 100 mmHg 以下。 100 µmol/kg/天的 Sparsentan 在其药代动力学持续期间基本上将自发性高血压大鼠转变为正常血压大鼠[1]。
|
| 动物实验 |
Rats: The first intravenous bolus injection of angiotensin II was administered to the rats as a control pressor response, following their gavage with vehicle. Angiotensin II is given to the rats at different intervals for a maximum of 240 minutes after irbesartan (30 µmol/kg) and sparsentan (30 µmol/kg) are administered orally (po). Every medication dosage involves 6–8 rats. Angiotensin II pressor effect inhibition is expressed as a percentage (%) based on the difference between the maximum blood pressure increase observed before and after the drug [1].
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Following administration of single doses of 200-1600 mg, the Cmax and AUC of sparsentan increase in a less than dose-proportional manner. Sparsentan has time-dependent pharmacokinetics, possibly due to it inducing its own metabolism over time, and at the approved recommended dosage, it reaches steady-state plasma levels within 7 days. Following a single oral dose of 400 mg, the Cmax, AUC and median time to peak plasma concentration of sparsentan are 6.97 μg/mL, 83 μg×h/mL, and 3 hours, respectively. Following daily doses of 400 mg sparsentan, the steady-state Cmax is 6.47 μg/mL, and the AUC is 63.6 μg×h/mL. The administration of a single oral dose (800 mg) of sparsentan with a high-fat, high-calorie meal (1000 kcal, 50% fat) increased the AUC and Cmax by 22% and 108%, respectively. With a single 200 mg dose, a high-fat, high-calorie meal did not have a clinically significant effect on sparsentan pharmacokinetics. Sparsentan is mainly excreted through feces and urine. In healthy subjects given a single dose (400 mg) of radiolabeled sparsentan, approximately 80% of the dose was recovered in feces (9% unchanged) and 2% in urine (negligible amount unchanged). Within a 10-day collection period, 82% of the dosed radioactivity was recovered. At the approved recommended dosage, sparsentan has an apparent volume of distribution at steady state of 61.4 L. Sparsentan has a time-dependent clearance, possibly due to it inducing its own metabolism over time. Following the initial 400 mg dose, sparsentan has an apparent clearance of 3.88 L/h. At steady state, the apparent clearance increases to 5.11 L/h. Metabolism / Metabolites Sparsentan is mainly metabolized by cytochrome P450 3A. Biological Half-Life Sparsentan has an estimated half-life of 9.6 hours at steady state. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
Sparsentan is more than 99% bound to human plasma proteins. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
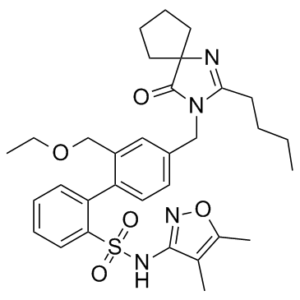
Sparsentan is a biphenyl that is 1,1'-biphenyl substituted by (4,5-dimethyl-1,2-oxazol-3-yl)aminosulfonyl, ethoxymethyl, and (2-butyl-4-oxo-1,3-diazaspiro[4.4]non-1-en-3-yl)methyl groups at positions 2, 2' and 4', respectively. It is a dual antagonist of endothelin and angiotensin II receptors approved for the reduction of proteinuria in adults with primary immunoglobulin A nephropathy at risk of rapid disease progression. It has a role as an angiotensin receptor antagonist, an antihypertensive agent, an endothelin A receptor antagonist and a nephroprotective agent. It is an azaspiro compound, a member of biphenyls, a sulfonamide, a member of isoxazoles and a benzyl ether.
Sparsentan is a dual antagonist of the endothelin type A receptor (ETAR) and the angiotensin II (Ang II) type 1 receptor (AT1R) with a similar affinity for both (9.3 nM for ETAR and 0.8 nM for AT1R). Sparsentan is first in its class and orally active, and was created by merging the structural elements of [irbesartan], an AT1R antagonist, and biphenylsulfonamide, an ETAR antagonist. In February 2023, the use of sparsentan to reduce proteinuria in adults with primary immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) at risk of rapid disease progression was approved by the FDA under accelerated approval based on reduction of proteinuria. Sparsentan was initially developed for the treatment of hypertension; however, it has shown to be efficient in the reduction of proteinuria in patients with IgAN and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). Compared to [irbesartan], sparsentan reduces proteinuria to a greater extent. Furthermore, it is the first non-immunosuppressive therapy for the reduction of proteinuria in IgAN. The use of sparsentan may cause hepatotoxicity and embryo-fetal toxicity. Sparsentan is an Endothelin Receptor Antagonist and Angiotensin 2 Receptor Blocker. The mechanism of action of sparsentan is as an Endothelin Receptor Antagonist and Angiotensin 2 Type 1 Receptor Antagonist and Cytochrome P450 2B6 Inducer and Cytochrome P450 2C9 Inducer and Cytochrome P450 2C19 Inducer and P-Glycoprotein Inhibitor and Breast Cancer Resistance Protein Inhibitor. Drug Indication Sparsentan is indicated to reduce proteinuria in adults with primary immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) at risk of rapid disease progression, generally a urine protein-to-creatinine ratio (UPCR) ≥1.5 g/g. Treatment of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis Treatment of primary IgA nephropathy Mechanism of Action Sparsentan is a molecule that acts as a dual antagonist of the endothelin type A receptor (ETAR) and the angiotensin II (Ang II) type 1 receptor (AT1R). It possesses two clinically validated mechanisms of action and selectively blocks the action of two potent vasoconstrictor and mitogenic agents, Ang II and endothelin 1 (ET-1), at their respective receptors. ET-1 and Ang II contribute to the pathogenesis of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN), a condition characterized by the increased production of galactose-deficient IgA1 (Gd-IgA1) antibodies. Gd-IgA1 antibodies lead to mesangial cell activation and proliferation, which stimulates and is stimulated by ET-1 and Ang II production. The pathological cycle of IgAN results in a compromised glomerular filtration barrier and subsequent proteinuria and haematuria. By acting as both an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) and an endothelin receptor antagonist (ERA), sparsentan reduces proteinuria in patients with IgAN. Sparsentan has a high affinity for both ETAR (Ki= 12.8 nM) and AT1R (Ki=0.36 nM), and greater than 500-fold selectivity for these receptors over the endothelin type B and angiotensin II subtype 2 receptors. Pharmacodynamics Sparsentan is a dual endothelin and angiotensin II receptor antagonist. At week 36, the exposure-response (E-R) relationship between sparsentan exposure and the percentage reduction from baseline in urine protein-to-creatinine ratio (UPCR) was not statistically significant over the observed sparsentan exposure range. E-R relationships were not statistically significant for any grade of hypotension or the worst grade of peripheral edema. In healthy subjects, sparsentan caused QTcF prolongation with a maximal mean effect of 8.8 msec at 800 mg and 8.1 msec at 1600 mg. The mechanism behind the observed QTc prolongation is unknown but is unlikely to be mediated via direct inhibition of hERG channels. At the recommended dose, no clinically relevant QTc prolongation is expected. The use of sparsentan may cause hepatotoxicity, embryo-fetal toxicity, hypotension, acute kidney injury, hyperkalemia, and fluid retention. |
| 分子式 |
C32H40N4O5S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
592.7488
|
| 精确质量 |
592.272
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 64.84; H, 6.80; N, 9.45; O, 13.50; S, 5.41
|
| CAS号 |
254740-64-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Sparsentan-d5; 1801597-09-0
|
| PubChem CID |
10257882
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| LogP |
7.066
|
| tPSA |
122.48
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
12
|
| 重原子数目 |
42
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1060
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O=S(C1=CC=CC=C1C2=CC=C(CN3C(CCCC)=NC4(CCCC4)C3=O)C=C2COCC)(NC5=NOC(C)=C5C)=O
|
| InChi Key |
WRFHGDPIDHPWIQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C32H40N4O5S/c1-5-7-14-29-33-32(17-10-11-18-32)31(37)36(29)20-24-15-16-26(25(19-24)21-40-6-2)27-12-8-9-13-28(27)42(38,39)35-30-22(3)23(4)41-34-30/h8-9,12-13,15-16,19H,5-7,10-11,14,17-18,20-21H2,1-4H3,(H,34,35)
|
| 化学名 |
2-[4-[(2-butyl-4-oxo-1,3-diazaspiro[4.4]non-1-en-3-yl)methyl]-2-(ethoxymethyl)phenyl]-N-(4,5-dimethyl-1,2-oxazol-3-yl)benzenesulfonamide
|
| 别名 |
RE-021; BMS 346567; RE021; Filspari; PS-433540; BMS346567; RE 021; PS 433540; DARA-a; BMS-346567
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~100 mg/mL (~168.7 mM)
Ethanol: ~40 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.51 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 2.08 mg/mL (3.51 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.51 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.6871 mL | 8.4353 mL | 16.8705 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3374 mL | 1.6871 mL | 3.3741 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1687 mL | 0.8435 mL | 1.6871 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT04663204 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Sparsentan | Kidney Diseases Glomerulonephritis |
University of Leicester | December 10, 2020 | Phase 2 |
| NCT03493685 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: sparsentan Drug: Irbesartan |
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis |
Travere Therapeutics, Inc. | April 17, 2018 | Phase 3 |
| NCT01613118 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Irbesartan Drug: RE-021 (Sparsentan) |
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis |
Travere Therapeutics, Inc. | March 2014 | Phase 2 |
| NCT03762850 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: sparsentan Drug: irbesartan Drug: Dapagliflozin |
Immunoglobulin A Nephropathy |
Travere Therapeutics, Inc. | December 11, 2018 | Phase 3 |
| NCT05003986 | Recruiting | Drug: Sparsentan | IgA Vasculitis Alport Syndrome |
Travere Therapeutics, Inc. | August 12, 2021 | Phase 2 |