| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
AR/androgen receptor
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Bicalutamide 的 IC50 为 160 nM,在全细胞结合实验(LNCaP/AR (cs) 细胞)中与雄激素竞争与 AR 的结合 [1]。比卡鲁胺部分抵消了 R1881(一种合成雄激素)的作用,同时以剂量依赖性方式诱导 VCaP 细胞增殖 [1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在前列腺癌小鼠模型中,贝利卡特胺(10 mg/kg;每日注射;持续 28 天)显示出抗癌功效 [1]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
配体结合研究[1]
全细胞LNCaP/AR:全细胞竞争性结合试验在LNCaP/AR(密码子开关)(LNCaP/AR(cs))(含有外源性野生型AR和内源性突变型AR的混合物(T877A))和在补充了10%胎牛血清(FBS)的Iscove或RPMI培养基中繁殖的细胞中进行,或在试验过程中用10%木炭剥离、葡聚糖处理的胎牛血清进行。将细胞与18F-FDHT预孵育,加入浓度逐渐增加(1pM至1μM)的冷竞争对手,并根据已公布的程序进行测定,以测量18F-FDDT的特异性摄取。 配体结合研究要么在全细胞测定(LNCaP/AR(cs))中进行,使用全细胞提取物(MDA-MB-453),要么在体外用纯化的受体进行。增殖试验(VCaP)以激动剂或拮抗剂模式进行(无/有R1881)。从LNCaP/AR细胞中分离RNA,用AR靶基因特异性引物(补充表1)进行RT-PCR分析。如前所述,在转染了AR-EYFP的LNCaP细胞中进行了荧光显微镜观察。AR抗体PG-21 与PSA 和TMPRSS2 增强子引物一起用于染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)实验(LNCaP/AR(cs))。在表达VP16-AR的LNCaP/AR-luc或Hep-G2细胞中进行萤光素酶报告基因检测[1]。 |
| 细胞实验 |
增殖试验[1]
将胰蛋白酶化的VCaP细胞在无酚红的RPMI 1640(含5%CSS)中调节至每毫升100000个细胞的浓度,并将16µL的等分试样分配到CellBIND 384孔板中。将细胞孵育48小时,然后将16µL体积的配体加入RPMI培养基中。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Castrate male mice, bearing LNCaP/AR(cs) xenograft tumors[1]
Doses: 10 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage), daily, for 28 days Experimental Results: Inhibited tumor growth. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Bicalutamide is well-absorbed following oral administration, although the absolute bioavailability is unknown. Apparent oral cl=0.32 L/h [Normal Males] Bicalutamide is well-absorbed following oral administration, although the absolute bioavailability is unknown. Co-administration of bicalutamide with food has no clinically significant effect on rate or extent of absorption. Bicalutamide is highly protein-bound (96%). ... Bicalutamide metabolites are excreted almost equally in urine and feces with little or no unchanged drug excreted in urine; conversely, unchanged drug predominates in plasma. Bicalutamide in feces is thought to arise from hydrolysis of bicalutamide glucuronide and from unabsorbed drug. ... ... Healthy male volunteers (n = 15) were administered single oral doses of bicalutamide (50 mg) after food and after fasting as part of a three-treatment, three-period, randomized cross-over study, with a 9 week washout. After fasting, plasma concentrations of (R)-bicalutamide were much higher than those of (S)-bicalutamide; the mean (R)-enantiomer Cmax (734 ng mL-1) was about nine times higher than the (S)-enantiomer value (84 ng mL-1). The corresponding tmax values were 19 and 3 hr for (R)- and (S)-bicalutamide, respectively. Elimination of (R)-bicalutamide from plasma was monoexponential and slow (t1/2 = 5.8 d). Elimination of (S)-bicalutamide was biphasic in some volunteers but monophasic in others (terminal t1/2 =1.2 d; n = 11). There was no significant effect of food on AUC, tmax, or t1/2 data for either enantiomer. The observed slightly higher values of Cmax for (R)-bicalutamide (14%) and (S)-bicalutamide (19%), when dosing with food, achieved statistical significance. ... For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for BICALUTAMIDE (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Bicalutamide undergoes stereo specific metabolism. The S (inactive) isomer is metabolized primarily by glucuronidation. The R (active) isomer also undergoes glucuronidation but is predominantly oxidized to an inactive metabolite followed by glucuronidation. Bicalutamide undergoes stereospecific metabolism. The S (inactive) isomer is metabolized primarily by glucuronidation. The R (active) isomer also undergoes glucuronidation but is predominantly oxidized to an inactive metabolite followed by glucuronidation. Both the parent and metabolite glucuronides are eliminated in the urine and feces. The S-enantiomer is rapidly cleared relative to the R-enantiomer, with the R-enantiomer accounting for about 99% of total steady-state plasma levels. Bicalutamide undergoes stereo specific metabolism. The S (inactive) isomer is metabolized primarily by glucuronidation. The R (active) isomer also undergoes glucuronidation but is predominantly oxidized to an inactive metabolite followed by glucuronidation. Half Life: 5.9 days Biological Half-Life 5.9 days ... Elimination of (S)-bicalutamide was biphasic in some volunteers but monophasic in others (terminal t1/2 =1.2 d; n = 11). ... /The/ apparent plasma elimination half-life observed following repeated administration was 8.4 +/- 1.1 days. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
Bicalutamide competes with androgen for the binding of androgen receptors, consequently blocking the action of androgens of adrenal and testicular origin which stimulate the growth of normal and malignant prostatic tissue. Organic nitriles decompose into cyanide ions both in vivo and in vitro. Consequently the primary mechanism of toxicity for organic nitriles is their production of toxic cyanide ions or hydrogen cyanide. Cyanide is an inhibitor of cytochrome c oxidase in the fourth complex of the electron transport chain (found in the membrane of the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells). It complexes with the ferric iron atom in this enzyme. The binding of cyanide to this cytochrome prevents transport of electrons from cytochrome c oxidase to oxygen. As a result, the electron transport chain is disrupted and the cell can no longer aerobically produce ATP for energy. Tissues that mainly depend on aerobic respiration, such as the central nervous system and the heart, are particularly affected. Cyanide is also known produce some of its toxic effects by binding to catalase, glutathione peroxidase, methemoglobin, hydroxocobalamin, phosphatase, tyrosinase, ascorbic acid oxidase, xanthine oxidase, succinic dehydrogenase, and Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase. Cyanide binds to the ferric ion of methemoglobin to form inactive cyanmethemoglobin. (L97) Hepatotoxicity Bicalutamide therapy is associated with mild, asymptomatic and transient elevations in serum aminotransferase levels in approximately 6% of patients. The frequency and height of the ALT elevations appears to be less with bicalutamide than flutamide. Similarly, there have been rare case reports of clinically apparent liver injury due to bicalutamide, but less frequently than with flutamide. In the Spanish pharmacovigilance study, there were 11 reports of hepatotoxicity from bicalutamide, none of which were fatal. On the other hand, the product label for bicalutamide mentions that a few cases of fatal hepatic failure have been reported. The clinical pattern of liver injury with bicalutamide appears to resemble that of flutamide. The latency to onset is usually 2 to 3 months, but can be shorter with reexposure and occasionally arises 4 to 6 months after starting. The typical pattern of serum enzyme elevations is hepatocellular and severe, fulminant cases have been described. Rash, fever and eosinophilia are not common and autoantibody formation is not described. Likelihood score: B (likely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Protein Binding 96% Interactions In vitro protein-binding studies have shown that bicalutamide can displace coumarin anticoagulants from binding sites. Prothrombin times should be closely monitored in patients already receiving coumarin anticoagulants who are started on /bicalutamide/. In vitro studies have shown that R-bicalutamide is an inhibitor of CYP 3A4 with lesser inhibitory effects on CYP 2C9, 2C19 and 2D6 activity. Clinical studies have shown that with co-administration of bicalutamide, mean midazolam (a CYP 3A4 substrate) levels may be increased 1.5 fold (for Cmax) and 1.9 fold (for AUC). Hence, caution should be exercised when bicalutamide is co-administered with CYP 3A4 substrates. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Androgen Antagonists; Antineoplastic Agents /Bicalutamide/ 50 mg daily is indicated for use in combination therapy with a luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) analogue for the treatment of Stage D2 metastatic carcinoma of the prostate. /Included in US product label/ /Bicalutamide/ 150 mg daily is not approved for use alone or with other treatments. /Included in US product label/ Drug Warnings /Bicalutamide/ is contraindicated in any patient who has shown a hypersensitivity reaction to the drug or any of the tablet's components. /Bicalutamide/ has no indication for women, and should not be used in this population, particularly for non-serious or non-life threatening conditions. FDA Pregnancy Risk Category: X /CONTRAINDICATED IN PREGNANCY. Studies in animals and or humans, or investigational or post-marketing reports, have demonstrated positive evidence of fetal abnormalities or risk which clearly outweighs any possible benefit to the patient./ It is not known whether /bicalutamide/ drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when /bicalutamide/ is administered to a nursing woman. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for BICALUTAMIDE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Bicalutamide is an antineoplastic hormonal agent primarily used in the treatment of prostate cancer. Bicalutamide is a pure, nonsteroidal anti-androgen with affinity for androgen receptors (but not for progestogen, estrogen, or glucocorticoid receptors). Consequently, Bicalutamide blocks the action of androgens of adrenal and testicular origin which stimulate the growth of normal and malignant prostatic tissue. Prostate cancer is mostly androgen-dependent and can be treated with surgical or chemical castration. To date, antiandrogen monotherapy has not consistently been shown to be equivalent to castration. |
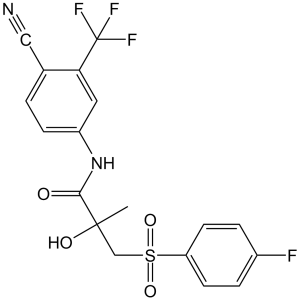
| 分子式 |
C18H14F4N2O4S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
430.37
|
| 精确质量 |
430.061
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 50.23; H, 3.28; F, 17.66; N, 6.51; O, 14.87; S, 7.45
|
| CAS号 |
90357-06-5
|
| 相关CAS号 |
(R)-Bicalutamide;113299-40-4;Bicalutamide-d4;1185035-71-5
|
| PubChem CID |
2375
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.5±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
650.3±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
191-193°C
|
| 闪点 |
347.1±31.5 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.578
|
| LogP |
4.94
|
| tPSA |
115.64
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
9
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
29
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
750
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
LKJPYSCBVHEWIU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H14F4N2O4S/c1-17(26,10-29(27,28)14-6-3-12(19)4-7-14)16(25)24-13-5-2-11(9-23)15(8-13)18(20,21)22/h2-8,26H,10H2,1H3,(H,24,25)
|
| 化学名 |
N-(4-cyano-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanamide
|
| 别名 |
ICI-176334; ICI 176334; ICI176334; CDX. US trade name: Casodex; Cosudex. Calutide;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.81 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.81 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.81 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3236 mL | 11.6179 mL | 23.2358 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4647 mL | 2.3236 mL | 4.6472 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2324 mL | 1.1618 mL | 2.3236 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
 |
|---|
|
|