| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
mTORC1 (IC50 = 2-10 nM); mTORC2 (IC50 = 2-10 nM); mTOR (IC50 = 3 nM); DNA-PK (IC50 = 1 μM); PI3K-α (IC50 = 1.8 μM); ATM (IC50 = 0.6 μM); hVps34 (IC50 = 3 μM); Autophagy
Torin 1 is an ATP-competitive inhibitor that targets mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), inhibiting both mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) and mTOR complex 2 (mTORC2). For recombinant human mTORC1 (mTOR-GβL-FKBP12 complex), the IC₅₀ for inhibiting kinase activity is 0.2 nM; for recombinant human mTORC2 (mTOR-Rictor-GβL complex), the IC₅₀ is 0.6 nM [1,2] - Torin 1 exhibits high selectivity over PI3K family kinases: IC₅₀ for PI3Kα = 200 nM, PI3Kβ = 300 nM, PI3Kγ = 400 nM, which are >1000-fold higher than its IC₅₀ for mTOR [2] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在野生型 MEF 中,Torin1 (250 nM) 完全抑制增殖并导致 G1/S 细胞周期停滞,并且比 50 nM 雷帕霉素更大程度地减小细胞大小[1]。除 DNA-PK 外,Torin1 与其他 PIKK 家族激酶相比具有很强的选择性,mTOR 和 PI3Kis 之间的选择性超过 800 倍[2]。
癌细胞中mTOR下游信号抑制:100 nM Torin 1处理HeLa细胞24小时,显著降低mTORC1和mTORC2底物的磷酸化水平(Western blot检测):磷酸化p70S6K(Thr389)较对照组降低90%,磷酸化4E-BP1(Thr37/46)降低85%,磷酸化Akt(Ser473)降低80%;p70S6K、4E-BP1和Akt的总蛋白水平无变化 [1] - 跨癌细胞系抗增殖活性:采用MTT法(处理72小时)检测,Torin 1对HeLa(宫颈癌)、U2OS(骨肉瘤)和HCT116(结直肠癌)细胞的增殖抑制IC₅₀分别为25 nM、30 nM和22 nM;100 nM浓度时,对三种细胞系的增殖抑制率均>80% [1] - 侵袭性B细胞淋巴瘤细胞凋亡诱导:100 nM Torin 1处理SU-DHL-4和OCI-Ly10 B细胞淋巴瘤细胞48小时,凋亡率升高(Annexin V-FITC/PI染色):早期凋亡细胞(Annexin V⁺/PI⁻)从对照组的5%升至SU-DHL-4的35%和OCI-Ly10的32%,晚期凋亡/坏死细胞(Annexin V⁺/PI⁺)从对照组的3%升至SU-DHL-4的12%和OCI-Ly10的10%;该凋亡效应伴随4EBP1磷酸化(Thr37/46)的完全抑制 [3] - 对结直肠癌细胞的差异性作用:在APC缺失的SW480结直肠癌细胞中,50 nM Torin 1处理72小时(CellTiter-Glo法)抑制增殖60%;在APC野生型HCT116细胞中,相同浓度仅抑制增殖45%。Western blot显示,Torin 1使SW480细胞中cyclin D1表达降低55%,而在HCT116细胞中仅降低30% [4] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
以剂量依赖性方式,Deforolimus 对携带 PC-3(前列腺)、HCT-116(结肠)、MCF7(乳房)、PANC-1(胰腺)或 A549(肺)异种移植物的小鼠具有显着的抗肿瘤作用。此外,Deforolimus 还能抑制 SK-LMS-1 异种移植模型中的 mTOR 信号传导,这与肿瘤生长抑制有关。 [1]
结肠炎诱导的结直肠癌(CRC)模型疗效:6周龄雄性C57BL/6小鼠通过4个周期的3%硫酸葡聚糖钠(DSS)处理(7天DSS饮水+14天正常饮水,共10周)诱导CRC。治疗组从第1周到第10周腹腔注射Torin 1(10 mg/kg,每日1次)。与溶剂对照组相比:(1)CRC发生率从85%降至40%;(2)每只小鼠平均肿瘤数量从5.2个降至2.1个;(3)平均肿瘤体积从180 mm³降至80 mm³;治疗组无显著体重下降 [4] - 对APC缺失依赖性肿瘤发生的保护作用:4周龄雄性APC^(min/+)小鼠从第4周到第12周腹腔注射Torin 1(10 mg/kg,每日1次)。治疗组表现为:(1)平均存活时间从对照组的120天延长至150天;(2)每只小鼠肠道息肉数量从35个降至20个;(3)息肉平均直径从2.5 mm降至1.2 mm;组织学分析显示息肉中增殖细胞(Ki-67⁺)减少40% [4] |
| 酶活实验 |
使用水泡性口炎病毒 G 假型 MSCV 逆转录病毒,产生表达带有 N 末端 FLAG 标签的 Raptor 的 HEK-293T 细胞系,以产生可溶性 mTORC1。表达带有 N 末端 FLAG 标签的 Protor-1 的 HeLa 细胞是专为 mTORC2 创建的。为了纯化这两种复合物,将细胞溶解在含有 50 mM HEPES、pH 7.4、10 mM 焦磷酸钠、10 mM β-甘油磷酸钠、100 mM NaCl、2 mM EDTA 和 0.3% CHAPS 的溶液中。 4°C 细胞裂解 30 分钟后,以 13,000 rpm 微量离心 10 分钟分离不溶部分。 FLAG-M2 单克隆抗体-琼脂糖孵育 1 小时后,将上清液在裂解缓冲液中洗涤四次,并在最终氯化钠浓度为 0.5 mol/L 的裂解缓冲液中洗涤一次。在 50 mM HEPES、pH 7.4、100 mM NaCl、100 μg/mL 3 FLAG 肽中用于洗脱纯化的 mTORC1。洗脱液可以等分并保存在-80°C 下。以 150 ng 无活性 S6K1 或 Akt1 作为底物,在含有激酶缓冲液(25 mM HEPES,pH 7.4,50 mM KCl,10 mM MgCl2, 500 M ATP)。添加 80 μL 样品缓冲液并将混合物煮沸 5 分钟终止反应。之后,使用 SDS-PAGE 和免疫印迹分析样品。
mTORC1激酶活性测定(文献[1]): 1. 重组mTORC1制备:通过抗mTOR抗体免疫沉淀从HEK293细胞中纯化mTOR-GβL-FKBP12复合物,用激酶缓冲液(25 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5、10 mM MgCl₂、1 mM DTT)重悬至终浓度0.1 μg/μL [1] 2. 药物预孵育:将系列浓度Torin 1(0.01 nM–10 nM)与50 μL mTORC1溶液、1 μM非放射性ATP混合,30°C预孵育15分钟,使药物与酶充分结合 [1] 3. 激酶反应启动:加入1 μg重组p70S6K(mTORC1底物)和10 μCi [γ-³²P]-ATP启动反应,总反应体积100 μL,30°C孵育30分钟 [1] 4. 终止与检测:加入20 μL 4×SDS-PAGE上样缓冲液终止反应;样品经10% SDS-PAGE分离后转移至PVDF膜,放射自显影显影;用磷屏成像仪定量磷酸化p70S6K条带的放射性,将抑制率与Torin 1浓度拟合剂量-反应曲线,得IC₅₀=0.2 nM [1] - mTORC2激酶活性测定(文献[1]): 1. 重组mTORC2制备:通过抗Rictor抗体免疫沉淀从HEK293细胞中纯化mTOR-Rictor-GβL复合物,用与mTORC1相同的激酶缓冲液重悬(0.1 μg/μL) [1] 2. 药物预孵育与反应:系列浓度Torin 1(0.05 nM–20 nM)与mTORC2预孵育15分钟;加入1 μg重组Akt1(mTORC2底物)和10 μCi [γ-³²P]-ATP启动反应,30°C孵育30分钟 [1] 3. 终止与检测:步骤同mTORC1测定,得mTORC2抑制IC₅₀=0.6 nM [1] |
| 细胞实验 |
第 0 天,96 孔板每孔接种 500 个细胞并生长过夜。第一天将适当的化合物应用于细胞,然后在第 3-5 天检查细胞。将 50 L CellTiter-Glo 试剂添加到板的每个孔中,然后在定轨摇床上混合 12 分钟。然后将板在室温下孵育 60 分钟,然后进行分析。在普通板发光计上测量发光。
MTT细胞增殖实验(文献[1]): 1. 细胞接种:HeLa、U2OS、HCT116细胞以2×10³个/孔接种于96孔板,37°C、5% CO₂培养过夜,使细胞贴壁 [1] 2. 药物处理:Torin 1用DMSO溶解后,用完全培养基稀释至0.1 nM–100 nM;每孔加入100 μL稀释后的药物(每个浓度3复孔),设置溶剂对照组(0.1% DMSO) [1] 3. 孵育与MTT反应:培养72小时后,每孔加入20 μL MTT溶液(5 mg/mL,溶于PBS),37°C孵育4小时形成甲瓒结晶;小心吸弃上清,每孔加入150 μL DMSO溶解结晶 [1] 4. 吸光度检测:酶标仪测定570 nm处吸光度,细胞存活率=(药物组A₅₇₀/对照组A₅₇₀)×100%,从剂量-反应曲线推导IC₅₀ [1] - mTOR下游信号Western blot检测(文献[1,3]): 1. 细胞处理:HeLa细胞(1×10⁶个/6孔板)用100 nM Torin 1处理24小时;SU-DHL-4细胞(1×10⁶个/6孔板)用100 nM Torin 1处理12小时 [1,3] 2. 蛋白提取:冰预冷PBS洗涤细胞2次,加入含蛋白酶和磷酸酶抑制剂的RIPA裂解液冰上裂解30分钟;4°C、12,000 × g离心15分钟,收集上清液(总蛋白提取物) [1,3] 3. 蛋白定量与电泳:BCA法测定蛋白浓度;每泳道上样30 μg蛋白,与4×SDS-PAGE上样缓冲液混合煮沸5分钟后,经10% SDS-PAGE分离 [1,3] 4. 免疫检测:蛋白转移至PVDF膜,用含5%脱脂牛奶的TBST(20 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5、150 mM NaCl、0.1% Tween-20)室温封闭1小时;4°C孵育一抗(抗p-p70S6K Thr389、抗p-4E-BP1 Thr37/46、抗p-Akt Ser473、抗GAPDH)过夜,室温孵育HRP标记二抗1小时;ECL化学发光显影,ImageJ定量条带强度 [1,3] - 凋亡实验(Annexin V-FITC/PI双染色,文献[3]): 1. 细胞处理:SU-DHL-4细胞以1×10⁶个/孔接种于6孔板,用100 nM Torin 1处理48小时 [3] 2. 细胞收集与染色:胰酶消化收集细胞,冰预冷PBS洗涤2次,用1×结合缓冲液重悬至1×10⁶个/mL;向100 μL细胞悬液中加入5 μL Annexin V-FITC和5 μL PI,室温避光孵育15分钟 [3] 3. 流式细胞术分析:1小时内用流式细胞仪分析,早期凋亡定义为Annexin V⁺/PI⁻,晚期凋亡/坏死定义为Annexin V⁺/PI⁺ [3] |
| 动物实验 |
Torin 1 powder is first dissolved in 100% N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone at a concentration of 25 mg/mL for pharmacodynamic experiments, and then diluted 1:4 with sterile 50% PEG400 before injection. The night before receiving medication, male C57BL/6 mice aged six weeks are fasted. The mice are administered either vehicle (for 10 hours) or 26 (20 mg/kg for 2, 6, or 10 hours) by IP injection, and they are then given food again 1 hour before being sacrificed (by CO2 asphyxiation). A collection of tissues is placed on dry ice and frozen. The frozen tissue is thawed on ice and lysed by sonication in tissue lysis buffer (50 mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 40 mM NaCl, 2 mM EDTA, 1.5 mM sodium orthovanadate, 50 mM sodium fluoride, 10 mM sodium pyrophosphate, 10 mM sodium β-glycerophosphate, 0.1% SDS, 1.0% sodium deoxycholate and 1.0% Triton, supplemented with protease inhibitor cocktail tablets). Using the Bradford assay, the amount of clear lysate is determined. After samples are normalized for protein content and subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting analysis, the results are reported.
Colitis-induced CRC model (Literature [4]): 1. Animal selection and grouping: 6-week-old male C57BL/6 mice were randomized into 2 groups (n=15/group): vehicle control and Torin 1 treatment [4] 2. CRC induction: Mice were given 3% DSS in drinking water for 7 days (1st cycle), followed by normal drinking water for 14 days. This cycle was repeated 4 times (total 10 weeks) to induce chronic colitis and subsequent CRC [4] 3. Drug preparation and administration: Torin 1 was dissolved in a mixture of DMSO, polyethylene glycol 400 (PEG400), and normal saline (1:4:5, v/v/v) to a concentration of 2 mg/mL. The treatment group received Torin 1 via intraperitoneal injection at 10 mg/kg once daily from week 1 to week 10; the control group received the same volume of vehicle [4] 4. Sample collection and analysis: At week 10, mice were euthanized by cervical dislocation. Colons were dissected, washed with PBS, and opened longitudinally. Tumor number and size (length and width) were measured with a vernier caliper, and tumor volume was calculated as (length × width²) / 2 [4] - APC^(min/+) mouse tumor model (Literature [4]): 1. Animal selection and grouping: 4-week-old male APC^(min/+) mice were randomized into 2 groups (n=12/group): vehicle control and Torin 1 treatment [4] 2. Drug administration: Torin 1 was prepared as described above. The treatment group received 10 mg/kg Torin 1 via intraperitoneal injection once daily from week 4 to week 12; the control group received vehicle [4] 3. Monitoring and sample analysis: Mice were monitored daily for survival. At week 12, surviving mice were euthanized, and small intestines were dissected. Intestinal polyps were counted under a dissecting microscope, and polyp diameter was measured. Paraffin-embedded intestinal tissues were sectioned and stained with Ki-67 antibody for proliferation analysis [4] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Plasma protein binding: In vitro equilibrium dialysis using human plasma showed that Torin 1 had a plasma protein binding rate of 95%, primarily binding to albumin [2]
- Metabolic stability: In human liver microsomes, Torin 1 exhibited good metabolic stability with a half-life (t₁/₂) of 180 minutes; less than 20% of the drug was metabolized within 2 hours [2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
In vitro toxicity to normal cells: Human dermal fibroblasts (HDF) treated with Torin 1 at concentrations ≤200 nM for 72 hours showed >90% cell viability (MTT assay), with no significant cytotoxicity compared to the vehicle control [1]
- In vivo general toxicity: C57BL/6 and APC^(min/+) mice treated with Torin 1 (10 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection, daily for 8–10 weeks) had no significant weight loss (<5% vs. baseline). Serum levels of alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and serum creatinine (Scr) were within normal ranges. Histopathological examination of liver, kidney, and colon tissues revealed no signs of damage (e.g., inflammation, necrosis) [4] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
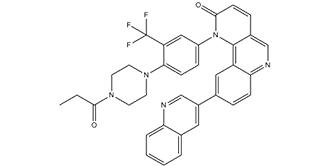
Torin 1 is a member of the class of pyridoquinolines that is 9-(quinolin-3-yl)benzo[h][1,6]naphthyridin-2-one bearing an additional 4-(4-propionylpiperazin-1-yl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl substituent at position 1. It is a potent inhibitor of mTOR and exhibits anti-cancer properties. It has a role as a mTOR inhibitor and an antineoplastic agent. It is a N-acylpiperazine, a N-arylpiperazine, an organofluorine compound, a pyridoquinoline and a member of quinolines.
Mechanism of action advantage: Unlike rapamycin (which only inhibits mTORC1), Torin 1 fully inhibits both mTORC1 and mTORC2. It binds to the ATP-binding pocket of mTOR, blocking ATP hydrolysis and suppressing all mTOR-mediated signaling—including rapamycin-resistant mTORC1 functions (e.g., complete inhibition of 4E-BP1 phosphorylation), leading to stronger suppression of cap-dependent protein translation and cell proliferation [1,3] - Research tool application: Torin 1 is a widely used research tool in mTOR signaling studies. It is particularly valuable for investigating the biological roles of mTORC2 and rapamycin-insensitive mTORC1 activities, as well as evaluating mTOR targeting in cancer and metabolic diseases [1] - Tumor-specific effects: Torin 1 exerts differential effects on colorectal tumorigenesis: it inhibits inflammation-driven CRC (colitis-induced) but protects against APC loss-dependent tumors. This difference is attributed to distinct roles of mTOR signaling in inflammatory vs. genetic (APC mutation)-driven tumor initiation pathways [4] |
| 分子式 |
C35H28F3N5O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
607.6243
|
| 精确质量 |
607.219
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 69.18; H, 4.64; F, 9.38; N, 11.53; O, 5.27
|
| CAS号 |
1222998-36-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
1222998-36-8
|
| PubChem CID |
49836027
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to yellow solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
817.2±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
448.0±34.3 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.9 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.663
|
| LogP |
5.26
|
| tPSA |
71.33
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
45
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1110
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
FC(C1C([H])=C(C([H])=C([H])C=1N1C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N(C(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])=O)C([H])([H])C1([H])[H])N1C(C([H])=C([H])C2=C([H])N=C3C([H])=C([H])C(C4C([H])=NC5=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C5C=4[H])=C([H])C3=C12)=O)(F)F
|
| InChi Key |
AKCRNFFTGXBONI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C35H28F3N5O2/c1-2-32(44)42-15-13-41(14-16-42)31-11-9-26(19-28(31)35(36,37)38)43-33(45)12-8-24-20-40-30-10-7-22(18-27(30)34(24)43)25-17-23-5-3-4-6-29(23)39-21-25/h3-12,17-21H,2,13-16H2,1H3
|
| 化学名 |
1-[4-(4-propanoylpiperazin-1-yl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-9-quinolin-3-ylbenzo[h][1,6]naphthyridin-2-one
|
| 别名 |
Torin-1; Torin1; Torin 1
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~2 mg/mL (~3.3 mM)
Water: <1 mg/mL Ethanol: <1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 0.25 mg/mL (0.41 mM) (饱和度未知) in 5% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 50% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
*生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 0.25 mg/mL (0.41 mM) (饱和度未知) in 5% DMSO + 95% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: 0.05 mg/mL (0.08 mM) in 1% DMSO 99% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 30% PEG 400+0.5% Tween80+5% Propylene glycol: 30mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.6458 mL | 8.2288 mL | 16.4577 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3292 mL | 1.6458 mL | 3.2915 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1646 mL | 0.8229 mL | 1.6458 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT05343611 | Recruiting | Dietary Supplement: HPP Choko Dietary Supplement: HPP/VE Choko |
Dementia Malnutrition |
Massimo Venturelli, PhD | May 1, 2022 |
mTORC1 regulation of 4E-BP1 phosphorylation and binding to eIF-4E reveals rapamycin-resistant functions.J Biol Chem.2009 Mar 20;284(12):8023-32.
|
Torin1 is a potent and selective mTOR inhibitor.J Biol Chem.2009 Mar 20;284(12):8023-32. |
Torin1 inhibits mTORC1-dependent processes that are resistant to rapamycin.J Biol Chem.2009 Mar 20;284(12):8023-32. |