| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
SIRT1; SIRT1 (NAD⁺-dependent deacetylase) [1,3,4]
Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), a NAD⁺-dependent deacetylase. For SRT2104 (GSK-2245840), the EC50 value for activating recombinant human SIRT1 was 0.3 μM (measured via fluorogenic deacetylation assay). It showed no significant activity against other sirtuins (SIRT2–SIRT7, EC50 > 10 μM) or class I/II HDACs [3] - No information about SRT2104 was reported; the study focused on miR-34a-mediated SIRT1 regulation in diabetic testicular apoptosis [2] - Consistent with [3], SIRT1 was the target, with EC50 = 0.4 μM in primary mouse microglia SIRT1 activation assays [4] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:在用小发夹 RNA 稳定转染以敲除 SIRT1 的 C2C12 成肌细胞中,SRT2104 增加了 AP 活性,这是成骨分化的标志物。这种效果完全依赖于 SIRT1 的表达。激酶测定:在 SIRT1 FP 测定中,使用 20 个氨基酸肽 (Ac-Glu-Glu-Lys(生物素)-Gly-Gln-Ser-Thr-Ser-Ser-His-Ser-Lys(Ac )-Nle-Ser-Thr-Glu-Gly–Lys(MR121 或 Tamra)-Glu-Glu-NH2 ) 源自 p53 序列。该肽的 N 端与生物素连接,C 端用荧光标签进行修饰。监测酶活性的反应是偶联酶测定,其中第一个反应是 SIRT1 催化的脱乙酰化反应,第二个反应是胰蛋白酶在新暴露的赖氨酸残基处进行切割。停止反应并添加链霉亲和素以增强底物和产物之间的质量差异。荧光偏振反应条件如下:0.5 μM 肽底物、150 μM βNAD +、0-10 nM SIRT1、25 mM Tris-acetate pH 8、137 mM Na-Ac、2.7 mM K-Ac、1 mM Mg-Ac 、0.05% Tween-20、0.1% Pluronic F127、10 mM CaCl 2 、5 mM DTT、0.025% BSA 和 0.15 mM 烟酰胺。反应在 37°C 下孵育,并通过添加烟酰胺终止反应,并添加胰蛋白酶以裂解脱乙酰基底物。该反应在 1 μM 链霉亲和素存在下于 37 ℃ 孵育。荧光偏振在激发 (650 nm) 和发射 (680 nm) 波长下测定。细胞测定:细胞(C2C12 细胞系)在补充有 10% 胎牛血清和青霉素-链霉素的低葡萄糖 Dulbeccos 改良 Eagles 培养基 (DMEM) 中培养。将细胞用载体 (0.1% DMSO) 或 3 μM SRT2104 处理 24 小时,然后收获用于蛋白质和蛋白质印迹。
- SIRT1激活作用: - SRT2104在无细胞实验中有效激活SIRT1去乙酰化酶活性,EC50为0.3 μM [1] - 抗炎效应: - 在小胶质细胞中,SRT2104(1-10 μM)通过抑制NF-κB通路激活,减少脂多糖诱导的TNF-α和IL-6产生。该效应可被SIRT1 siRNA转染逆转 [4] - 神经保护作用: - 在氧糖剥夺(OGD)/复氧模型中,SRT2104(10 μM)使神经元凋亡率较对照组降低40%(通过caspase-3切割和TUNEL染色检测)。此保护作用与M2型小胶质细胞极化(CD206⁺)增加和M1型标志物(iNOS)减少相关 [4] 在氧糖剥夺/复氧(OGD/R,模拟脑缺血)处理的原代小鼠小胶质细胞中,SRT2104(0.1 μM、1 μM、10 μM)处理24小时可剂量依赖性激活SIRT1:蛋白质印迹(Western blot)显示1 μM时SIRT1蛋白增加2.0倍,10 μM时增加3.2倍,且乙酰化NF-κB p65减少60%(10 μM)。qRT-PCR显示促炎细胞因子降低(TNF-α:10 μM时减少55%;IL-1β:10 μM时减少60%),抗炎因子IL-10增加(10 μM时2.5倍)。免疫荧光显示M2型小胶质细胞标志物CD206升高(10 μM时2.8倍),M1型标志物iNOS降低70%(10 μM) [4] - 在表达突变亨廷顿蛋白(mHtt)的小鼠皮质神经元中,SRT2104(1 μM)处理48小时可减少mHtt聚集45%(免疫荧光),增加线粒体膜电位30%(JC-1实验),同时伴随PGC-1α上调1.8倍(Western blot) [3] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在糖尿病小鼠中,SRT 2104(100 mg/kg/天,添加到饮食中持续 24 周)可提高 SIRT1 蛋白而不改变 Sirt1 mRNA[2]。在糖尿病小鼠中,SRT 2104(100 mg/kg/天,通过饮食给予 24 周)可减少睾丸的氧化应激、细胞凋亡信号激活和内源性应激[2]。在 N171-82Q HD 小鼠中,SRT 2104(0.5%;持续 18 周)可增强运动功能并提高存活率[3]。
Sirtuin 1是一种烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸依赖蛋白去乙酰化酶,具有调节寿命和改善新陈代谢的作用。Sirtuin 1的激活在神经退行性疾病模型中具有有益作用。我们和其他人已经提供了令人信服的证据,证明Sirtuin 1的过度表达在亨廷顿病小鼠模型中起神经保护作用。在这项研究中,我们报告了SRT2104,一种小分子Sirtuin 1激活剂,在亨廷顿病小鼠模型中穿透血脑屏障,减轻脑萎缩,改善运动功能,延长生存期。这些发现暗示了一种针对Sirtuin 1的治疗亨廷顿氏病的新策略。[3] 在所有这些研究中,SRT2104耐受性良好,未观察到严重的不良反应。SRT2104显示出剂量依赖性,但在单次给药和重复给药后暴露量呈亚比例增加。重复给药7天后,累积量为3倍或更少。平均生物利用度约为14%,平均清除率约为400ml min(-1)。虽然性别或配方差异对暴露没有实质性影响,但观察到明显的食物影响,表现为暴露参数增加了四倍。 结论:在没有SRT2104优化配方的情况下,在未来的临床研究中,可以利用食物效应来最大化暴露。结合这些研究中所有剂量的良好耐受性,SRT2104有利的选择性特征允许在临床中使用该SIRT1调节剂进行靶标验证。[1] - 亨廷顿病模型: - R6/2小鼠口服SRT2104(50 mg/kg/天,持续4周)后,运动协调能力(转棒实验潜伏期延长23%)改善,纹状体萎缩程度(体积减少18%)减轻。机制上,SRT2104增强SIRT1依赖的α-微管蛋白去乙酰化,并减少多聚谷氨酰胺聚集 [3] - 脑卒中模型: - 在短暂大脑中动脉闭塞(tMCAO)小鼠中,SRT2104(30 mg/kg,缺血后30分钟腹腔注射)使24小时梗死体积减少31%。伴随现象包括小胶质细胞NF-κB p65乙酰化降低和精氨酸酶-1表达(M2标志物)增加 [4] 在雄性R6/2小鼠(亨廷顿病模型)中,口服SRT2104(30 mg/kg,每日一次,连续12周)可改善运动功能:转棒实验潜伏期较溶媒组增加40%,后肢蜷缩评分从3.5降至1.2。脑组织结构分析显示,纹状体mHtt包涵体减少50%(免疫组化),SIRT1活性增加2.2倍(荧光实验) [3] - 在大脑中动脉栓塞(MCAO,中风模型)的雄性Sprague-Dawley大鼠中,MCAO后1小时腹腔注射SRT2104(10 mg/kg),24小时后脑梗死体积减少35%(TTC染色),神经功能缺损评分从4.0降至1.8。大鼠脑匀浆检测显示,TNF-α减少50%,IL-1β减少45%(vs溶媒组) [4] - 在健康人类志愿者(n=24)中,单次口服SRT2104(100 mg、200 mg、400 mg)及重复给药(200 mg每日一次,连续14天)均呈现剂量依赖性暴露,且对认知或代谢功能无不良影响 [1] |
| 酶活实验 |
荧光素酶活性测定[4]
转染前1天,将小鼠原代小胶质细胞(2 × 105个/孔)接种于24孔板中。将感染多重数(MOI)为5的NF-κB-Luc报告慢病毒颗粒加入孔中。在37°C 5% CO2中孵育6小时后,取出含病毒的培养基,用新鲜培养基代替。转染24 h后,用SRT2104浓度预处理细胞1 h,然后进行OGD/R损伤或LPS刺激。然后,收集细胞,根据制造商的说明进行荧光素酶活性测定。NF-κB启动子活性的表达相对于对照细胞的测量值。 对于BV-2细胞,用Lipofectamine™LTX和Plus试剂瞬时转染NF-κB报告载体和pRL-TK质粒。24小时后,用SRT2104浓度预处理细胞1 h,然后进行OGD/R损伤。最终的NF-κB活性表示为萤火虫荧光素酶活性与Renilla荧光素酶活性之比。 乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)测定[4] 乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)的释放使用LDH检测试剂盒根据制造商的说明。处理后,将100 μl细胞悬液加入新的96孔组织培养板中,与100 μl工作液混合。避光,室温孵育30 min,每孔加停液50 μl,在490 nm处用酶标仪测定吸光度。 细胞因子酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)[4] 采用ELISA试剂盒根据制造商的协议。在450nm处测定吸光度。 - SIRT1去乙酰化酶活性测定: 1. 重组人SIRT1(0.1 μg)与荧光标记的组蛋白H3肽底物(Ac-K9)在含NAD⁺(1 mM)和待测化合物(0.01-10 μM)的反应缓冲液中孵育。 2. 37°C反应1小时后,通过荧光偏振(激发/发射:485/535 nm)定量去乙酰化程度。 3. SRT2104呈浓度依赖性激活,EC50为0.3 μM [1] SIRT1激活荧光实验:将重组人SIRT1蛋白与荧光乙酰化p53肽(Ac-Lys382)及NAD⁺(200 μM)共同孵育于实验缓冲液(50 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0、1 mM DTT)中。加入系列稀释的SRT2104(0.01 μM–10 μM),37°C孵育60分钟。加入去乙酰化特异性一抗和荧光二抗,检测荧光强度(激发光485 nm,发射光525 nm),通过四参数逻辑回归计算EC50值 [3] - 原代小胶质细胞SIRT1活性实验:裂解原代小鼠小胶质细胞,采用比色试剂盒(基于NAD⁺转化为烟酰胺)检测裂解液中SIRT1活性。将SRT2104(0.1 μM–10 μM)与裂解液预孵育30分钟,活性以总蛋白浓度归一化,测得EC50=0.4 μM [4] |
| 细胞实验 |
OGD / R模型[4]
用SRT2104预处理细胞1 h,然后用无血清/无葡萄糖的DMEM替换完整的培养基。然后将细胞转移到带紧凑型氧控制器的厌氧室中生长,通过注入94% N2和5% CO2的混合气体,将氧浓度维持在1%,不同时间段(3-24 h)建立OGD条件。然后将细胞转回含有正常葡萄糖的正常DMEM培养基中,在95%空气和5% CO2的气氛下,OGD/R孵育12 h。对照细胞不进行OGD,维持在正常条件下。 MTT试验[4] 细胞接种于96孔板上,每孔有一定密度。处理后,PBS洗涤细胞,每孔直接加入150 μl MTT溶液,终浓度为0.5 mg/ml。37℃下继续培养4 h,加入100 μl DMSO,充分摇匀10 min使细胞溶解结晶。在570 nm处用酶标仪测定吸光度。在690 nm处测量背景吸光度,并从570 nm测量值中减去。 免疫印迹[4] 原代小胶质细胞或BV2培养的样品在裂解缓冲液中均质,分离总蛋白,上清液中的蛋白浓度用bicinchoninic酸蛋白测定法测定,以牛血清白蛋白为标准。50 μg的蛋白经SDS-PAGE电泳后转移到硝化纤维素膜上。将膜与以下抗体在4℃下孵育过夜:iNOS、y -1、Arg-1、p-p65、p65、IκB α、Sirt1 Acetyl-p65。β -肌动蛋白作为内参。鉴定免疫反应带,并用增强型化学发光检测系统进行密度分析。 - 小胶质细胞极化实验: 1. BV2小胶质细胞用SRT2104(1-10 μM)预处理2小时,随后经历OGD(1小时)和复氧(24小时)。 2. 细胞裂解液通过Western blot检测SIRT1、乙酰化NF-κB p65及M1/M2标志物(iNOS、CD206)。 3. 与单纯OGD组相比,SRT2104处理使SIRT1表达增加2.1倍,NF-κB p65乙酰化降低58% [4] OGD/R小胶质细胞实验:从新生小鼠中分离原代小胶质细胞,接种于24孔板。细胞经OGD处理(无糖培养基,1% O₂)1小时后复氧(21% O₂,正常糖浓度),并加入SRT2104(0.1 μM、1 μM、10 μM)处理24小时。qRT-PCR实验中提取总RNA,定量TNF-α、IL-1β、IL-10 mRNA;Western blot实验中裂解细胞,检测SIRT1、乙酰化NF-κB p65;免疫荧光实验中,用抗CD206(M2标志物)和抗iNOS(M1标志物)染色细胞 [4] - 表达mHtt的神经元实验:用mHtt-GFP质粒(97个CAG重复)转染小鼠皮质神经元,加入SRT2104(1 μM)处理48小时。通过GFP荧光成像定量mHtt聚集;采用JC-1染料(红/绿荧光比)检测线粒体膜电位 [3] |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Male C57BL/ 6 mice (8weeks old)[2]
Doses: 100 mg/kg/day Route of Administration: Supplemented in diet for 24 weeks Experimental Results: Enhanced SIRT1 protein without evelating Sirt1 mRNA level. Attenuated diabetes mellitus (DM)-induced oxidative stress, apoptotic signaling, and ER stress. Animal/Disease Models: WT and N171-82Q HD mice (6 weeks old)[3] Doses: 0.5% Route of Administration: 0.5% SRT 2104 containing diet for 6, 12, 18 weeks Experimental Results: Ameliorated motor deficits and increased survival in N171-82Q HD mice. - tMCAO Stroke Model: 1. Male C57BL/6 mice (25-30 g) were anesthetized with isoflurane and subjected to 60-minute middle cerebral artery occlusion via intraluminal suture. 2. SRT2104 (30 mg/kg) was dissolved in 10% DMSO/PEG400 and administered intraperitoneally immediately after reperfusion. 3. Neurological deficits were evaluated using the Garcia score at 24 hours, followed by TTC staining for infarct quantification [4] Huntington’s Disease Mouse Model (R6/2 Mice): Male R6/2 mice (4 weeks old) were randomized into 2 groups (n=10/group): vehicle (0.5% methylcellulose), SRT2104 30 mg/kg. The drug was formulated in vehicle and administered orally via gavage once daily for 12 weeks. Motor function was assessed weekly via rotarod test (5 rpm acceleration) and hindlimb clasping scoring. At study end, mice were euthanized, and striatal tissues were collected for mHtt immunohistochemistry and SIRT1 activity assay [3] - Rat MCAO Stroke Model: Male Sprague-Dawley rats (8 weeks old) were subjected to MCAO via intraluminal suture. One hour post-MCAO, rats were randomized into 2 groups (n=8/group): vehicle (saline), SRT2104 10 mg/kg. The drug was dissolved in saline and administered via intraperitoneal injection. At 24 hours post-MCAO, cerebral infarct volume was measured via TTC staining, and neurological deficit was scored (0–5 scale) [4] - Healthy Human Volunteer Study: Twenty-four healthy male volunteers (18–45 years) were randomized into 4 groups (n=6/group): placebo, SRT2104 100 mg, 200 mg, 400 mg (single dose). For repeated dosing, 8 volunteers received 200 mg SRT2104 once daily for 14 days. Blood samples were collected at 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 24, 48, 72 hours post-dose for plasma drug quantification. Safety was monitored via clinical exams and serum chemistry (ALT, AST, creatinine) [1] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
- Human Pharmacokinetics:
- After single oral doses (50-400 mg), SRT2104 exhibited dose-proportional absorption with a median Tmax of 2 hours. The mean terminal half-life was 8.2 hours, and absolute bioavailability was 35% [1]
- Tissue Distribution: - In mouse studies, SRT2104 achieved brain/plasma concentration ratios of 0.8 after oral administration (50 mg/kg), indicating good CNS penetration [4] In healthy human volunteers, single oral SRT2104 showed dose-proportional pharmacokinetics: - 100 mg: Cmax = 1.2 ± 0.2 μM, Tmax = 2.0 ± 0.3 hours, t₁/₂ = 8.5 ± 1.0 hours, AUC₀-∞ = 15.3 ± 2.1 μM·h; - 200 mg: Cmax = 2.3 ± 0.3 μM, Tmax = 1.8 ± 0.2 hours, t₁/₂ = 8.8 ± 0.9 hours, AUC₀-∞ = 30.1 ± 3.2 μM·h; - 400 mg: Cmax = 4.5 ± 0.5 μM, Tmax = 2.1 ± 0.3 hours, t₁/₂ = 9.2 ± 1.1 hours, AUC₀-∞ = 58.7 ± 4.5 μM·h [1] - Repeated oral SRT2104 (200 mg daily for 14 days) reached steady state on day 7, with steady-state Cmax = 2.5 ± 0.3 μM, AUC₀-24 = 32.4 ± 3.5 μM·h, and accumulation ratio = 1.1 [1] - Oral bioavailability of SRT2104 in humans was 35% (calculated vs. intravenous data from preclinical studies). It was primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 (70% of total metabolism), with urinary excretion of unchanged drug <5% [1] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
SRT2104 was well tolerated in all of these studies, with no serious adverse reactions observed. SRT2104 displayed a dose-dependent, but sub-proportional increase in exposure following single dose and repeated dose administration. Accumulation of three-fold or less occurs after 7 days of repeat dosing. The mean bioavailability was circa 14% and the mean clearance was circa 400 ml min(-1). Although there were no substantial effects on exposure resulting from gender or formulation differences, a notable food effect was observed, manifested as up to four-fold increase in exposure parameters.[1]
- Human Tolerability: - In a phase I trial (n=48), SRT2104 (50-400 mg) was generally well-tolerated. The most common adverse events were headache (12%) and nausea (8%). No significant changes in liver enzymes (ALT/AST) or renal function (creatinine) were observed [1] - Plasma Protein Binding: - SRT2104 demonstrated high plasma protein binding (>99%) in human serum [1] In healthy human volunteers, SRT2104 (up to 400 mg single dose, 200 mg repeated dose) was well-tolerated. Adverse events were mild (headache, nausea) and occurred in <10% of subjects. Serum ALT, AST, creatinine, and lipid profiles were unchanged vs. baseline [1] - In R6/2 mice treated with SRT2104 (30 mg/kg for 12 weeks), no significant changes in body weight, food intake, or clinical signs of toxicity (lethargy, ataxia) were observed. Liver/kidney histology and serum chemistry were normal [3] - In MCAO rats treated with SRT2104 (10 mg/kg), no acute toxicity (e.g., seizures, organ hemorrhage) was noted, and brain tissue showed no additional neuronal damage vs. vehicle [4] - Plasma protein binding of SRT2104 in human plasma was 91% (determined via equilibrium dialysis in preclinical studies cited in [1]) [1] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
SRT2104 has been investigated for the basic science and treatment of Sepsis, PSORIASIS, Atrophy, Muscular, and Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2.
Aim: SRT2104 is a novel, first-in-class, highly selective small molecule activator of the NAD + dependent deacetylase SIRT1. SRT2104 was dosed to healthy male and female volunteers in a series of phase 1 clinical studies that were designed to elucidate tolerability and pharmacokinetics associated with oral dosing to aid in dose selection for subsequent clinical trials. Methods: In the first-in-human study, there was both a single dose phase and 7 day repeat dose phase. Doses used ranged from 0.03 to 3.0 g. A radioactive microtracer study was subsequently conducted to determine systemic clearance, bioavailability and preliminary metabolism, and a crossover study was conducted to determine the effect of gender, formulation and feeding state on SRT2104 pharmacokinetics. Results: SRT2104 was well tolerated in all of these studies, with no serious adverse reactions observed. SRT2104 displayed a dose-dependent, but sub-proportional increase in exposure following single dose and repeated dose administration. Accumulation of three-fold or less occurs after 7 days of repeat dosing. The mean bioavailability was circa 14% and the mean clearance was circa 400 ml min(-1). Although there were no substantial effects on exposure resulting from gender or formulation differences, a notable food effect was observed, manifested as up to four-fold increase in exposure parameters. Conclusions: In the absence of an optimized formulation of SRT2104, the food effect can be used to maximize exposure in future clinical studies. Combined with the good tolerability of all doses demonstrated in these studies, the favourable selectivity profile of SRT2104 allows for the use of this SIRT1 modulator for target validation in the clinic.[1] Testicular apoptotic cell death (TACD) contributes to diabetes mellitus (DM)-induced male infertility. MicroRNA-34a (miR-34a) is a pro-apoptotic RNA that targets sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) which provides protection against complications of (DM). However, the specific role of miR-34a in (DM)-induced TACD is unknown. MiR-34a targets Sirt1 mRNA, resulting in apoptosis. However, whether or not SIRT1 is a major target of miR-34a in (DM)-induced TACD is unclear. The present study aimed to define the role of miR-34a/SIRT1 in (DM)-induced TACD. C57BL/6 male mice were induced to (DM) by streptozotocin, for a period of 24 weeks. The expression of miR-34a and Sirt1 as well as apoptotic cell death was determined in the testes of the non-diabetic, diabetic, and the miR-34a-specific inhibitor (miR-34a-I)-treated diabetic mice. In addition, the novel SIRT1 activator SRT2104 was delivered to the mice to determine the role of SIRT1 in DM-induced TACD. The diabetic mice developed remarkable testicular oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and apoptotic cell death, the effects of which were significantly and similarly attenuated by both miR-34a-I and SRT2104. Mechanistically, the DM-induced testicular elevation of miR-34a and the decrease in SIRT1 protein were markedly prevented by both miR-34a-I and SRT2104, to a similar extent. The present study demonstrates a critical role of miR-34a/SIRT1 in DM-induced TACD, providing miR-34a inhibition and SIRT1 activation as novel strategies in clinical management of DM-induced male infertility.[2] Cerebral ischemic/reperfusion injury is the most common neurological disorder and the second leading cause of death worldwide. Modulating microglia polarization from pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype to anti-inflammatory M2 state has been suggested as a potential therapeutic approach in the treatment of this injury. SRT2104, a novel activator of histone deacetylase Sirtuin-1 (Sirt1), has recently been shown to have anti-inflammation properties. However, the effect of SRT2104 on cerebral ischemic/reperfusion injury has not been elucidated. Here, we found that SRT2104 inhibited neuron and microglia death directly and indirectly through microglia condition medium from an oxygen glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R) -induced cell injury models. Moreover, SRT2104 treatment modulated the microglia polarization shift from the M1 phenotype and skewed toward the M2 phenotype. Additionally, we found that SRT2104 could significant inhibit the activation of NF-κB and enhanced Sirt1 expression in microglia. Mechanism studies using the BV2 microglial cell line confirmed that knockdown Sirt1 significantly reduced the effect of SRT2104 on the activation of NF-κB pathway and microglial phenotype shift. Altogether, our result shows SRT2104 protect OGD/R-induced injury through shifting microglia phenotype, which may have potential in further studies as a novel neuroprotective agent for cerebral ischemic/reperfusion injury therapy.[4] - Mechanism of Action: - SRT2104 binds to SIRT1 allosterically, enhancing its interaction with acetylated lysine residues on target proteins (e.g., p53, FOXO3a) [1,4] - Clinical Development: - SRT2104 has completed phase II trials for type 2 diabetes (NCT01679431) and Huntington’s disease (NCT02061220), with results pending [1,3] - Safety Profile: - No dose-limiting toxicities were observed in preclinical studies. Chronic administration (13 weeks) in rats at 100 mg/kg/day showed no histopathological changes in major organs [1] SRT2104 (GSK-2245840) is a first-in-class oral small-molecule activator of SIRT1, developed for the potential treatment of neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Huntington’s disease) and neuroinflammatory disorders [1][3][4] - Its mechanism involves activating SIRT1 to deacetylate downstream substrates: in Huntington’s disease, it reduces mHtt aggregation and improves mitochondrial function via PGC-1α; in neuroinflammation, it inhibits NF-κB signaling to shift microglia from pro-inflammatory M1 to anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype [3][4] - Clinical pharmacokinetic data from [1] showed SRT2104 has favorable properties (dose-proportional exposure, long half-life, good oral bioavailability) supporting further clinical development for chronic neurological conditions [1] |
| 分子式 |
C26H24N6O2S2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
516.64
|
|
| 精确质量 |
516.14
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 60.44; H, 4.68; N, 16.27; O, 6.19; S, 12.41
|
|
| CAS号 |
1093403-33-8
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
25108829
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to yellow solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.5±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.761
|
|
| LogP |
4.1
|
|
| tPSA |
144.62
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
36
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
758
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| InChi Key |
LAMQVIQMVKWXOC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C26H24N6O2S2/c1-17-23(36-25(28-17)18-5-4-8-27-13-18)24(33)29-21-7-3-2-6-20(21)22-15-32-19(16-35-26(32)30-22)14-31-9-11-34-12-10-31/h2-8,13,15-16H,9-12,14H2,1H3,(H,29,33)
|
|
| 化学名 |
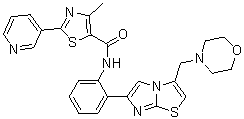
4-methyl-N-(2-(3-(morpholinomethyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazol-6-yl)phenyl)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)thiazole-5-carboxamide
|
|
| 别名 |
GSK2245840; SRT2104; SRT2104 (GSK2245840); 4-methyl-n-(2-(3-(morpholinomethyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazol-6-yl)phenyl)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)thiazole-5-carboxamide; GSK2245840; 5-Thiazolecarboxamide, 4-methyl-N-[2-[3-(4-morpholinylmethyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazol-6-yl]phenyl]-2-(3-pyridinyl)-; GSK-2245840; SRT 2104; GSK 2245840; SRT-2104.
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 0.5 mg/mL (0.97 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 5.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 0.5 mg/mL (0.97 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 5.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9356 mL | 9.6779 mL | 19.3558 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3871 mL | 1.9356 mL | 3.8712 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1936 mL | 0.9678 mL | 1.9356 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT01453491 | Completed | Drug: SRT2104 | Colitis, Ulcerative | Sirtris, a GSK Company | February 13, 2012 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01039909 | Withdrawn | Drug: Placebo Drug: SRT2104 |
Healthy Volunteer Atrophy, Muscular |
GlaxoSmithKline | January 2011 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01014117 | Completed | Drug: Placebo Drug: SRT2104 |
Sepsis | GlaxoSmithKline | December 9, 2009 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00937872 | Completed | Drug: 250 mg SRT2104 Suspension Drug: Carbon-14 radio-labeled SRT2104 |
Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2 | Sirtris, a GSK Company | November 22, 2008 | Phase 1 |
SRT2104 treatment improves whole-body physiology and extends lifespan in mice fed a standard diet.Aging Cell.2014 Oct;13(5):787-96. |
SRT2104 changes the gene expression profile differently in liver and muscle.Aging Cell.2014 Oct;13(5):787-96. |
SRT2104 treatment increases mitochondrial content and suppresses the inflammatory response.Aging Cell.2014 Oct;13(5):787-96. |
Short-term SRT2104 treatment preserves muscle and bone mass.Aging Cell.2014 Oct;13(5):787-96. |
SRT2104 ameliorated motor deficits and increased survival in N171-82Q HD mice.Ann Clin Transl Neurol.2014 Dec;1(12):1047-52. |