| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Abl1 (IC50 = 2.8 nM); TrkA (IC50 = 6 nM); Abl1 (IC50 = 2.8 nM); TrkB (IC50 = 9 nM); Tie-2 (IC50 = 22 nM); Aurora B (IC50 = 98 nM)
BCR–ABL1 (binding to the myristoyl pocket) [2] ABL1 (binding to the myristoyl pocket,) [3] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:Asciminib 是一种有效的选择性 BCR-ABL 抑制剂,在大多数突变(包括 T315I)中保持活性,具有独特的变构作用机制。 Asciminib 结合在野生型 ABL 中通常由肉豆蔻酰基占据的调节位点,并通过与催化位点抑制剂不同的机制抑制 ABL 激酶活性。它与 BCR-ABL 激酶结构域上的口袋结合,该结构域通常由 ABL1 的肉豆蔻酰化 N 末端占据。与 BCR 融合后,这种用于自动调节 ABL1 活性的肉豆蔻酰化 N 末端就会丢失。 Asciminib 通过占据其空的结合位点来在功能上模拟肉豆蔻酰化 N 末端的作用,并恢复激酶活性的负调节。 Asciminib 选择性抑制慢性粒细胞白血病 (CML) 和 Ph+ ALL 细胞的生长,效力范围为 1-10 nM,而 BCR-ABL 阴性细胞系在浓度高 1000 倍时仍不受影响。 NMR 和生物物理研究证实,Asciminib 能有效结合(解离常数 (Kd) = 0.5-0.8 nM)并选择性地结合 ABL1 的肉豆蔻酰口袋,并诱导无活性的 C 末端螺旋构象。 Asciminib 对包括 SRC 在内的 60 多种激酶缺乏活性,并且对 G 蛋白偶联受体、离子通道、核受体和转运蛋白同样没有活性。激酶测定:Asciminib 是一种有效的选择性 BCR-ABL1 变构抑制剂,解离常数 (Kd) 为 0.5-0.8 nM,对 ABL1 的肉豆蔻酰口袋具有选择性。细胞测定:用一系列浓度的 ABL001、尼洛替尼或达沙替尼处理 KCL-22 细胞 1 小时。收获细胞,产生蛋白质裂解物并使用蛋白质印迹进行分析。
Asciminib(ABL001)是一种强效且选择性的BCR–ABL1变构抑制剂,可结合ABL1的豆蔻酰口袋并诱导激酶形成失活构象[2][3] 在表达BCR–ABL1的Ba/F3细胞48小时增殖实验中,Asciminib在一定剂量范围内抑制细胞增殖,细胞 potency与第二代催化抑制剂尼洛替尼相近;实验采用Britelite荧光素酶检测法,分为有或无IL-3组,每组设四次重复[3] 72小时生长实验中,KCL-22细胞对Asciminib、尼洛替尼和达沙替尼均表现出敏感性,每种化合物设两次重复测试[3] KCL-22细胞与Asciminib孵育1小时(不同浓度)后,蛋白质印迹法检测显示STAT5(Tyr694)、BCR–ABL1(Tyr245)和CRKL(Tyr207)的磷酸化水平降低,而这些蛋白的总水平及内参GAPDH保持稳定[3] 协同作用研究表明,Asciminib与伊马替尼、尼洛替尼或达沙替尼联合使用可抑制KCL-22细胞生长;细胞与化合物组合孵育72小时后,以DMSO处理组为对照,检测生长水平[3] 表达BCR–ABL1变异体(Ala337Val和Thr315Ile)的KCL-22细胞克隆对Asciminib的敏感性与尼洛替尼不同;Asciminib对部分对催化抑制剂耐药的变异体仍保留活性[3] 诱变和基因条形码实验显示,Asciminib的耐药谱与催化位点抑制剂不同,Asciminib和尼洛替尼之间无共同耐药突变[2][3] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在 KCL-22 小鼠异种移植模型中,Asciminib 显示出有效的抗肿瘤活性,观察到肿瘤完全消退,并且与 pSTAT5 抑制具有明显的剂量依赖性相关性。阿西米尼在所有物种中具有中等的口服吸收、分布体积和半衰期。它作为单一药物可诱导临床抗肿瘤活性,并且迄今为止在经过大量预先治疗的慢性粒细胞白血病患者亚组中具有良好的耐受性。至于Asciminib的药代动力学、药效学和功效,小鼠、大鼠和狗单次静脉注射1mg/kg、2mg/kg和1mg/kg后的CL(清除率)分别为12、16和6mL/min/kg , 分别。在小鼠和狗中,单次静脉注射 1 mg/kg 剂量后,T1/2 期限为 1.1 和 3.7 小时。在大鼠中,T1/2 期限是单次静脉注射 2 mg/kg 剂量后的 2.7 小时。当以30 mg/kg口服剂量给药时,小鼠和大鼠中阿西米尼的口服生物利用度分别为35%和27%,而在狗中,阿西米尼的口服生物利用度为111%(15毫克/千克,口服)。
在KCL-22异种移植模型中,单次口服给予Asciminib(3-30 mg/kg)后,肿瘤细针穿刺样本中的pSTAT5(Tyr694)水平降低,采用MSD法检测(每组两次重复,均值±标准差),pSTAT5水平以给药前(t=0)为基准计算百分比[3] Asciminib以3-30 mg/kg的剂量每日两次(BID)或每日一次(QD)给药时,在KCL-22异种移植模型中表现出抗肿瘤活性,持续监测肿瘤体积(均值±标准误)[3] 在三种患者来源的ALL系统性异种移植模型(ALL-7015、AL-7119、AL-7155)中,Asciminib(7.5 mg/kg BID或30 mg/kg BID,给药3周)可降低血液中每活细胞中CD45⁺细胞的百分比(通过流式细胞术监测),设PBS对照组;数据为均值±标准误(每组n=6)[3] Asciminib或尼洛替尼单药治疗会导致CML异种移植模型产生获得性耐药,但两者联合使用可实现完全疾病控制,并在停药后根除肿瘤且无复发[2][3] 在KCL-22 Thr315Ile突变体异种移植模型中,Asciminib(3-30 mg/kg BID)表现出疗效,以尼洛替尼(75 mg/kg BID)作为对照;记录肿瘤体积比(T/C)和消退情况(均值±标准误,每组n=7)[3] |
| 酶活实验 |
ABL1生化激酶测定[3]
在Sf21细胞中与YopH共表达产生ABL1 WT (64-515aa)蛋白。细胞离心后重悬于25mM Tris pH 7.0、500 mM NaCl、5%甘油、10 mM咪唑、1x完全蛋白酶抑制剂片、Benzonase (1:10 000 v:v)和1 mM TCEP中。用浆液均质法裂解细胞,离心清除细胞。ABL1 WT (64- 515aa)采用Ni-SepharoseFF柱亲和层析纯化,使用上述重悬浮缓冲液(分别含有10 mM和35mM咪唑)进行两次连续洗涤,并在含有250 mM咪唑的缓冲液中洗脱。将含有ABL1的馏分混合并上载到预平衡的SEC柱上,溶液为25 mM Tris pH 7.0、200 mM NaCl、5%甘油和1 mM TCEP。采用DELFIA®TRF法检测酶活性和化合物抑制作用。反应混合物含有500 nM Biotin-EAIYAAPFAKKK肽,10或2000µM ATP和25 pM ABL1 WT (64-515 aa)酶,反应缓冲液含有50 mM HEPES pH 7.2, 10 mM MgCl2, 2 mM DTT和0.01% Triton-X100。反应在60µL的体积中进行40 min,用20µL 500 mM EDTA(终浓度125 mM)淬火。将50µL的反应液转移到neutroavidin包被的384孔板上,室温下振荡孵育1小时。用100µL/孔TBST缓冲液洗涤后,加入50µL/孔Eu-anti-p-Tyr, 4℃摇瓶孵育过夜。加入50µL/孔DELFIA®增强液,在室温下孵育5分钟。在EnVision上使用时间分辨荧光Ex/Em: 340/615 nm读取板。对于抑制研究,化合物在DMSO中连续稀释,使用16点3倍格式,从5毫米的最高浓度。然后通过声传递系统将系列稀释化合物每孔100 nL转移到Grenier聚丙烯v底384孔分析板上。DMSO终浓度为0.16%,抑制剂终浓度为50µM ~ 3.48E-6µM。每个化合物重复测试,使用GraphPad Prism v6.02基于对照归一化的归一化IC50回归曲线拟合分析抑制剂的剂量响应曲线。[3] Asciminib是BCR-ABL1的强选择性变构抑制剂,解离常数(Kd)为0.5-0.8 nM,对ABL1肉豆荚基口袋具有选择性。 采用核磁共振(NMR)化学位移实验确定Asciminib与ABL1的结合位点[3] 利用Val525的共振信号进行核磁共振构象实验,监测有无Asciminib存在时螺旋I的“弯曲”状态[3] 通过等温滴定量热法(ITC)测定Asciminib与ABL1的结合亲和力(Ka)[3] 开展生化实验评估Asciminib对BCR–ABL1激酶活性的抑制作用,重点关注其与催化位点抑制剂不同的变构机制[2][3] |
| 细胞实验 |
Ba/F3增殖试验[3]
对于每个细胞系,细胞密度调整为50 000个细胞/ml, 384孔检测板每孔加50ul(2500个细胞)。将测试化合物以10mM浓度的二甲基亚砜重悬。在384孔板中使用Janus液体分配器对每种化合物用DMSO进行连续三倍稀释。2nL化合物通过ATS-100 (EDC)的声传递以50µL的体积递送到含有2500个细胞的检测板中。细胞与化合物在37°C加5%二氧化碳的潮湿环境中孵育48小时。根据制造商的说明配制Britelite plus溶液,每孔加入25µl。培养皿孵育7分钟,在EnVision多模读板仪上检测发光。发光的程度与每孔中细胞的数量有关。因此,可以计算出每种抑制剂浓度的影响,并生成IC50。 将Ba/F3细胞暴露于浓度范围(0-10,000 nM)的阿西米尼48小时。Britelite荧光素酶检测法用于定量细胞的增殖。 在表达BCR–ABL1的Ba/F3细胞中进行48小时增殖实验,采用Britelite荧光素酶检测法(有或无IL-3),测试不同剂量范围的Asciminib和尼洛替尼(四次重复)[3] 在KCL-22细胞(亲本及表达BCR–ABL1 Ala337Val/Thr315Ile变异体的克隆)中进行72小时生长实验,评估对Asciminib、尼洛替尼和达沙替尼的敏感性(两次重复测试)[3] 用不同浓度的Asciminib处理KCL-22细胞1小时,通过蛋白质印迹法检测STAT5(Tyr694)、BCR–ABL1(Tyr245)、CRKL(Tyr207)的总蛋白和磷酸化蛋白水平,以及GAPDH[3] 将Asciminib与伊马替尼/尼洛替尼/达沙替尼按不同剂量组合孵育KCL-22细胞72小时,以DMSO为对照,检测细胞生长水平,开展协同作用研究[3] 采用基因条形码技术分析经Asciminib或催化抑制剂处理后细胞的克隆动态和耐药突变[3] |
| 动物实验 |
Mice: Asciminib efficacy is measured using FACS monitoring of the percentage of CD45+ cells per live cell in blood samples obtained at different times following dosing with either 7.5 mg/kg BID (group 2) or 30 mg/kg BID (group 3) asciminib for three weeks in three patient-derived ALL systemic xenograft models (ALL-7015, AL-7119, and AL-7155).
ABL001 (free base, solid dispersion form) was suspended in phosphate-buffered saline. Dosing solutions were prepared fresh every 3-4 days for dosing. ABL001 (free base, solution form) was formulated in 30% PEG 300, 6% Solutol HS15 in an acidic buffered solution. Dosing solutions were freshly prepared weekly for dosing. Efficacy studies [3] For efficacy studies in subcutaneous KCL-22 xenograft model, mice bearing tumors of 100- 300mm3 were randomized into treatment groups (n=6 per group) for daily compound treatment. Body weight and tumor volume were recorded twice weekly for the duration of each study. In ABL001 dose-response studies, studies were terminated when vehicle-treated animals reached 1500mm3 mean tumor volume. In ABL001 and nilotinib combination efficacy study, select randomized groups animals were dosed daily with either ABL001 or nilotinib as single agents until tumor relapse (tumor volume >500mm3), then switched to the other agent continuously until second relapse. Animals are terminated as their final tumor volume reached >600mm3 . Another randomized group received combination of both ABL001 and nilotinib daily treatment then continued monitoring post-treatment cessation. For efficacy studies in systemic primary Ph+ ALL xenograft models, mice were injected intravenously with 5x106 ALL cells. Blood was sampled weekly from tail snip to monitor tumor burden, and engrafted mice with >10% human CD45+ cells were randomized into treatment groups for compound treatment (n=6 mice per group). Pharmacokinetics (PK) / Pharmacodynamics (PD) studies [3] Baseline tumor PD samples were collected from KCL-22 xenografts by fine needle biopsy before drug treatment. Animals received a single oral dose of ABL001 at 7.5 – 30 mg/kg. Blood was collected by serial tail bleed at designated time points (1-20h) for plasma PK analyses, and matching tumor PD samples were collected by fine needle biopsy at the same timepoints. Establish KCL-22 (parental and Thr315Ile mutant) xenograft models in mice; administer Asciminib orally at 3–30 mg/kg (BID/QD) or nilotinib at 75 mg/kg BID, monitor tumor volume over time, and calculate T/C ratios and regression [3] Set up patient-derived ALL systemic xenograft models (ALL-7015, AL-7119, AL-7155) in mice; assign to control (PBS) or Asciminib groups (7.5 mg/kg BID or 30 mg/kg BID), treat for 3 weeks, and collect blood samples at varying time points for FACS analysis of CD45⁺ cells [3] For pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic studies, administer a single oral dose of Asciminib (3–30 mg/kg) to mice bearing KCL-22 xenografts; collect plasma and tumor fine needle aspirates to measure drug concentrations and pSTAT5 (Tyr694) levels [3] Assess the tolerability of Asciminib in mice by dosing BID at increasing concentrations, monitoring body weight 2–3 times per week (mean ± s.e.m., n=5 per group) [3] Establish CML xenograft models; treat with single-agent Asciminib (30 mg/kg BID), nilotinib (75 mg/kg BID), or their combination, stop dosing after achieving tumor control, and monitor for recurrence [3] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
The median Tmax of asciminib following oral administration is 2.5 hours. At a dose of 80mg once daily, the steady-state Cmax and AUCtau were 1781 ng/mL and 15112 ng.h/mL, respectively. At a dose of 40mg twice daily, the steady-state Cmax and AUCtau were 793 ng/mL and 5262 ng.h/mL, respectively. At a dose of 200mg twice daily (for treatment of T315I mutants), the steady-state Cmax and AUCtau were 5642 ng/mL and 37547 ng.h/mL, respectively. As compared to the fasted state, the co-administration of asciminib with a high-fat meal decreased the AUC and Cmax by 62% and 68%, respectively, and its co-administration with a low-fat meal decreased the AUC and Cmax by 30% and 35%, respectively. Asciminib is eliminated via biliary secretion facilitated by breast cancer-resistant protein (BCRP) transporters. Following oral administration, approximately 80% and 11% of an asciminib dose was recovered in the feces and urine, respectively. Unchanged parent drug accounted for 57% of drug material recovered in the feces and 2.5% in the urine. At steady-state, the apparent volume of distribution of asciminib is 151 L. The total apparent clearance of asciminib is 6.7 L/h at a total daily dose of 80mg and 4.1 L/h at a dose of 200mg twice daily. Metabolism / Metabolites Asciminib is negligibly metabolized, with unchanged parent drug comprising the main drug component in plasma (~93%) and following excretion (~57% in feces). The main circulating metabolites are M30.5, M44, and M29.5, accounting for approximately 5%, 2%, and 0.4% of the total administered dose, respectively. The oxidative metabolism of asciminib is mediated by CYP3A4, and the glucuronidation of asciminib is mediated by UGT2B7 and UGT2B17. Biological Half-Life The terminal elimination half-life asciminib is 5.5 hours when administered at 40mg twice daily and 9.0 hours when administered at 200mg twice daily. In mouse, rat, and dog, Asciminib shows oral bioavailability (BA), with pharmacokinetic parameters including AUC (area under the curve), CL (clearance), Cₘₐₓ (maximum concentration), t₁/₂term (terminal half-life), Tₘₐₓ (time at maximum concentration), and Vss (volume of distribution) after single intravenous (IV) or oral (PO) dosing [3] After single oral administration in mice, Asciminib achieves detectable plasma concentrations, with drug levels correlating with pharmacodynamic effects (pSTAT5 inhibition) in xenografts [3] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In the prelicensure clinical trials of asciminib in patients with refractory and extensively treated CML, ALT elevations arose in 13% of patients but were usually self-limited and mild. ALT elevations above 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) were uncommon, being found in 3% of treated patients. The ALT elevations were typically transient and rarely required dose interruption or modification. In the open label and controlled trials supporting the approval of asciminib, there were no instances of clinically apparent liver injury, hepatic failure or deaths from liver injury. Furthermore, patients with aminotransferase elevations during therapy with first and second line BCR-ABL1 inhibitors did not have an increased rate of such elevations during asciminib therapy. Since its approval in the United States and Europe, there have been no reported cases of clinically apparent liver injury associated with asciminib therapy. Likelihood score: E* (unproven but suspected rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Protein Binding _In vitro_, asciminib is 97% bound to plasma proteins, although the specific protein(s) to which it binds are unclear. In mouse tolerability studies, Asciminib dosed BID at increasing concentrations does not cause significant body weight loss, indicating acceptable safety within tested dose ranges [3] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Asciminib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) used in the treatment of chronic-phase Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia (Ph+ CML). More specifically, it is an inhibitor of the ABL1 kinase activity of the BCR-ABL1 fusion protein which serves as a driver of CML proliferation in most patients with the disease. It has also shown benefit in Ph+ CML with the T315I mutation, which produces a mutant BCR-ABL1 which is typically treatment-resistant as compared to wild-type BCR-ABL1. Existing inhibitors of ABL compete at the ATP binding sites of these proteins and can be classified into those that target the active conformation of the kinase domain ([dasatinib], [bosutinib]) and those that target the inactive kinase domain ([imatinib], [nilotinib], [ponatinib]). Asciminib is unique in that it acts as an allosteric inhibitor, binding at the myristoyl pocket of the BCR-ABL1 protein and locking it into an inactive conformation. Asciminib received FDA approval on October 29, 2021 (Scemblix, Novartis AG).
Asciminib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that specifically targets myristoyl pocket of ABL1 and is used to treat refractory forms of Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myelocytic leukemia. Serum aminotransferase elevations occur in a proportion of patients treated with asciminib, but episodes of clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice have not been reported with its use. Asciminib is an orally bioavailable, allosteric Bcr-Abl1 tyrosine kinase inhibitor, with antineoplastic activity. Upon administration, asciminib targets and binds to the myristoyl pocket of the Bcr-Abl1 fusion protein at a location that is distinct from the ATP-binding domain, thereby inhibiting the activity of both wild-type Bcr-Abl and certain mutation forms, including the T315I mutation. This binding results in the inhibition of Bcr-Abl1-mediated proliferation and enhanced apoptosis of Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) hematological malignancies. The Bcr-Abl1 fusion protein tyrosine kinase is an abnormal enzyme produced by leukemia cells that contain the Philadelphia chromosome. See also: Asciminib Hydrochloride (has salt form). Drug Indication Asciminib is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia (Ph+ CML) in chronic phase who have been previously treated with ≥2 tyrosine kinase inhibitors. It is also indicated in the treatment of Ph+ CML in adult patients with the T315I mutation. Scemblix is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukaemia in chronic phase (Ph+ CML CP) previously treated with two or more tyrosine kinase inhibitors (see section 5. 1). Treatment of chronic myeloid leukaemia Mechanism of Action In most patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), progression of the disease is driven primarily by a translocation of the Philadelphia chromosome that creates an oncogenic fusion gene, _BCR-ABL1_, between the _BCR_ and _ABL1_ genes. This fusion gene produces a resultant fusion protein, BCR-ABL1, which exhibits elevated tyrosine kinase and transforming activities that contribute to CML proliferation. Asciminib is an allosteric inhibitor of the BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase. It binds to the myristoyl pocket of the ABL1 portion of the fusion protein and locks it into an inactive conformation, preventing its oncogenic activity. Pharmacodynamics Asciminib exerts its therapeutic activity by inhibiting an oncogenic protein responsible for the proliferation of CML. It may be administered orally once or twice a day depending on the condition being treated. By increasing the total daily dose 5-fold as compared to standard therapy (80mg daily vs. 400mg daily), it can be used to treat Ph+ CML with the T315I mutation, a typically treatment-resistant variant of the disease. As with many other chemotherapeutic agents, asciminib treatment can result in various forms of myelosuppression, including thrombocytopenia and neutropenia. Patients should receive frequent laboratory monitoring throughout therapy and dose adjustments may be required based on the severity of observed effects. Patients may also experience pancreatic and/or cardiovascular toxicity, both of which require frequent monitoring and may require dose adjustments as per prescribing information. Asciminib (formerly ABL001) is an allosteric inhibitor undergoing clinical development for chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph⁺) acute lymphoblastic leukemia [3] Its mechanism of action involves binding to the myristoyl pocket of ABL1, distinct from catalytic site inhibitors (imatinib, nilotinib, dasatinib), enabling dual targeting of BCR–ABL1 [3] Pre-existing clonal populations with resistance to Asciminib do not share resistance with nilotinib, supporting combination therapy to block resistance development [2][3] Asciminib has entered phase I clinical testing, showing safety and promising single-agent activity in patients with CML who failed prior tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy [3] In patients with CML achieving deep molecular responses with TKIs, treatment withdrawal can lead to treatment-free remission; Asciminib aims to improve outcomes by eradicating CML cells [2] |
| 分子式 |
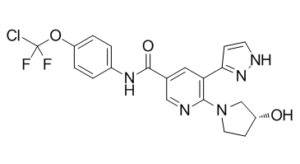
C20H18CLF2N5O3
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
449.84
|
|
| 精确质量 |
449.106
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 53.40; H, 4.03; Cl, 7.88; F, 8.45; N, 15.57; O, 10.67
|
|
| CAS号 |
1492952-76-7
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Asciminib hydrochloride;2119669-71-3
|
|
| PubChem CID |
72165228
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.5±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
631.7±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
335.8±31.5 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.9 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.662
|
|
| LogP |
2.1
|
|
| tPSA |
103Ų
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
31
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
626
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
ClC(OC1C=CC(=CC=1)NC(C1C=NC(=C(C2=CC=NN2)C=1)N1CC[C@H](C1)O)=O)(F)F
|
|
| InChi Key |
VOVZXURTCKPRDQ-CQSZACIVSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C20H18ClF2N5O3/c21-20(22,23)31-15-3-1-13(2-4-15)26-19(30)12-9-16(17-5-7-25-27-17)18(24-10-12)28-8-6-14(29)11-28/h1-5,7,9-10,14,29H,6,8,11H2,(H,25,27)(H,26,30)/t14-/m1/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
N-[4-[chloro(difluoro)methoxy]phenyl]-6-[(3R)-3-hydroxypyrrolidin-1-yl]-5-(1H-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridine-3-carboxamide
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.56 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.56 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.56 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2230 mL | 11.1151 mL | 22.2301 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4446 mL | 2.2230 mL | 4.4460 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2223 mL | 1.1115 mL | 2.2230 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
A phase 3, multi-center, open-label, randomized study of oral asciminib versus bosutinib in patients with Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia in chronic phase (CML-CP), previously treated with 2 or more tyrosine kinase inhibitors
CTID: null
Phase: Phase 3 Status: Ongoing, GB - no longer in EU/EEA, Completed
Date: 2017-10-09
ABL001 is an allosteric inhibitor of BCR–ABL1 that selectively inhibits growth of BCR–ABL1-driven cells.Nature.2017 Mar 30;543(7647):733-737. |
|---|
ABL001 has a resistance profile that is distinct from catalytic-site BCR–ABL1 inhibitors.Nature.2017 Mar 30;543(7647):733-737. |
The non-overlapping resistance profiles of ABL001 and nilotinib enable durable tumour eradication when used in combination.Nature.2017 Mar 30;543(7647):733-737. |
Clonal evolution of resistance mutations in a patient treated with ABL001 after previous dasatinib treatment.Nature.2017 Mar 30;543(7647):733-737. |
|---|