| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
p38α (IC50 = 4 nM-20 nM)
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
将血小板与 VX-702 (1 μM) 预孵育可防止或减少血小板激动剂(如凝血酶、SFLLRN、AYPGKF、U46619 和胶原蛋白)引起的 p38 激活(IC50 4 至 20 nM)。无论是否使用抗血小板药物,VX-702对任何p38 MAPK激动剂引起的血小板聚集均无影响。 [1] VX-702 剂量依赖性地减少 IL-6、IL-1β 和 TNFα 的产生(IC50 分别 = 59、122 和 99 ng/mL)。 [2]
|
||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
VX-702的分布容积为73 L/kg,半衰期为16至20小时,中位清除率为3.75 L/h。对于主要通过肾脏清除的 VX-702,AUC 和 Cmax 值均与剂量成正比。 [2] 当每天两次以 0.1 mg/kg 的剂量给药时,VX-702 与甲氨蝶呤 (0.1 mg/kg) 具有相似的效果。通过比较腕关节糜烂抑制百分比和炎症评分,VX-702(5 mg/kg,每日两次)也具有与泼尼松龙(10 mg/kg,每日一次)相当的效果。 [3] VX-702 对 ERK 或 JNK 没有影响,同时选择性抑制缺血后 p38 MAPK 的激活。与5mg/kg组和赋形剂组相比,50mg/kg组的MI/AAR比率显着较低。 [4]
|
||
| 酶活实验 |
对于半衰期,通过将血小板与 VX-702 (1 μM) 预孵育,可以完全或部分抑制由血小板激动剂(例如凝血酶、SFLLRN、AYPGKF、U46619 和胶原蛋白)引起的血小板活化(IC50 4 至 20 nM)。无论是否存在抗血小板治疗,VX-702 对任何 p38 MAPK 激动剂引起的血小板聚集都没有影响。 VX-702 以剂量依赖性方式抑制 IL-6、IL-1β 和 TNFα 的产生(IC50 值分别为 59、122 和 99 ng/mL)。
全身炎症已被证明是急性冠状动脉综合征(ACS)患者动脉粥样硬化斑块不稳定的一个因素。VX-702是一种新型的p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)抑制剂,目前正在对患有不稳定型心绞痛的ACS患者进行研究,以评估其在经皮冠状动脉介入治疗(PCI)期间的安全性和有效性。使用选择性第二代p38 MAPK抑制剂VX-702检测p38 MAPK在正常个体血小板聚集中的作用。用凝血酶(激活PAR1和PAR4凝血酶受体)、SFLLRN(PAR1)、AYPGKF(PAR4)、胶原蛋白(α2β1和GPVI/FGammaIIR受体)和U46619(TXA(2))治疗血小板导致p38 MAPK的强烈激活。瑞斯托霉素激活GPIb von Willebrand因子受体不会刺激p38 MAPK。用1微米VX-702预处理血小板完全抑制了凝血酶、SFLLRN、AYPGKF、U46619和胶原蛋白对p38 MAPK的激活。在有或没有阿司匹林、肝素或apyrase的情况下,VX-702对任何激动剂诱导的血小板聚集没有影响。据推测,p38 MAPK的一个潜在作用是激活磷脂酶a(2)(cPLA(2)),磷脂酶a催化花生四烯酸的形成,导致血栓素的产生。有趣的是,我们显示了p38 MAPK抑制与阿司匹林抑制对胶原诱导的血小板聚集的对比作用。阿司匹林阻断TXA2的产生会显著抑制胶原蛋白的活化。然而,VX-702对胶原介导的血小板聚集没有影响,这表明阻断p38 MAPK不会影响人血小板中血栓素的产生。因此,与阿司匹林阻断血小板中血栓素的产生不同,p38 MAPK抑制剂如VX-702不会显著影响血小板功能,也不会导致治疗患者出血副作用的风险增加。 [1] |
||
| 细胞实验 |
VX-702 在离体灌注大鼠肾 (IPRK) 模型中给药,剂量范围为 100 至 600 ng/mL,呈线性排泄,清除率数据与肾脏的净重吸收一致。肾脏有机阴离子和有机阳离子转运系统也显示不使用 VX-702 作为底物。
|
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 参考文献 | |||
| 其他信息 |
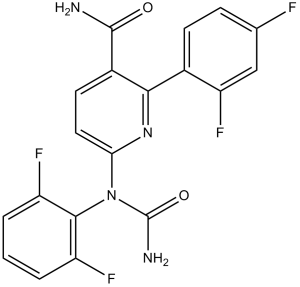
6-(N-carbamoyl-2,6-difluoroanilino)-2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-3-pyridinecarboxamide is a phenylpyridine.
VX-702 is a small molecule investigational oral anti-cytokine therapy for treatment of inflammatory diseases, specifically rheumatoid arthritis (RA). It acts as a p38 MAP kinase inhibitor. In the future, VX-702 may be investigated for combination with methotrexate, a commonly used therapy for RA. Drug Indication Investigated for use/treatment in coronary artery disease, inflammatory disorders (unspecified), and rheumatoid arthritis. Mechanism of Action This p38 MAP kinase inhibitor effectively inhibits LPS-stimulated TNF|[alpha]|, IL-6 and IL-1|[beta]| production. Pharmacodynamics VX-703 is an anti-cytokine therapy in which p38 MAP kinase inhibitor effectively inhibits LPS-stimulated TNF|[alpha]|, IL-6 and IL-1|[beta]| production. Systemic inflammation has been shown to be a contributing factor to the instability of atherosclerotic plaques in patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS). VX-702, a novel p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) inhibitor, is currently under investigation in ACS patients with unstable angina to evaluate its safety and efficacy during percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). The role of p38 MAPK in platelet aggregation of normal individuals was examined using the selective second generation p38 MAPK inhibitor VX-702. Treatment of platelets with thrombin (activates PAR1 and PAR4 thrombin receptors), SFLLRN (PAR1), AYPGKF (PAR4), collagen (alpha2beta1 and GPVI/FCgammaIIR receptors) and U46619 (TXA(2)) resulted in strong activation of p38 MAPK. Activation of the GPIb von Willebrand factor receptor with ristocetin did not stimulate p38 MAPK. Pre-treatment of platelets with 1 microM VX-702 completely inhibited activation of p38 MAPK by thrombin, SFLLRN, AYPGKF, U46619, and collagen. There was no effect of VX-702 on platelet aggregation induced by any of the agonists in the presence or absence of aspirin, heparin or apyrase. It has been postulated that a potential role of p38 MAPK is to activate phospholipase A(2) (cPLA(2)) which catalyses formation of arachidonic acid leading to production of thromboxane. Interestingly, we show contrasting effects of p38 MAPK inhibition as compared to aspirin inhibition on platelet aggregation in response to collagen. Blockade of TXA(2) production by aspirin results in significant inhibition of collagen activation. However,VX-702 has no effect on collagen-mediated platelet aggregation, suggesting that blocking p38 MAPK does not effect thromboxane production in human platelets. Therefore, unlike aspirin blockade of thromboxane production in platelets, p38 MAPK inhibitors such as VX-702 do not significantly affect platelet function and would not be expected to contribute to an elevated risk of bleeding side-effects in treated patients.[1] |
| 分子式 |
C19H12F4N4O2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
404.3
|
|
| 精确质量 |
404.089
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 56.44; H, 2.99; F, 18.80; N, 13.86; O, 7.91
|
|
| CAS号 |
745833-23-2
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
10341154
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.5±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
555.2±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
289.6±32.9 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.629
|
|
| LogP |
0.76
|
|
| tPSA |
102.31
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
29
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
603
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
FC1C([H])=C(C([H])=C([H])C=1C1=C(C(N([H])[H])=O)C([H])=C([H])C(=N1)N(C(N([H])[H])=O)C1C(=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C=1F)F)F
|
|
| InChi Key |
FYSRKRZDBHOFAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C19H12F4N4O2/c20-9-4-5-10(14(23)8-9)16-11(18(24)28)6-7-15(26-16)27(19(25)29)17-12(21)2-1-3-13(17)22/h1-8H,(H2,24,28)(H2,25,29)
|
|
| 化学名 |
6-(N-carbamoyl-2,6-difluoroanilino)-2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)pyridine-3-carboxamide
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.18 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.18 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液添加到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: 30% PEG400+0.5% Tween80+5% propylene glycol: 30mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4734 mL | 12.3671 mL | 24.7341 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4947 mL | 2.4734 mL | 4.9468 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2473 mL | 1.2367 mL | 2.4734 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。