| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Stiripentol (STP) is an anticonvulsant drug that can block CYP3A4's (noncompetitively) and CYP2C19's (competitively) N-demethylation of CLB to N-desmethylclobazam (NCLB). The best models to explain the inhibition of CLB demethylation by Stiripentol (STP) are the competitive inhibition model with Ki=0.52 μM for the cDNA-expressing CYP2C19 and the noncompetitive inhibition model with apparent Ki=1.6 μM for the cDNA-expressing CYP3A4. Stiripentol (STP) has a Ki=0.14 μM and competitively inhibits the formation of OH-NCLB from NCLB by cDNA-expressing CYP2C19[1].
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Stiripentol (STP) 是一种抗惊厥药物,可以阻断 CYP3A4(非竞争性)和 CYP2C19(竞争性)CLB 的 N-去甲基化为 N-去甲基氯巴扎姆 (NCLB)。解释Stiripentol (STP)抑制CLB去甲基化的最佳模型是表达cDNA的CYP2C19的竞争性抑制模型(Ki=0.52 μM)和表达cDNA的CYP3A4的表观Ki=1.6 μM的非竞争性抑制模型。 Stiripentol (STP) 的 Ki=0.14 μM,通过表达 CYP2C19 的 cDNA 竞争性抑制 NCLB 形成 OH-NCLB [1]。
Stiripentol 竞争性抑制由cDNA表达的CYP2C19介导的N-去甲基氯巴占(NCLB)羟基化为4′-羟基-N-去甲基氯巴占(OH-NCLB)的过程,Ki为0.139 ± 0.025 μM,IC50为0.276 μM。 Stiripentol 非竞争性抑制由cDNA表达的CYP3A4介导的氯巴占(CLB)N-去甲基化为NCLB的过程,Ki为1.59 ± 0.07 μM,IC50为1.58 μM。 Stiripentol 竞争性抑制由cDNA表达的CYP2C19介导的CLB N-去甲基化为NCLB的过程,Ki为0.516 ± 0.065 μM,IC50为3.29 μM。 Stiripentol 对CYP3A4介导的CLB去甲基化的抑制作用远弱于酮康唑(IC50 = 0.023 μM),而其对CYP2C19介导的NCLB羟基化的抑制作用则远强于奥美拉唑(IC50 = 2.99 μM)。 [1] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
接受司替戊醇(STP)单药治疗的小鼠中,BT1(39.67±1.09°C)和BT2(41.32±1.05°C)之间的温度差异达到统计学显着性(t=3.097,p<0.05)。司替戊醇 (STP) 单药治疗与 CLB 单药治疗之间,BT2 存在统计学显着性差异 (t=2.615,p<0.05)。接受司替戊醇(STP)+CLB联合治疗的小鼠BT1(40.18±0.58℃)和BT2(43.03±0.49℃)之间的差异达到统计学意义(t=10.44,p<0.01)[2]。
在一项针对婴儿严重肌阵挛性癫痫(SMEI)患儿的随机、安慰剂对照试验中,将stiripentol(平均日剂量49 ± 2 mg/kg/天)与氯巴占(0.5 mg/kg/天)和丙戊酸盐联用,与基线相比导致血浆浓度发生显著变化。 CLB和NCLB的平均标准化最低血浆浓度分别从0.39显著增加至0.84 (mg/l)/(mg/kg)和从3.6显著增加至11.6 (mg/l)/(mg/kg)。 OH-NCLB的平均标准化最低血浆浓度从0.258显著下降至0.063 (mg/l)/(mg/kg)。 NCLB/CLB血浆浓度比增加了269%,而OH-NCLB/NCLB比下降了86%。在患者血浆中未检测到OH-CLB。 [1] |
| 酶活实验 |
孵育混合物包含100 mM磷酸盐缓冲液(pH 7.4)、0.5 mg/ml MgCl2、1 mM NADP+、0.5 mg/ml葡萄糖-6-磷酸、0.5 U/ml葡萄糖-6-磷酸脱氢酶、抑制剂(stiripentol、酮康唑或奥美拉唑)和底物(CLB或NCLB),终体积为0.5 ml。CLB和NCLB浓度选择在治疗性血浆浓度范围内(分别为2 μM和14 μM)。通过加入cDNA表达的人CYP3A4或CYP2C19(终P450浓度50 nM)启动反应。孵育在37°C下进行10分钟(CYP3A4)或30分钟(CYP2C19),并通过加入冰乙腈终止。
为测定抑制常数(Ki),将不同浓度的CLB(2–100 μM)与递增浓度的stiripentol(0–5 μM)一起孵育,用于CYP3A4和CYP2C19介导的去甲基化研究。对于CYP2C19介导的NCLB羟基化,将不同浓度的NCLB(1.5–14 μM)与递增浓度的stiripentol(0–2 μM)一起孵育。所有孵育均重复进行。 为测定IC50,将底物(2 μM CLB或14 μM NCLB)与递增浓度的stiripentol(0.001–10 μM)共孵育。为进行比较,也使用类似浓度范围测定了酮康唑和奥美拉唑的IC50值。 [1] |
| 动物实验 |
150, 300 mg/kg; i.p. Mice
Heterozygous Scn1aRX/+ mice (a model of Dravet syndrome) and age-matched wild-type mice were used. Mice were anesthetized with isoflurane, and EEG electrodes were implanted into the skull at least 24 hours before seizure induction. Hyperthermia-induced seizures were provoked by placing the mouse in a heated box, with body temperature gradually increased by approximately 0.1°C per 10 seconds using a hot plate and an electric light bulb. Rectal temperature was monitored continuously. The heating was stopped when a seizure was observed on EEG or when rectal temperature reached 45°C. For drug efficacy testing, baseline seizure-inducing body temperature (BT₁) and seizure duration (D₁) were first determined in Scn1aRX/+ mice. After a 48-hour recovery period, drugs were administered via intraperitoneal injection. Stiripentol was suspended in saline (0.9% NaCl) containing 1% Tween 80 (v/v). Seizure induction was repeated 1 hour after drug administration to determine post-treatment seizure-inducing body temperature (BT₂) and duration (D₂). Two age groups were tested: young mice (p1M, aged 4 weeks) and older mice (p5M, aged 5–10 months). In the young group, mice received either Stiripentol monotherapy (300 mg/kg), clobazam (CLB) monotherapy (6.62 mg/kg), or combination therapy (Stiripentol 150 mg/kg + CLB 6.62 mg/kg). The Stiripentol dose in the young combination group was reduced from 300 mg/kg due to severe toxicity (hypothermia and death) observed at the higher dose in pilot studies. In the older group, mice received either Stiripentol monotherapy (300 mg/kg), CLB monotherapy (6.62 mg/kg), or combination therapy (Stiripentol 300 mg/kg + CLB 6.62 mg/kg). Blood samples were collected 1 hour and 20 minutes after drug administration for measurement of plasma drug concentrations. [1] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
After oral administration, stiripentol is quickly and readily absorbed with a median Tmax of two to three hours. The systemic exposure increases dose-proportionally. Stiripentol has a low bioavailability due to water insolubility and extensive metabolism. Stiripentol is mainly eliminated via metabolism. Its metabolites are excreted mainly via the kidney. Urinary metabolites of stiripentol accounted collectively for the majority (73%) of an oral acute dose whereas a further 13-24% was recovered in feces as unchanged drug. The average volume of distribution is 1.03 L/kg but does not display a dose-dependent relationship. Following administration, stiripentol enters the brain and accumulates in the cerebellum and medulla. Plasma clearance decreases markedly at high doses; it falls from approximately 40 L/kg/day at the dose of 600 mg/day to about 8 L/kg/day at the dose of 2,400 mg. Clearance is decreased after repeated administration of stiripentol, probably due to inhibition of the cytochrome P450 isoenzymes responsible for its metabolism. Metabolism / Metabolites Stiripentol is extensively metabolized. About 13 different metabolites have been found in urine. The main metabolic processes are demethylenation (oxidative cleavage of the methylenedioxy ring system) and glucuronidation, although precise identification of the enzymes involved has not yet been achieved. Other metabolic pathways include O-methylation of catechol metabolites, hydroxylation of the t-butyl group, and conversion of the allylic alcohol side-chain to the isomeric 3-pentanone structure. _In vitro_ studies suggested that the phase I metabolism of stiripentol is catalyzed by CYP1A2, CYP2C19 and CYP3A4 and possibly other enzymes. Biological Half-Life The elimination half life is approximately ranges from 4.5 to 13 hours, in a dose-dependent manner. The mean minimum plasma concentration of stiripentol at steady-state in pediatric patients receiving a mean daily dose of 49 ± 2 mg/kg/day was 10.0 ± 3.6 mg/l (equivalent to 42.7 ± 15.4 μM). [1] Usual steady-state plasma concentrations of stiripentol are reported to be in the range of 10 to 60 μM. [1] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Limited data are available on the safety of stiripentol, based mainly on open-label and small, placebo controlled clinical trials in children with Dravet syndrome. In these studies, addition of stiripentol to chronic clobazam therapy was not associated with an increased frequency of serum aminotransferase elevations, and there were no instances of clinically apparent liver injury. Long term therapy with stiripentol has been linked to low rates of ALT and alkaline phosphatase elevations but with increases in gamma glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) in up to 38% of cases. Since its general availability, there have been no published case reports of stiripentol hepatotoxicity. Thus, clinically apparent liver injury due to stiripentol must be rare, if it occurs at all. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Because no information is available on the use of stiripentol during breastfeeding, an alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Protein binding of stiripentol is 99%. In a pilot experiment, administration of a high-dose combination of Stiripentol (300 mg/kg) and clobazam (6.62 mg/kg) via intraperitoneal injection to four 1-month-old Scn1aRX/+ mice caused severe hypothermia (body temperature around 20°C) and death within 1 hour. This severe toxicity prompted the reduction of the Stiripentol dose to 150 mg/kg in the combination therapy regimen for the young mouse group in the main study. [1] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Pharmacodynamics
Stiripentol is an antiepileptic agent that works to reduce seizure frequency. It demonstrates anticonvulsant properties when administered alone and may potentiate GABAergic inhibition via several proposed mechanisms. It provides a therapeutic advantage in improving the efficacy of other antiepileptic drugs by inhibiting cytochrome P450 enzymes that normally metabolize those drugs. The anticonvulsant activity of stiripentol is age-dependent, with increased efficacy in younger patients. Stiripentol is an anticonvulsant agent used as an add-on treatment with clobazam and valproate for severe myoclonic epilepsy in infancy (SMEI). Its clinical efficacy is associated with its ability to inhibit cytochrome P450 enzymes, particularly CYP2C19, thereby increasing plasma concentrations of the active clobazam metabolite N-desmethylclobazam (NCLB) and potentiating the antiepileptic effect of clobazam. This drug interaction is utilized therapeutically rather than being solely an adverse effect. [1] The inhibitory effect of stiripentol may be influenced by CYP2C19 genetic polymorphism. Patients carrying defective CYP2C19 alleles may experience different degrees of metabolic interaction. [1] |
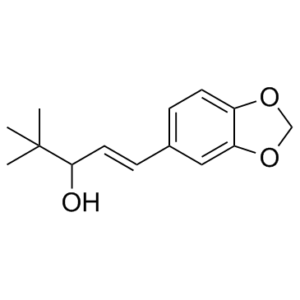
| 分子式 |
C₁₄H₁₈O₃
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
234.29
|
|
| 精确质量 |
234.125
|
|
| CAS号 |
49763-96-4
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Stiripentol-d9;1185239-64-8
|
|
| PubChem CID |
5311454
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.1±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
365.4±11.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
73-74ºC
|
|
| 闪点 |
174.8±19.3 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.579
|
|
| LogP |
3.39
|
|
| tPSA |
38.69
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
17
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
280
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
CC(C)(C)C(/C=C/C1=CC2=C(C=C1)OCO2)O
|
|
| InChi Key |
IBLNKMRFIPWSOY-FNORWQNLSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C14H18O3/c1-14(2,3)13(15)7-5-10-4-6-11-12(8-10)17-9-16-11/h4-8,13,15H,9H2,1-3H3/b7-5+
|
|
| 化学名 |
(E)-1-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-4,4-dimethylpent-1-en-3-ol
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (8.88 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (8.88 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (8.88 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.2682 mL | 21.3411 mL | 42.6821 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8536 mL | 4.2682 mL | 8.5364 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4268 mL | 2.1341 mL | 4.2682 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。