| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
PAI-1/plasminogen activator inhibitor-1PAI-1
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
HT1080、HCT116、Daoy、MDA-MB-231 和 Jurkat 细胞均被 TM-5441剂量依赖性地降低,IC50 范围为 13.9 至 51.1 μM[1]。在 HT1080 和 HCT116 细胞中,TM5441 以剂量依赖性方式增加 caspase 3/7 活性。 TM5441 导致 HT1080 和 HCT116 细胞发生更多凋亡[1]。线粒体去极化是由 TM5441 诱导的[1]。 TM5441 逆转 PAI-1 诱导的纤溶酶活性抑制,并有效阻断小鼠近端肾小管上皮细胞中的纤维化和炎症标志物 mRNA 表达[2]。
TM5275和TM-5441降低了HT1080和HCT116细胞的增殖[1] 为了研究TM抑制剂对细胞增殖的影响,我们使用BrdU掺入来测试细胞周期活性。该分析(图2)显示,用TM5275和TM5441处理的两种细胞系的BrdU阳性细胞百分比均显著降低(分别从DMSO处理的细胞的48.5%和48.7%降至TM5275处理的HT1080和HCT116细胞的38.1%和42.5%,TM5441治疗的细胞的28.3%和34.6%)。这些结果表明,TM5275和TM5441部分通过减少增殖来降低肿瘤细胞的存活率。 TM5275和TM-5441增加了HT1080和HCT116细胞的凋亡[1] 由于之前的研究表明PAI-1保护肿瘤细胞免于凋亡[10,12,26],我们研究了TM5275和TM5441对HT1080和HCT116细胞凋亡的影响。使用胱天蛋白酶3/7活性测定,我们证明了暴露于这些抑制剂的HT1080和HCT116细胞的胱天蛋白酶3/7活性呈剂量依赖性增加(图3A)。TM5441对胱天蛋白酶3/7活性的影响在统计学上比TM5275强得多(在100μM时分别为37倍和32倍;P值分别为0.0005和0.003)。通过流式细胞术分析膜联蛋白V和碘化丙啶(PI)染色,证实了抑制剂对细胞凋亡的影响(图3B)。数据表明,与DMSO处理的细胞相比,用TM5275或TM5441抑制剂处理的HT1080和HCT116细胞的早期和晚期凋亡呈统计学上显著的剂量依赖性增加。作为PAI-1对uPA活性的读数,我们测量了纤溶酶活性随时间的变化。该分析揭示了细胞相关纤溶酶活性的增加,在8至24小时之间达到峰值,并与凋亡的增加相关(图3C)。 我们还测试了浓度为1μM至25μM的TM-5441是否会影响HT1080和HCT116细胞对几种化疗药物(阿霉素、依托泊苷、奥沙洛铂和5-氟尿嘧啶(5-FU))的敏感性。数据显示,TM5441在1μM时不会增强这些化疗药物的活性。即使在更高浓度(25μM)下使用,TM5441也不会增强阿霉素的细胞毒性活性(S2图)。 TM5275和TM-5441诱导线粒体去极化[1] 为了探索外源性和内源性凋亡途径在TM抑制剂诱导的凋亡中的相对贡献,我们通过蛋白质印迹检测了这些抑制剂对胱天蛋白酶3、8和9切割(激活)的影响。数据(图4A)显示,在用TM5275或TM5441处理后,两种细胞系中都没有胱天蛋白酶8的激活。相比之下,他们表明胱天蛋白酶9和3被激活,聚己二酰核糖聚合酶(PARP)被相应地切割,PARP是胱天蛋白酶3的底物,这与TM抑制剂激活内在凋亡途径是一致的。用TM抑制剂(50μM)处理的HT1080和HCT116细胞的线粒体膜去极化检查证实了这一点(图4B)。数据表明,用TM5275和TM5441处理的细胞线粒体去极化增加,TM5441的作用更为明显,如之前在胱天蛋白酶3/7活性测定中观察到的那样(图3A)。这些结果表明,TM5275,特别是TM5441,是肿瘤细胞内在凋亡的强效刺激剂。 TM5275和TM-5441抑制HUVEC分支 在体外EC上进一步研究了TM5441对体内肿瘤血管系统的破坏作用(图6)。该分析揭示了TM5441对3D Matrigel培养物中HUVEC分支形态发生的剂量依赖性抑制作用(图6A)。然而,这种效应与对EC存活率的直接影响无关,因为TM5441在50μM的浓度下对HUVEC存活(图6B)和凋亡(图6C)没有影响,而对体外分支形态发生有显著影响。TM5275对EC也有类似的影响(S1和S7图)。因此,数据表明TM抑制剂具有显著的血管破坏活性,与它们的凋亡活性无关。 TM化合物在体外抑制PAI-1诱导的纤维化和炎症反应[2] 为了证实TM化合物作为PAI-1抑制剂在肾脏中的功效,我们研究了TM5275和TM-5441对mProx细胞中PAI-1诱导的纤维化和炎症标志物的影响。PAI-1治疗显著增加了TGF-β、Iα1型胶原、Iα2型胶原和MCP-1的mRNA表达(图4A-4D),这表明PAI-1具有促纤维化和促炎作用;值得注意的是,TM化合物的治疗有效地降低了PAI-1诱导的纤维化和炎症反应(图4A-4D),这证实了TM化合物作为PAI-1抑制剂的有效性。正如预期的那样,用TM化合物处理后,PAI-1诱导的纤溶酶活性抑制也受到抑制(图4E)。总之,这些结果表明,TM化合物可以有效改善PAI-1诱导的肾脏纤维化和炎症反应。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
当TM-5441(每天 20 毫克/千克)给 HT1080 和 HCT116 异种移植小鼠口服时,它会显着破坏肿瘤脉管系统并增加肿瘤细胞凋亡,这与肿瘤生长的减少和生存的增加有关。口服后1小时,平均血药峰浓度为11.4μM,23小时后检测不到[1]。 TM5441 可延长 klotho 缺失小鼠的寿命,减少 Nω-硝基-L-精氨酸甲酯诱导的心源性高血压和血管衰老的影响,并在癌症中具有抗肿瘤和抗血管生成特性[3]。
TM-5441在体内具有生物效应[1] 由于TM5441在体外具有较高的凋亡作用,因此选择TM5441来测试其在异种移植HT1080细胞的小鼠体内的抗肿瘤活性(图5)。该实验表明,用TM-5441(每天20 mg/kg)治疗的荷瘤小鼠显示出生长较慢的肿瘤的趋势,平均25.8(±3.4)天时肿瘤体积达到1500 mm3,而对照组为21.2(±2.5)天(P值=0.10)(图5A和5B)。然而,在TM5441治疗组中,随着时间的推移,生物发光活性(相对萤光素酶单位(RLU)作为肿瘤细胞存活率的指标)在统计学上显著降低(图5C)。TM5441治疗对生存率的影响显示,TM5441处理组的生存率呈上升趋势,但无统计学意义(P值=0.10)(图5D)。苏木精和伊红(H&E)对这些肿瘤的组织学分析表明,TM5441治疗小鼠的肿瘤中存在较大的出血区域,血管系统受损。CD31(PECAM)染色证实了肿瘤血管系统的这种破坏,该染色揭示了EC中包含血管的多个不连续区域,TM5441治疗组的血管密度在统计学上显著降低(P值=0.002)(图5F)。TM5441治疗小鼠的肿瘤中TUNEL阳性染色(肿瘤细胞凋亡的标志物)的数量也有所增加(P值=0.05)(图5G)。综上所述,数据表明TM5441在体内对肿瘤血管系统和肿瘤细胞具有生物活性,但不足以显著影响肿瘤生长。在我们的体内HCT116肿瘤模型中也观察到了类似的结果(S3图)。药代动力学研究显示,在用20mg/kg治疗的小鼠中,平均峰值浓度为11.4μM(仅略低于HT1080的IC50 13.9μM),谷值水平无法检测到(S4图)。给药50 mg/kg和100 mg/kg的TM5441,虽然分别将峰值血浆浓度水平提高到15.0μM和35.6μM,但并没有显著提高谷值水平,也没有影响肿瘤生长(S5图)。有趣的是,TM5441的给药对用50或100mg/kg治疗的小鼠的出血时间没有全身性影响(S6A图)。在体外人血浆凝块溶解试验中,TM5275有效地抑制了PAI-1维持凝块,并允许溶解发生,类似于添加tPA(S6B图)。 糖尿病肾病是全球终末期肾病的主要原因,但目前尚无有效的治疗策略。由于纤溶酶原激活物抑制剂-1(PAI-1)越来越被认为是糖尿病肾病细胞外基质(ECM)积聚的关键因素,本研究考察了TM5275和TM-5441在链脲佐菌素(STZ)诱导的糖尿病小鼠中的肾脏保护作用,这两种新型口服活性PAI-1抑制剂不会引发出血事件。对STZ诱导的糖尿病和年龄匹配的对照小鼠口服TM5275(50mg/kg)和TM5441(10mg/kg)16周。与对照组小鼠相比,糖尿病小鼠的血糖和肌酐水平、尿白蛋白排泄、肾与体重比、肾小球体积和系膜面积分数显著升高(p<0.05)。糖尿病小鼠肾脏中的纤维化和炎症标志物以及PAI-1也上调,TM5275和TM5441治疗有效地抑制了糖尿病肾脏中的蛋白尿、系膜扩张、ECM积聚和巨噬细胞浸润。此外,在小鼠近端肾小管上皮(mProx24)细胞中,TM5275和TM5441均有效抑制了PAI-1诱导的纤维化和炎症标志物的mRNA表达,并逆转了PAI-1对纤溶酶活性的抑制,这证实了TM化合物作为PAI-1抑制剂的功效。这些数据表明,TM化合物可用于预防糖尿病肾损伤。[2] TM化合物改善STZ诱导的糖尿病小鼠的肾功能和形态[1] 注射STZ后16周,与年龄匹配的对照组小鼠相比,小鼠的体重增加较低,血糖水平升高。糖尿病小鼠的血糖水平不受TM5275(50mg/kg)或TM-5441(10mg/kg)治疗的影响(表1)。糖尿病小鼠的肾脏与体重比(表1)和血浆肌酐水平(图1A)也有所增加,这些变化同样没有受到TM化合物的显著影响(图1A。此外,STZ诱导的糖尿病小鼠尿白蛋白排泄、肾小球体积和FMA显著增加。有趣的是,TM化合物有效地减少了糖尿病小鼠的蛋白尿和FMA(图1B、1C和1E),尽管这两种抑制剂都没有对STZ诱导的肾小球肥大产生很大影响(图1C和1D)。这些数据共同表明,TM化合物TM5275和TM5441保护小鼠免受糖尿病诱导的蛋白尿和系膜扩张,而不影响高血糖。 |
| 细胞实验 |
流式细胞术[1]
细胞以每孔120000个细胞的密度在6孔板上一式三份,第二天用50μM TM5275或TM-5441处理8小时(溴脱氧尿苷(BrdU)掺入)或24和48小时(线粒体去极化)。对于膜联蛋白V,用指定剂量处理细胞48小时。对于BrdU掺入,根据制造商的建议,在使用异硫氰酸荧光素(FITC)BrdU Flow试剂盒(BD)收获细胞之前,用10μM BrdU脉冲细胞20分钟。根据制造商的建议,使用MitoProbe 5,5′,6,6′-四氯-1,1′,3,3′-四乙基苯并咪唑基碳菁碘化物(JC-1)检测试剂盒 评估线粒体去极化。根据制造商的建议,使用Annexin V FITC凋亡检测试剂盒I(BD)评估凋亡细胞(早期凋亡的Annexin V+/PI-细胞和晚期凋亡的Annexin V+/PI+细胞)。使用DiVA软件(6.0版,BD)在BD LSR II系统(BD)中通过流式细胞术分析细胞。 半胱天冬酶3/7活性测定[1] 按照细胞存活率的描述对细胞进行铺板,并用浓度逐渐增加的TM5275或TM-5441处理48小时。ApoLive-Glo试剂盒 用于用荧光染料测量细胞存活率,然后根据制造商的建议在室温下用发光活性测量胱天蛋白酶3/7活性。将半胱天冬酶3/7活性标准化为细胞活力,并绘制为与DMSO对照细胞相比的倍数变化。 细胞培养[2] 将小鼠近端肾小管上皮(mProx24)细胞在含有10%胎牛血清、100 U/mL青霉素和100 g/mL链霉素的DMEM中在37°C、5%CO2的加湿气氛中培养。将接近融合的细胞与无血清培养基孵育24小时,用50μM的TM5275或10μM的TM-5441预处理4小时,然后用重组PAI-1刺激(约90%的生物活性)。 |
| 动物实验 |
20 mg/kg; oral
Mice bearing HT1080 and HCT116 xenotransplanted tumors [1] For in vivo experiments, TM-5441 (20, 50 or 100 mg/kg) was dissolved in DMSO and incorporated into individual servings of peanut butter and honey. Controls were given equal amounts of vehicle (equal volumes of DMSO mixed in peanut butter and honey). Each mouse was then administered the inhibitor or vehicle mixture until it had eaten the entire dose.[1] HT1080 cells were transduced with a firefly luciferase lentiviral vector and selected against 100 μg/ mL geneticin for two weeks. Cells were then maintained with geneticin. Five-week-old nu/nu female mice were injected with 5x106 HT1080-luciferase cells subcutaneously into the right flank as described previously. Palpable tumors and mouse weight were measured every 2–3 days. Mice were sacrificed when tumor volume reached a maximum of 1,500 mm3 calculated with the modified ellipsoid formula: tumor volume (mm3) = (width in mm)2 X (length in mm) X π/6. For bioluminescence imaging, mice were injected intravenously (i.v.) with D-luciferin (0.3 mL) at a dose of 5 mg/kg and luciferase activity was determined after 15 minutes with a two-second exposure time using the Xenogen IVIS system. Bioluminescence emitted from the HT1080 tumor cells (total flux) was measured and plotted as relative luciferase units. For bleeding time testing, the dorsal tail vein was cut using an automated Surgicutt Newborn device 0.5 mm deep and 2.5 mm long. Filter paper was carefully blotted against the bleeding wound every 15 seconds until the incision stopped bleeding. Bleeding time was performed on the last day one hour after administration of the last dose of TM-5441 and before the mice were sacrificed (at day 16–30). Measurements were recorded to the nearest 15 seconds.[1] We used 6-week-old male C57BL/6 mice, which were divided into 6 groups. Diabetes was induced by intraperitoneally injecting the mice with 150 mg/kg streptozotocin (STZ). Age-matched control mice were injected with an equivalent volume of sodium citrate buffer (100 mM sodium citrate, 100 mM citric acid, pH 4.5). TM5275 at 50 mg/kg/day and TM-5441 at 10 mg/kg/day were orally administered in control and diabetic mice for 16 weeks. The effective doses of TM5275 and TM-5441 were determined based on previous studies and our preliminary studies (data not shown). Mice that were not administered the TM compounds were injected with an equivalent volume of 0.5% carboxymethyl cellulose, the vehicle for TM5275 and TM-5441. Mice were monitored at least once a day, and no deaths occurred during the experimental period. All mice were sacrificed at 16 weeks after STZ injection via anesthesia with 16.5% urethane (10 mL/kg). Blood was collected in a heparinized syringe. We collected blood for measurement of plasma glucose and creatinine, urine for protein measurement, and kidneys for immunohistochemical analysis. [2] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Numerous studies have shown a paradoxical positive correlation between elevated levels of plasminogen activator inhibitior-1 (PAI-1) in tumors and blood of cancer patients with poor clinical outcome, suggesting that PAI-1 could be a therapeutic target. Here we tested two orally bioavailable small molecule inhibitors of PAI-1 (TM5275 and TM-5441) for their efficacy in pre-clinical models of cancer. We demonstrated that these inhibitors decreased cell viability in several human cancer cell lines with an IC50 in the 9.7 to 60.3 μM range and induced intrinsic apoptosis at concentrations of 50 μM. In vivo, oral administration of TM5441 (20 mg/kg daily) to HT1080 and HCT116 xenotransplanted mice increased tumor cell apoptosis and had a significant disruptive effect on the tumor vasculature that was associated with a decrease in tumor growth and an increase in survival that, however, were not statistically significant. Pharmacokinetics studies indicated an average peak plasma concentration of 11.4 μM one hour after oral administration and undetectable levels 23 hours after administration. The effect on tumor vasculature in vivo was further examined in endothelial cells (EC) in vitro and this analysis indicated that both TM5275 and TM5441 inhibited EC branching in a 3D Matrigel assay at concentrations where they had little effect on EC apoptosis. These studies bring novel insight on the activity of PAI-1 inhibitors and provide important information for the future design of inhibitors targeting PAI-1 as therapeutic agents in cancer. [1]
This data represents a first in vivo analysis of TM-5441 PAI-1 inhibitor activity in cancer. TM5275 and TM5441 induced intrinsic apoptosis in several human cancer cell lines and inhibited EC branching in a manner that was independent from their apoptotic activity on EC in vitro. These in vivo results in HT1080 and HCT116 xenograft models showed that although TM5441 had a vascular disruptive effect (and a trend of decreased tumor growth and increased survival in the HT1080 model), these effects were not sufficient to affect tumor growth even as we documented a significant decrease in TUNEL staining in vivo. As a basis for comparison, the IC50 of TM5275 and TM-5441 treatment is similar to the IC50 of PAI-039, another previously reported PAI-1 inhibitor. The IC50 measured by tPA-dependent hydrolysis for the compounds were 8.37 μM for PAI-749, which is a more potent derivative of PAI-039, and 6.95 μM for TM5275. When defined on the basis of cell viability, the IC50 of PAI-039 was calculated from previous data to be 29 μM and 32 μM for HT1080 and HCT116 cells, respectively, which is in the range of the IC50 found for TM5275 and TM5441. There was no correlation between the IC50 of the TM compounds and the total PAI-1 levels measured in the cell lysates. This suggested that other factors besides PAI-1 played a role, which may include membrane-associated plasmin, uPA, or sensitivity to apoptosis that all contributed to the control of cell viability. [1] This study was conducted to provide experimental evidence that two novel orally active PAI-1 inhibitors, TM5275 and TM-5441, can prevent the development and progression of diabetic kidney injury, and to suggest the use of TM compounds as a new strategy for preventing diabetic nephropathy. Accordingly, at 16 weeks after injection of STZ, the diabetic mice showed an increase (relative to control mice) in various parameters of kidney injury, such as plasma creatinine level, urinary albumin excretion, kidney-to-body weight ratio, glomerular volume, and FMA. Notably, treatment with TM5275 and TM5441 effectively reduced urinary albumin excretion and FMA. Consistent with our results, another compound of TM series significantly reduced proteinuria in NEP25/LMB2 podocyte injury mouse model. With regard to the mechanic explanation for the role of PAI-1 on urine albumin levels, PAI-1/uPA complex-mediated uPAR-dependent podocyte β1-integrin endocytosis has been proposed in progressive podocyte injury leading to proteinuria. However, inhibition of PAI-1 did not affect plasma glucose levels in STZ-induced diabetic mice, which agreed with the results of a previous study [26]. These data indicate that TM compounds improve kidney function and morphology in diabetic mice. TM5007, the parent compound of TM5275 and TM-5441, prevents bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in mice, and tiplaxtinin (an indole oxoacetic acid derivative) attenuates angiotensin II-induced aortic remodeling in mice. These two previous studies suggest that the best-in-class PAI-1 inhibitors could be effective antifibrotic agents. Here, our study demonstrating the antifibrotic effect of TM5275 and TM5441 in diabetic kidney injury is consistent with previous studies conducted using PAI-1 null mice. PAI-1 deficiency reduces ECM accumulation and tubulointerstitial or glomerular fibrosis in STZ-induced diabetic mice and db/db diabetic mice. In summary, the TM compounds improved kidney function, fibrosis, and inflammation in STZ-induced diabetic mice. Therefore, oral administration of TM5275 and TM-5441, two novel PAI-1 inhibitors that do not induce bleeding episodes, could emerge as an effective measure for treating diabetic nephropathy. |
| 分子式 |
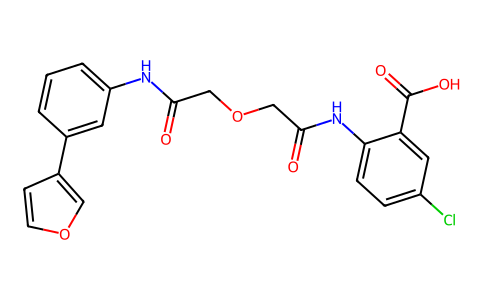
C21H17CLN2O6
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
428.8225
|
|
| 精确质量 |
428.077
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 58.82; H, 4.00; Cl, 8.27; N, 6.53; O, 22.39
|
|
| CAS号 |
1190221-43-2
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
44250349
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| LogP |
3.3
|
|
| tPSA |
118
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
30
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
618
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
ClC1C([H])=C([H])C(=C(C(=O)O[H])C=1[H])N([H])C(C([H])([H])OC([H])([H])C(N([H])C1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C(C2=C([H])OC([H])=C2[H])=C1[H])=O)=O
|
|
| InChi Key |
BGGMLMAPVODXAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C21H17ClN2O6/c22-15-4-5-18(17(9-15)21(27)28)24-20(26)12-30-11-19(25)23-16-3-1-2-13(8-16)14-6-7-29-10-14/h1-10H,11-12H2,(H,23,25)(H,24,26)(H,27,28)
|
|
| 化学名 |
5-chloro-2-[[2-[2-[3-(furan-3-yl)anilino]-2-oxoethoxy]acetyl]amino]benzoic acid
|
|
| 别名 |
TM-5441; TM 5441; 1190221-43-2; 5-chloro-2-(2-(2-((3-(furan-3-yl)phenyl)amino)-2-oxoethoxy)acetamido)benzoic acid; 5-chloro-2-[[2-[2-[3-(furan-3-yl)anilino]-2-oxoethoxy]acetyl]amino]benzoic acid; BGGMLMAPVODXAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N; 33S35WFR9H; TM5441;BMS-790052; BMS-790052; BMS790052; EBP 883; EBP-883; EBP883
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.83 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.83 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3320 mL | 11.6599 mL | 23.3198 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4664 mL | 2.3320 mL | 4.6640 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2332 mL | 1.1660 mL | 2.3320 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
 Decreased cell viability in cancer cells treated with TM5275 and TM5441.PLoS One.2015 Jul 24;10(7):e0133786. |
|---|
 Treatment with TM5275 or TM5441 increases intrinsic apoptosis.PLoS One.2015 Jul 24;10(7):e0133786. |
 Increased apoptosis in cancer cells treated with TM5275 and TM5441.PLoS One.2015 Jul 24;10(7):e0133786. |
 Decreased proliferation in cancer cells treated with TM5275 and TM5441.PLoS One.2015 Jul 24;10(7):e0133786. |
|---|
 Pre-clinical activity of TM5441 in vivo.PLoS One.2015 Jul 24;10(7):e0133786. |
 TM5441 inhibits EC branching morphogenesis.PLoS One.2015 Jul 24;10(7):e0133786. |
 TM compounds improve kidney function and morphology in STZ-induced diabetic mice.PLoS One.2016 Jun 3;11(6):e0157012. |
|---|
 TM compounds inhibit kidney fibrosis in STZ-induced diabetic mice.PLoS One.2016 Jun 3;11(6):e0157012. |
 TM compounds inhibit kidney inflammation in STZ-induced diabetic mice.
TM compounds inhibit PAI-1-induced fibrotic and inflammatory responsesin vitro.PLoS One.2016 Jun 3;11(6):e0157012. |