| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在 MDA-MB-468 细胞中,AZ9482 的 EC50 为 24 nM[1]。使用 AZ0108 治疗会导致 CHK1 过度磷酸化并抑制 MARylation,从而导致 MPS 形成和细胞周期失调 [1]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
此外,AZ0108表现出体内毒性,其分子原因仍不清楚,这限制了AZ0108的药理学评估[1]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定 [1]
细胞类型: MDA-MB-468 细胞。 测试浓度:0-10μM。 孵化持续时间:3天。 实验结果:EC50 为 24 nM。 |
| 参考文献 |
| 分子式 |
C26H22N6O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
450.49
|
| 精确质量 |
450.18
|
| CAS号 |
1825345-33-2
|
| PubChem CID |
92045137
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to yellow solid powder
|
| LogP |
2.6
|
| tPSA |
102
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
34
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
842
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
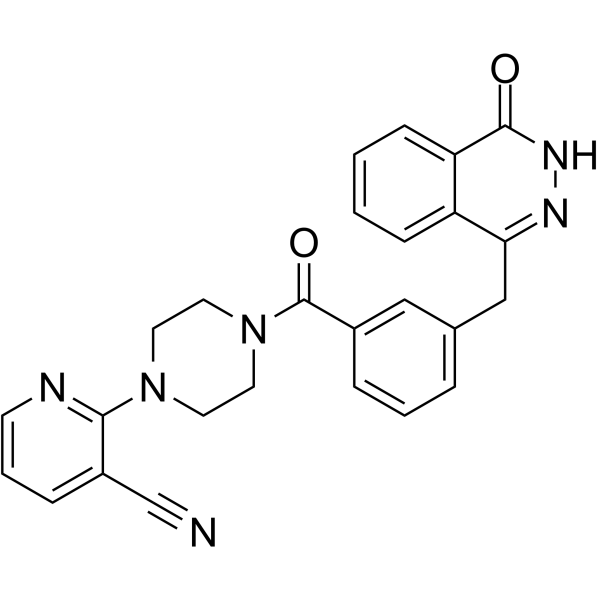
| SMILES |
C1=CC=NC(=C1C#N)N1CCN(CC1)C(=O)C1=CC=CC(CC2C3=C(C(NN=2)=O)C=CC=C3)=C1
|
| InChi Key |
ZDDPBFWHZOJFHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C26H22N6O2/c27-17-20-7-4-10-28-24(20)31-11-13-32(14-12-31)26(34)19-6-3-5-18(15-19)16-23-21-8-1-2-9-22(21)25(33)30-29-23/h1-10,15H,11-14,16H2,(H,30,33)
|
| 化学名 |
2-[4-[3-[(4-oxo-3H-phthalazin-1-yl)methyl]benzoyl]piperazin-1-yl]pyridine-3-carbonitrile
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~125 mg/mL (~277.48 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 2.08 mg/mL (4.62 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浮液;超声助溶。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 2.08 mg/mL (4.62 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.62 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2198 mL | 11.0990 mL | 22.1981 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4440 mL | 2.2198 mL | 4.4396 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2220 mL | 1.1099 mL | 2.2198 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
|
|
|