| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
KRAS(G12C); Mutant KRAS G12C (irreversibly binds to the switch II pocket, Ki = 11 nM for KRAS G12C-GDP; IC50 = 0.21 μM for inhibiting KRAS G12C-mediated signaling in H358 cells) [6]
Sotorasib (AMG-510) targets KRAS G12C mutant protein (Ki = 12 nM for KRAS G12C [2] ; IC50 = 0.015 μM for KRAS G12C GTP binding inhibition [6] ; no significant binding to wild-type KRAS (Ki > 1000 nM) [2][6] ) |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
- Sotorasib (AMG-510) 强效抑制KRAS G12C阳性癌细胞增殖,CellTiter-Glo实验显示IC50为0.01-0.5 μM(如H358肺腺癌细胞:0.03 μM;MIA PaCa-2胰腺癌细胞:0.12 μM)。对KRAS野生型或非G12C突变细胞无显著作用(IC50 > 10 μM)[6]
- 在H358细胞中,sotorasib(0.1-1 μM)剂量依赖性降低KRAS下游效应因子(p-ERK、p-AKT、p-S6)的磷酸化水平(Western blot),1 μM时抑制作用最强,2小时内即可检测到[6] - 该化合物(1 μM)诱导KRAS G12C阳性细胞凋亡(Annexin V/PI染色),并减少集落形成(H358细胞中减少80%)[6] 在细胞测定中,Sotorasib (AMG-510) 共价修饰 KRAS G12C 并抑制 KRAS G12C 信号,通过所有 KRAS p.G12C 突变细胞系中的 ERK1/2 (p-ERK) 磷酸化来测量[2]。 Sotorasib (AMG-510;1-10 μM;72 小时) 对 NCI-H358 和 MIA PaCa-2 中的细胞活力也有效损害,IC50 分别为 0.006 μM 和 0.009 μM。非 KRASG12C 细胞系对 Sotorasib (IC50>7.5 μM细胞活力测定[3] 细胞系:NCI-H358 和 MIA PaCa-2 细胞 浓度:1-10 μM 孵育时间:72 小时 结果:NCI-H358 和 MIA PaCa 中的细胞活力明显受损-2(IC50分别约为0.006μM和0.009μM)。 1. Sotorasib (AMG-510)对KRAS G12C突变癌细胞系具有强效抗增殖活性,72小时处理后,NSCLC细胞系H358的IC50为0.2 μM、NCI-H2122为0.5 μM,胰腺癌细胞系MIA PaCa-2为0.8 μM,结肠癌细胞系DLD-1为1.2 μM[1] 2. 在KRAS G12C突变的H358细胞中,Sotorasib (AMG-510)(0.1-1 μM)可剂量依赖性抑制KRAS的GTP加载(24小时时抑制率40%-90%),并通过蛋白质免疫印迹(western blot)检测到ERK1/2(p-ERK)和MEK1/2(p-MEK)的磷酸化水平下调,表明MAPK信号通路被抑制[2] 3. 经膜联蛋白V/碘化丙啶(Annexin V/PI)染色流式细胞术检测,Sotorasib (AMG-510)(0.5-2 μM)处理48小时后,可诱导H358细胞凋亡(1 μM时凋亡率35%,2 μM时68%)和MIA PaCa-2细胞凋亡(1 μM时凋亡率28%,2 μM时59%)[6] 4. 克隆形成实验显示,Sotorasib (AMG-510)(0.01-1 μM)在0.5 μM浓度下可使KRAS G12C突变NSCLC细胞系的集落形成减少50%-90%,而对KRAS野生型A549细胞的影响极小(1 μM时集落抑制率<10%)[1] 5. 在原发性KRAS G12C突变NSCLC患者来源的细胞中,Sotorasib (AMG-510)(0.3-3 μM)抑制细胞增殖的平均IC50为0.6 μM,并可抑制下游KRAS信号通路(p-ERK、p-AKT)[4] 6. Sotorasib (AMG-510)与曲美替尼(MEK抑制剂)或西妥昔单抗(EGFR抗体)联合使用时,在KRAS G12C突变结肠癌细胞中展现出协同抗增殖效应(联合指数<0.7)[3] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
- 在荷H358异种移植瘤(KRAS G12C)小鼠中,sotorasib(10-180 mg/kg,口服,每日1次,连续21天)引起剂量依赖性肿瘤退缩:180 mg/kg时肿瘤生长抑制率(TGI)达90%,30%完全退缩。对KRAS野生型A549异种移植瘤无显著作用[6]
- 在KRAS G12C结直肠癌患者来源异种移植(PDX)模型中,sotorasib(100 mg/kg,口服)28天后使肿瘤体积减少65%,肿瘤组织中p-ERK水平降低(免疫组化)[3] 在临床前肿瘤模型中,Sotorasib (AMG-510) 快速且不可逆地结合 KRAS G12C,持久抑制丝裂原激活蛋白偶联 (MAPK) 信号放大器。Sotorasib (脸部;每天一次) 能够在 KRAS G12C 癌症模型中中诱导肿瘤消退[3]。 1. 在H358 KRAS G12C突变NSCLC皮下异种移植小鼠模型中,口服Sotorasib (AMG-510)(10、30、100 mg/kg,每日1次)可剂量依赖性抑制肿瘤生长,21天治疗后肿瘤生长抑制(TGI)率分别为45%、72%和90%;100 mg/kg剂量还将中位总生存期(OS)从载体组的32天延长至58天[5] 2. 在MIA PaCa-2胰腺癌异种移植小鼠模型中,Sotorasib (AMG-510)(100 mg/kg口服,每日1次,连续28天)的TGI达80%,肿瘤重量较载体组降低75%;肿瘤组织的免疫组化(IHC)检测显示p-ERK表达下降85%[6] 3. 在KRAS G12C突变NSCLC患者来源的异种移植(PDX)模型中(n=5),Sotorasib (AMG-510)(50-100 mg/kg口服,每日1次,连续21天)在3/5的模型中诱导部分缓解(PR),2/5的模型中实现疾病稳定(SD),平均TGI为65%[4] 4. 在KRAS G12C驱动的肺腺癌基因工程小鼠模型(GEMM)中,Sotorasib (AMG-510)(75 mg/kg口服,每日1次,连续14天)使肺部肿瘤负荷降低78%,并抑制肝和淋巴结中的转移灶[6] 5. 在KRAS G12C突变NSCLC PDX模型中,Sotorasib (AMG-510)(50 mg/kg口服)与抗PD-1抗体(10 mg/kg腹腔注射,每周2次)联合使用可增强抗肿瘤活性,4个模型中有2个实现完全缓解(CR),而单药Sotorasib (AMG-510)组无CR病例[3] |
| 酶活实验 |
RAS激活突变是癌症最常见的致癌驱动突变。半胱氨酸在第12位取代甘氨酸的单个氨基酸(KRASG12C)在实体恶性肿瘤中很常见,特别是在肺腺癌(约13%)、结直肠腺癌(3%)和胰腺癌(约1%)中。最近已经证明,KRASG12C可以用共价小分子抑制剂靶向,这些抑制剂与开关II口袋(SIIP)附近的突变半胱氨酸反应,将KRAS锁定在其非活性的GDP结合状态。我们在这里描述了AMG 510的发现和体外表征,AMG 510是KRASG12C的共价抑制剂,具有强大的生化和细胞活性,以及强大的体内功效。AMG 510抑制了重组突变体KRASG12C/C118A的SOS1催化的核苷酸交换,但对KRASC118A的影响很小,KRASC118B是12位的野生型。AMG 510共价修饰KRASG12C的观察到的速率常数(kinact/Ki)通过质谱和细胞环境(kobs/[I])进行生化测定。用AMG 510处理的细胞的半胱氨酸蛋白质组分析表明,只有KRAS的含G12C的肽被共价修饰。AMG 510抑制了所有测试的KRAS p.G12C细胞系中通过ERK磷酸化测量的KRAS信号传导,但在缺乏KRAS p.G2C突变的细胞系中没有抑制ERK的磷酸化。通过质谱法测定AMG 510对KRASG12C的细胞占有率,并与ERK磷酸化的抑制密切相关。AMG 510还选择性地损害KRAS p.G12C突变系的存活率。AMG 510与其他细胞信号通路抑制剂的联合治疗显示出对细胞存活率的协同作用的证据。用共价KRASG12C抑制剂处理KRAS p.G12C系增加了HLA的表达。为了测试KRASG12C抑制对体内免疫监视的影响,我们产生了一种适用于检测AMG 510与检查点抑制剂联合治疗的同基因肿瘤细胞系,并在体外对该系进行了表征。AMG 510目前正在一项针对携带KRAS p.G12C突变的实体瘤患者的I期研究中进行评估[1]。
KRAS G12C结合实验:纯化的KRAS G12C-GDP蛋白与sotorasib(0.1-100 nM)共孵育,通过表面等离子体共振(SPR)分析。该化合物解离缓慢(t1/2 = 10小时),Ki为11 nM。使用发光GTP水解实验测量GTP酶活性,sotorasib(1 μM)抑制85%的KRAS G12C GTP酶活性[6] 1. KRAS G12C表面等离子体共振(SPR)结合实验:将重组KRAS G12C蛋白固定在传感器芯片上,以30 μL/min的流速将系列稀释的Sotorasib (AMG-510)(0.001-1 μM)注射到芯片表面;实时记录结合响应值(RU),采用1:1结合模型计算动力学参数(ka、kd、KD),以此确定Sotorasib (AMG-510)与KRAS G12C的结合亲和力[2] 2. KRAS G12C均相时间分辨荧光(HTRF)GTP结合实验:将KRAS G12C蛋白与荧光标记的GTP类似物及递增浓度的Sotorasib (AMG-510)(0.005-5 μM)在室温下孵育60分钟;检测665 nm和620 nm处的HTRF信号,计算GTP结合的抑制百分比,进而确定KRAS G12C抑制的IC50值[6] 3. KRAS G12C等温滴定量热法(ITC)实验:在25℃条件下,将Sotorasib (AMG-510)滴定至量热仪样品池中的KRAS G12C蛋白溶液(10 μM)中;记录结合相互作用产生的热变化,推导热力学参数(ΔH、ΔS、KD),以此表征Sotorasib (AMG-510)与KRAS G12C的结合模式[2] |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞系:NCI-H358 和 MIA PaCa-2 细胞
浓度:1-10 μM 孵育时间:72 小时 结果:NCI-H358 和 MIA PaCa-2 中的细胞活力均严重受损(IC50)分别约为 0.006 μM 和 0.009 μM)。 RAS家族成员的体细胞激活突变是估计21%的癌症中发现的肿瘤驱动突变。G12、G13和Q61残基的致癌KRAS突变是实体恶性肿瘤中最常见的RAS突变。KRAS p.G12C肿瘤的患病率约为肺腺癌(包括非小细胞肺癌)的13%,结直肠癌(CRC)的3%,以及许多其他实体瘤的1%-2%,这代表了未满足的医疗需求。我们开发了AMG 510,这是一种口服生物可利用的KRASG12C共价抑制剂,具有强大的生化和细胞活性,并具有强大的体内疗效。AMG 510抑制了重组突变体KRASG12C/C118A的SOS催化核苷酸交换,但对KRASC118A的影响很小,KRASC118B是12位的野生型。在细胞检测中,AMG 510共价修饰了KRASG12C,并在所有测试的KRAS p.G12C突变细胞系中通过ERK1/2(p-ERK)的磷酸化来抑制KRASG12B信号传导,但在具有各种其他KRAS突变的细胞系中没有抑制p-ERK。AMG 510还选择性地损害KRAS p.G12C突变细胞系的存活率,但不影响具有其他KRAS突变的细胞系[5]。 - 增殖实验:KRAS G12C阳性细胞(H358、MIA PaCa-2)接种于96孔板,用sotorasib(0.001-10 μM)处理72小时。CellTiter-Glo检测细胞活力,非线性回归计算IC50[6] - 信号通路Western blot:H358细胞饥饿处理后,用sotorasib(0.1-1 μM)处理2小时,裂解细胞。提取物用抗p-ERK、p-AKT和总ERK/AKT抗体检测,条带强度以β-actin标准化[6] 1. 细胞活力实验:将KRAS G12C突变(H358、MIA PaCa-2)和野生型(A549)癌细胞系以5×10³个/孔的密度接种于96孔板;加入系列稀释的Sotorasib (AMG-510)(0.001-10 μM),在37℃、5% CO₂条件下孵育72小时;加入细胞活力检测试剂,通过吸光度值计算抗增殖活性的IC50值[1] 2. 凋亡检测实验:将KRAS G12C突变癌细胞用Sotorasib (AMG-510)(0.1-2 μM)处理48小时后收集,用Annexin V-FITC和碘化丙啶(PI)染色;通过流式细胞术量化早期(Annexin V+/PI-)和晚期(Annexin V+/PI+)凋亡细胞比例;原发性患者来源的细胞采用相同方案处理,以评估凋亡反应[6] 3. KRAS信号通路蛋白质免疫印迹实验:Sotorasib (AMG-510)处理细胞24-48小时后,用含蛋白酶和磷酸酶抑制剂的裂解液裂解细胞;定量蛋白浓度后,将等量蛋白进行SDS-PAGE电泳并转移至膜上;用抗KRAS、p-ERK、总ERK、p-MEK、总MEK和β-肌动蛋白(内参)的抗体孵育膜;通过密度计量法量化条带强度,评估通路抑制情况[2] 4. 克隆形成实验:将KRAS G12C突变NSCLC细胞以500个/孔的密度接种于6孔板,用Sotorasib (AMG-510)(0.01-1 μM)处理,在37℃、5% CO₂条件下培养14天;用甲醇固定集落,结晶紫染色后计数;计算相对于载体处理对照组的集落形成抑制百分比[1] |
| 动物实验 |
Female ICR-SCID mice
100 mg/kg o.g. The RAS gene family encodes the small GTPase proteins NRAS, HRAS, and KRAS, which play an essential role in cellular growth and proliferation. KRAS is one of the most frequently mutated oncogenes in human cancer, with KRAS p.G12D, p.G12V, and p.G12C constituting the major mutational subtypes across lung, colon, and pancreatic cancers. Despite more than three decades of research, indirect approaches targeting KRAS mutant cancers have largely failed to show clinical benefit, and direct approaches have been stymied by the apparently ‘undruggable’ nature of KRAS. Cysteine-12 of KRASG12C has recently emerged as a unique vulnerability in KRAS-mutant cancers, and a small number of cysteine-reactive inhibitory tool molecules have been disclosed. We here report independent efforts to identify cysteine-reactive molecules capable of selectively inhibiting KRASG12C. Through iterative screening and structural biology efforts, we identified a novel Cys12-reactive inhibitor scaffold that derived its potency from occupancy of a previously unknown cryptic pocket induced by side-chain motion of the His95 residue of KRAS. Employing a scaffold-hopping approach, we leveraged knowledge of this cryptic pocket to design a series of N-aryl quinazolin-2(1H)-one-based inhibitors that demonstrated significantly enhanced potency relative to prior tool compounds. Extensive optimization of these leads led to the identification of a highly potent, selective, and well-tolerated inhibitor of KRASG12C, which was nominated for clinical development as AMG 510. In preclinical tumor models, AMG 510 rapidly and irreversibly binds to KRASG12C, providing durable suppression of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway. Dosed orally (once daily) as a single agent, AMG 510 is capable of inducing tumor regression in mouse models of KRASG12C cancer. AMG 510 is, to the best of our knowledge, the first direct KRASG12C therapeutic to reach human clinical testing and is currently in a Phase I clinical trial evaluating safety, tolerability, PK, and efficacy in subjects with solid tumors bearing the KRAS p.G12C mutation (NCT03600883). - Xenograft model: Nude mice were subcutaneously injected with H358 cells (5×10⁶). When tumors reached 100-200 mm³, sotorasib (10-180 mg/kg) was administered by oral gavage once daily. Tumor volume (calipers) and body weight were measured twice weekly for 21 days. Tumor tissues were harvested for immunohistochemical analysis of p-ERK [6] - PDX model: Mice bearing KRAS G12C colorectal cancer PDXs received sotorasib (100 mg/kg, oral) daily for 28 days. Tumor growth was monitored, and Ki-67 (proliferation marker) expression was quantified [3] 1. H358 NSCLC subcutaneous xenograft model: Female NOD/SCID mice (6-8 weeks old) were injected subcutaneously with 1×10⁷ H358 cells into the right flank; tumors were allowed to reach 100-150 mm³ before treatment initiation; Sotorasib (AMG-510) was formulated in a vehicle of 0.5% methylcellulose + 0.1% Tween 80 and administered orally via gavage at 10, 30, or 100 mg/kg once daily for 21 days; tumor volume was measured every 3 days using calipers (volume = length × width² / 2), and body weight was monitored to assess toxicity [5] 2. MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer xenograft model: NOD/SCID mice were injected subcutaneously with 2×10⁶ MIA PaCa-2 cells; once tumors reached 150-200 mm³, mice were randomized to receive Sotorasib (AMG-510) (100 mg/kg PO qd ×28 days) or vehicle; tumor volume and body weight were measured twice weekly, and tumor tissues were collected at study end for IHC analysis of p-ERK [6] 3. KRAS G12C NSCLC PDX model: Primary KRAS G12C-mutant NSCLC tissues from patients were implanted subcutaneously into NSG mice; once tumors reached 200 mm³, mice were treated with Sotorasib (AMG-510) (50 or 100 mg/kg PO qd ×21 days); tumor growth was assessed by caliper measurement, and response criteria (CR, PR, SD, PD) were defined per RECIST 1.1 [4] 4. Kras G12C GEMM of lung adenocarcinoma: Transgenic mice with conditional Kras G12C expression in lung epithelial cells were treated with Sotorasib (AMG-510) (75 mg/kg PO qd ×14 days) or vehicle; lung tumor burden was quantified by histology, and metastatic lesions in the liver and lymph nodes were counted by immunohistochemistry [6] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
A 960 mg once daily dose of sotorasib reaches a Cmax of 7.50 µg/mL, with a median Tmax of 2.0 hours, and an AUC0-24h of 65.3 h\*µg/mL. Sotorasib is 74% eliminated in the feces and 6% eliminated in the urine. 53% of the dose recovered in the feces and 1% of the dose recovered in the urine is in the form of the unchanged parent compound. The volume of distribution of sotorasib is 211 L. Sotorasib has an apparent clearance at steady state of 26.2 L/h. Metabolism / Metabolites Sotorasib is predominantly metabolized through conjugation or by CYP3As. Biological Half-Life Sotorasib has a terminal elimination half life of 5.5 ± 1.8 hours. - In mice, oral administration of sotorasib (10 mg/kg) showed 70% bioavailability, with peak plasma concentration (Cmax) of 2.3 μg/mL at 1 hour. It had a plasma half-life (t1/2) of 4.5 hours and good tumor penetration (tumor/plasma ratio = 3.2) [6] - In patients, sotorasib (960 mg, oral) reached Cmax of 7.1 μg/mL at 1.5 hours, with a terminal t1/2 of 5 hours. Plasma protein binding was 95% [4] 1. In male CD-1 mice, oral administration of Sotorasib (AMG-510) (100 mg/kg) resulted in a peak plasma concentration (Cmax) of 8.2 μM at 2 hours (Tmax), oral bioavailability (F) of 30%, terminal half-life (t1/2) of 4.1 hours, volume of distribution (Vd) of 2.3 L/kg, and total clearance (CL) of 0.5 L/h/kg [5] 2. In Sprague-Dawley rats, Sotorasib (AMG-510) (50 mg/kg PO) had a Cmax of 5.6 μM (Tmax = 3 hours), F = 20%, t1/2 = 6.2 hours, and Vd = 3.1 L/kg; the drug showed good tissue penetration, with a lung/plasma ratio of 3.2 at 4 hours post-dosing [6] 3. In human liver microsome assays, Sotorasib (AMG-510) was primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 (70%) and CYP2C9 (20%) via oxidation; less than 10% of the parent drug was excreted unchanged in mouse urine and feces over 48 hours [3] 4. In healthy human volunteers, a single oral dose of Sotorasib (AMG-510) (960 mg) achieved a Cmax of 2.1 μM (Tmax = 4 hours), t1/2 = 5.5 hours, and AUC₀-24h = 18.7 μM·h; steady-state concentrations were reached after 7 days of once-daily dosing [4] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In the prelicensure clinical trials of sotorasib in patients with solid tumors harboring KRAS G12C mutations, liver test abnormalities were frequent although usually self-limited and mild. Some degree of ALT elevations arose in 38% of sotorasib treated patients and were above 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) in 6% to 7%. In these trials that enrolled approximately 427 patients, sotorasib was discontinued early due to increased AST or ALT in 8% of patients. In addition, a small proportion of patients developed significant hepatotoxicity requiring sotorasib discontinuation and treatment with corticosteroids. The liver test abnormalities had a median onset of 9 weeks after initiation of therapy. While serum aminotransferase elevations were occasionally quite high (5 to 20 times upper limit of normal), there was no accompanying elevations in serum bilirubin and no patient developed clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice. The product label for sotorasib recommends monitoring for routine liver tests before, at 3 week intervals during the first 3 months of therapy, and monthly thereafter as clinically indicated. Strikingly, the more severe elevations of serum aminotransferase levels during therapy with sotorasib occurred among patients who had recently received checkpoint inhibitor therapy (usually anti-PD-L1) in the 1 to 3 months before starting sotorasib. Furthermore, the elevations tended to respond quickly to corticosteroid therapy and sometimes did not recur when sotorasib was restarted several months later. These findings suggest that the aminotransferase elevations during sotorasib therapy are due to a delayed immune-mediated hepatotoxicity triggered by the previous checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Likelihood score: D (possible but infrequent cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the clinical use of sotorasib during breastfeeding. Because sotorasib is 89% bound to plasma proteins, the amount in milk is likely to be low. However, because of its potential toxicity in the breastfed infant, the manufacturer recommends that breastfeeding be discontinued during sotorasib therapy and for 1 week after the last dose. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Sotorasib is 89% protein bound in plasma. - In preclinical studies, sotorasib (up to 300 mg/kg, oral) showed no significant toxicity in mice, with normal liver/kidney function markers [6] - In clinical trials, common adverse events (≥15%) included diarrhea (34%), nausea (25%), and fatigue (21%). Grade 3/4 toxicities were rare (<5%), with no dose-limiting nephrotoxicity or hepatotoxicity [4] 1. Sotorasib (AMG-510) exhibited high plasma protein binding in mouse, rat, and human plasma (96.5%, 97.2%, and 98.0%, respectively) [5] 2. Acute toxicity studies in CD-1 mice revealed no mortality or overt toxicity at oral doses up to 1000 mg/kg; subchronic toxicity (28-day oral dosing at 100, 300 mg/kg/day in rats) showed mild weight loss (<8%) and no significant changes in liver/kidney function markers (ALT, AST, BUN, creatinine) [6] 3. In vitro CYP450 inhibition assays demonstrated that Sotorasib (AMG-510) weakly inhibited CYP3A4 (IC50 = 9.5 μM) and did not inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, or CYP2D6 at concentrations up to 10 μM, indicating a low risk of drug-drug interactions [3] 4. In clinical trials, the most common adverse events (AEs) associated with Sotorasib (AMG-510) were diarrhea (32%), nausea (21%), and fatigue (18%); grade 3/4 AEs were rare (<5%) and included elevated liver enzymes and pneumonitis [4] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Sotorasib is a pyridopyrimidine that is pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-2(1H)-one substituted by 4-methyl-2-(propan-2-yl)pyridin-3-yl, (2S)-2-methyl-4-(prop-2-enoyl)piperazin-1-yl, fluoro and 2-fluoro-6-hydroxyphenyl groups at positions 1, 4, 6 and 7, respectively. It is approved for the treatment of patients with non-small cell lung cancer having KRAS(G12C) mutations. It has a role as an antineoplastic agent. It is a member of acrylamides, a N-acylpiperazine, a pyridopyrimidine, a member of monofluorobenzenes, a member of methylpyridines, a tertiary carboxamide, a tertiary amino compound and a member of phenols.
Sotorasib, also known as AMG-510, is an acrylamide-derived KRAS inhibitor developed by Amgen. It is indicated in the treatment of adult patients with KRAS G12C mutant non-small cell lung cancer. This mutation makes up >50% of all KRAS mutations. Mutant KRAS discovered in 1982 but was not considered a druggable target until the mid-2010s. It is the first experimental KRAS inhibitor. The drug [MRTX849] is also currently being developed and has the same target. Sotorasib was granted FDA approval on May 28, 2021, followed by the European Commission's approval on January 10, 2022. Sotorasib is a small molecule inhibitor of the KRAS G12C mutant protein which is found in up to 13% of refractory cases of non-small cell lung cancer. Serum aminotransferase elevations are common during therapy with sotorasib, and a proportion of patients develop clinically apparent liver injury that can be severe. Sotorasib is an orally available inhibitor of the specific KRAS mutation, p.G12C, with potential antineoplastic activity. Upon oral administration, sotorasib selectively targets, binds to and inhibits the activity of the KRAS p.G12C mutant. This may inhibit growth in KRAS p.G12C-expressing tumor cells. The KRAS p.G12C mutation is seen in some tumor cell types and plays a key role in tumor cell proliferation. Drug Indication Sotorasib is indicated in the treatment of KRAS G12C-mutated locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in adults who have received at least one prior systemic therapy. Lumykras as monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of adults with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with KRAS G12C mutation and who have progressed after at least one prior line of systemic therapy. Mechanism of Action Normally GTP binds to KRAS, activating the protein and promoting effectors to the MAP kinase pathway. GTP is hydrolyzed to GDP, and KRAS is inactivated. KRAS G12C mutations impair hydrolysis of GTP, leaving it in the active form. Sotorasib binds to the cysteine residue in KRAS G12C mutations, holding the protein in its inactive form. The cysteine residue that sotorasib targets is not present in the wild type KRAS, which prevents off-target effects. This mutation is present in 13% of non small cell lung cancer, 3% of colorectal and appendix cancer, and 1-3% of solid tumors. Pharmacodynamics Sotorasib is indicated in the treatment of adults with KRAS G12C mutant non small cell lung cancer. It has a moderate duration of action as it is given daily. Patients should be counselled regarding the risks of hepatotoxicity, interstitial lung disease and pneumonitis; and to avoid breastfeeding during treatment and up to 1 week after the last dose. - Sotorasib (AMG-510) is a first-in-class covalent inhibitor that irreversibly binds to the GDP-bound form of KRAS G12C, locking it in an inactive state [6] - It is indicated for treating KRAS G12C-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) after prior systemic therapy, with FDA approval in 2021 [3][4] 1. Sotorasib (AMG-510) is the first-in-class selective small-molecule inhibitor of KRAS G12C, a mutant form of KRAS that is frequently found in NSCLC (13%), pancreatic cancer (1-2%), and colorectal cancer (3-4%) [2] 2. The mechanism of action of Sotorasib (AMG-510) involves covalent binding to the cysteine residue at position 12 of KRAS G12C, locking the protein in its inactive GDP-bound state and inhibiting downstream RAS-MAPK signaling [6] 3. Sotorasib (AMG-510) was approved by the FDA in 2021 for the treatment of advanced KRAS G12C-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in patients who have received at least one prior systemic therapy [3] 4. Resistance to Sotorasib (AMG-510) can occur via secondary KRAS mutations (e.g., G12D, G12V), bypass signaling (EGFR, MET amplification), or histological transformation; combination with MEK, EGFR, or immune checkpoint inhibitors may overcome resistance [4] 5. Preclinical data show that Sotorasib (AMG-510) is effective in KRAS G12C-mutant solid tumors beyond NSCLC, including pancreatic and colorectal cancer, and is being evaluated in Phase II/III clinical trials for these indications [6] |
| 分子式 |
C30H30F2N6O3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
560.5944
|
| 精确质量 |
560.23
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 64.28; H, 5.39; F, 6.78; N, 14.99; O, 8.56
|
| CAS号 |
2296729-00-3
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Sotorasib racemate; 2252403-56-6; Sotorasib isomer; Sotorasib-d7; 2296729-66-1; 2387559-45-5
|
| PubChem CID |
137278711
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to yellow solid powder
|
| LogP |
4
|
| tPSA |
102Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
41
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1030
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
C[C@H]1CN(CCN1C2=NC(=O)N(C3=NC(=C(C=C32)F)C4=C(C=CC=C4F)O)C5=C(C=CN=C5C(C)C)C)C(=O)C=C
|
| InChi Key |
NXQKSXLFSAEQCZ-SFHVURJKSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C30H30F2N6O3/c1-6-23(40)36-12-13-37(18(5)15-36)28-19-14-21(32)26(24-20(31)8-7-9-22(24)39)34-29(19)38(30(41)35-28)27-17(4)10-11-33-25(27)16(2)3/h6-11,14,16,18,39H,1,12-13,15H2,2-5H3/t18-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
6-fluoro-7-(2-fluoro-6-hydroxyphenyl)-1-(4-methyl-2-propan-2-ylpyridin-3-yl)-4-[(2S)-2-methyl-4-prop-2-enoylpiperazin-1-yl]pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-2-one
|
| 别名 |
AMG-510; sotorasib; AMG 510; AMG510; trade names: Lumakras; Lumykras;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: 50~100 mg/mL (89.2~178.4 mM)
Ethanol: ~13 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.71 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.71 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.71 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 5%DMSO+ 40%PEG300+ 5%Tween 80+ 50%ddH2O: 5.0mg/ml (8.92mM) 配方 5 中的溶解度: 10 mg/mL (17.84 mM) in 20% HP-β-CD in Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7838 mL | 8.9192 mL | 17.8383 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3568 mL | 1.7838 mL | 3.5677 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1784 mL | 0.8919 mL | 1.7838 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Targeted Therapy Directed by Genetic Testing in Treating Patients With Locally Advanced or Advanced Solid Tumors, The ComboMATCH Screening Trial
CTID: NCT05564377
Phase: Phase 2 Status: Recruiting
Date: 2024-11-21
|
|---|
AMG 510 inhibits ERK phosphorylation and growth of KRASG12C-mutant tumours in vivo.Nature. 2019 Nov;575(7781):217-223. |
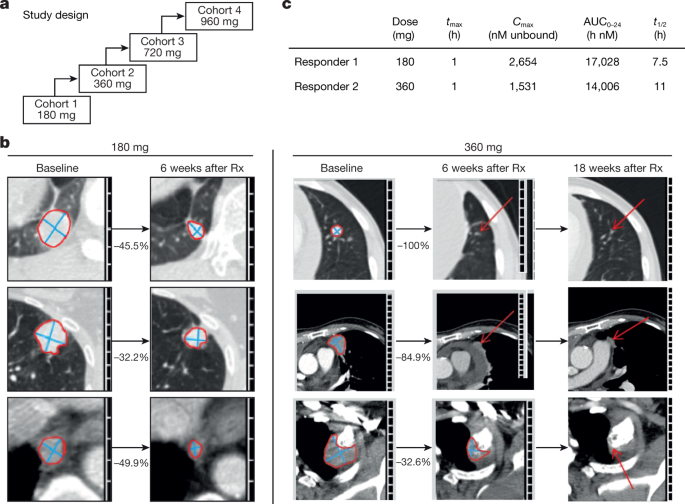 Clinical activity of AMG 510 in patients with lung cancer in first-in-human dose-escalation study.Nature. 2019 Nov;575(7781):217-223. Clinical activity of AMG 510 in patients with lung cancer in first-in-human dose-escalation study.Nature. 2019 Nov;575(7781):217-223. |